CARDIO
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
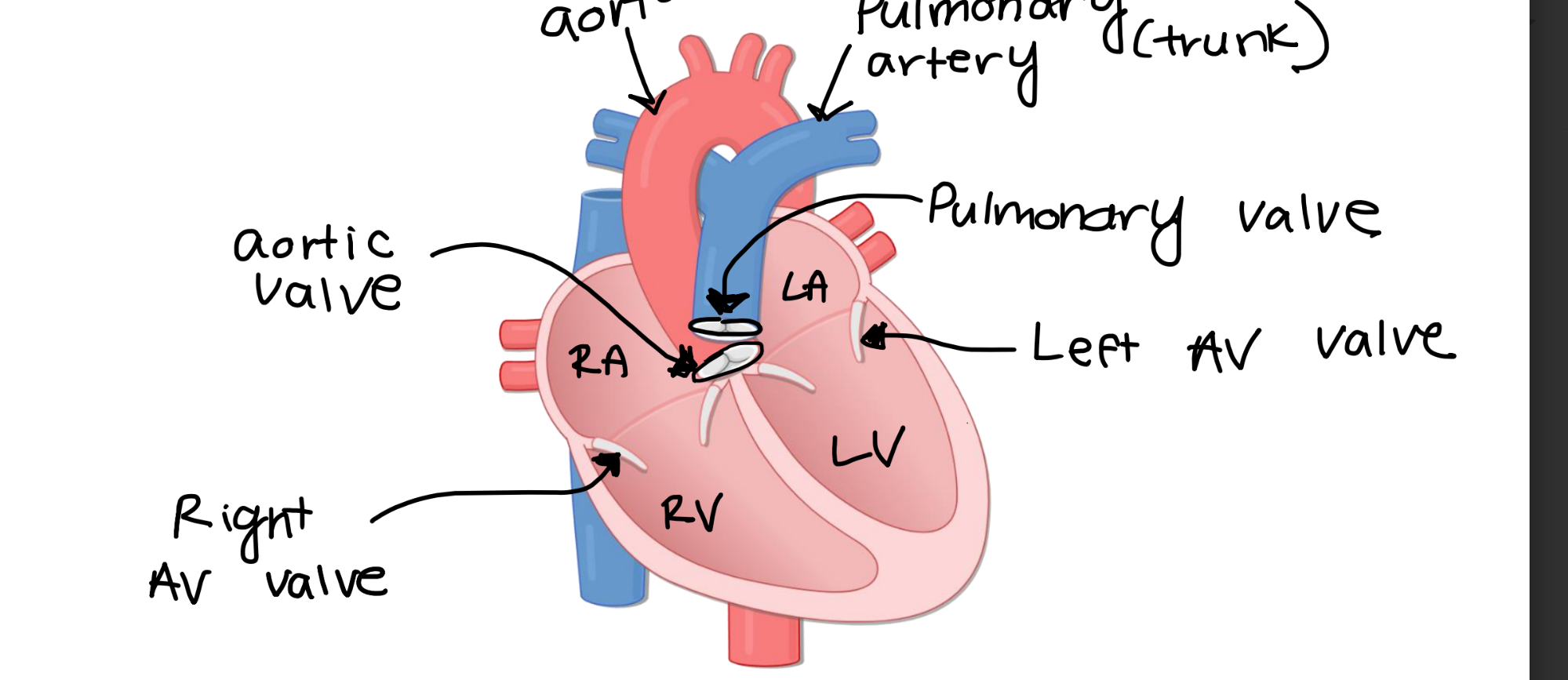
The right atrioventricular valve
the one-way flow of blood from the right atria to the
right ventricle.
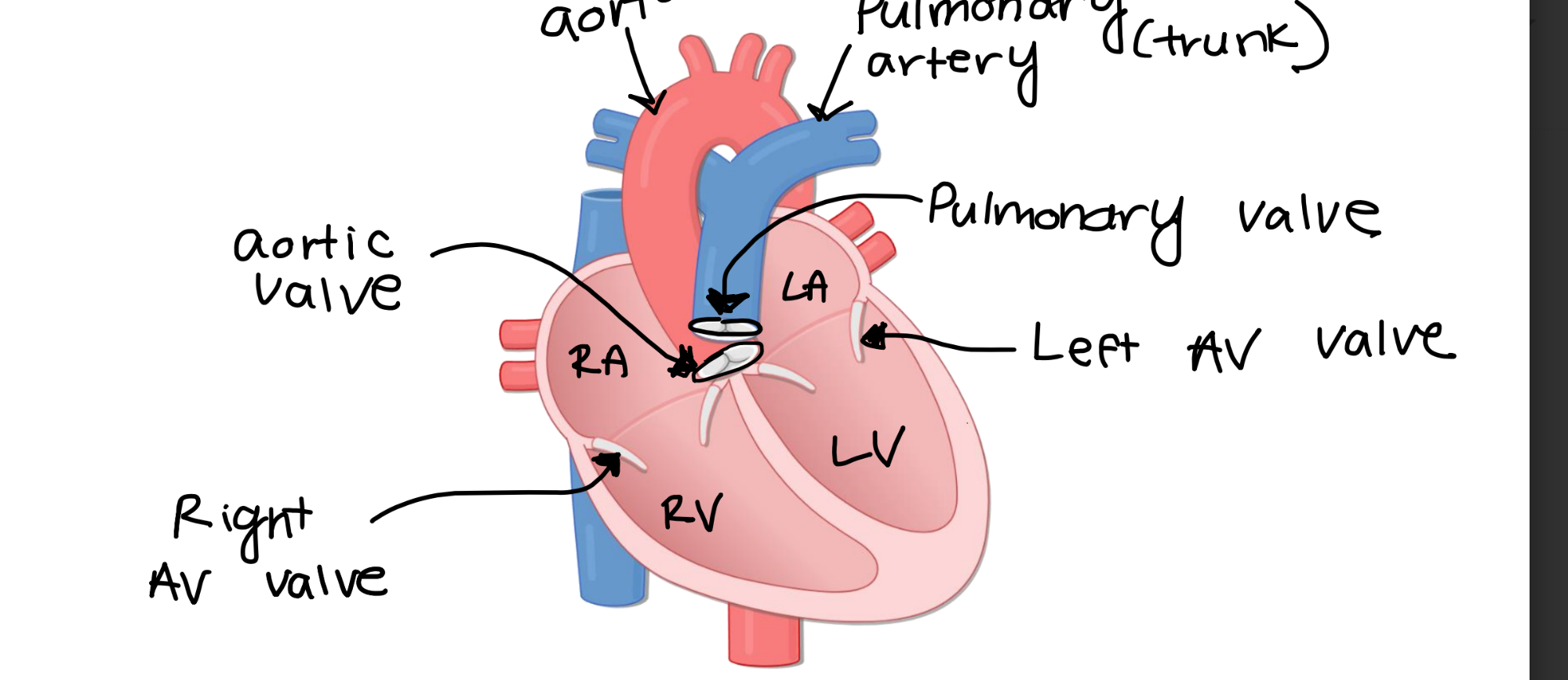
The left atrioventricular valve ensures the one-way flow of blood from the
left atria to the left ventricle.
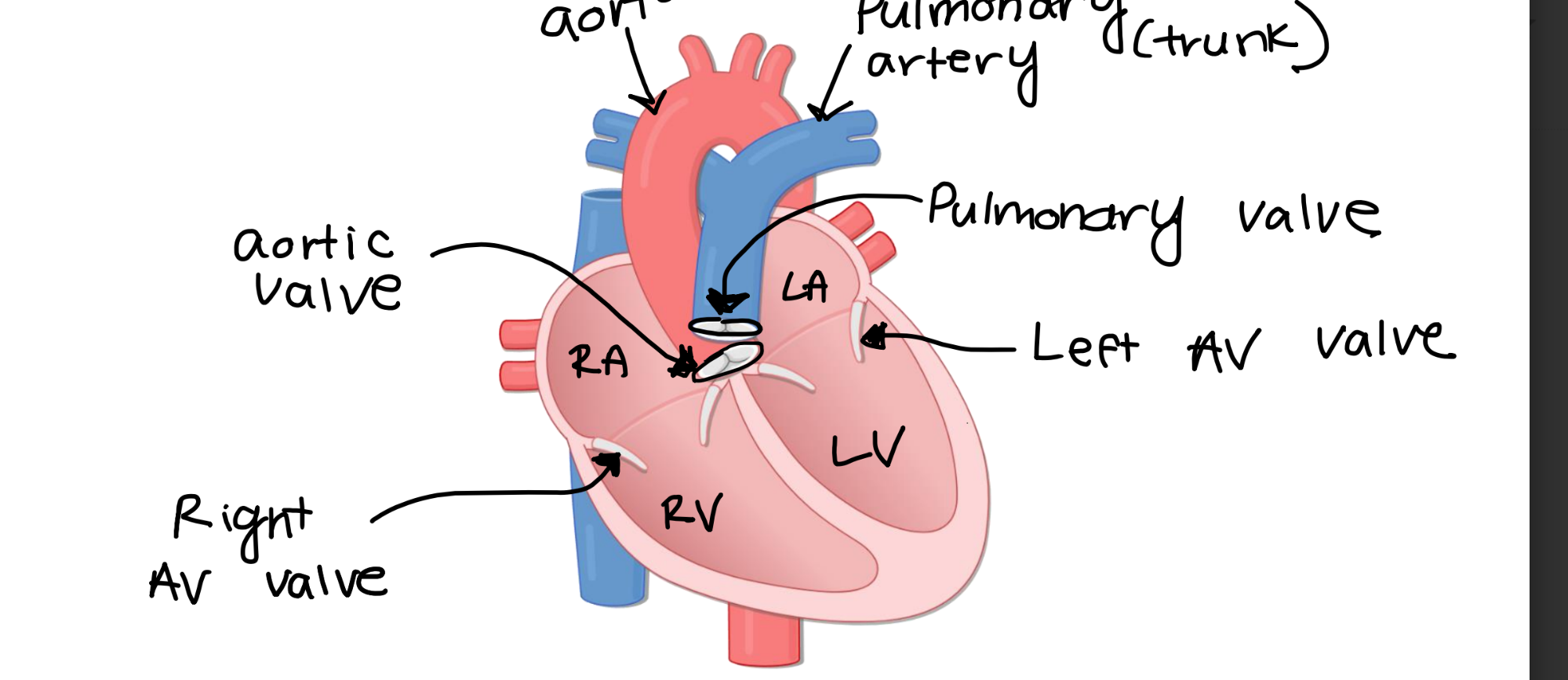
The aortic valve ensures the one-way flood of blood from the
left ventricle to the aorta.
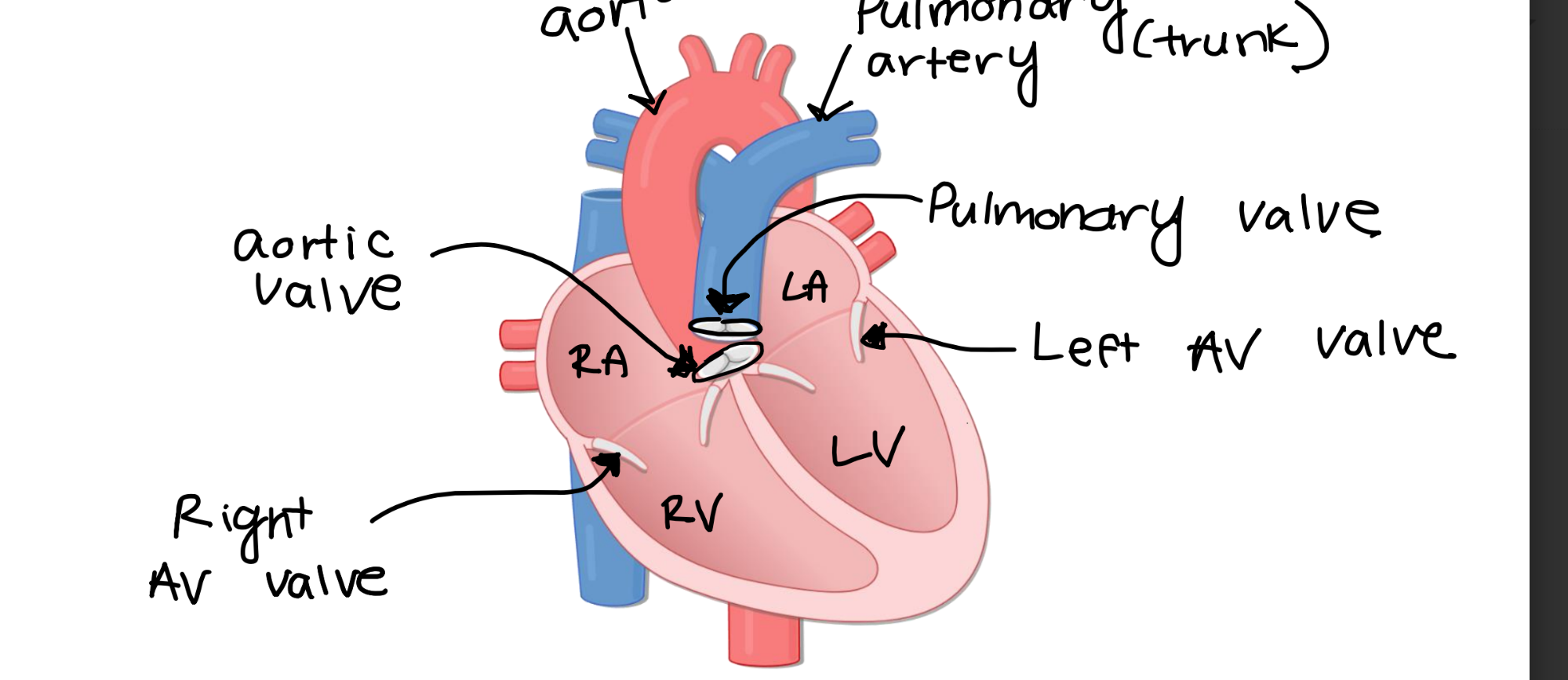
The pulmonary valve ensures the one-way flow of blood from the
right ventricle to the pulmonary artery.
Describe the direction of the flow of blood in the right side of the heart.
Right atria → right ventricle → pulmonary artery → lungs
Starting at the left atrium
Left atria → left ventricle → aorta → systemic circulation.
. True or False: All 4 valves of the heart can be opened at once.
False.
If all four valves were open, blood would not be able to move to the lungs or rest of body.
Diastole
>relaxation.
>During diastole, or filling of the ventricle
>length of the sarcomere increases.
Systole
>contraction.
> ejection of blood from the ventricle
>length of the sarcomere shortens.
Ventricular diastole:
SL CLOSED
AV OPEN
Ventricular systole:
SL valves OPEN
AV CLOSED
S1
>LUB
>ventricular systole during isovolumetric contraction.
>AV CLOSE
ventricular pressure > atrial pressure.
S2
DUB
SL VALVES close.
>This occurs when ventricular pressure < aortic and pulmonary pressure.
>Beginning of ventricular diastole/ Isovolumetric relaxation
>the T-wave.