EHS590 Midterm Study Flashcards
1/131
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These are the flashcards for Module 1 EHS90 Midterm Exam. Date: October 5 2023
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
132 Terms
Disability Adjusted Life Years (DALYs)
Sum of years of life lost due to premature death + years with disability
Approximately what percentage of DALYs are attributable to environmental factors?
20%
3 MULTIPLE CHOICE OPTIONS
3 Ps - Major Determinants of Environmental Health
(1) Population
(2) Poverty
(3) Pollution
Toxicology
The study of adverse effects of chemical, physical or biological agents on people, animals and the environment. Identify at what level of exposure and through what exposure route they may become hazardous.
Environmental Health
the branch of public health that addresses physical, chemical, biological, social and psychosocial factors in the environment
Which of the following factors has been the most significant contributor to this population growth?
Improved nutrition & basic sanitation
3 MULTIPLE CHOICE OPTIONS
Demographic transition model (DTM)
a model that describes population change over time
DTM Stage 1
High stationary stage:
-high birth & death rates (young population)
-population stable/slow growth (~1%)
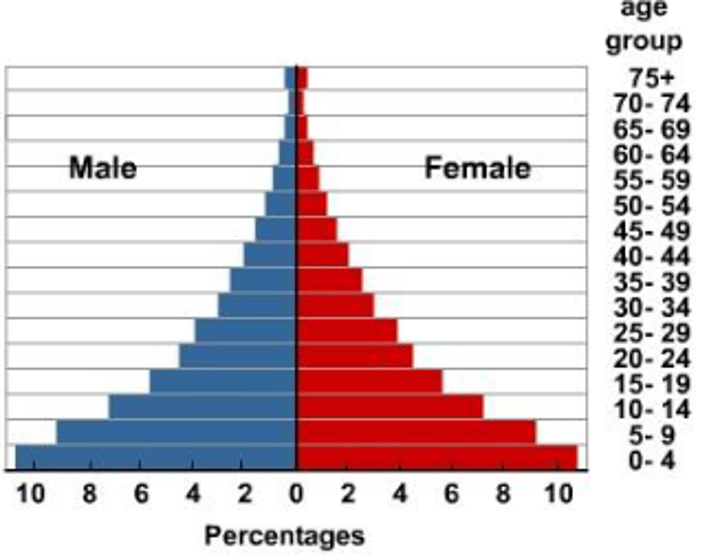
DTM Stage 2
Early Expanding Stage:
-high birth & decreasing mortality rates (young population)
-population growing rapidly
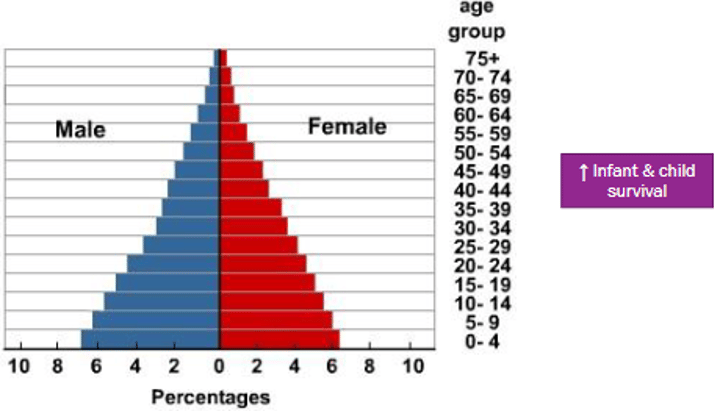
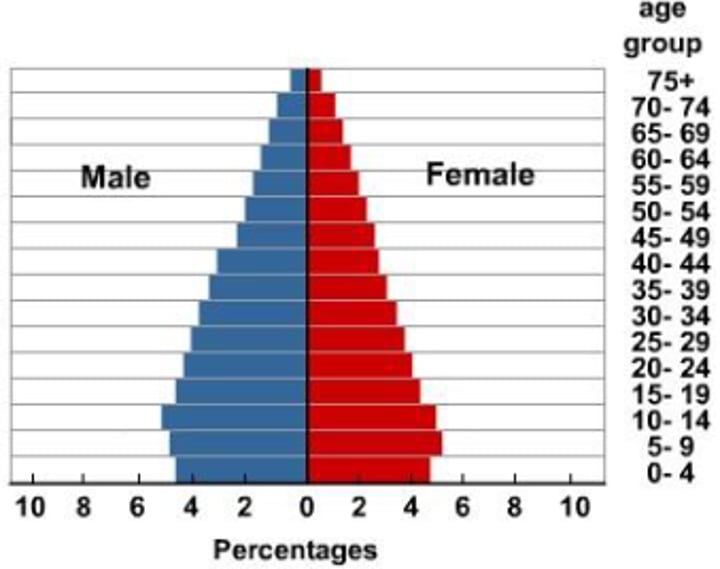
DTM Stage 3
Late Expanding Stage:
-decreasing birth & mortality rates (more uniform age distribution)
-population still grows b/c birth rates are higher than death rates
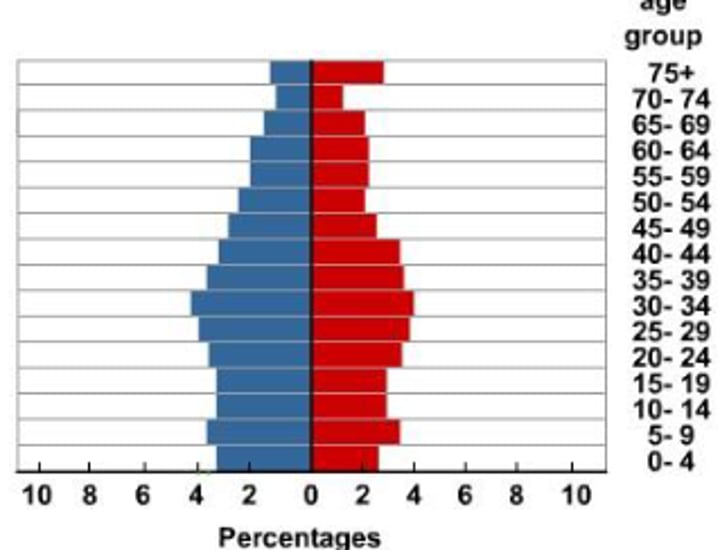
DTM Stages 4-5
Low stationary & Declining Stages:
-low birth & mortality rates, population remains stable/declining
demographic transition
Shift from high birth and mortality rates in underdeveloped societies to lower fertility and lower mortality rates as a result of development
world population growth is currently...
growing population, decreasing growth rate
3 MULTIPLE CHOICE OPTIONS
limitation of DTM
Model does not consider migration and how it may effect population
3 MULTIPLE CHOICE OPTIONS
which is most strongly associated with total fertility rate (TFR)?
avg. female education
3 MULTIPLE CHOICE OPTIONS
epidemiologic transition
a shift in morbidity and mortality patterns from communicable diseases (CD) to non-communicable diseases (NCD)
environmental health effects of urbanization
-increases exposures to pollutants & pathogens
environmental risk transition
the process by which traditional communities with associated environmental health issues become more economically developed and experience new health issues
World Health Organization (WHO)
Organization: Mission is to advocate and catalyze global and country actions to resolve the human resources for health crisis
3 MULTIPLE CHOICE OPTIONS
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
Organization: Mission is to protect human health and the environment.
3 MULTIPLE CHOICE OPTIONS
National Center for Environmental Health(NCEH)/Agency for Toxic Substances & Disease Registry (ATSDR) - U.S. CDC
plans, directs, and coordinates a program to protect the American people from environmental hazards.
3 MULTIPLE CHOICE OPTIONS
National Institute for Environmental Health Sciences(NIEHS) - U.S. NIH
Mission is to discover how the environment affects people, in order to promote healthier lives.
3 MULTIPLE CHOICE OPTIONS
4 Principles of Developing Environmental Health Policies
1. Precautionary principle
2. Environmental justice
3. Environmental sustainability
4. Polluter-Pays principle
Polluter-Pays principle
Polluters bear the expense of carrying out pollution prevention & control & necessary remediation measures to ensure that the environment is in an acceptable state
Environmental justice goal
everyone enjoys:
-the same degree of protection from environmental and health hazards
-equal access to the decision making process to have a healthy environment in which to live, learn, and work.
precautionary principle
preventive, anticipatory measures applied when weight of evidence suggests possibility of adverse health consequences
poison
any agent capable of producing a deleterious response in a biological system
3 MULTIPLE CHOICE OPTIONS
Toxic agent
Material or factor that can be harmful to biological systems
3 MULTIPLE CHOICE OPTIONS
Toxin
Toxic substance made by living organisms including reptiles, insects, plants and microorganisms
3 MULTIPLE CHOICE OPTIONS
Toxicant
Toxic substances that are man-made or result from human activity
3 MULTIPLE CHOICE OPTIONS
Toxicity
Degree to which an agent is poisonous
3 MULTIPLE CHOICE OPTIONS
Areas of Toxicology
-Regulatory
-Forensic
-Clinical
-Reproductive
-Developmental
-Genetic
-Environmental
Ebers Papyrus (1500 BC)
Egyptian 20 m scroll with 700 drugs in 900 formulas
Paracelsus
Known as the "Father of Toxicology"
-Formulated many revolutionary views that remain an integral part of Toxicology and Pharmacology today
Mathieu Orfila
Known as the "Father of Forensic Toxicology"
-the 1st toxicologist to use autopsy material and chemical analysis systematically as legal proof of poisoning
exposure dose
the amount of a substance encountered in the environment
external dose
a dose acquired by contact w/ contaminated environmental sources
absorbed dose
the amount of a substance that is available to internal organs of the body
internal dose
the portion of a substance that becomes internalized in the body through ingestion, absorption, and other means
administered dose
the quantity of a substance that is administered
biologically effective dose
the portion of the internal dose that is required to cause a health outcome
total dose
the dosage acquired by adding together all the individual doses
how is dose often expressed?
- μg/ml of blood
- mg/kg of body weight
3 MULTIPLE CHOICE OPTIONS
LD50
The lethal dose of a substance that kills 50% of the exposed population (mg/kg body weight). Determines based on a single acute exposure in test animals
LD50/30
the dose that kills 50% within 30 days
LD50/60
the dose that kills 50% within 60 days
true or false. All substances can be toxic
true
1 MULTIPLE CHOICE OPTION
LD50 uses
➢ compare the acute toxicities of chemicals
➢ classify chemicals by poisoning potential
➢ identify target organs
➢ provide dose-ranging guidance for other studies
LD50 limitations
does not reflect the full spectrum of toxicity of the substance or predict delayed effects
dose-response relationship
Quantitatively describes the association between exposure to a compound and the effects produced by that exposure
A pharmaceutical is non-toxic if...
ED50 is lower than TD50
3 MULTIPLE CHOICE OPTIONS
dose-response models
-Linear Non-Threshold (LNT) model
-Threshold model
-Hormetic (U-Shaped) model
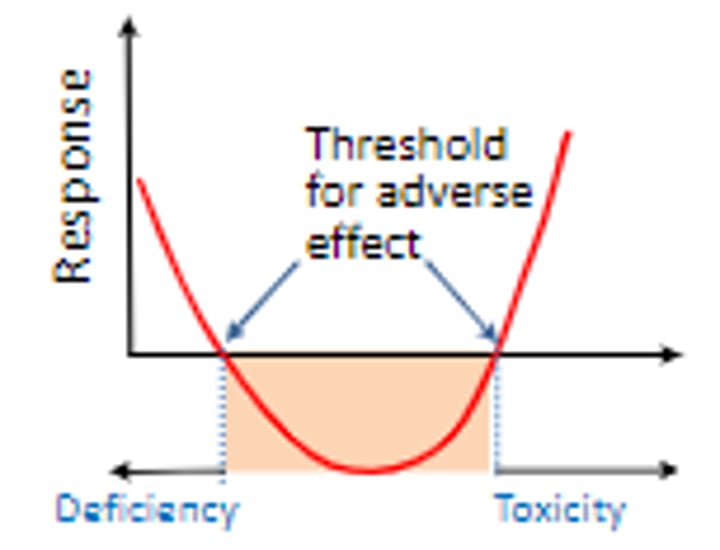
Hormesis
Adverse effects observed at very low doses (deficiency) or high doses (toxicity), while moderate doses are beneficial
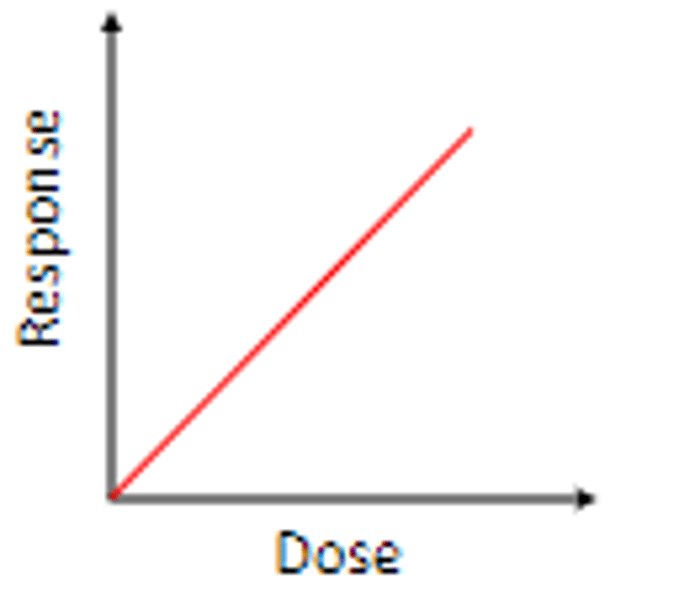
Linear Non-Threshold (LNT)
dose response model
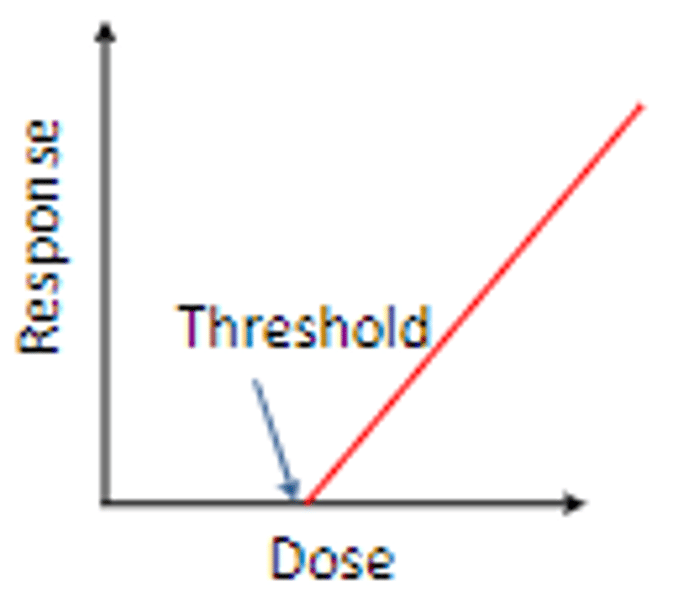
Threshold model
dose response model (non-carcinogens)
Hormetic model
U-shaped dose-response relationship in which cancer rates decline at very low doses of a carcinogen and then begin to rise as the dose is further increased
Reference Dose (RfD)
A dose that does not cause adverse effects.
Formula = NOAEL or LOAEL / UF(s) x MF
Factors influencing toxicity of an agent
-route of exposure
-absorption, distribution, metabolism, & excretion (ADME)
-duration of exposure
-interactions among chemicals
individual susceptibility
Major routes of exposure
inhalation, ingestion, dermal contact, intravenous injection (IV)
ADME
Absorption (A)
Distribution (D)
Metabolism (M)
Excretion (E)
Duration of exposure
Acute, subacute, subchronic, chronic
Acute exposure duration
usually a single exposure for less than 24h
Subacute exposure duration
exposure for 1 month or less
Subchronic exposure duration
exposure for 1-3 months
Chronic exposure duration
exposure for more than 3 months
Additive Effect
the combined effect of the two chemicals is equal to the sum of the effects of each agent given alone. (most common) 2+2=4
Hyponatremia
water intoxication
Synergistic Effect
occurs when the combined effects of two chemicals are much greater than the sum of the effects of each agent given alone. 2+2=20
Potentiation
occurs when one compound does not have a toxic effect on a certain organ or system but when added to another chemical makes that chemical much more toxic. 0+2=10
Antagonism
occurs when two chemicals administered together interfere with each other's action or one interferes with the action of the other. (4 types) (-2) + 2 =0
trace elements
elements required by an organism in only minute quantities
Cancer risk formula
Cancer = Cancer slope factor x exposure
Carcinogens Group 1
carcinogenic to humans
Carcinogens Group 2A
probably carcinogenic
Carcinogenic Group 2B
possibly carcinogenic to humans
Carcinogenic Group 3
not classifiable as to carcinogenicity to humans
UF
Uncertainty factor
MF
Modifying factor
NOAEL
No Observed Adverse Effect Level
LOAEL
Lowest Observed Adverse Effect Level
individual susceptibility
• Genetic polymorphisms: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in metabolism genes, DNA repair genes
Epigenetic changes:– Methylation (suppresses protein translation)– Acetylation (enhances protein translation)
• Health and Nutritional status:– Availability of amino acids/trace elements necessary for detoxification pathways
• Gender
• Age
Methods for testing for toxicity
- in vitro
- in vivo
-Ames Assay (in vitro)
Ames Assay
"Gold standard" method for determination of mutagenic activity of test agents (most widely used)
2 MULTIPLE CHOICE OPTIONS
In vivo testing
Animals exposed purposely. "Gold standard" method for determination of carcinogenic powers of test agents.
2 MULTIPLE CHOICE OPTIONS
In vitro testing
Cells derived from humans, animals, yeast or bacteria used to screen for different toxic properties of test agents
2 MULTIPLE CHOICE OPTIONS
risk assessment
A process of determining risks to health attributable to environmental and other hazards.
'Red Book'
1. Hazard identification
2. Dose-response assessment
3. Exposure assessment
4. Risk characterization
risk assessment objectives
1. Balance risk and benefits
2. Set target levels of risk
3. Set priorities for program activities
4. Estimate residual risk and extent of risk reduction after steps are taken to reduce risk
epidemiology
Study of distribution, patterns, and determinants of health and disease in human populations
disease measures of epidemiology
prevalence and incidence
environmental epidemiology
The study of environmental health effects from involuntary exposure to the human body
prevalence
# existing cases/total population (at a point in time)
- Important for: hypothesis generation, policy decisions, budget preparation, resource allocation
incidence
CI = # new cases/total population at risk (during span of time)
IR = # new cases/total person-time of observation
- Important for: Describing risk in a population, Necessary for establishing causality, Predicting future events
epidemiology study designs
- Descriptive studies
- Ecologic (correlational) studies
- Analytical (etiologic) studies
Descriptive studies
describe patterns in disease occurrence in terms of demographic and other variables
Ecologic studies
assesses overall frequency of disease in a series of populations and looks for a correlation with the average exposure in the populations.
Major limitation of ecologic studies
critically limited by ecological fallacy
Analytical studies
clinical trials (controlled experiments), observational studies (cohort studies, case-controlled studies, cross-sectional studies)
Cohort studies (analytical)
- Seek to replicate an experiment using observational data
- Provide risk/rate ratios to estimate associations between exposure and disease
*estimates true risk
Risk Ratio (P, CI, IR)
risk in exposed group/risk in unexposed group
Case-controlled studies (analytical)
*hypothesis-testing studies
- Provide odds ratios (OR) - odds for exposure
- Start with an diseased (cases) and non-diseased (controls) groups and look backwards in time to determine the odds of exposures in each group