Lesson 10: Cohort studies
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What type of studies are cohort studies?
They are observational, analytical and longitudinal studies
What is the objective of a cohort study?
To follow up one or more groups of healthy people along time, and to measure the appearance of a disease or study condition.
What is the usefulness of cohort studies?
Causality investigation to test hypotheses
What is the initial requirement for subjects in a cohort study?
All subjects in the study population are free of the studied disease at the beginning.
How are subjects classified?
As exposed and non-exposed.
What happens during follow-up?
Subjects are followed over time to identify new cases of the disease.
What measures can be estimated in both groups?
Incidence and/or incidence rates.
What is the measure of association in cohort studies?
The Relative Risk (RR).
What are cohort studies used to assess?
Whether a given exposure is associated with a disease.
What are the three axes of analytical cohort studies?
Directionality of the study, follow-up, and tracking time.
What is a prospective cohort study?,
Forward in time, from exposure to outcome (disease).
What is a retrospective cohort study?
Exposure and outcome occurred earlier; historical or retrospective cohort.
What is a mixed or ambispective study?
Exposure occurred in the past and the outcome is detected now.
How are individuals selected in a cohort study?
By exposure (exposed sample), with a non-exposed comparison sample selected from the same population base.
How is tracking time measured?
In years or months.
What is a closed or static cohort?
A cohort with a fixed number of individuals at the beginning and throughout the follow-up.
What is an open or dynamic cohort?
A cohort where individuals continuously come in and out.
What measure is used in open or dynamic cohorts?
The incidence rate (incidence density), using the term person-years.
What are the uses of cohort studies?,
-Estimate incidence of disease in exposed and non-exposed individuals;
-estimate the risk of disease in the exposed relative to the non-exposed (RR);
-estimate existence of a dose-response relation;
-study the natural history of a disease;
-study more than one health consequence of exposures."
What are the advantages of cohort studies?
-Calculation of incidences and obtaining the RR
-reduced possibility of bias
-allow study of infrequent exposures
-allows study of associations between risk factors and disease occurrence
-have a higher degree of scientific evidence."
What are the disadvantages of cohort studies?
-Only a small number of risk factors can be studied
-loss of patient follow-up
-high cost in time and money
-chronic processes require long-duration studies
-low frequency diseases may need very large sample sizes; difficult reproducibility
-complex and analytical
What does RR = 1 mean?
There is no association; incidence rate is the same in exposed and non-exposed groups.
What does RR > 1 indicate?
Higher or increased risk for the exposed group; positive association.
What does RR < 1 indicate?
Lower or reduced risk for the exposed group (protective factor); negative or beneficial association.
What do nested case-control studies allow?
Identification of a pool of diseased subjects at the end of the follow-up period within a cohort.
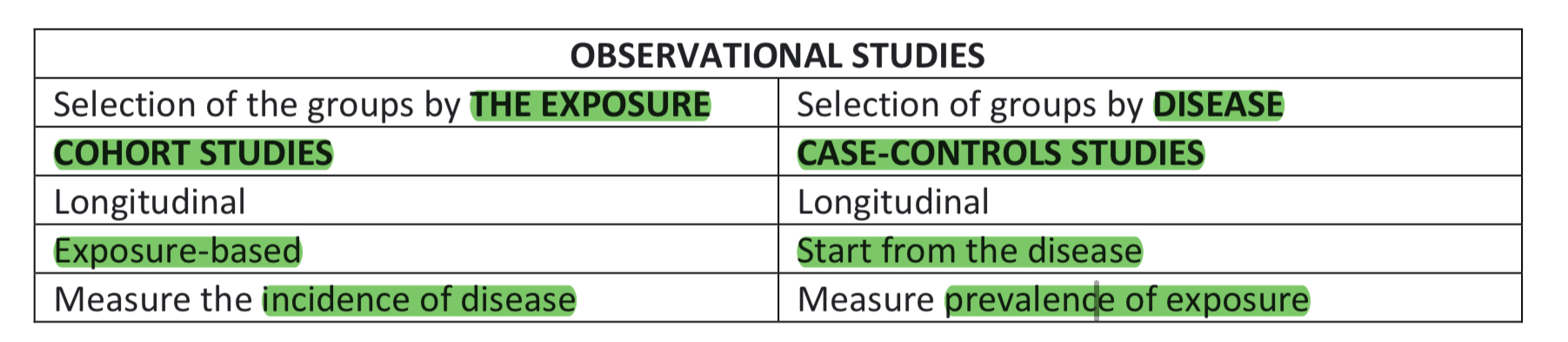
How do cohort and case-control studies differ in group selection?,
Cohort: selection of groups by exposure; Case-control: selection of groups by disease."
Differences of case control and cohort