Cross Sectional Anatomy I Chapter 9 Instrumentation
1/233
Earn XP
Description and Tags
After reading this chapter, you will be able to: Differentiate between the different types of magnetism. Understand the differences in MRI scanner design and form-factor. Explain the function of the technical components found inside an MRI scanner.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
234 Terms
True/False
The clavicle connects the upper limb to the trunk of the body and provides attachments for several muscles and ligaments
True
True/False
The scapula is a long, slender bone that forms the posterior portion of the shoulder girdle.
False
True/False
The glenoid labrum deepens the articular surface of the glenoid fossa.
True
True/False
The shoulder joint is surrounded by a thick and rigid articular joint capsule.
False
True/False
The subacromial-subdeltoid bursa is the largest bursa in the body
True
True/False
The humerus articulates with the scapula superiorly and the radius and ulna inferiorly
True
True/False
The radius is located medially within the forearm.
False
True/False
The elbow joint primarily relies on the collateral ligaments for stability
True
True/False
The thenar group of hand muscles includes the abductor digiti minimi.
False
True/False
The axillary artery is the primary artery of the elbow.
False
Clavicle:
A long, slender bone connecting the upper limb to the trunk
Glenoid Labrum:
Deepens the articular surface of the glenoid fossa
Subacromial-Subdeltoid Bursa:
Largest bursa within the body
Triceps Brachii:
A muscle in the dorsal group of the upper arm
Ulna:
A medial bone in the forearm with olecranon and coronoid processes
Thenar Group:
Includes abductor pollicis brevis and opponens pollicis
Distal Humerus:
Contains the medial and lateral condyles with associated epicondyles
Radiocarpal Joint:
A joint connecting the distal radius and proximal carpals
Radial Artery:
A major artery of the elbow and forearm
Palmar Plate:
Fibrocartilaginous tissue covering the palmar surface of joints
True/False
The small conical projection on the medial bone of the forearm surface is called the ulnar styloid process.
True
Because of its superficial location, the ___________ nerve is the most frequently injured nerve of the body.
ulnar
True/False
The common interosseous artery begins at the level of the radial head and courses beneath the brachioradialis muscle.
False
The majority of rotator cuff lesions are a result of chronic impingement of the supraspinatus tendon against the acromial arch. The most susceptible area is approximately 1 cm from the insertion site of the supraspinatus tendon. This location is commonly referred to as the ____________ ____________.
critical zone
The major stabilizing element of the distal radioulnar joint is the:
Triangular fibrocartilage complex
What ligament in the elbow attaches to the annular ligament?
Radial collateral
Which rotator cuff tendon is the most frequently injured?
Supraspinatus
The Anconeous muscle's primary action is:
Assists triceps brachii in extension of elbow
Which of the following elbow joint ligaments consists of an anterior band, a posterior band, and a transverse band (ligament of Cooper)?
Ulnar collateral
Which nerve courses through the carpal tunnel?
Median
Which of the following carpal bones is located in the proximal row?
Scaphoid
Which of the following muscles is located in the posterior muscle group of the elbow?
Anconeus
The ulnar nerve is located:
Between the medial epicondyle of the humerus and the olecranon process
Which of the following arteries courses inferiorly on the medial side of the humerus, then continues anterior to the cubital fossa of the elbow and is the principal arterial supply to the arm?
Brachial
Which rotator cuff muscle is located on the anterior surface of the scapula?
Subscapularis
True/False
The supraspinatus tendon inserts on lesser tubercle of the humerus.
False
Which muscle is the main flexor of the forearm?
Biceps brachii
Which ligament bids the radial head to the ulna?
Annular
The most medial and superficial muscle located in the anterior compartment of the forearm is the:
Flexor carpi ulnaris
This is a small triangular-shaped muscle that spans between the first rib and clavicle, and acts to stabilize the clavicle and depress the shoulder:
subclavius
The infraspinatus tendon inserts on the:
greater tubercle
The teres major primary action is to ___________ and medially rotate the humerus
A) adduct
Which muscle is NOT a muscle of the scapula?
Subclavius
Which ligaments protects the humeral head from direct trauma?
Coracoacromial
The cephalic vein opens into which vein?
Axillary
The proximal surface of the radiocarpal articulation is formed by the articular carpal surface of the ____________ and the TFCC
radius
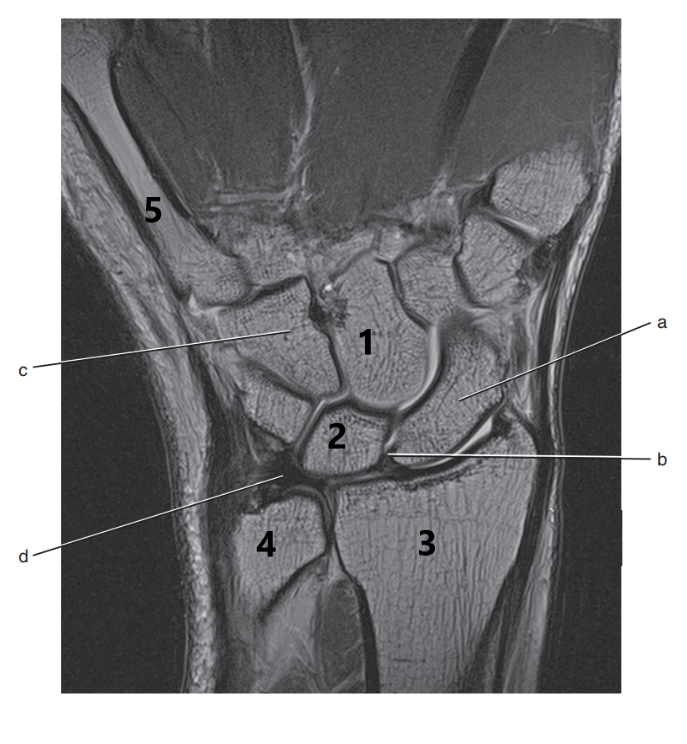
What is # 3 ?
Radius
Which rotator cuff muscle inserts on the lesser tubercle of the humerus?
Subscapularis
It is a long, slender bone located anteriorly that extends transversely from the sternum to the acromion process of the scapula.
clavicle
DRUJ Stands for:
Distal radioulnar joint
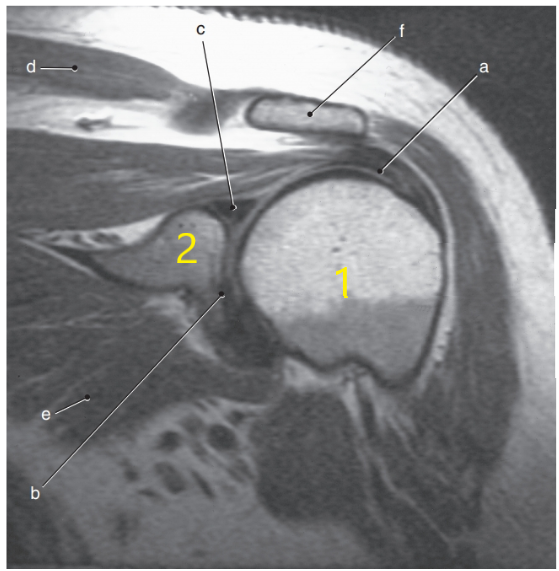
What anatomy is # 2 ?
Scapula
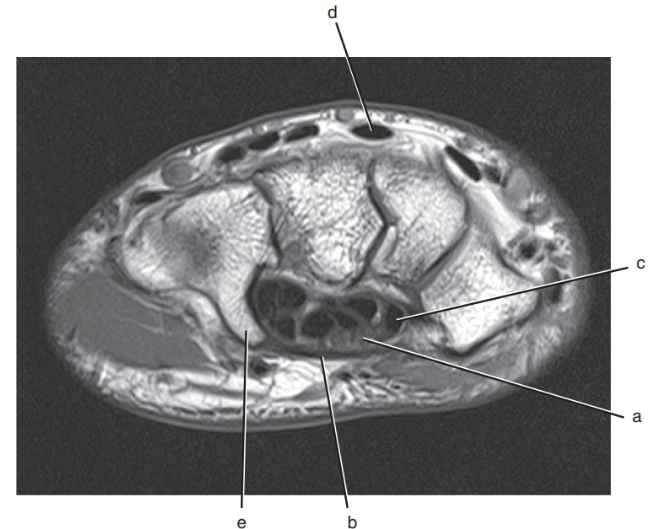
What is letter a?
Median nerve
The distal radioulnar joint is created when the ulnar notch of the radius moves around the articular circumference of the _________
ulna
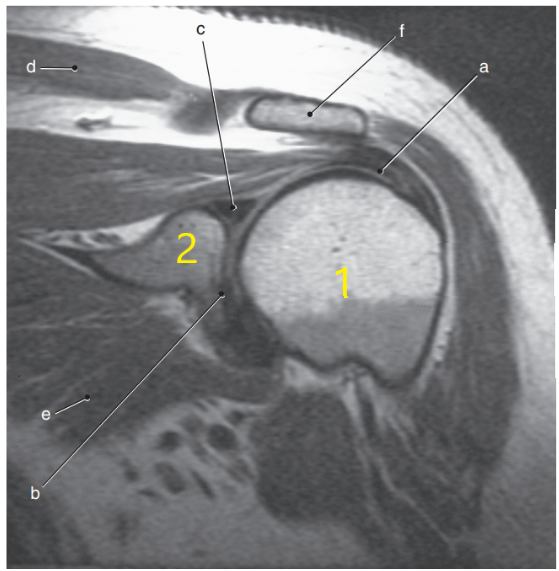
What anatomy is # 1 ?
Humeral head
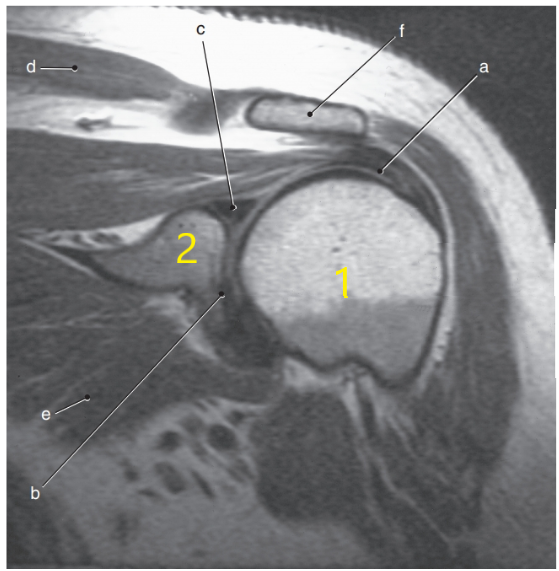
What is letter c ?
Superior glenoid labrum
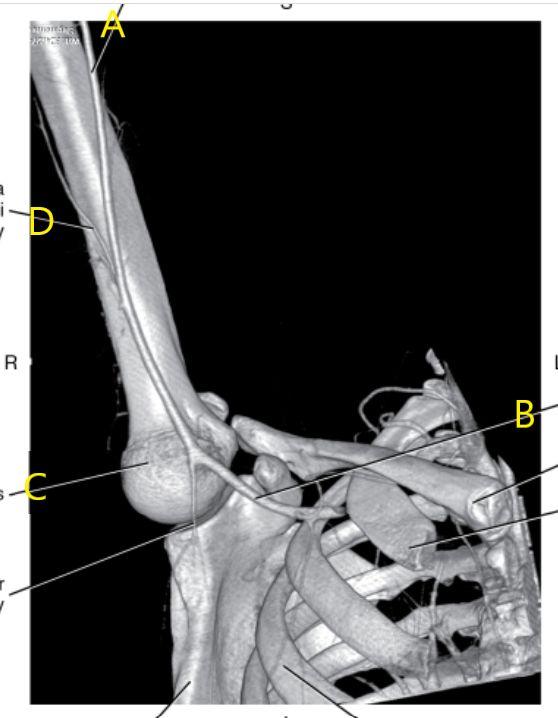
What is letter A?
Brachial artery
The oblique coronal views for an MRI of the shoulder need to be oriented ---
Parallel to the supraspinatus tendon
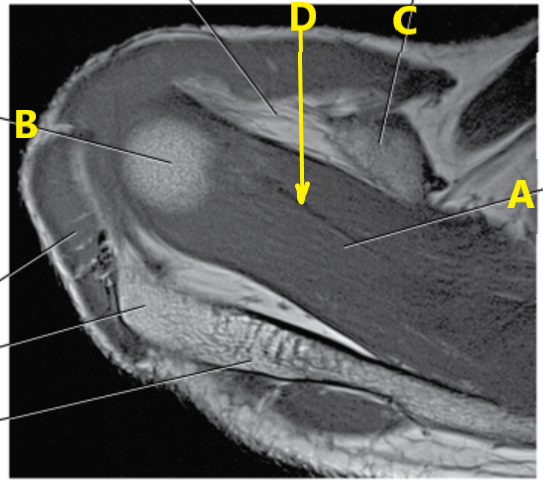
What is letter B pointing to ?
Humerus
The _________phalanges that make up the fingers.
14
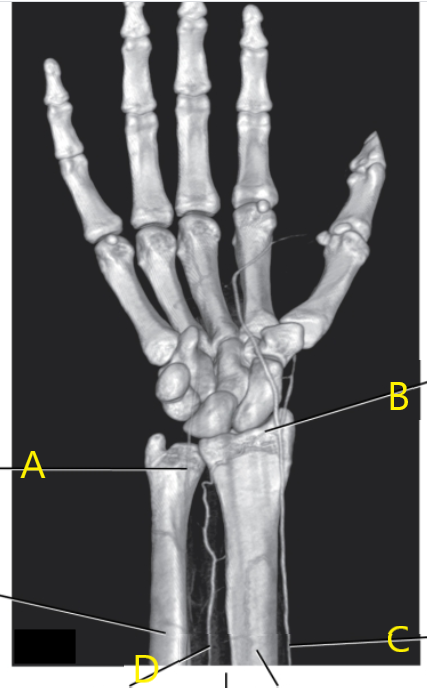
What is letter A arrow pointing to ?
Ulnar artery
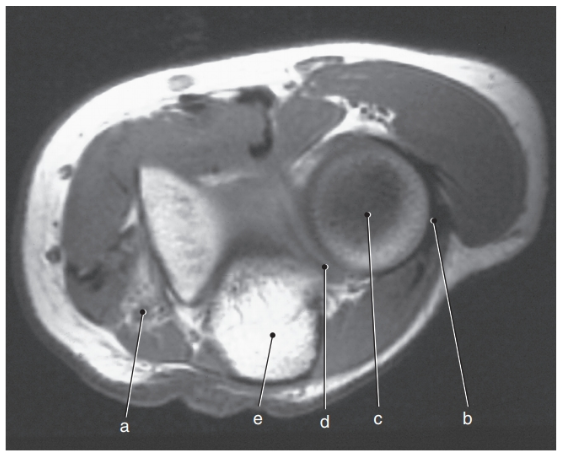
What is letter e ?
Olecranon process
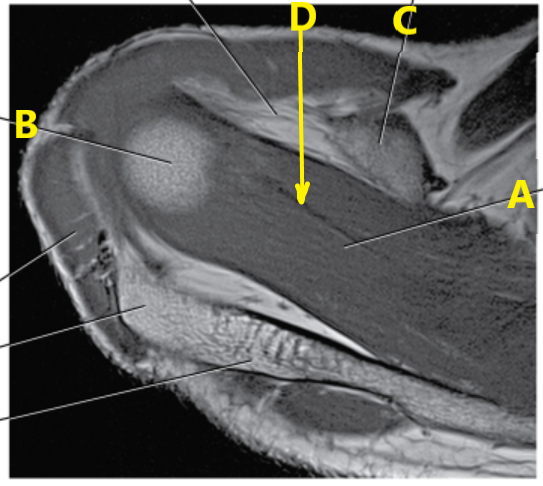
What is letter C pointing to ?
Coracoid process
How many carpal bones are there ?
8
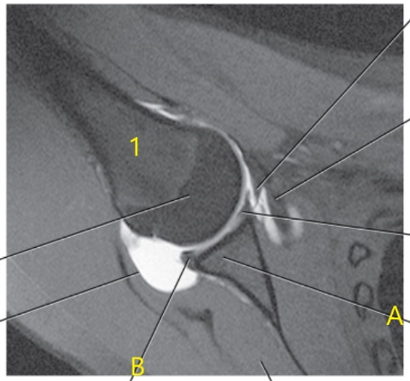
What is this special view of the shoulder joint called ?
Abduction external rotation
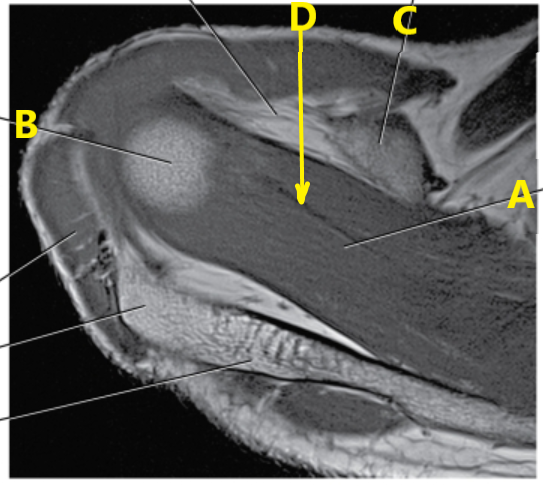
What is letter A pointing to ?
Supraspinatus muscle
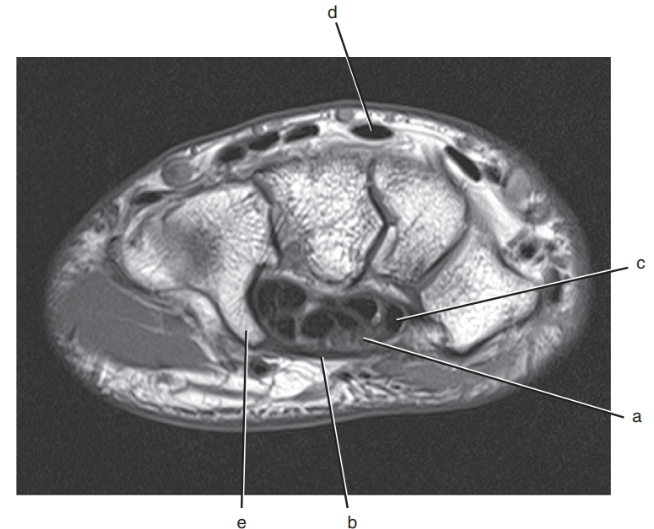
What is letter e ?
Hook of the hamate
The primary function of the glenoid labrum is to:
Deepen the glenoid fossa
The primary arteries of the shoulder are the brachial artery and the:
axillary
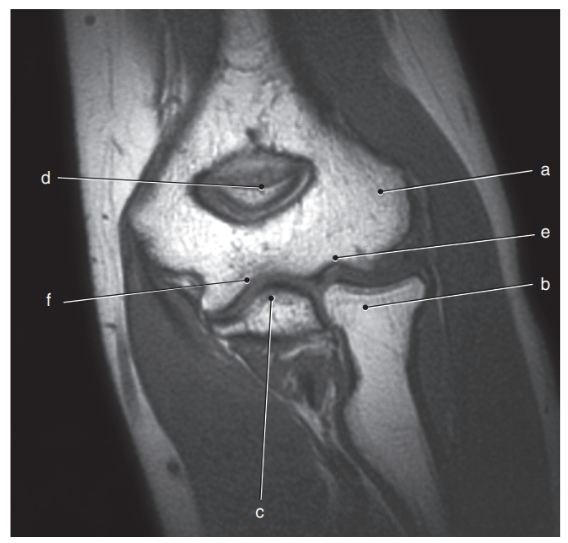
What is letter a ?
Lateral epicondyle
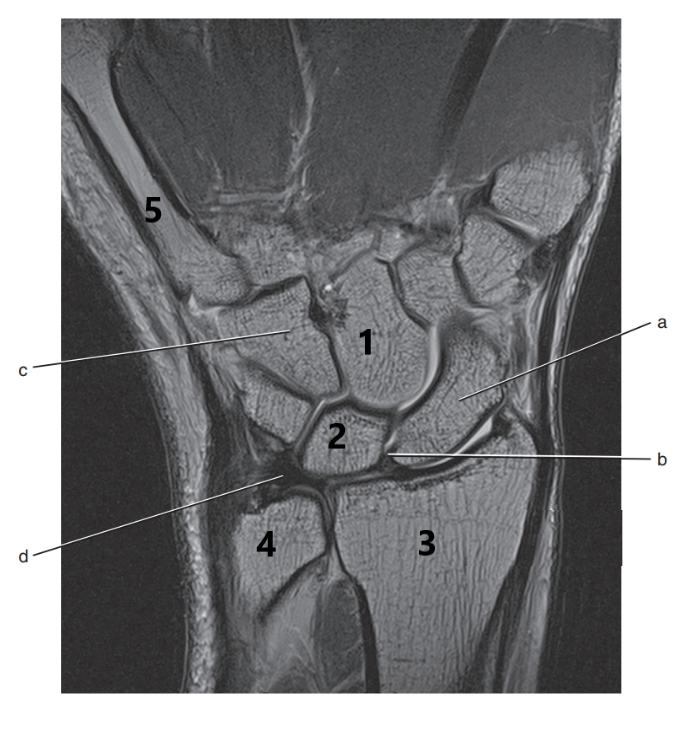
What is letter a ?
Scaphoid
What ligamentous structure spans the wrist to create an enclosure for the passage of tendons?
Flexor retinaculum
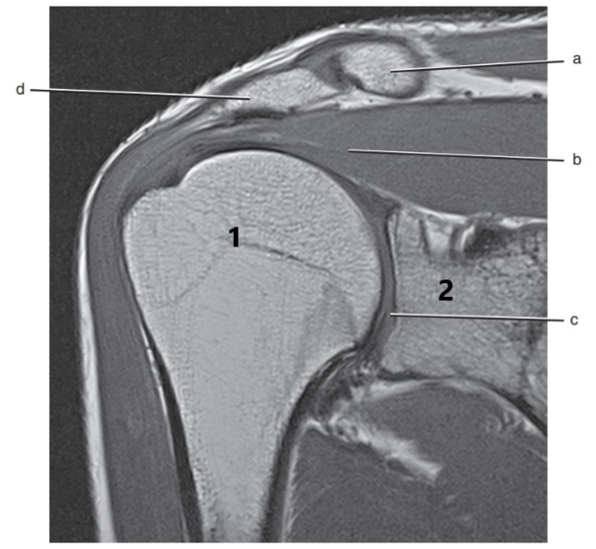
What is letter c ?
Glenohumeral joint
The majority of rotator cuff lesions are a result of chronic impingement of the supraspinatus tendon against the acromial arch. The most susceptible area is approximately 1 cm from the insertion site of the supraspinatus tendon. This location is commonly referred to as the ________________ ____________.
critical zone
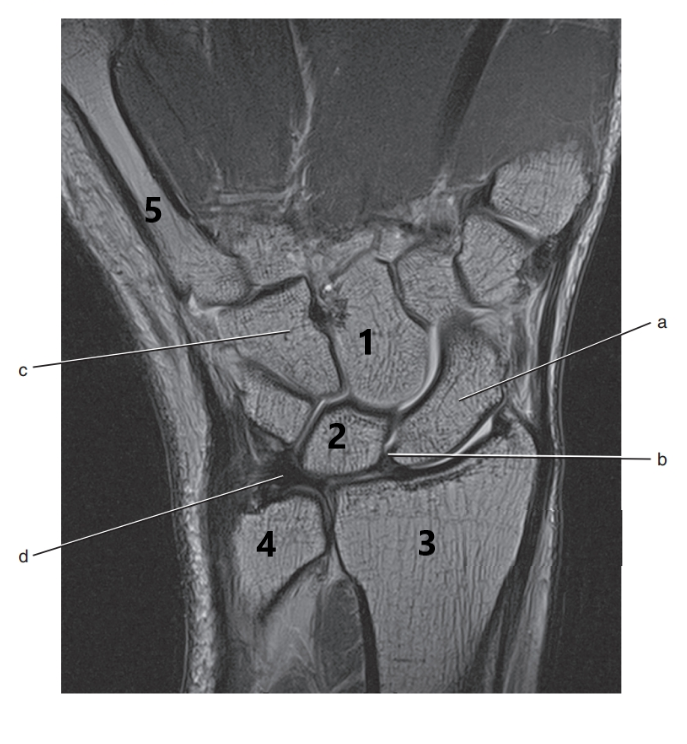
What is # 2 ?
Lunate
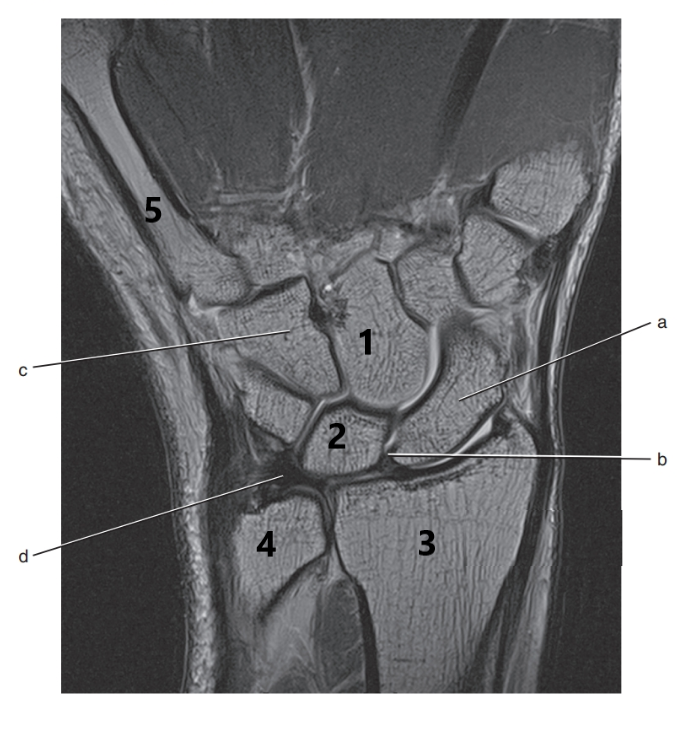
What is letter d ?
Triangular fibrocartilage complex
Because of its superficial location, the ____________ ________ is the most frequently injured nerve of the body.
ulnar nerve
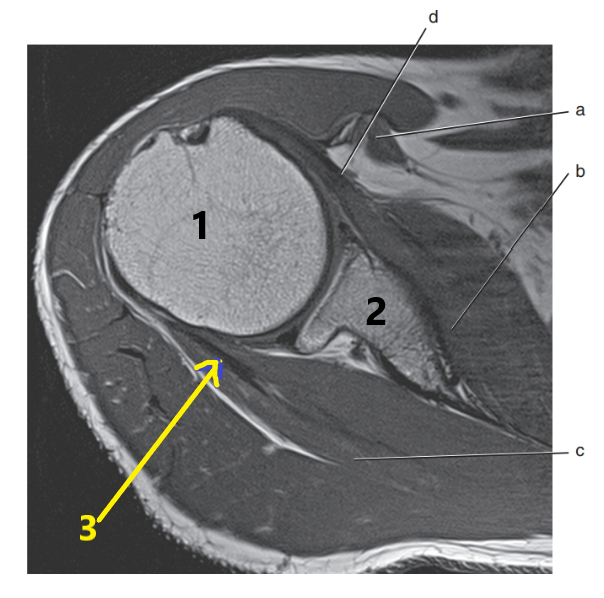
What is arrow # 3 ?
Teres minor tendon
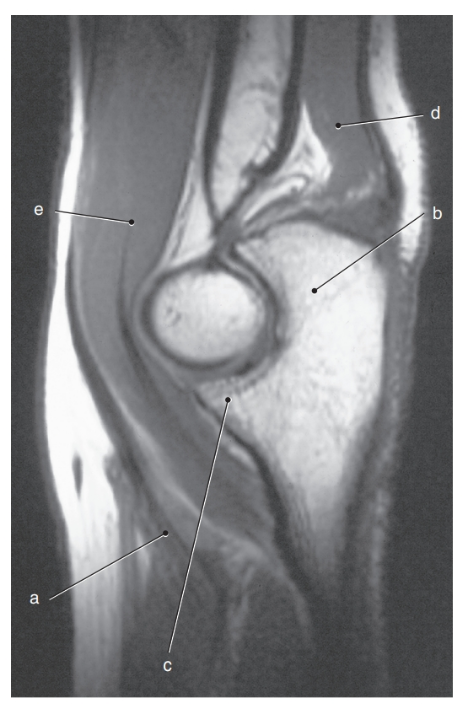
What is letter c ?
Coronoid process
The ulna is located _____________ within the arm.
medial
The main stabilizing element of the _________ is an articular disk called the triangular fibrocartilage complex
DRUJ
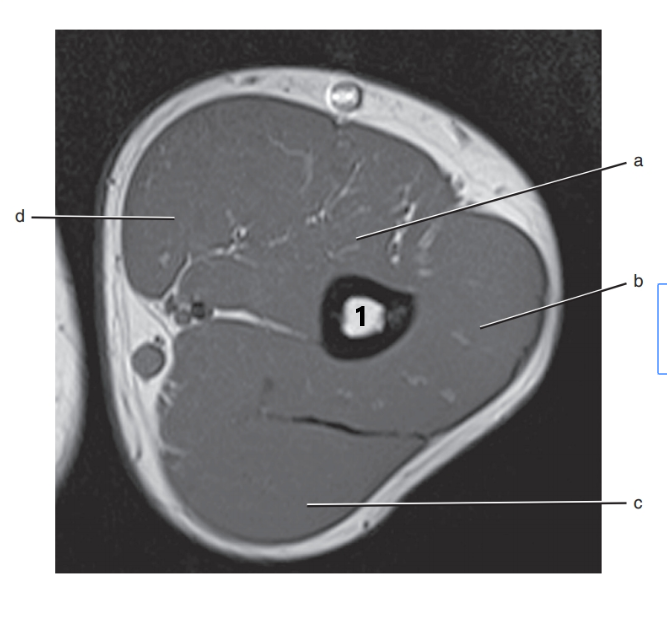
What is # 1 ?
humerus
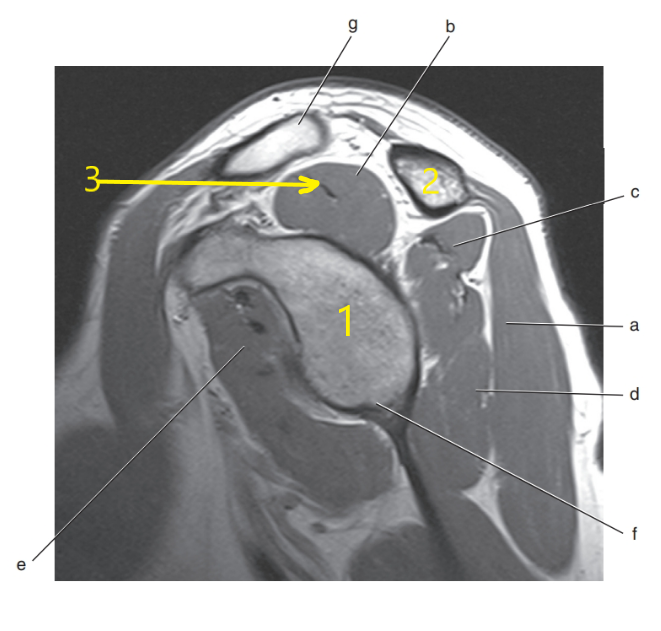
What is # 2 ?
Acromion Process
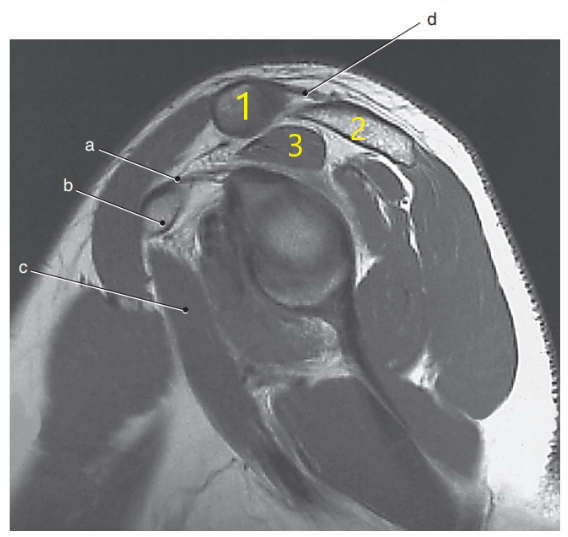
What is letter d ?
Acromioclavicular ligament
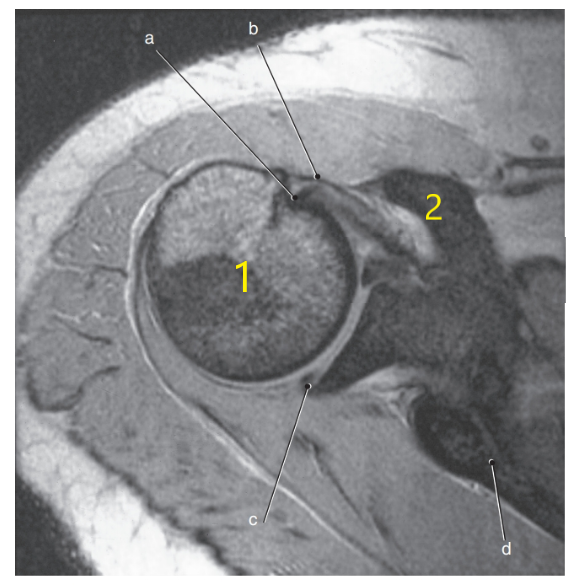
What is letter a?
Biceps brachii tendon
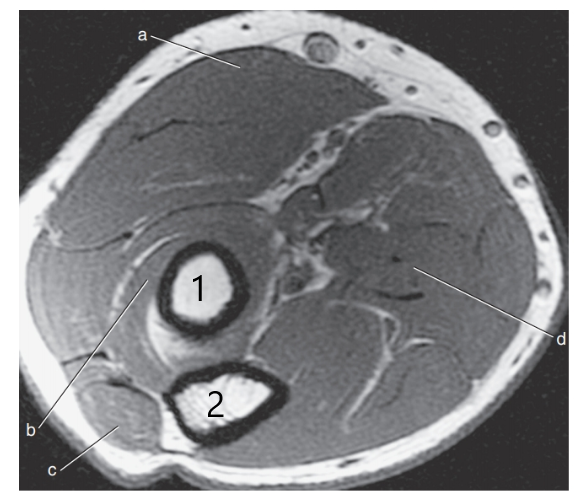
What anatomy is # 2 ?
Ulna
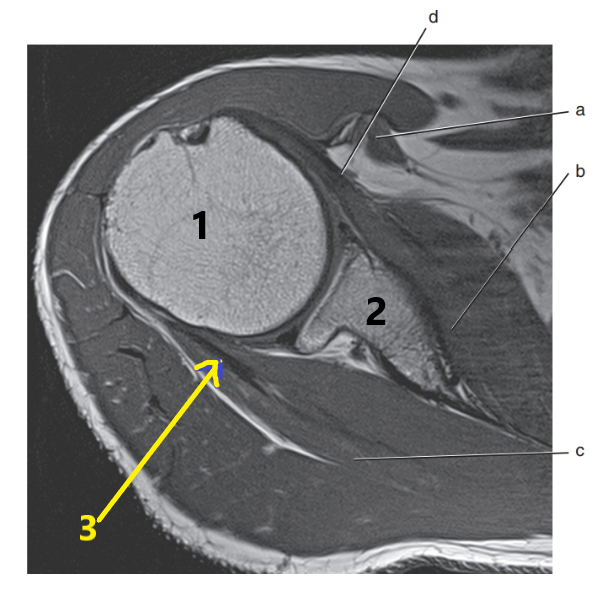
What is letter d ?
Subscapularis tendon
The outer rim of the glenoid fossa is surrounded by a fibrocartilaginous ring termed the:
glenoid labrum
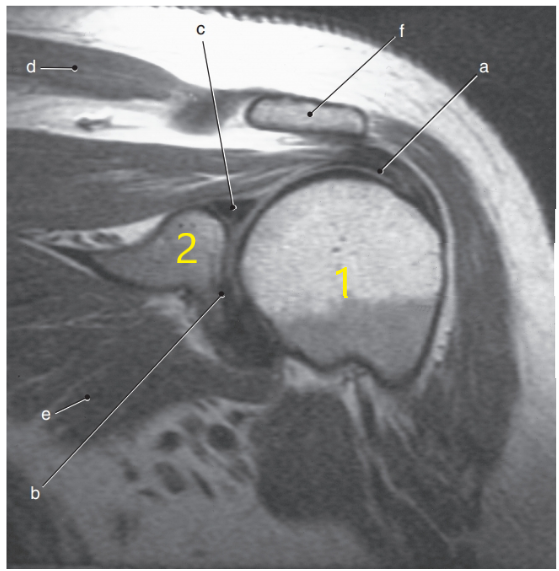
What is letter f ?
Acromion process
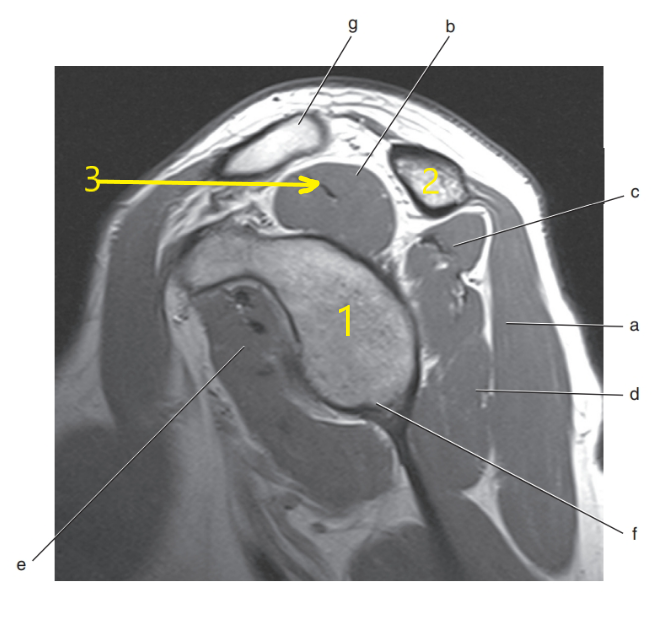
What is letter b ?
Supraspinatus muscle
Which rotator cuff tendon is the most frequently injured?
Supraspinatus
A fracture of the ____________ may result in a nonunion injury because of the traction of associated muscles. The ulnar nerve runs close to the hook of the hamate and may be injured as well, resulting in decreased grip strength of the hand.
hamate
What is the major stabilizing mechanism for the distal radioulnar joint?
Triangular fibrocartilage complex
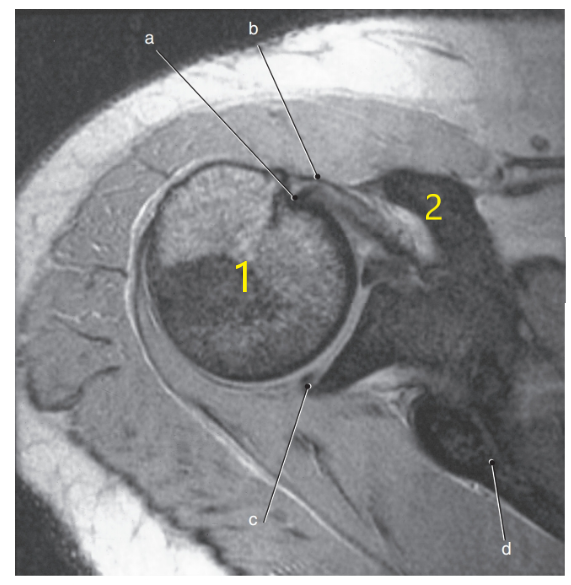
What is letter c ?
Posterior glenoid labrum
Located on the anterior surface of the scapula is a beaklike process termed the ____________________.
Corocoid process
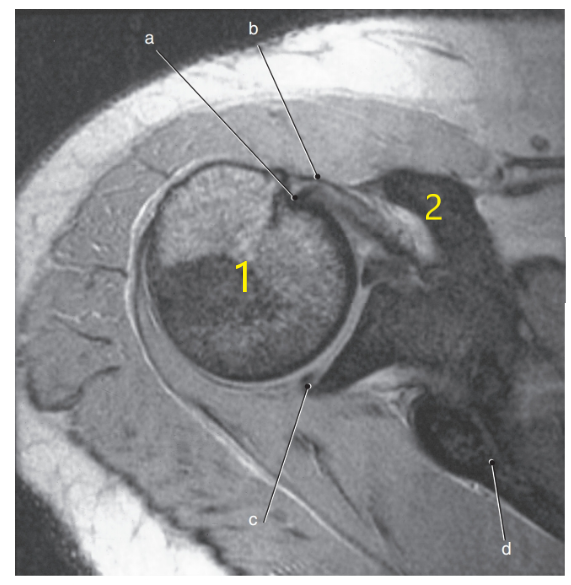
What is letter d ?
Scapular spine
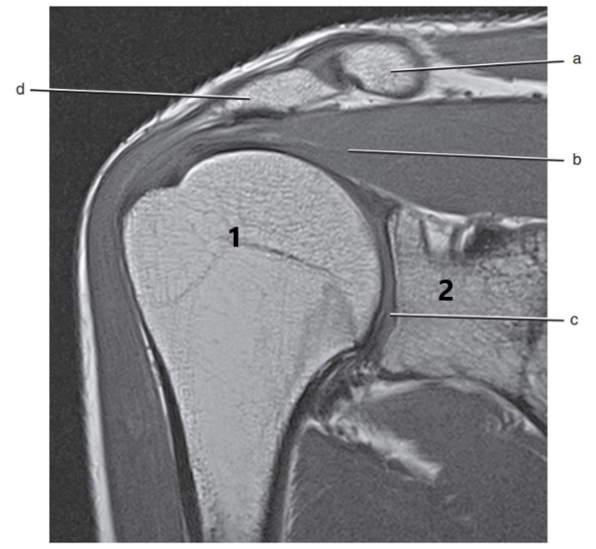
What is # 2 ?
Scapula
The anterior surface of the scapula, the____________ _________, is flat and slightly concave.
subscapular fossa
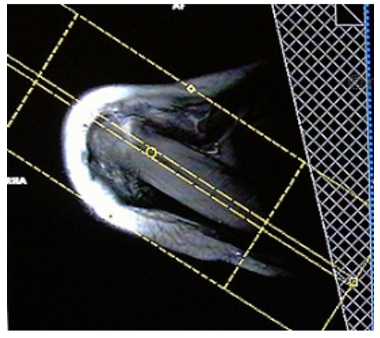
What images will be created with this slice prescription ?
oblique coronal
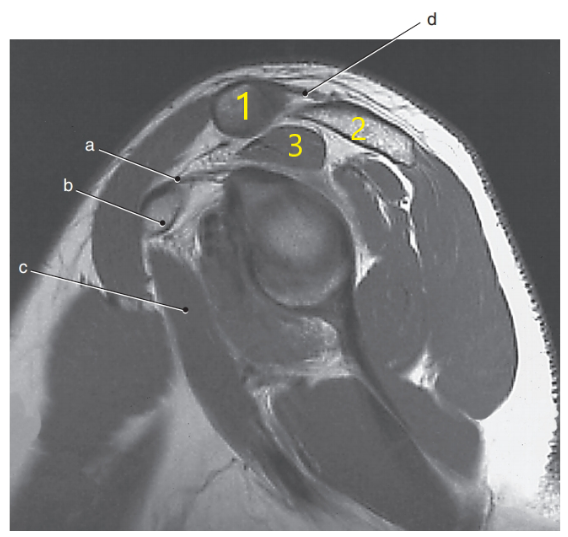
What is # 3 ?
Supraspinatus muscle
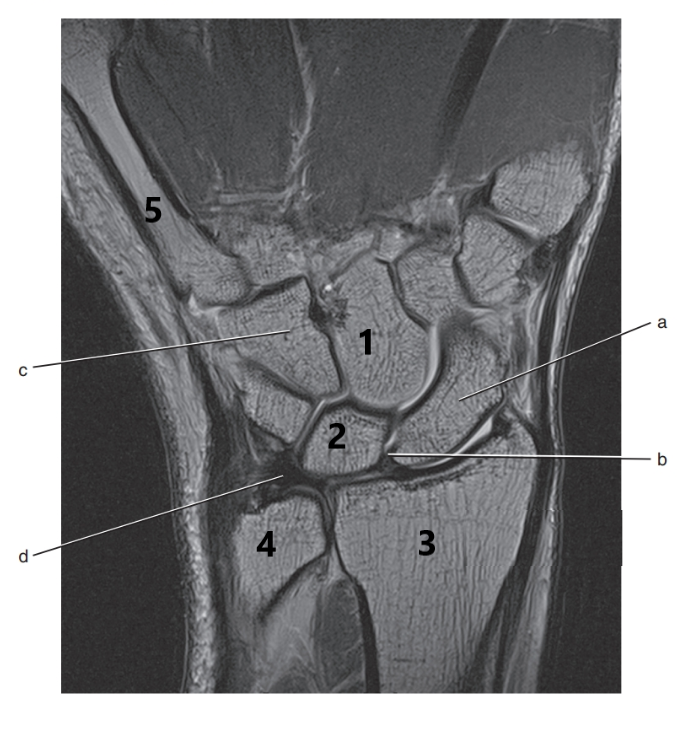
What is # 4 ?
Ulna