ch 22b: physiologic and behavioral adaptations of newborn
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
immune system 5
Immature at birth → ↑ susceptibility to infection
passive immunity from mother
B cells & T cells = present, but immature
slower inflammation response
immunoglobulins GAMED
IgG: passed in last 3 months of pregnancy passively from mother
IgM: Made by fetus from 8 weeks gestation; low at birth; responds to blood-borne pathogens
igA: Present in breast milk (not formula); protects GI tract (allergies/intolerance)
igD and igE: Develop gradually, reach full levels in early childhood.
tdap
TDAP vaccine given to mom at 28 weeks/third trimester to pass to baby
baby cant get vaccine until 2 months
signs of infection 9
Hypothermia (more than fever)
hypotonia
Poor feeding
vomiting/diarrhea
Lethargy
irritability
Pale/mottled skin
unusual discharge or rash
resp distress: Apnea, tachypnea, grunting, retractions
rfs
5 important italics
8 total
Prematurity (most significant)
Prolonged rupture of membranes
Maternal fever
chorioamnionitis
Invasive procedures
Asphyxia (before or during labor)
Congenital anomalies
Stress (physical or metabolic)
integumentary system
6
All skin layers present at birth; skin is thin & loosely bound.
covered in vernix caseosa
Initial erythema, fades to normal tone.
Mottling common, especially in extremities.
Acrocyanosis (blue hands/feet) normal first 48 hrs, may reappear with cold.
Desquamation: Normal peeling occurs a few days after birth.
excess = postmaturity
COMMON SKIN FINDINGS
4
Sweat Glands & Milia
Sweat glands present but inactive at birth.
Milia: white sebaceous cysts on face; normal.
Mongolian spots/CONGENTIAL MELANOCYTOSIS
Nevus simplex (Stork bites/Angel kisses)
Flat, pink, blanchable spots
Infantile hemangioma
Bright red or bluish raised lesion
Signs of Integumentary Problems
4 total
abnormal skin color: Pallor, central cyanosis, jaundice
Petechiae: if scattered → possible infection or low platelets.
Bruising: from birth trauma; ↑ risk for hyperbilirubinemia
hematoma
reproductive female 3
labial edema
Vernix caseosa may be present between labia – do not forcibly remove.
mucoid or bloody vaginal discharge (normal) from Estrogen withdrawal after birth
reproductive male
2 normals
2 abnormals
Epithelial pearls (small white lesions on glans): benign.
Hydrocele: fluid-filled sac; transilluminates, usually resolves.
Bluish scrotum: possible testicular torsion → emergency.
testes should be descende, if undescended (Cryptorchidism)
usually resolves spontaneously
Breast Tissue (Both Sexes)
Swelling due to maternal estrogen
May secrete “witch’s milk”
Resolves spontaneously
Signs of Reproductive Abnormalities 4
Fecal discharge from vagina: vaginal fistula
Hypospadias/epispadias: Abnormal urethral opening
circumcision contraindicated
Undescended testes: Cryptorchidism
Inguinal hernia; May resolve; more visible when crying
Molding, caput, cephalhematoma, subgaleal hemorrhage
describe/key details
M: Overlapping of skull bones during birth
caput: Edema across scalp (crosses suture lines)
cephal: Blood between skull & periosteum (does not cross suture lines)
subgaleal: Blood under scalp aponeurosis

Signs of subgaleal hemorrhage: 6
int: 2
Boggy scalp
pallor
↑ head circumference
Ear displacement
tachycardia
edema at neck
Needs immediate imaging + blood replacement
Spine
should be straight and midline; easily flexed
pilonidal dimple: may indicate spina bifida if sinus or hairy nevus present
sinus: hollow space
HN: pigmented bm; nexus + hair
IMAGING
Extremities
NORMALS 2
ABNORMAL 3
Limbs should be symmetric, equal in length
Nails present on all digits
ABNORMAL
Oligodactyly Fewer than 5 digits
Polydactyly Extra digits
Syndactyly Fused fingers/toes
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH) rfs 4
Breech birth
first-born
female
family history
SIGNS OF DDH
2
tests 2
Asymmetric gluteal/thigh folds
Uneven knee height
Positive Barlow test (dislocates hip)
Positive Ortolani maneuver (relocates hip)
⚠ Only trained clinicians should perform Barlow/Ortolani tests.
Neuromuscular System: BRAIN
growth rate
needs
Rapid growth in infancy/early childhood
Slows during later childhood & adolescence
requires high oxygen and glucose for energy → assess hypoglycemia risk
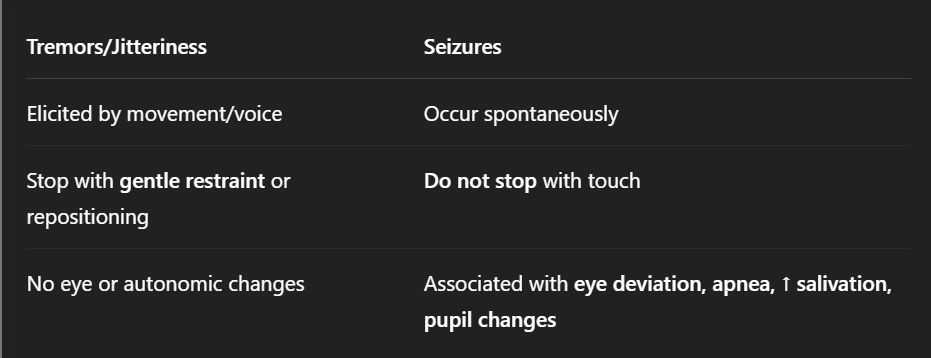
Tremors vs. Seizures 3
cause
touch
changes
Transient tremors (mouth, chin, arms, hands) are normal in first few weeks
Persistent or full-body tremors → pathologic
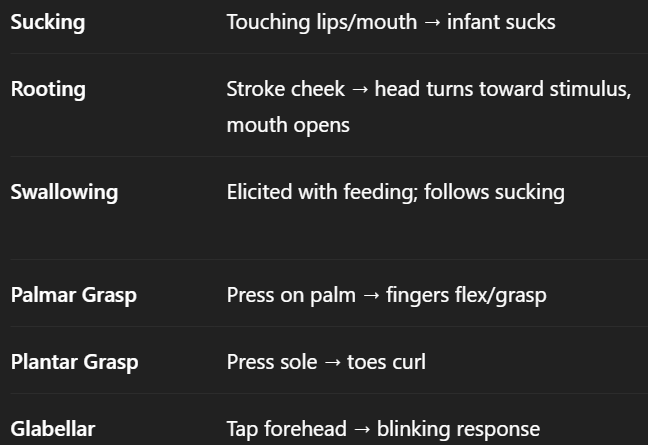
newborn reflexes
Sucking
rooting
swallowing
palmar and plantar grasp
glabellar
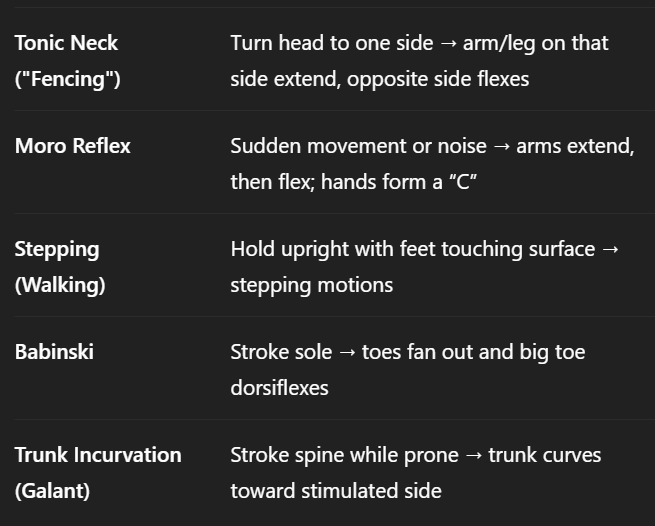
reflexes 2
tonic neck
moro reflex
stepping/walking
babinski
Trunk Incurvation (Galant)
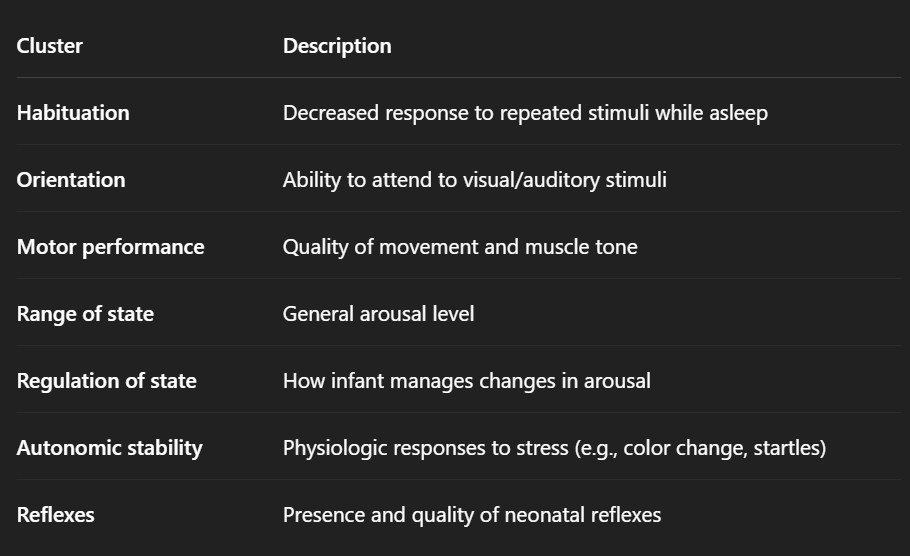
Brazelton Neonatal Behavioral Assessment Scale (NBAS) – Clusters
Real Hot Moms Rarely React After Overeating
sleep wake states
6 total: 2 sleep, 4 awake
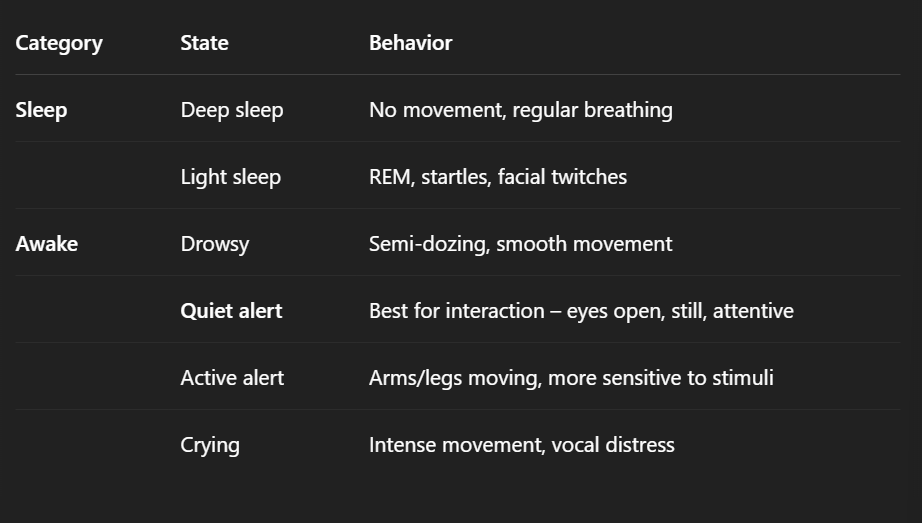
sleep pattern/cycle
Sleeps 16–19 hours/day (early weeks)
Wakefulness increases → initially hunger-driven, later includes social interaction
factors influencing newborn behavior
Gestational Age
Time
Environmental Stimuli
Maternal Medications
gest age/time
Gestational Age: affects CNS maturity
TIme:
Time since birth: affects initial behavioral organization.
Time since last feeding and time of day: influence alertness and responsiveness.
env stimuli/maternal meds
env stimuli
Infants react to sounds, lights, and emotional tone of caregivers.
Overstimulation (e.g., NICU alarms, bright lights, loud noises) can impact stability.
Infant may sense caregiver stress or tension, which affects behaviors like feeding.
maternal meds
No proven direct effect of labor epidurals on neonatal behavior.
Opioids during postpartum: may pass through breast milk → CNS depression, sedation, respiratory depression in infant.
levels of behavioral organization
autonomic, motor, state, attention/interaction
Autonomic Regulation:
Controls involuntary functions (HR, temp, breathing)Motor Organization:
Muscle tone, control of movement, reduction of random activityState Regulation:
Ability to modulate between states (sleep/wake, alertness)Attention & Interaction:
Responds to visual/auditory stimuli, maintains alertness, social engagement
Behavioral Cues: engaged vs disengaged
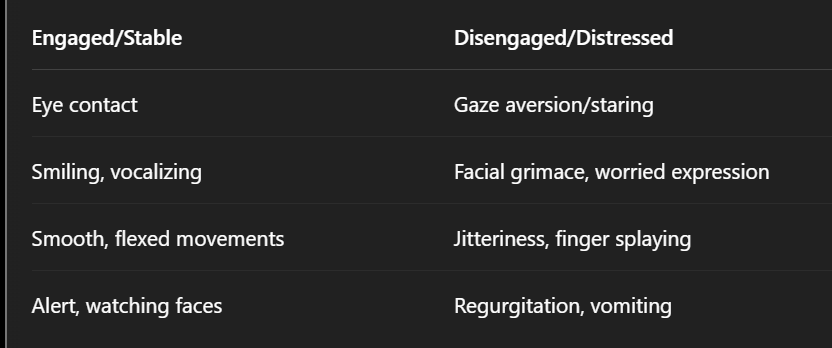
senses + vision and hearing
v: 2; h 3
all senses developed at birth
vision
immature at birth; least well developed
see 8-12 inches
hearing
bonding: Prefer mother’s voice and high-pitched tones
screening before d/c
heartbeat rhythm and lullabies are soothing
senses 2
smell 3
taste/touch 2
smell
well devt at birth
React to strong odors (e.g., vinegar) by turning away; Attracted to sweet smells
can recognize mother’s scent and milk
taste
Prefer sweet tastes
Early oral sensitivity helps with feeding and soothing
touch
Most sensitive: mouth, hands, feet
Sensitive to pain and comforting touch
Response to Environmental Stimuli
o Temperament
o Habituation
o Consolability
o Cuddliness
o Irritability
o Crying
Temperament – Individual behavioral style or response pattern to stimuli
Habituation – Decreased response to repeated or continuous stimulation
Consolability – Infant’s ability to self-soothe or be soothed by others
Cuddliness – Degree to which an infant relaxes and molds into the caregiver when held
Irritability – Sensitivity to stimuli; how easily an infant becomes upset
crying
primary communication tool
➤ Hunger
➤ Pain
➤ Discomfort
➤ Desire for attention
➤ Overstimulation
high pitched cry
A potentially abnormal cry that may signal neurologic issues