UD BISC 305: cell bio van golen prep for EC quiz
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
which of the following can be described as the smallest living unit?
A) cell
B) DNA
C) organelle
D) protein
A) cell
what unit of length would you generally use to measure a typical plant or animal cell?
A) nanometers
B) micrometers
C) millimeters
D) centimeters
B) micrometers
The _____ is made up of two concentric membranes and is continuous with the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum.
A) mitochondrial membrane
B) Golgi network
C) nuclear envelop
D) plasma membrane
C) nuclear envelope
Which of the following organelles has both an outer and an inner membrane?
A) endoplasmic reticulum
B) mitochondrion
C) peroxisome
D) lysosome
B) mitochondrio
The mitochondrial proteins found in the inner membrane are involved in the conversion of ADP to ATP, a source of energy for the cell. This process consumes which of the following substances?
A) sulfur
B) oxygen
C) nitrogen
D) carbon dioxide
B) oxygen
Which of the following best describe the role of the lysozome?
A) transport of material to the Golgi apparatus
B) clean up, recycling, and disposal of macromolecules
C) inactivation of toxic molecules via hydrogen peroxide
D) storage of excess macromolecules
B) clean up, recycling, and disposal of macromolecules
_____ are small, membrane-bound organelles that provide a safe place w/in the cell to carry out biochemical reactions that generate and remove harmful, highly reactive oxygen species like superoxide and hydrogen peroxide.
A) endosomes
B) lysosomes
C) vesicles
D) peroxisomes
D) peroxisomes
Cells that are specialized for the secretion of proteins are likely to have which of the following features?
A) large population of mitochondria
B) enlarged endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
C) long bundles of actin/myosin proteins
D) small volume of cytoplasm
B) enlarged endoplasmic reticulum
Chemical rxns carried out by living systems depend on the ability of some organisms to capture and use atoms from nonliving sources in the environment. The specific subset of these rxns that break down nutrients in food can be described as:
A) biosynthetic
B) anabolic
C) metabolic
D) catabolic
D) catabolic
The energy used by the cell to generate specific biological molecules and highly ordered structures is stored in the form of
A) light waves
B) brownian motion
C) heat
D) chemical bonds
D) chemical bonds
Unlike what occurs when fuel is burned to make a fire, all living systems use the energy from heat-generating rxns to create and maintain:
A) order
B) light
C) electricity
D) movement
A) order
Oxidation is the process by which oxygen atoms are added toa target molecule. Generally, the atom that is oxidized will experience which of the following with respect to the electrons in its outer shell in the covalent bond?
A) a net loss
B) an equal sharing
C) a net gain
D) partial loss
A) a net loss
Chemical rxns that lead to a release of ffree energy are referred to as “energetically favorable.” Another way to describe these rxns is:
A) activated
B) uncatalyzed
C) spontaneous
D) uphill
C) spontaneous
ΔG° indicates that change in the standard free energy as a reactant is converted to product. Given what you know about these values, which rxn below is the most favorable?
A) glucose → CO2 + H2O ΔG° = −686 kcal/mole
B) glucose + fructose → sucrose ΔG° = +5.5 kcal/mole
C) glucose 1-phosphate → glucose 6-phosphate ΔG° = −1.7 kcal/mole
D) ADP + Pi → ATP ΔG° = +7.3 kcal/mole
A) glucose → CO2 + H2O ΔG° = −686 kcal/mole
(most negative number)
Catalysts are molecules that lower the activation energy for a given rxn. Cells produces their own catalysts, called:
A) enzymes
B) complexes
C) proteins
D) cofactors
A) enzymes
The potential energy stored in high-energy bonds is commonly harnessed when the bonds are split by the addition of _____ in a process called _____.
A) hydroxide; hydration
B) ATP; phosphorylation
C) water; hydrolysis
D) acetate; acetylation
C) water; hydrolysis
The Vmax of an enzymatic rxn is an important piece of info regarding how the enzyme works. What series of measurements can be taken to infer that the max velocity of an enzyme-catalyzed rxn has been reached?
A) the rate of substrate consumption shortly after mixing the enzyme and substrate, for several substrate concentrations
B) the rate of substrate consumption after the system reaches equilibrium, for several reactant concentrations
C) the rate of product consumption shortly after mixing the enzyme and substrate
D) the rate of substrate consumption at high levels of enzyme concentration
A) the rate of substrate consumption shortly after mixing the enzyme and substrate, for several substrate concentrations
Energy cannot be created/destroyed, but it can be converted into other types of energy. Cells harvest some of the potential energy in the chemical bonds of foodstuffs to generate stored chemical energy in the form of activated carrier molecules, which are often employed to join two molecules together in _____ rxns.
A) condensation
B) hydrolysis
C) oxidation
D) dehydrogenation
A) condensation
NADH and NADPH are activated carrier molecules that function in completely different metabolic reactions. Both carry two additional __________ and one additional __________. This combination can also be referred to as a hydride ion.
A) Hydrogens; electron
B) electrons; phosphate
C) protons; electron
D) electrons; proton
D) electrons; proton
Molecular chaperones can work by creating an “isolation chamber.” What is the purpose of this chamber?
A) This chamber serves to protect unfolded proteins from interacting with other proteins in the cytosol, until protein folding is completed.
B) This chamber serves to transport unfolded proteins out of the cell.
C) The chamber acts as a garbage disposal, degrading improperly folded proteins so that they do not interact with properly folded proteins.
D) This chamber is used to increase the local protein concentration, which will help speed up the folding process.
A) This chamber serves to protect unfolded proteins from interacting with other proteins in the cytosol, until protein folding is completed.
Protein structures have several levels of organization. The primary structure of a protein is its amino acid sequence. The secondary and tertiary structures are more complicated. Consider the definitions below. Which best fits the term “protein domain”?
A) the tertiary structure of a substrate-binding pocket
B) a protein segment that folds and has no function
C) a small cluster of α helices, β sheets, and random coils that provide a function to a protein
D) a complex of more than one polypeptide chain
C) a small cluster of α helices, β sheets, and random coils that provide a function to a protein
Which of the following globular proteins is used to form filaments as an intermediate step to assembly into hollow tubes?
A) actin
B) keratin
C) tubulin
D) collagen
C) tubulin
The assembly of individual polypeptides into a complex tertiary structure like microtubules, intermediate filaments, or the viral capsid of the SV40 virus requires_____
A) many noncovalent bonds between each subunit.
B) a few covalent bonds at strategic locations in the protein.
C) disulfide bonds
D) a specific ATP-dependent chaperone protein used to bind other proteins of a similar size and shape.
C) disulfide bonds
Lysozyme is an enzyme that specifically recognizes bacterial polysaccharides, which render it an effective antibacterial agent. Into what classification of enzymes does lysozyme fall?
A) isomerase
B) nuclease
C) hydrolase
D) protease
C) hydrolase
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) RNA polymerase catalyzes the linkage of ribonucleotides; DNA polymerase catalyzes the linkage of deoxyribonucleotides.
B) RNA polymerase can start making a new RNA molecule without a primer; DNA polymerase cannot.
C) RNA polymerase does not proofread its work; DNA polymerase does.
D) RNA polymerase adds bases in a 3′-to-5′ direction; DNA polymerase adds bases in a 5′-to-3′ direction.
D) RNA polymerase adds bases in a 3′-to-5′ direction; DNA polymerase adds bases in a 5′-to-3′ direction.
Genes in eukaryotic cells often have intronic sequences coded for within the DNA. These sequences are ultimately not translated into proteins. Why?
A) Introns are removed by catalytic RNAs in the cytoplasm.
B) Introns are not transcribed by RNA polymerase.
C) Intronic sequences are removed from RNA molecules by the spliceosome, which works in the nucleus.
D) The ribosome will skip over intron sequences when translating RNA into protein.
C) Intronic sequences are removed from RNA molecules by the spliceosome, which works in the nucleus.
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Ribosomes are large RNA structures composed solely of rRNA
B) Ribosomes are synthesized entirely in the cytoplasm
C) rRNA contains the catalytic activity that joins amino acids together.
D) A ribosome binds one tRNA at a time
C) rRNA contains the catalytic activity that joins amino acids together.
Which of the following methods is NOT used by cells to regulate the amount of a protein in the cell?
A) Genes can be transcribed into mRNA with different efficiencies
B) Many ribosomes can bind to a single mRNA molecule
C) Proteins can be tagged with ubiquitin, marking them for degradation
D) Nuclear pore complexes can regulate the speed at which newly synthesized proteins are exported from the nucleus into the cytoplasm.
D) Nuclear pore complexes can regulate the speed at which newly synthesized proteins are exported from the nucleus into the cytoplasm.
Which of the following is most likely to occur after the lipid bilayer is pierced?
A) the membrane reseals
B) a tear forms
C) the membrane expands
D) the membrane collapses
A) the membrane reseals
Which of the following functions of the plasma membrane is possible w/o membrane proteins?
A) import/export of molecules
B) selective permeability
C) cellular movements
D) intercellular communication
B) selective permeability
Which of the following membrane lipids does not contain a fatty acid tail?
A) phosphatidylcholine
B) phosphatidylserine
C) a glycolipid
D) cholesterol
D) cholesterol
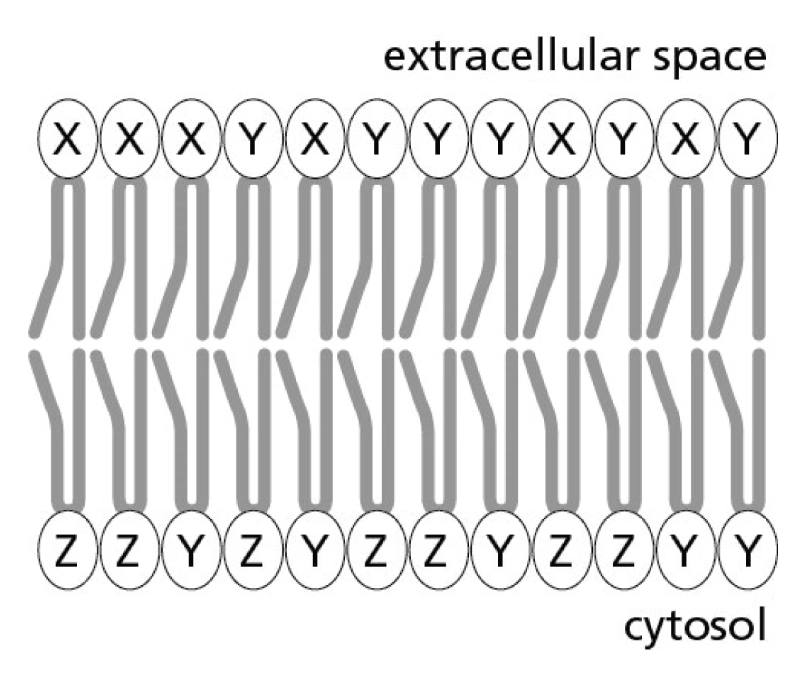
Three phospholipids, X, Y, and Z, are distributed in the plasma membrane as indicated in Figure 11-1. The composition of the extracellular (noncytosolic) layer is different from that of the cytosolic layer. Which of the following factors is responsible for establishing this compositional asymmetry?
A) flippase
B) scramblase
C) lipoyl tranferase
D) lipase
A) flippase
The following descriptions refer to the structures of various hydrophobic fatty acid tails in membrane phospholipids. Which one would yield the most highly mobile phospholipid?
A) 24 carbons with one double bonds
B) 15 carbons with two double bonds
C) 20 carbons with two double bonds
D) 16 carbons with no double bonds
B) 15 carbons with two double bond
New membrane phospholipids are synthesized by enzymes bound to the __________ side of the __________ membrane.
A) luminal; Golgi
B) cytosolic; ER
C) cytosolic; mitochondrial
D) extracellular; plasma
B) cytosolic; ER
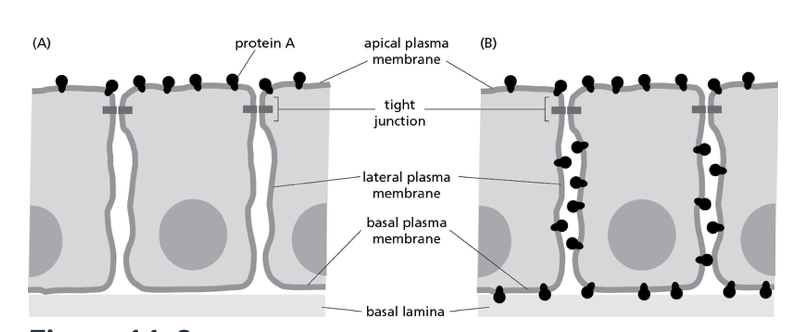
Consider the apical location of a particular protein expressed in epithelial cells, as illustrated in part A of Figure 11-3 below. Part B shows the redistribution of this protein around the entire cell. Which of the following defects is most likely to have caused this redistribution?
A) the truncation of a protein found in the extracellular matrix
B) a nonfunctional protein glycosylase
C) the deletion of a junctional protein
D) a nonfunctional flippase
C) the deletion of a junctional protein
The oligosaccharide chains found in the carbohydrates that are associated with the plasma membrane are incredibly diverse. All but one of the following options explain how this diversity is achieved. Which option is NOT a way that carbohydrates can vary at the plasma membrane?
A) variation in the number of branches in the sugar chains
B) variation in the types of sugar monomers used
C) variation in the types of covalent linkages between sugars
D) variation in the side of the plasma membrane to which they are bound
D) variation in the side of the plasma membrane to which they are bound
Carbon atoms can form double bonds with other carbon atoms, nitrogen atoms, and oxygen atoms. Double bonds can have important consequences for biological molecules because they are __________ compared to single covalent bonds.
A) unstable
B) long
C) weak
D) rigid w/ respect to rotation
D) rigid w/ respect to rotation
__________ play an important role in organizing lipid molecules with long hydrocarbon tails into biological membranes.
A) ionic bonds
B) van der waals attractions
C) hydrophobic forces
D) hydrogen bonds
C) hydrophobic forces
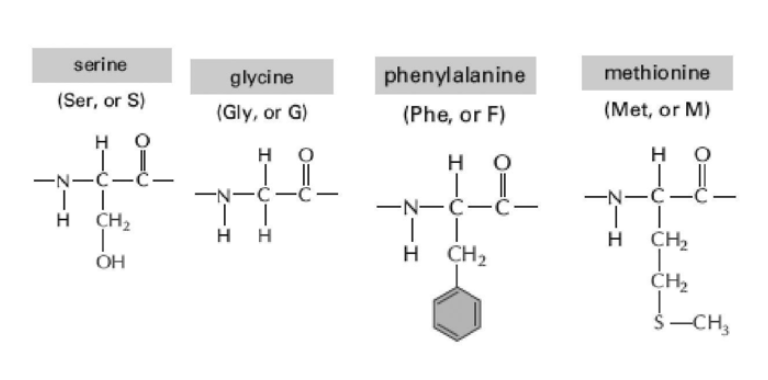
Oligosaccharides are short sugar polymers that can become covalently linked to proteins and lipids through condensation reactions. These modified proteins and lipids are called glycoproteins and glycolipids, respectively. Within a protein, which of the amino acids (shown in Figure 2-3) is the most probable target for this type of modification?
A) phenylalanine
B) serine
C) glycine
D) methionine
B) serine
The variations in the physical characteristics between different proteins are influenced by the overall amino acid compositions, but even more important is the unique amino acid
A) bonds
B) number
C) sequence
D) orientation
C) sequence
Maintaining pH and salt concentrations is critical to keeping proteins functional. What is the molecular mechanism by which pH affects protein function?
A) The hydrogen bonds within the polypeptide backbone that form the secondary structures are completely disrupted.
B) A few of the polar R-groups can change charge, and the new attraction or repulsion can alter the shape of the protein.
C) Only the primary structure is altered, which changes the folding and function of the protein
D) The N- and C-terminus amino acids with their amino and carboxyl ends can change the shape of the entire protein.
B) A few of the polar R-groups can change charge, and the new attraction or repulsion can alter the shape of the protein.
Which of the following statements is true?
A) The sequence of the atoms in the polypeptide backbone varies between different proteins
B) Peptide bonds are the only covalent bonds that can link two amino acids in proteins
C) There is free rotation around all covalent bonds in the polypeptide backbone.
D) Nonpolar amino acids tend to be found in the interior of proteins.
D) Nonpolar amino acids tend to be found in the interior of proteins.
Which of the following is FALSE about molecular chaperones?
A) They can interact with unfolded polypeptides in a way that helps the protein reach the least stable tertiary structure.
B) They assist polypeptide folding by helping the folding process follow the most energetically favorable pathway.
C) They can isolate proteins from other components of the cells until folding is complete
D) They help streamline the protein-folding process by making it a more efficient and reliable process inside the cell
A) They can interact with unfolded polypeptides in a way that helps the protein reach the least stable tertiary structure.
One of the key features of living systems is the use of energy to create and maintain order. A good example is the folding of newly synthesized proteins. Which activated carrier molecule is used by chaperone proteins to support protein folding?
A) NADPH
B) FADH2
C) NADH
D) ATP
D) ATP prot folding
Complete the sentence with the best option provided below. The secondary structures of a protein are the_____
A) temporary, unstable protein folding conformations.
B) noncovalent bonds that allow two polypeptides to bind, forming a dimer
C) presence of α helices and β sheets that help the protein achieve a low energy conformation
D) interactions between polar amino acid side chains in two different folds
C) presence of α helices and β sheets that help the protein achieve a low energy conformation
Which of the following is NOT a feature commonly observed in β sheets?
A) extended polypeptide backbone
B) parallel regions
C) coiled-coil patterns
D) antiparallel regions
C) coiled-coil patterns
Globular proteins fold up into compact, spherical structures that have uneven surfaces. They tend to form multisubunit complexes, which also have a rounded shape. Fibrous proteins, in contrast, span relatively large distances within the cell and in the extracellular space. Which of the proteins below is NOT classified as a fibrous protein?
A) keratin
B) elastin
C) elastase
D) collagen
C) elastase
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Disulfide bonds are formed by the cross-linking of methionine residues
B) Disulfide bonds are formed mainly in proteins that are retained within the cytosol
C) Disulfide bonds stabilize but do not change a protein’s final conformation
D) Disulfide bonds are more common for intracellular proteins, compared to extracellular proteins
C) Disulfide bonds stabilize but do not change a protein’s final conformation
Proteins bind selectively to small-molecule targets called ligands. The selection of one ligand out of a mixture of possible ligands depends on the number of weak, noncovalent interactions in the protein’s ligand-binding site. Where is the binding site typically located in the protein structure?
A) on the surface of the protein
B) on the surface of the protein in the presence of ligand
C) buried in the interior of the protein
D) inside a cavity on the protein surface
D) inside a cavity on the protein surface
Cyclic AMP (cAMP) is a small molecule that associates with its binding site with a high degree of specificity. Which types of noncovalent interactions are the most important for providing the “hand in a glove” binding of cAMP?
A) van der waals interactions
B) electrostatic interactions
C) H bonds
D) hydrophobic interactions
C) H bonds
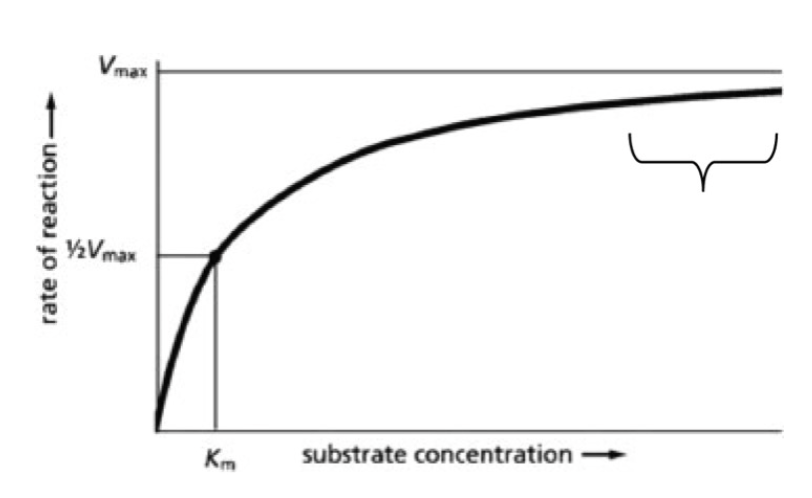
Which part of the Michaelis-Menton curve is represented by the portion marked with a bracket?
A) the lowest level of products produced, because the reaction is unfavorable
B) the substrate concentration at which the enzyme has the highest affinity for the substrate
C) nearly the maximal rate of enzyme activity at high substrate concentrations
D) the lowest rate of enzyme activity
C) nearly the maximal rate of enzyme activity at high substrate concentrations
Which of the following will double the Vmax of an enzymatic reaction after performing a kinetics assay?
A) add double the amount of substrate compared to the original assay
B) double the number of enzyme molecules compared to the original assay
C) add ATP so it can bind to the active sight and give the protein more energy
D) add less competitive inhibitor so that the active site is available to more substrate
B) double the number of enzyme molecules compared to the original assay
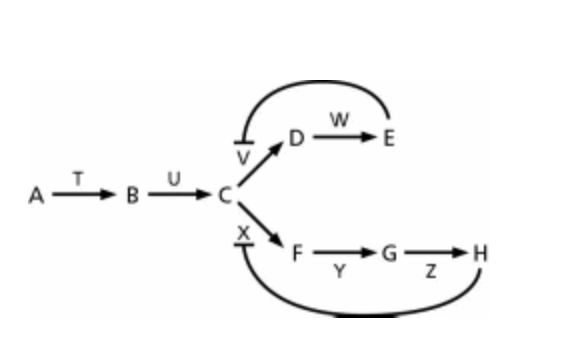
The biosynthetic pathway for the two amino acids E and H is shown schematically in Figure 4-4. You can show that E inhibits enzyme V, and H inhibits enzyme X. Which biosynthetic product is most likely the inhibitor of enzyme T?
A) H
B) B
C) C
D) E
C) C
The Ras protein is a GTPase that functions in many growth factor–signaling pathways. In its active form, with GTP bound, it transmits a downstream signal that leads to cell proliferation; in its inactive form, with GDP bound, the signal is not transmitted. Mutations in the gene for Ras are found in many cancers. Of the choices below, which alteration of Ras activity is most likely to contribute to the uncontrolled growth of cancer cells?
A) a change that decreases the rate of hydrolysis of GTP by Ras
B) a change that increases the affinity of Ras for GDP
C) a change the prevents Ras from being made
D) a change that decreases the affinity of Ras for GTP
A) a change that decreases the rate of hydrolysis of GTP by Ras
Instead of studying one or two proteins or protein complexes present in the cell at any given time, we can now look at a snapshot of all proteins being expressed in cells being grown in specific conditions. This large-scale, systematic approach to the study of proteins is called
A) proteomics
B) systems biology
C) structural biology
D) genomics
A) proteomics
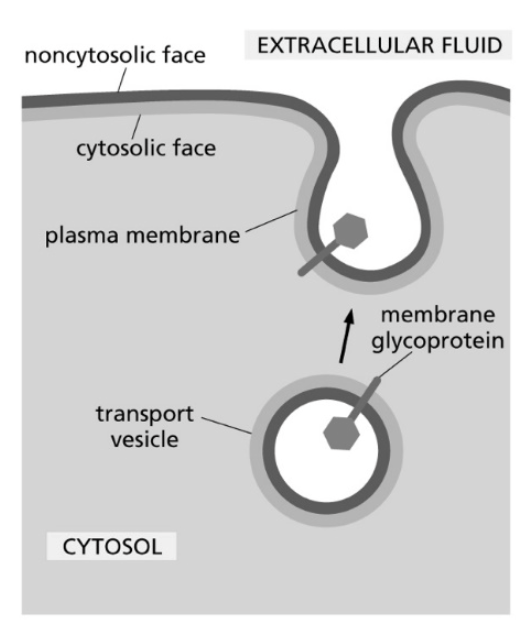
Consider a transport vesicle containing a membrane glycoprotein. The glycoprotein and the vesicle’s phospholipids are delivered to the plasma membrane, as shown in the figure below. Which of the following is an accurate description of the outcome of this process?
A) The portion of the glycoprotein that was inside of the vesicle ends up in the cytosol after it is delivered to the plasma membrane.
B) Some of the individual phospholipid molecules are released into the cytosol to prevent the plasma membrane, and thus the cell, from becoming too large.
C) The phospholipids that are delivered to the noncytosolic face of the plasma membrane used to be in the interior (luminal) face of the vesicle.
D) The fusion event between the vesicle and the plasma membrane randomizes the phospholipids between the cytosolic and noncytosolic faces of the bilayer.
C) The phospholipids that are delivered to the noncytosolic face of the plasma membrane used to be in the interior (luminal) face of the vesicle.
The second law of thermodynamics states that the disorder in any system is always increasing. In simple terms, you can think about dropping NaCl crystals into a glass of water. The solvation and diffusion of ions is favored because there is an increase in
A) stored energy
B) pH
C) entropy
D) ions
C) entropy
At first glance, it may seem that living systems are able to defy the second law of thermodynamics. However, on closer examination, it becomes clear that although cells create organization from raw materials in the environment (i.e., polymerize a DNA strand or a polypeptide), they also contribute to disorder in the environment by releasing
A) proteins
B) water
C) radiation
D) heat
D) heat
During respiration, energy is retrieved from the high-energy bonds found in certain organic molecules. Which of the following, in addition to energy, are the ultimate products of respiration?
A) CH3; H2O
B) CO2; O2
C) CO2; H2O
D) CH2OH; O2
C) CO2; H2O
Your body extracts energy from the food you ingest by catalyzing reactions that essentially “burn” the food molecules in a stepwise fashion. What is another way to describe this process?
A) solvation
B) dehydration
C) oxidation
D) reduction
C) oxidation
The best way to know if an organic molecule has been reduced is to see if there was an increase in the number of __________ bonds.
A) H-H
B) C-H
C) C-N
D) C-O
B) C-H
A chemical reaction is defined as spontaneous if there is a net loss of free energy during the reaction process. However, spontaneous reactions do not always occur rapidly. Favorable biological reactions require __________ to selectively speed up reactions and meet the demands of the cell.
A) enzymes
B) ions
C) heat
D) ATP
A) enzymes
Activated carriers are small molecules that can diffuse rapidly and be used to drive biosynthetic reactions in the cell. Their energy is stored in a readily transferable form such as high-energy electrons or chemical groups. Which of the molecules below donates a chemical group rather than electrons?
A) NADPH
B) FADH2
C) NADH
D) ATP
D) ATP (phosphate grp)
Vmax can be determined by measuring the amount of product accumulated late in the reaction.
A) True
B) False
B) False
Even though cellular macromolecules contain many carbon and hydrogen atoms, they are not all spontaneously converted into CO2 and H2O. This absence of spontaneous combustion is due to the fact that biological molecules are relatively __________, and an input of energy is required to reach lower energy states.
A) polar
B) unstable
C) stable
D) large
C) stable
Unlike DNA, which typically forms a helical structure, different molecules of RNA can fold into a variety of three-dimensional shapes. This is largely because RNA
A) contains uracil and uses ribose as the sugar
B) is single-stranded
C) bases cannot form H bonds w/ each other
D) nucleotides use a diff chem linkage between nucleotides compared to DNA
B) is single-stranded
Which of the following does NOT occur before a eukaryotic mRNA is exported from the nucleus?
A) RNA polymerase dissociates
B) The mRNA is polyadenylated at its 3′ end.
C) A guanine nucleotide with a methyl group is added to the 5′ end of the mRNA.
D) The ribosome binds to the mRNA
D) The ribosome binds to the mRNA
Which of the following statements about the genetic code is correct?
A) All codons specify more than one amino acid.
B) the genetic code is redundant
C) all AAs are specified by more than one codon
D) all codons specify an AA
B) the genetic code is redundant
The ribosome is important for catalyzing the formation of peptide bonds. Which of the following statements is true?
A) The catalytic site for peptide bond formation is formed primarily from an rRNA.
B) The large subunit of the ribosome is important for binding to the mRNA.
C) The number of rRNA molecules that make up a ribosome greatly exceeds the number of protein molecules found in the ribosome.
D) Once the large and small subunits of the ribosome assemble, they will not separate from each other until degraded by the proteasome
A) The catalytic site for peptide bond formation is formed primarily from an rRNA.
Ribozymes are known to catalyze which of the following reactions in cells?
A) RNA splicing
B) transcription
C) protein hydrolysis
D) DNA synthesis
A) RNA splicing
Foods are broken down into simple molecular subunits for distribution and use throughout the body. Which type of simple subunits, listed below, is used preferentially as an energy source?
A) proteins
B) simple sugars
C) free fatty acids
D) glycerol
B) simple sugars
The final metabolite produced by glycolysis is
A) pyruvate
B) 3-phosphoglycerate
C) glyceradlehyde 3-phosphate
D) acetyl CoA
A) pyruvate
A kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes
A) the oxidation of a molecule by removing a hydride ion.
B) the addition of phosphate groups to other molecules.
C) the rearrangement of bonds within a single molecule.
D) a change in the position of a specific chemical group within a single molecule.
B) the addition of phosphate groups to other molecules.
In the final stage of the oxidation of food molecules, a gradient of protons is formed across the inner mitochondrial membrane, which is normally impermeable to protons. If cells were exposed to an agent that causes the membrane to become freely permeable to protons, which of the following effects would you expect to observe?
A) NADH
B) the consumption of oxygen would fall
C) the ratio of ATP to ADP in the cytoplasm would fall
D) carbon dioxide production would cease
C) the ratio of ATP to ADP in the cytoplasm would fall
What is a primary reason that cells use enzymes in a series of steps to oxidize a fuel molecule such as glucose rather than oxidizing the fuel molecule in a single step (such as by direct burning in nonliving conditions)?
A) Energy is released in smaller packets that can be captured by carrier molecules.
B) Complete oxidation of glucose without enzymes fails to produce needed heat
C) Enzymes in cells must be kept active or they will be degraded
D) Even partial oxidation of glucose stepwise with enzymes requires oxygen that is abundant in the atmosphere.
A) Energy is released in smaller packets that can be captured by carrier molecules.