Nutrition
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:59 AM on 2/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
1
New cards
nutrients
Substances essential for health that the body cannot make or makes in quantities too small to support life
2
New cards
essential nutrients
Has a specific biological function
Absence from the diet leads to decline in biological function
Adding missing substance back to the diet before permanent damage occurs restores normal biological function
Absence from the diet leads to decline in biological function
Adding missing substance back to the diet before permanent damage occurs restores normal biological function
3
New cards
macronutrients
Needed in large amounts
* Carbohydrates
* Lipids
* Proteins
* Water
* Carbohydrates
* Lipids
* Proteins
* Water
4
New cards
micronutrients
Needed in small amounts
* Vitamins
* Minerals
* Vitamins
* Minerals
5
New cards
undernutrition
* Nutrient intake does not meet needs
* Nutrient stores are depleted
* Nutrient stores are depleted
6
New cards
over nutrition
* Consumption of more nutrients than the body needs
* Most common type in industrialized nations: excess energy intake
* Most common type in industrialized nations: excess energy intake
7
New cards
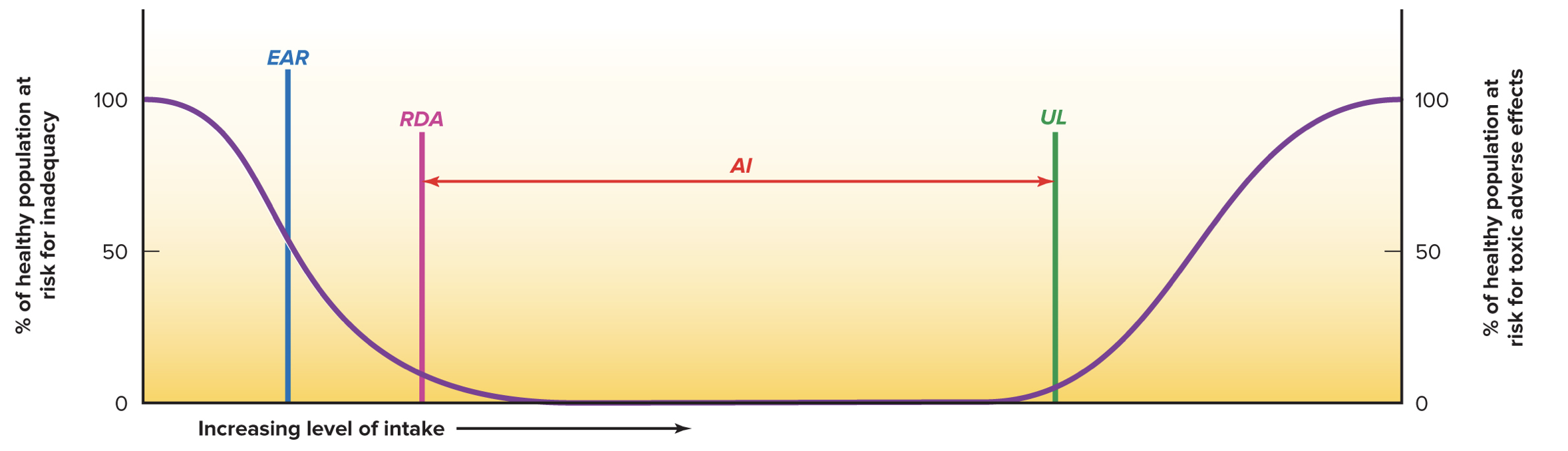
Where to look for credible sources of nutrition information
FDA, Food and Nutrition Board
8
New cards
Food Desert
* Geographic areas where fresh, affordable, healthy foods cannot be purchased easily
9
New cards
Qualities of Healthy Diet
10
New cards
Nutrient dense
foods high in nutrients but relatively low in calories
11
New cards
Energy dense
foods high in calories but lacking nutrients
12
New cards
American Diet
* 16% of energy intake as proteins
* 50% as carbohydrates
* 33% as fats
* Too many calories are being consumed
* Too much protein from animal sources; too little from plants
* Too many carbohydrates from simple sugars; too few from complex carbohydrates
* Too much fat from animal sources; too little from plants
* 50% as carbohydrates
* 33% as fats
* Too many calories are being consumed
* Too much protein from animal sources; too little from plants
* Too many carbohydrates from simple sugars; too few from complex carbohydrates
* Too much fat from animal sources; too little from plants
13
New cards
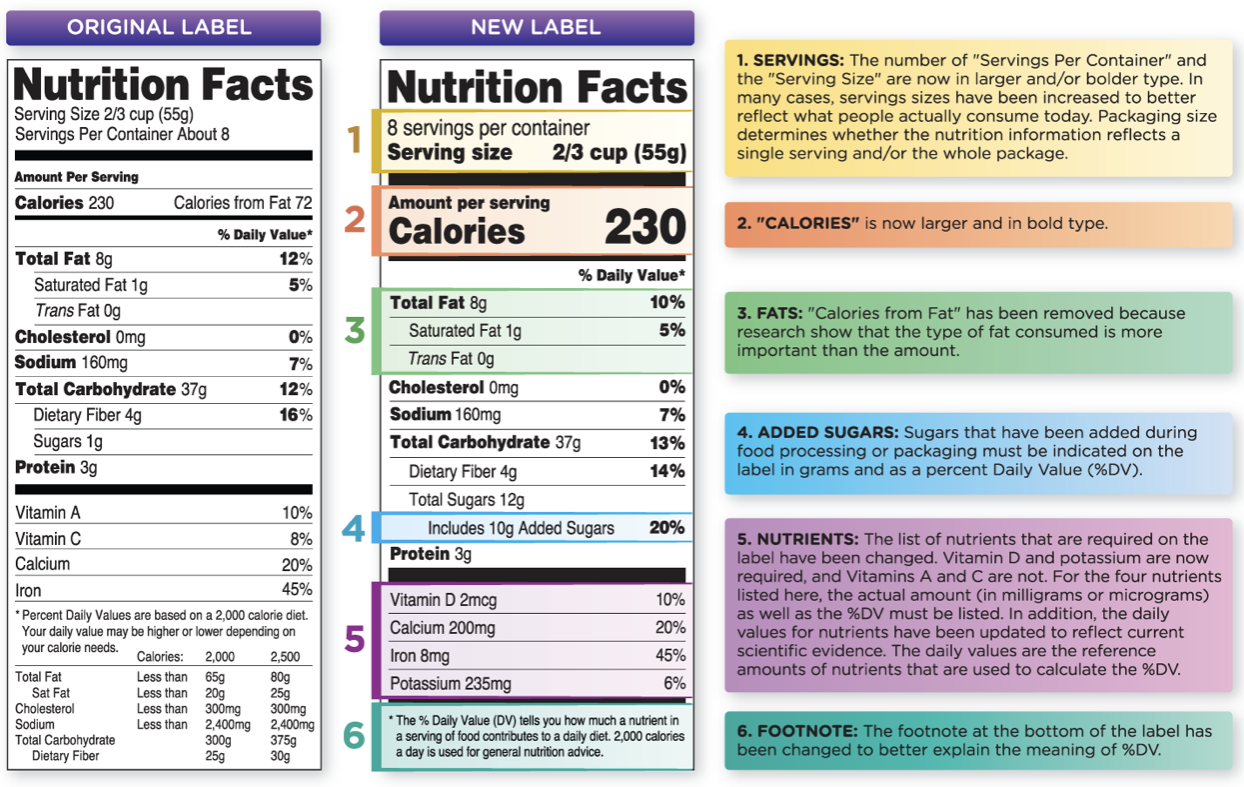
Food label
14
New cards
Health consequences of malnutrition and food insecurity for children and adults
* Report more asthma, stomachaches, headaches, and colds
* May not grow normally
* Are more likely to have behavioral problems in school and lower educational achievement
* Report higher rates of depression and suicidal symptoms and increased levels of psychological distress
* May not grow normally
* Are more likely to have behavioral problems in school and lower educational achievement
* Report higher rates of depression and suicidal symptoms and increased levels of psychological distress
15
New cards
Food security vs food insecurity
“access by all people at all times to enough food for an active, healthy life”
vs
* at fewer servings of nutrient-dense foods and consume poorer-quality diets
* linked with obesity, as individuals are more likely to overeat when food is more plentiful and purchase mostly inexpensive, high-energy-density foods
vs
* at fewer servings of nutrient-dense foods and consume poorer-quality diets
* linked with obesity, as individuals are more likely to overeat when food is more plentiful and purchase mostly inexpensive, high-energy-density foods
16
New cards
Major U.S. government programs designed to increase food security
* Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP)
* Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC)
* National School Lunch Program
* School Breakfast Program
* Child and Adult Care Food Program
* Programs for seniors: Meals on Wheels, Senior Farmers’ Market Nutrition Programs, congregate meal programs
* Food distribution programs: food banks and pantries
* Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC)
* National School Lunch Program
* School Breakfast Program
* Child and Adult Care Food Program
* Programs for seniors: Meals on Wheels, Senior Farmers’ Market Nutrition Programs, congregate meal programs
* Food distribution programs: food banks and pantries
17
New cards
Factors of food insecurity
* Skipping meals
* Reducing the size of meals
* Not eating when hungry
* poverty guidelines:
* $25,750 annually for a family of 4
* Reducing the size of meals
* Not eating when hungry
* poverty guidelines:
* $25,750 annually for a family of 4
18
New cards
organic foods vs conventional foods
* Biological pest management
* Composting
* Manure applications
* Crop rotation to maintain healthy soil, water, crops, and animals
vs
* Synthetic pesticides
* Fertilizers
* Hormones
* Antibiotics
* Sewage sludge
* Genetic engineering
* Irradiation
* Composting
* Manure applications
* Crop rotation to maintain healthy soil, water, crops, and animals
vs
* Synthetic pesticides
* Fertilizers
* Hormones
* Antibiotics
* Sewage sludge
* Genetic engineering
* Irradiation
19
New cards
Pros of GMO
1. GMOs improve the quality of the food that is grown. Genetically modified foods can be engineered to have a longer shelf life, which can limit food waste.
2. GMOs are easier for farmers to grow. \n Genetically modified foods can also be engineered to grow in specific, sometimes challenging environments.
3. It increases the food yields that we can produce on existing croplands. \n By the year 2050, the human population on our planet is expected to top 10 billion people.
4. GMOs can be shipped to remote areas of the planet. Many non-GMO crops spoil when attempted to ship to remote areas of the world.
5. Herbicide use on GMO crops is lower than other crops. Many GMO crops are already resistant and don’t need extra herbicide.
6. The FDA requires GMO foods to meet the same requirements as all other foods.
20
New cards
Mechanical digestion
Begins in the mouth
– Teeth masticate \n – Food bolus
• Esophagus – Peristalsis
• Stomach
* – Smooth muscle contractions
* – Storage
* – Chyme
• Smallintestine – Segmentation
– Teeth masticate \n – Food bolus
• Esophagus – Peristalsis
• Stomach
* – Smooth muscle contractions
* – Storage
* – Chyme
• Smallintestine – Segmentation
21
New cards
Chemical digestion
• Enzymes
• Hormones
• Mouth
– Salivary glands
• Saliva
• Amylase
• Lipase
• Stomach
– Gastric juices
• Acid
• Proteases
• Lipase
• Liver \n – Bile is synthesized
• Small Intestine
– CCK
• Gallbladder \n – Bile is released
• Pancreas
– Pancreatic juices
• Bicarbonate
• Amylase \n • Proteases
• Lipase
• Hormones
• Mouth
– Salivary glands
• Saliva
• Amylase
• Lipase
• Stomach
– Gastric juices
• Acid
• Proteases
• Lipase
• Liver \n – Bile is synthesized
• Small Intestine
– CCK
• Gallbladder \n – Bile is released
• Pancreas
– Pancreatic juices
• Bicarbonate
• Amylase \n • Proteases
• Lipase
22
New cards
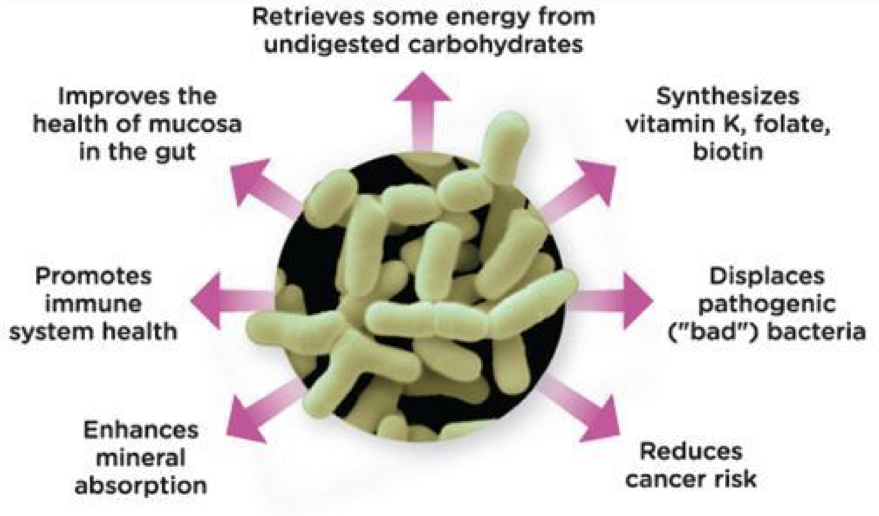
Importance of bacteria in the gut
* Probiotics \n – Beneficial bacteria
* Prebiotics
* – Food for the beneficial bacteria
* – Chicory, whole-grain rye, oats, wheat , barley, leeks, onions, and garlic
* Prebiotics
* – Food for the beneficial bacteria
* – Chicory, whole-grain rye, oats, wheat , barley, leeks, onions, and garlic
23
New cards
digestive disorders
* Diverticulitis
* Gastritis
* Ulcers
* Acid Reflex
* Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
* Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
* Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
* Ulcerative colitis
* Crohn’s disease
* Gallstones
* Celiac Disease
* \
* Gastritis
* Ulcers
* Acid Reflex
* Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
* Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
* Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
* Ulcerative colitis
* Crohn’s disease
* Gallstones
* Celiac Disease
* \
24
New cards
Calories per nutrient
Carbs: 4 kcal/g
Lipids: 9 kcal/g
Protein: 4 kcal/g
Lipids: 9 kcal/g
Protein: 4 kcal/g
25
New cards
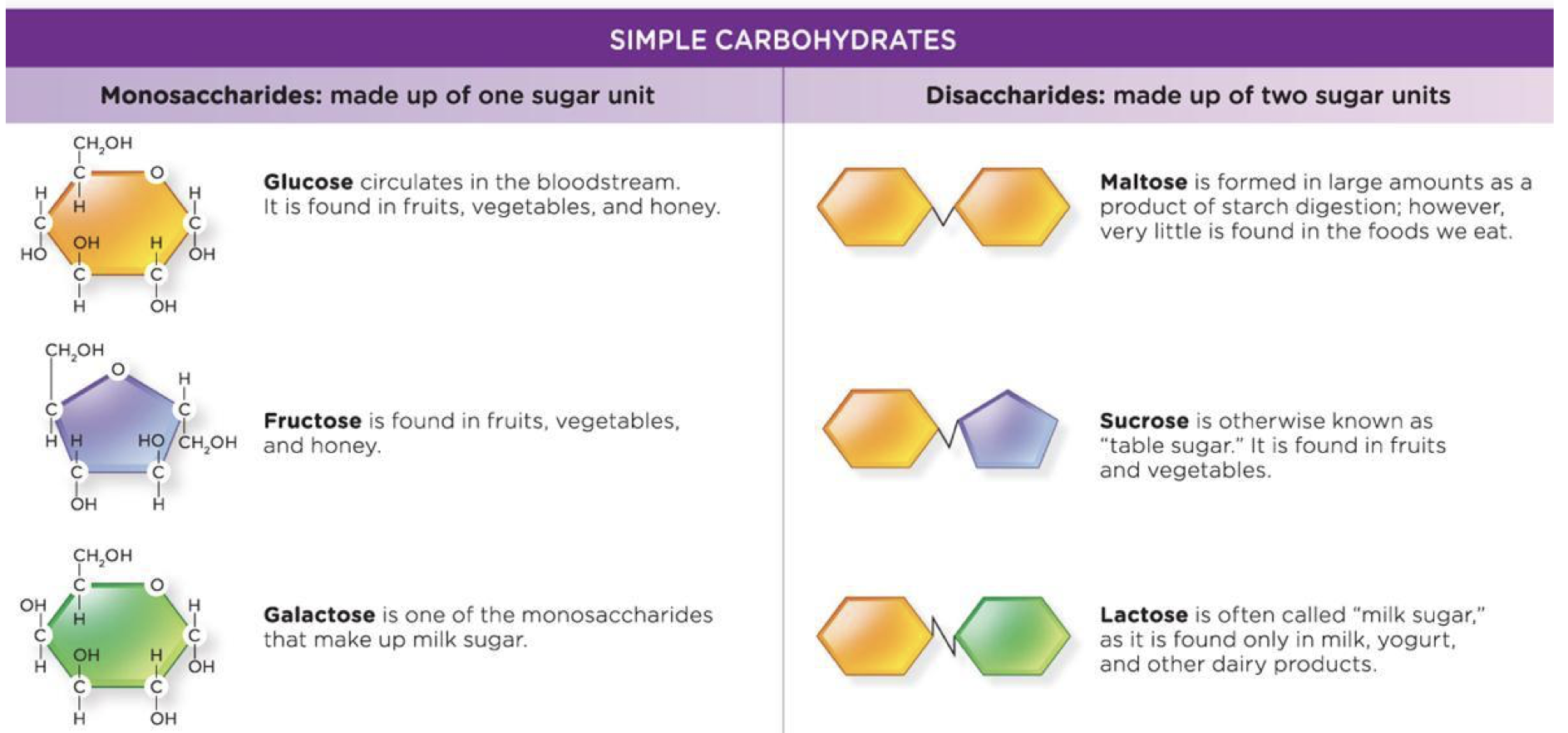
simple carbs
26
New cards
complex carbs
Starch, Fiber, Glycogen
27
New cards
storage form of carbs
stored as glucose, liver break down to give glucose to blood, muscles break down to do work
28
New cards
Lactose intolerence
Low lactase activity
• Lactose maldigestion
– Diarrhea
– Gas, cramps, abdominal pain
• Treatment
– Decrease dairy intake
– Lactase pills \n – Calcium-rich foods
• Lactose maldigestion
– Diarrhea
– Gas, cramps, abdominal pain
• Treatment
– Decrease dairy intake
– Lactase pills \n – Calcium-rich foods
29
New cards
components of whole grain
endosperm, bran, germ
30
New cards
types of grains
• Wholegrains
– Contain the endosperm, germ, and bran in original proportions
• Refined grains (white grain)
– Stripped of the germ and bran, leaving only the endosperm
• Enrichedgrains
– Some nutrients lost in processing are added back
– Contain the endosperm, germ, and bran in original proportions
• Refined grains (white grain)
– Stripped of the germ and bran, leaving only the endosperm
• Enrichedgrains
– Some nutrients lost in processing are added back
31
New cards
carb digestion
• Mouth \n – Amylase
– Breaks starch into smaller links of glucose
• Small intestine
– Amylase \n – Continue digestion of starch into maltose and glucose
• Small intestinal cells
• Maltase
– Hydrolyzes maltose to produce two glucose monosaccharides
• Sucrase
– Hydrolyzes sucrose to produce one glucose and one fructose monosaccharide
• Lactase
– Hydrolyzes lactose to produce one glucose and one galactose monosaccharide
– Breaks starch into smaller links of glucose
• Small intestine
– Amylase \n – Continue digestion of starch into maltose and glucose
• Small intestinal cells
• Maltase
– Hydrolyzes maltose to produce two glucose monosaccharides
• Sucrase
– Hydrolyzes sucrose to produce one glucose and one fructose monosaccharide
• Lactase
– Hydrolyzes lactose to produce one glucose and one galactose monosaccharide
32
New cards
blood glucose levels
* Normal fasting blood glucose levels: 70-100 mg/dl
* Liver determines amount of glucose that is needed to enter the bloodstream after a meal
* Pancreas secretes:
• Insulin
• Glucagon
* Liver determines amount of glucose that is needed to enter the bloodstream after a meal
* Pancreas secretes:
• Insulin
• Glucagon
33
New cards
diabetes
* Above 126 mg/dl is classified as diabetes (hyperglycemic)
• Hunger \n • Thirst \n • Frequent urination
• Weight loss
• Hunger \n • Thirst \n • Frequent urination
• Weight loss
34
New cards
added sugars
* Refined sugars are added to processed foods
– Add flavor
– Increase energy density
– Decrease nutrient density
– Contribute to obesity
– Add flavor
– Increase energy density
– Decrease nutrient density
– Contribute to obesity
35
New cards
nutritive sweeteners
– Provide calories, but fewer than sugars
– Have reduced absorption \n – Include sugar alcohols (polyols)
– Have reduced absorption \n – Include sugar alcohols (polyols)
36
New cards
non-nutritive sweeteners
– Calorie free
37
New cards
types of fiber
* • Insoluble fiber
* – Softens stool and decreases constipation
* – Decreases hemorrhoids and diverticular disease
* • Soluble fiber
* – Slows stomach emptying
* – Slows digestion and absorption
* – Reduces the risk of coronary artery disease
* • Dietary fibers
* • Nondigestible carbohydrates
* • These fibers pass through the small intestine into the large intestine, where they may be partially or completely fermented by gut bacteria.
* • Functional fiber
* • Isolated or purified carbohydrates that are nondigestible
* • Absorbed in the small intestine, and have beneficial physiological effects in humans
* – Softens stool and decreases constipation
* – Decreases hemorrhoids and diverticular disease
* • Soluble fiber
* – Slows stomach emptying
* – Slows digestion and absorption
* – Reduces the risk of coronary artery disease
* • Dietary fibers
* • Nondigestible carbohydrates
* • These fibers pass through the small intestine into the large intestine, where they may be partially or completely fermented by gut bacteria.
* • Functional fiber
* • Isolated or purified carbohydrates that are nondigestible
* • Absorbed in the small intestine, and have beneficial physiological effects in humans
38
New cards
categories of lipids
Fatty acids, triglycerides, sterols, phospholipids
39
New cards
types of fatty acids
Saturated, Monounsaturated, polyunsaturated, cis and trans
40
New cards
structure of triglyceride
* a three-carbon glycerol molecule with three fatty acids attached
41
New cards
structure of phospholipids
* a three-carbon glycerol molecule with two fatty acids and a phosphate group on the third carbon
42
New cards
lipid digestion and absorption
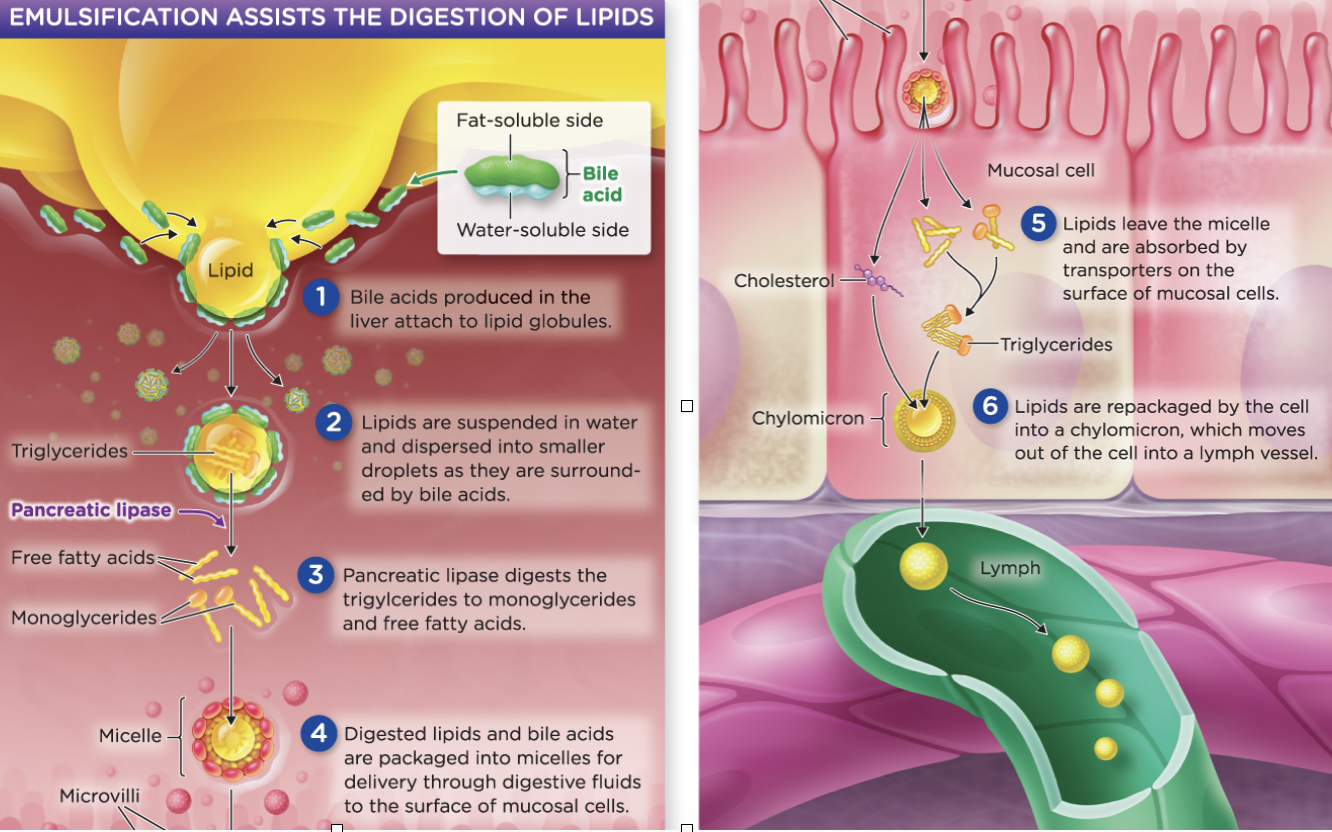
43
New cards
types of lipoproteins
* chylomicrons
* lipoproteins made in intestinal cells or enterocytes
* transport fat from the intestine to the body
* very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL)
* made in the liver
* transports fat from the liver to the body
* low-density lipoprotein (LDL)
* made in the liver
* transports cholesterol from the liver to the cells of the body
* "bad" cholesterol
* high-density lipoprotein (HDL)
* collects fat and cholesterol from the body to transport back to the liver (“reverse cholesterol transporter”)
* "good cholesterol"
* lipoproteins made in intestinal cells or enterocytes
* transport fat from the intestine to the body
* very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL)
* made in the liver
* transports fat from the liver to the body
* low-density lipoprotein (LDL)
* made in the liver
* transports cholesterol from the liver to the cells of the body
* "bad" cholesterol
* high-density lipoprotein (HDL)
* collects fat and cholesterol from the body to transport back to the liver (“reverse cholesterol transporter”)
* "good cholesterol"
44
New cards
essential fatty acids
* omega-3 fatty acids
* linolenic acid
* food sources: cold-water fish, flaxseed oil
* omega-6 fatty acids
* linoleic acid
* food sources: walnuts, plant oils
* linolenic acid
* food sources: cold-water fish, flaxseed oil
* omega-6 fatty acids
* linoleic acid
* food sources: walnuts, plant oils
45
New cards
trans fat
* behave like saturated fats and raise LDL cholesterol
* increase risk of heart disease
* increase risk of heart disease
46
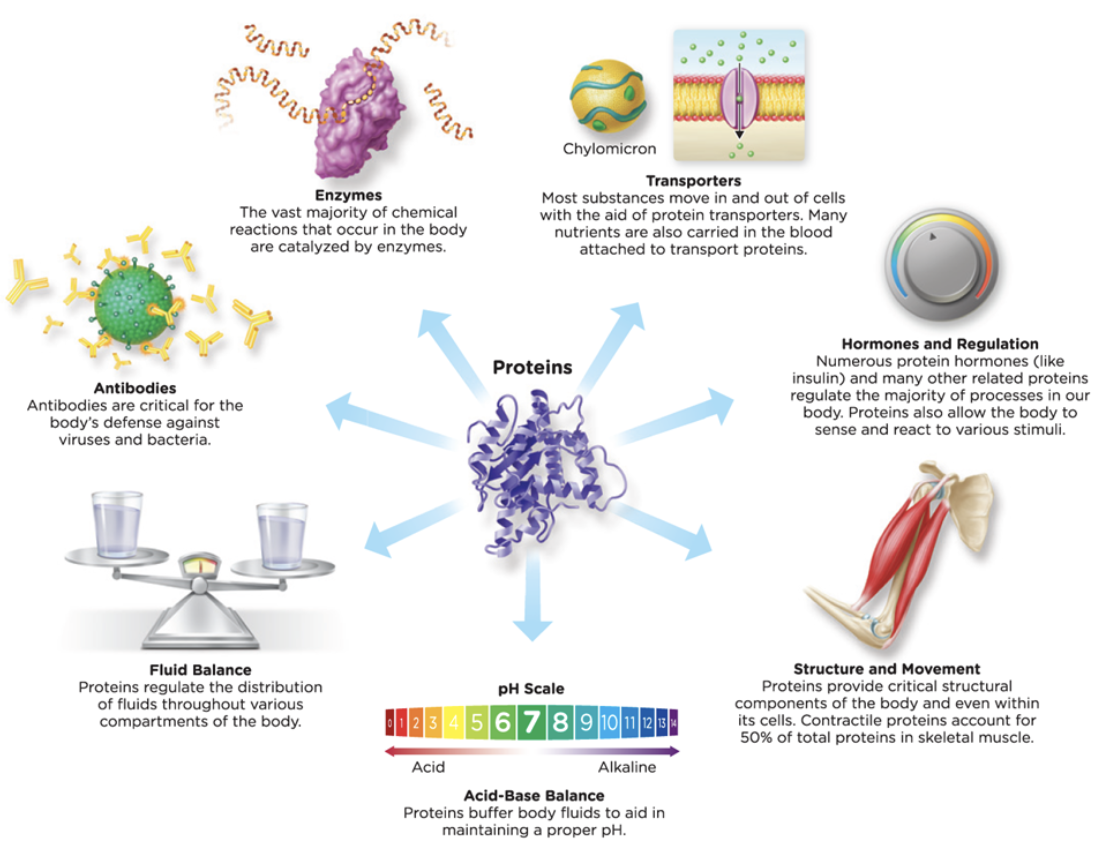
New cards
roles of protein
47
New cards
protein structure
* Building blocks of protein are amino acids
48
New cards
protein denaturation
* Caused by heat, light, change in pH, alcohol, or motion
* Affects the protein’s ability to function
* Affects the protein’s ability to function
49
New cards
protein folding
* After translation, amino acid chains fold into a particular shape
* The shape determines the protein’s function
* A protein must be folded correctly to function
* The shape determines the protein’s function
* A protein must be folded correctly to function
50
New cards
protein digestion
* Mouth
* Mechanical digestion
* Stomach
* Acidic juices
* Pepsin
* Small intestine
* Pancreatic proteases
* Absorption of amino acids
* Mechanical digestion
* Stomach
* Acidic juices
* Pepsin
* Small intestine
* Pancreatic proteases
* Absorption of amino acids
51
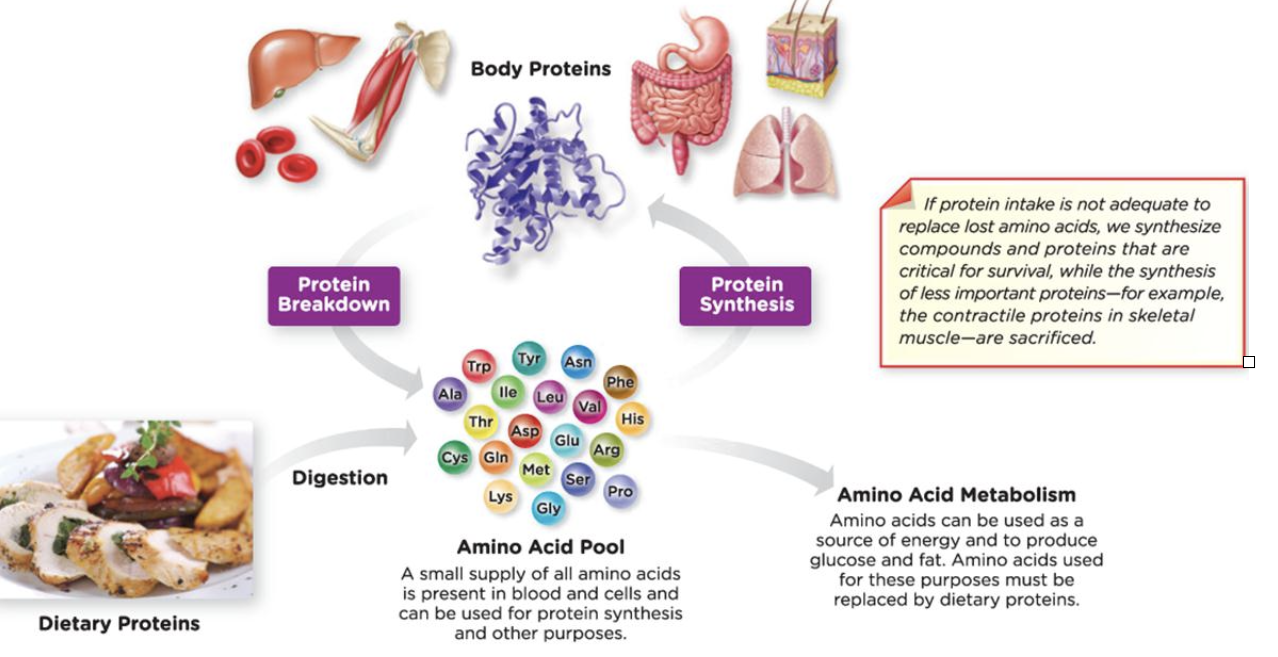
New cards
protein turnover
52
New cards
nitrogen balance
* Nitrogen can be used as a measure of protein
* Nin − Nout
* Nin
* Protein intake
* Nout
* Urine and feces
* Sweat and other secretions
* Skin, hair, and nails
* Nin − Nout
* Nin
* Protein intake
* Nout
* Urine and feces
* Sweat and other secretions
* Skin, hair, and nails
53
New cards
Protein AMDR and RDAs for different groups of people
* Adults 50 to 65 years of age
* 0.7 to 0.8 g/kg of body weight/day is beneficial
* Adults older than 65 years of age
* 1.2 g/kg of body weight/day is beneficial
* 0.7 to 0.8 g/kg of body weight/day is beneficial
* Adults older than 65 years of age
* 1.2 g/kg of body weight/day is beneficial
54
New cards
When should we consume protein? How much?
* 0.3-0.5g/kg/meal
55
New cards
Protein’s effect on fat mass
can cause loss fat mass
56
New cards
Diseases associated with Protein deficiency
* Edema (swollen belly)
* Proteins hold water and salt in the blood vessels
* Marasmas
* Protein energy malnutrition (PEM)
* Starvation
* “Skin and bones” appearance
* Proteins hold water and salt in the blood vessels
* Marasmas
* Protein energy malnutrition (PEM)
* Starvation
* “Skin and bones” appearance
57
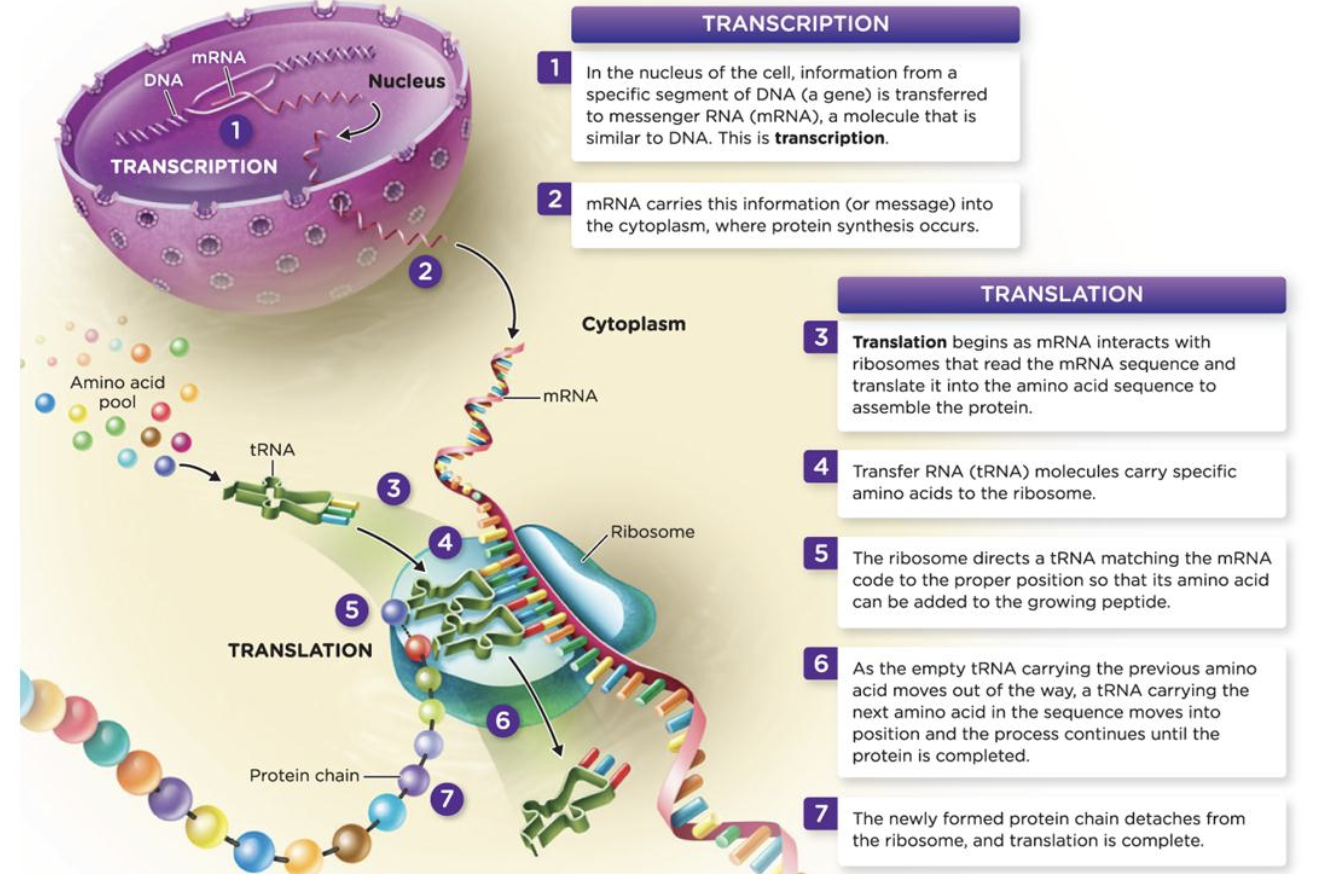
New cards
processes of Transcription and Translation
58
New cards
Cons of GMOs
1. They may contribute to an increase in food-related allergies. Information from the CDC shows that food allergies in children have increased from 3.4% to 5.1% in the last decade.
2. Genetic engineering can trigger allergies from alternative foods. \n GMOs that contained proteins from Brazil nuts were found to trigger an allergic reaction in people who are allergic to them.
3. GMOs may contribute to antibiotic resistance. \n GMOs are often incorporated with antibiotic-resistant genes in order to strengthen the crops that will grow.
4. One research paper connects GMOs to cancer formation. A paper that was first published in 2013 linked the herbicide that is found in Roundup-tolerant crops to cancer development in rats. –since retracted.
5. Just 6 companies control almost the entire GMO seed market and 70% of the global pesticide market. Much of the negative energy which surrounds GMOs tends to involve Monsanto.
6. Herbicide resistance happens naturally without the need for genetic engineering. There are currently 64 different types of weeds which have been proven to be resistant to atrazine.
7. Independent research is not allowed with GMO seeds from half of today’s controlling organizations. User agreements with half of today’s leading GMO seed producers prohibit the use of independent research on the final product.