OPT 319 Bumps, Cysts, Non-Malignant
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
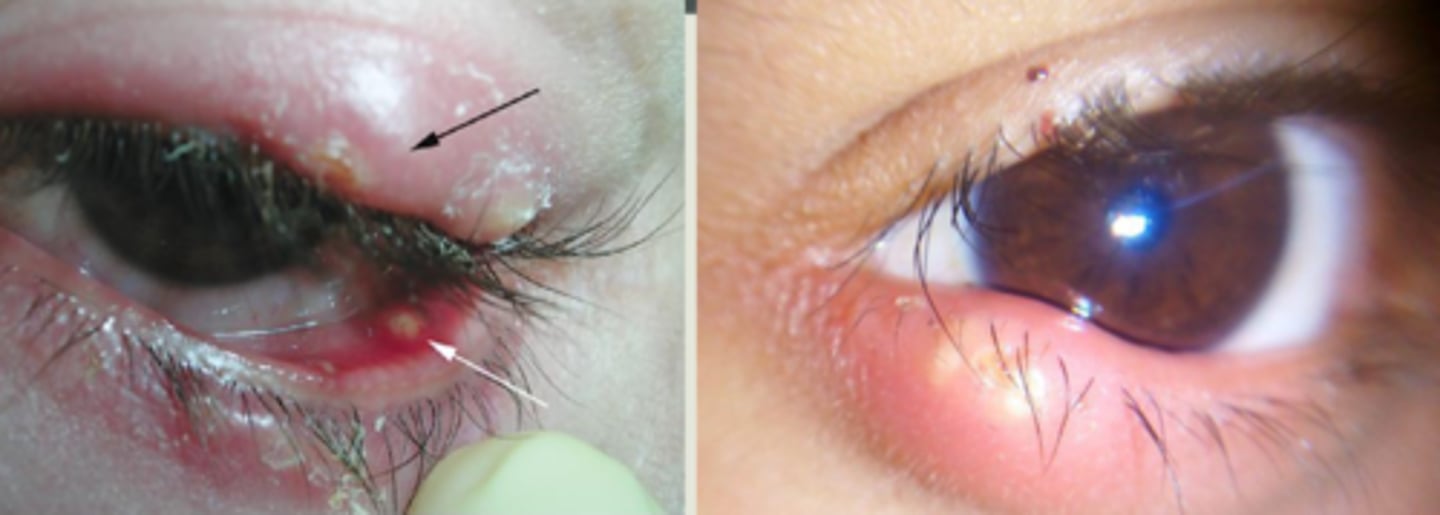
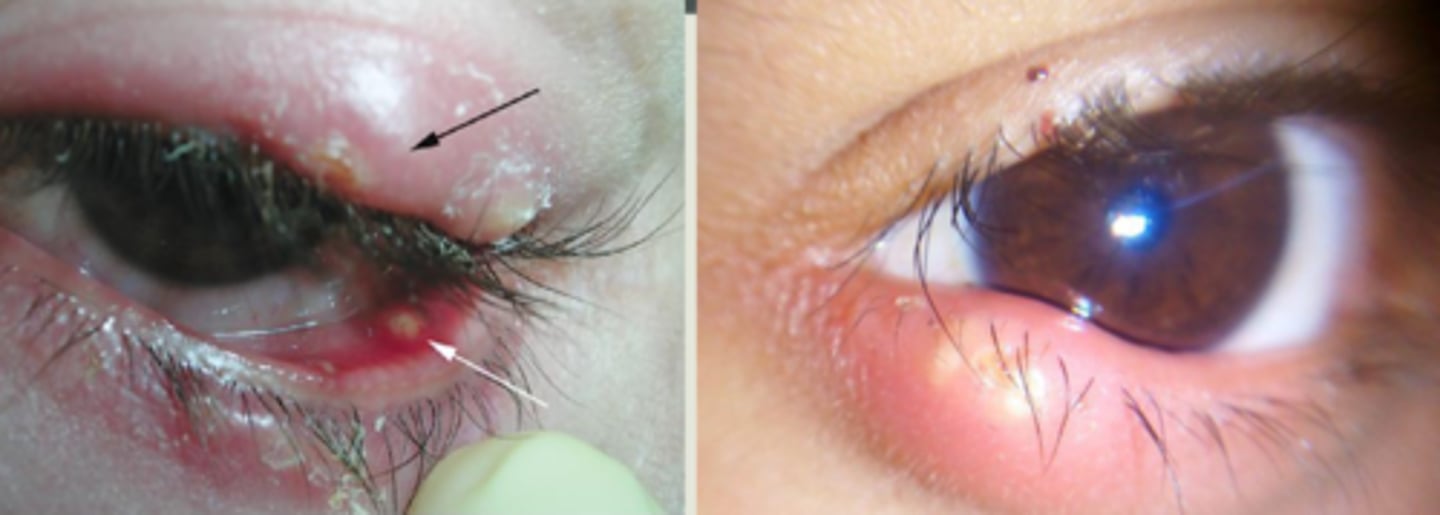
What is a hordeolum?
bacterial infection (Staph) of the sebaceous glands of the eyelid:
Gland of Zeis = lash follicle, more exterior
Meibomian gland = more interior
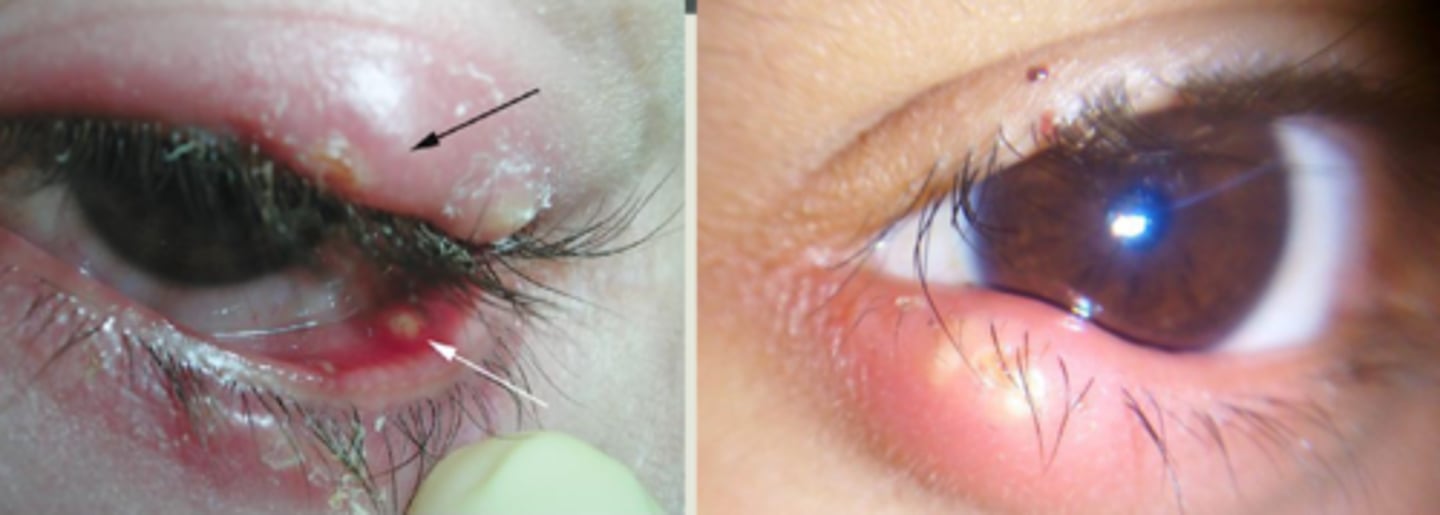
What are some S/S of a hordeolum?
redness
painful
pustular-like lesion
+/- conj. edema and purulent discharge
larger lesions may cause FB/ rubbing sensation = disrupt ocular surface, induce astigmatism
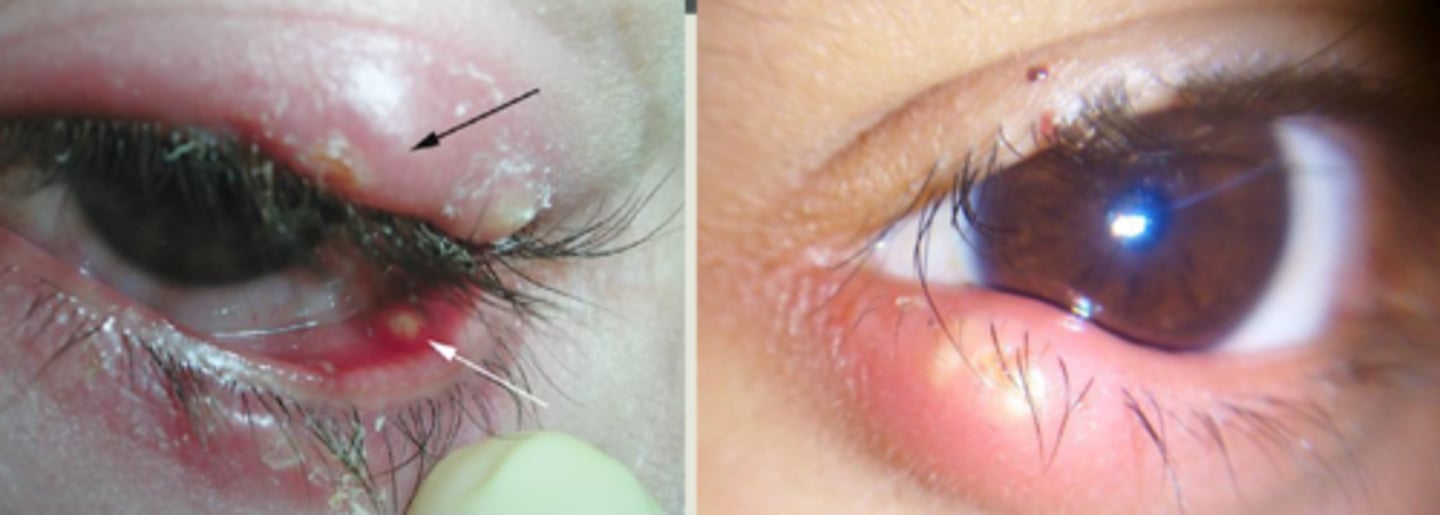
What are some associations with hordeolum?
poor hygiene
systemic infection
blepharitis
roseacea
trichiasis
ectropion
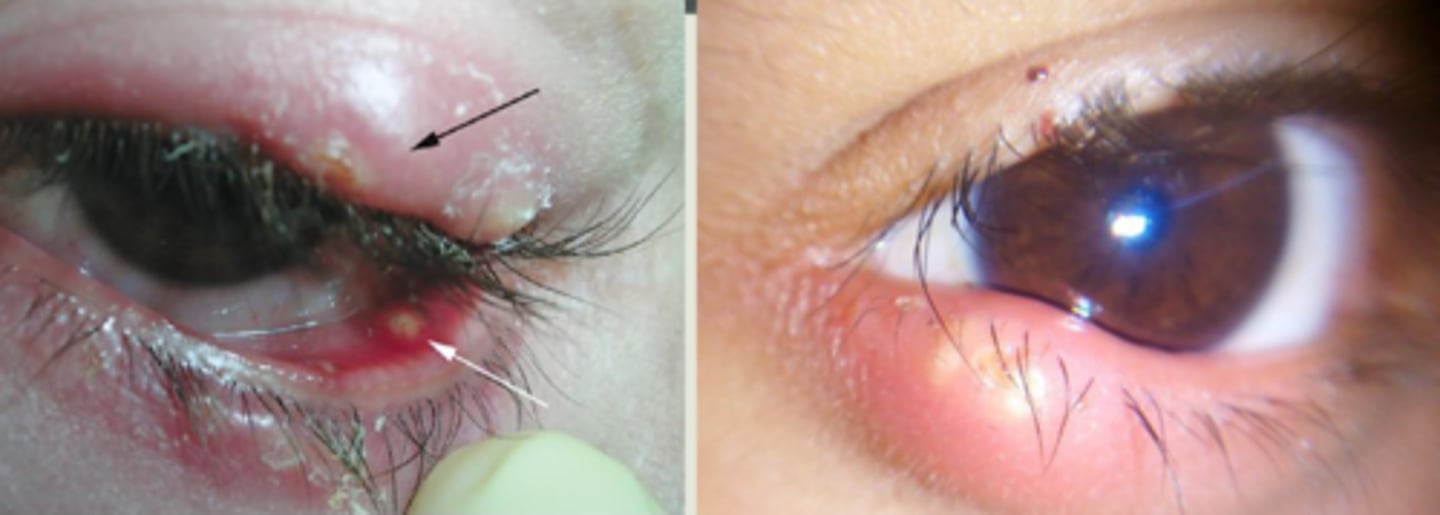
What is the underlying histology of a hordeolum?
abscess of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and necrotic tissue = pus head
What is the tx for a hordeolum?
hot, moist compresses
lid scrubs = mild soaps, shampoos, lid scrub products
lid massage
topical antibiotic gtts or ung = bacitracin, erythromycin, Neo-poly-dex = BUT these do not penetrate skin well
oral antibiotic = doxycycline 100 mg BID, Augmentin 500 mg BID
incision and drainage of the abscess if oral abx for 2 weeks does not resolve
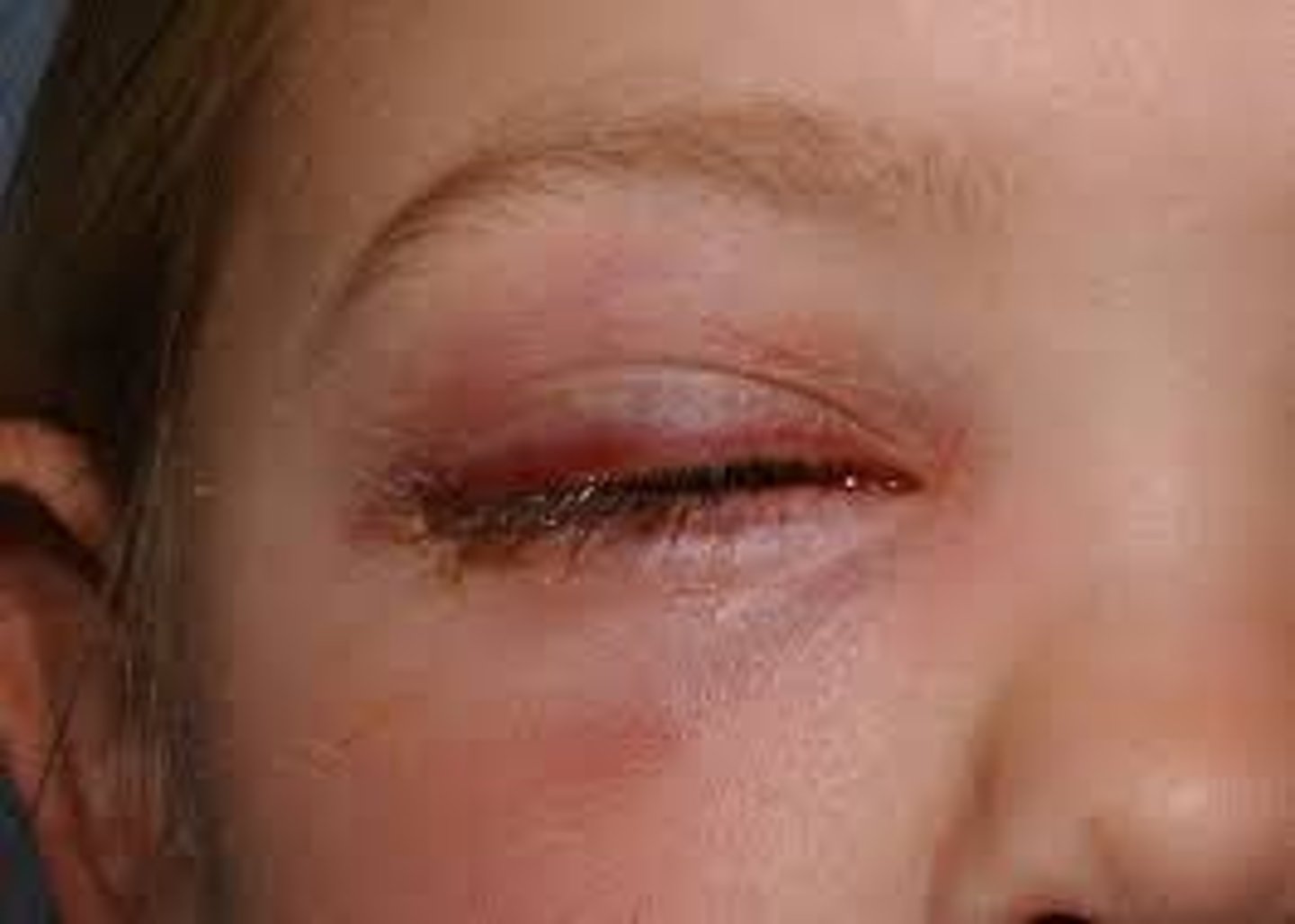
What is preseptal cellulitis?
infection (staph and strep) of the eyelid soft tissue anterior to the eyelid septum, commonly spread from adjoining tissues: sinuses, hordeola, dacryo-adenitis/-cystitis
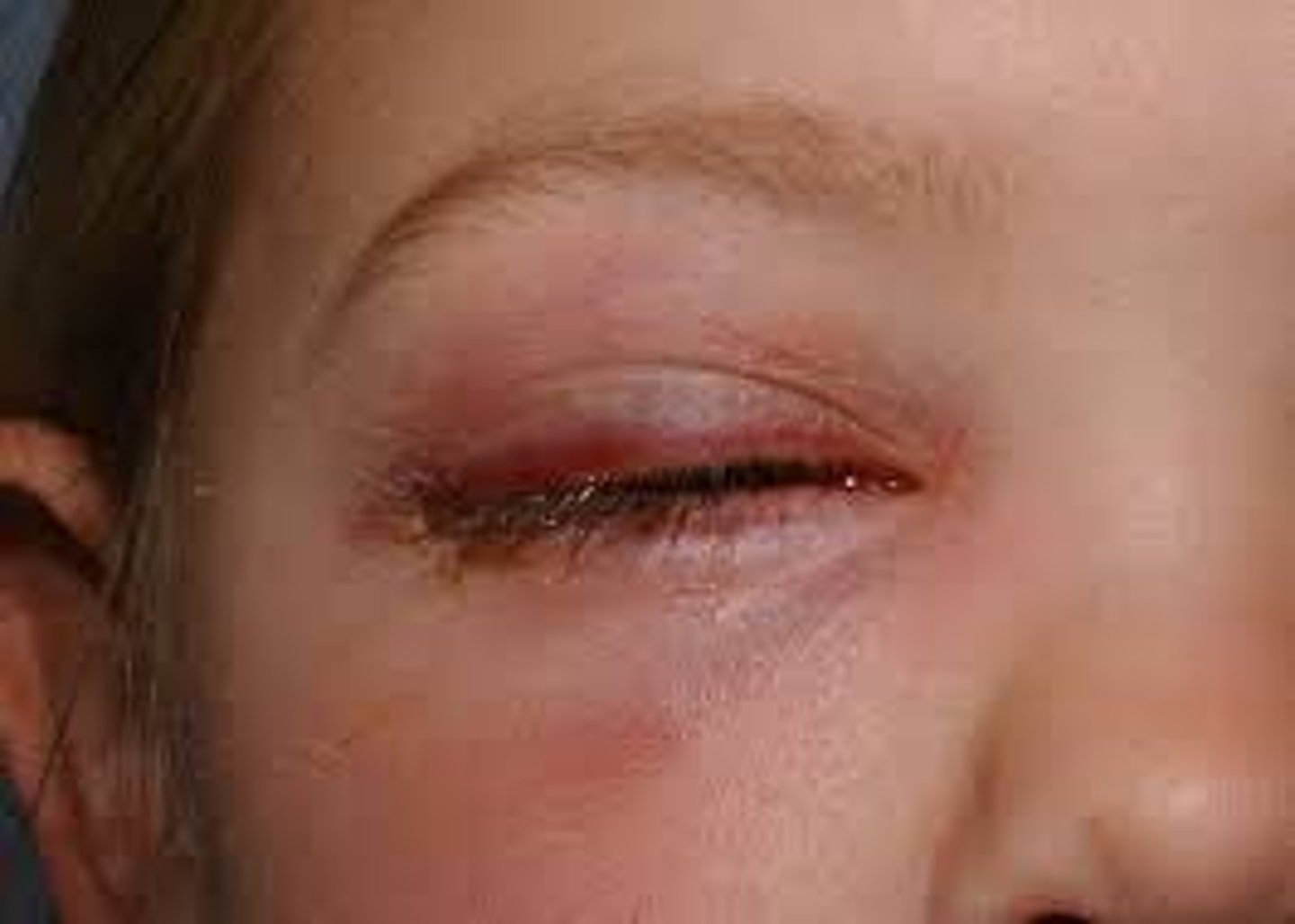
What are some S/S of preseptal cellulitis?
diffuse eyelid swelling and redness
+/- preauricular lymphadenopathy
+/- fever and malaise
What are some things that are seen in orbital cellulitis that helps differentiate it from preseptal cellulitis?
decreased vision
decreased color saturation
possible APD
possible proptosis
conj chemosis
altered / painful EOMs
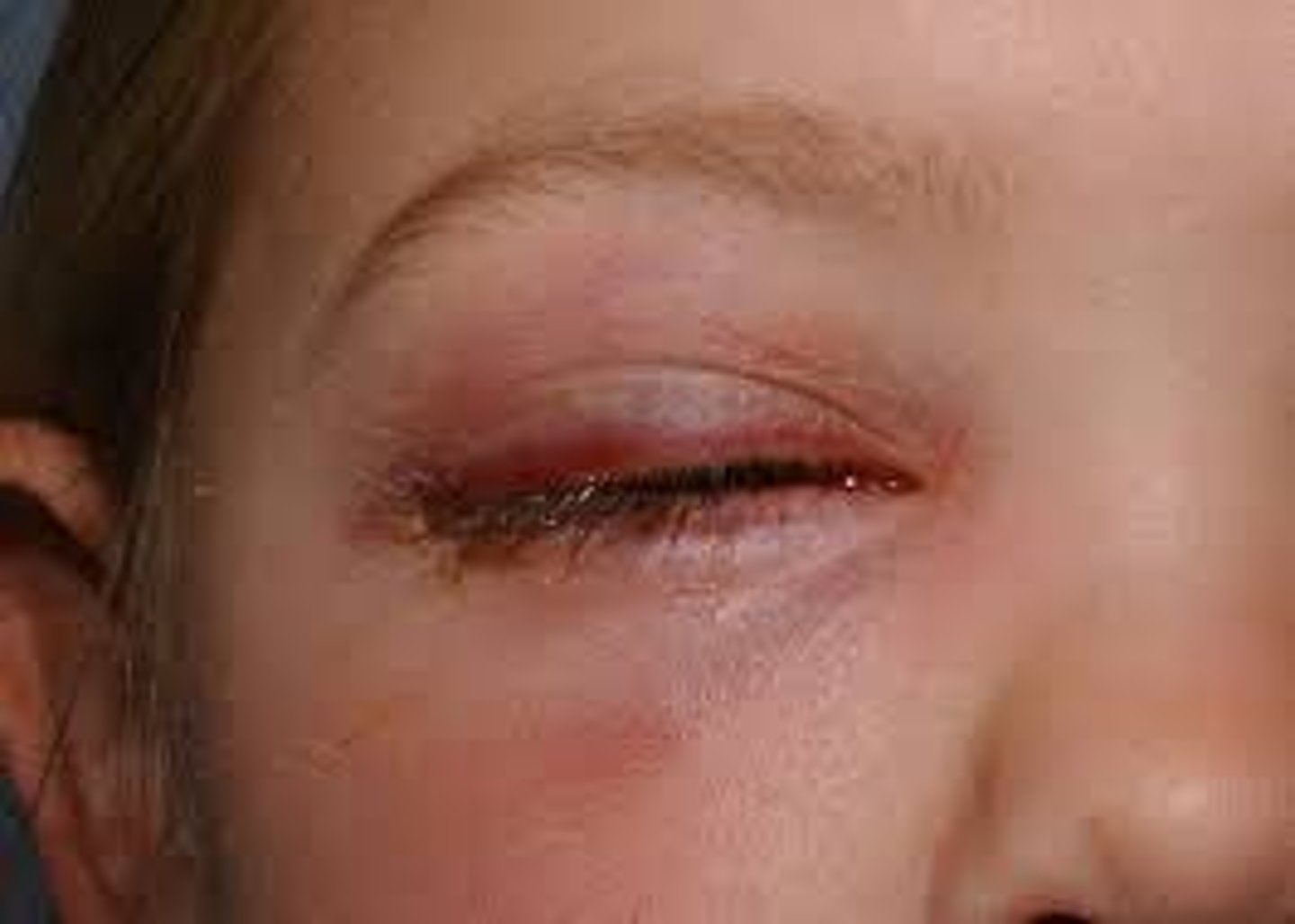
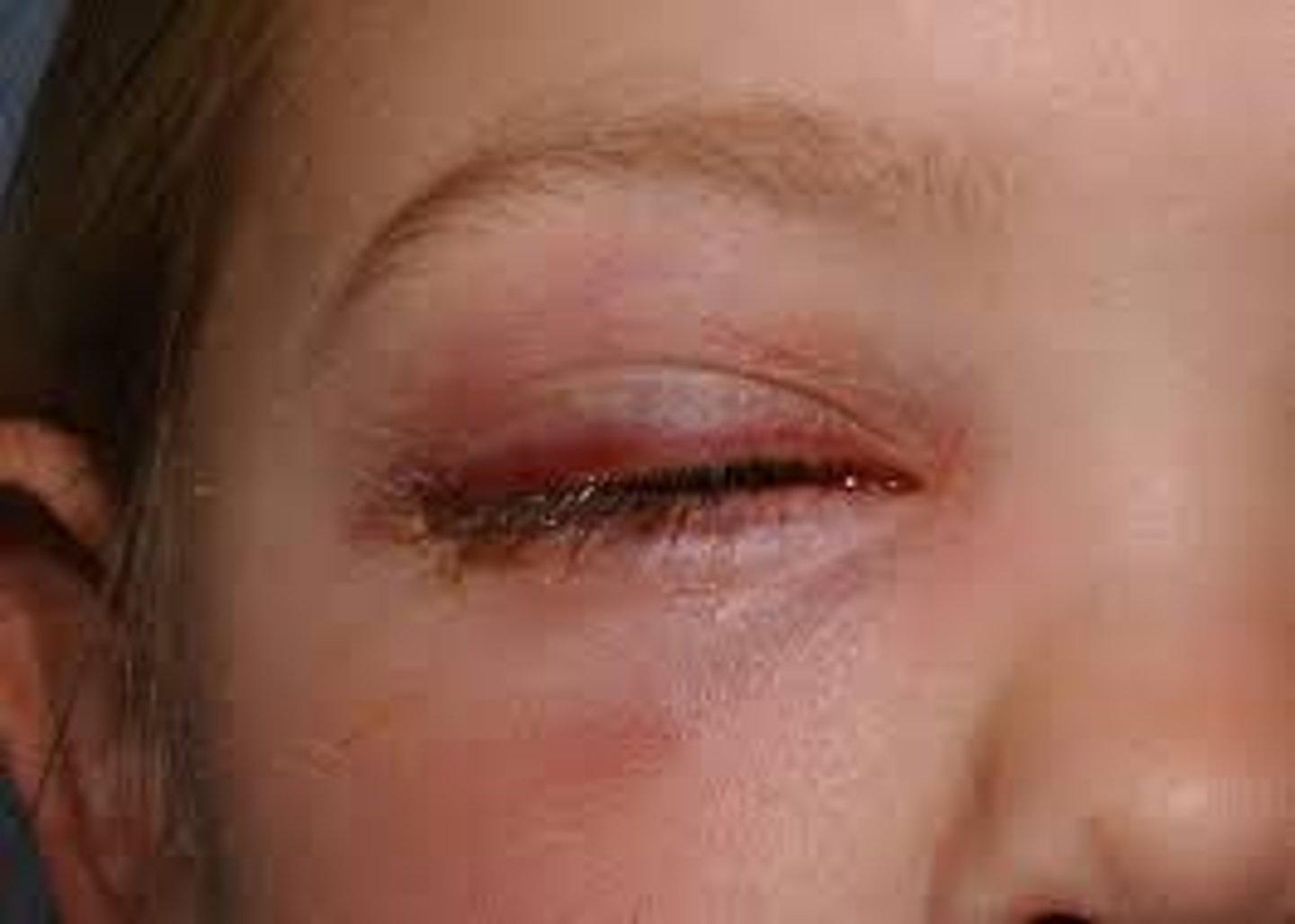
What is the tx for preseptal cellulitis?
oral antibiotics = Augmentin, Levofloxacin, Azithromycin
IV abx if non-responsive, severe, or pediatric
CT, CBC, cultures if severe
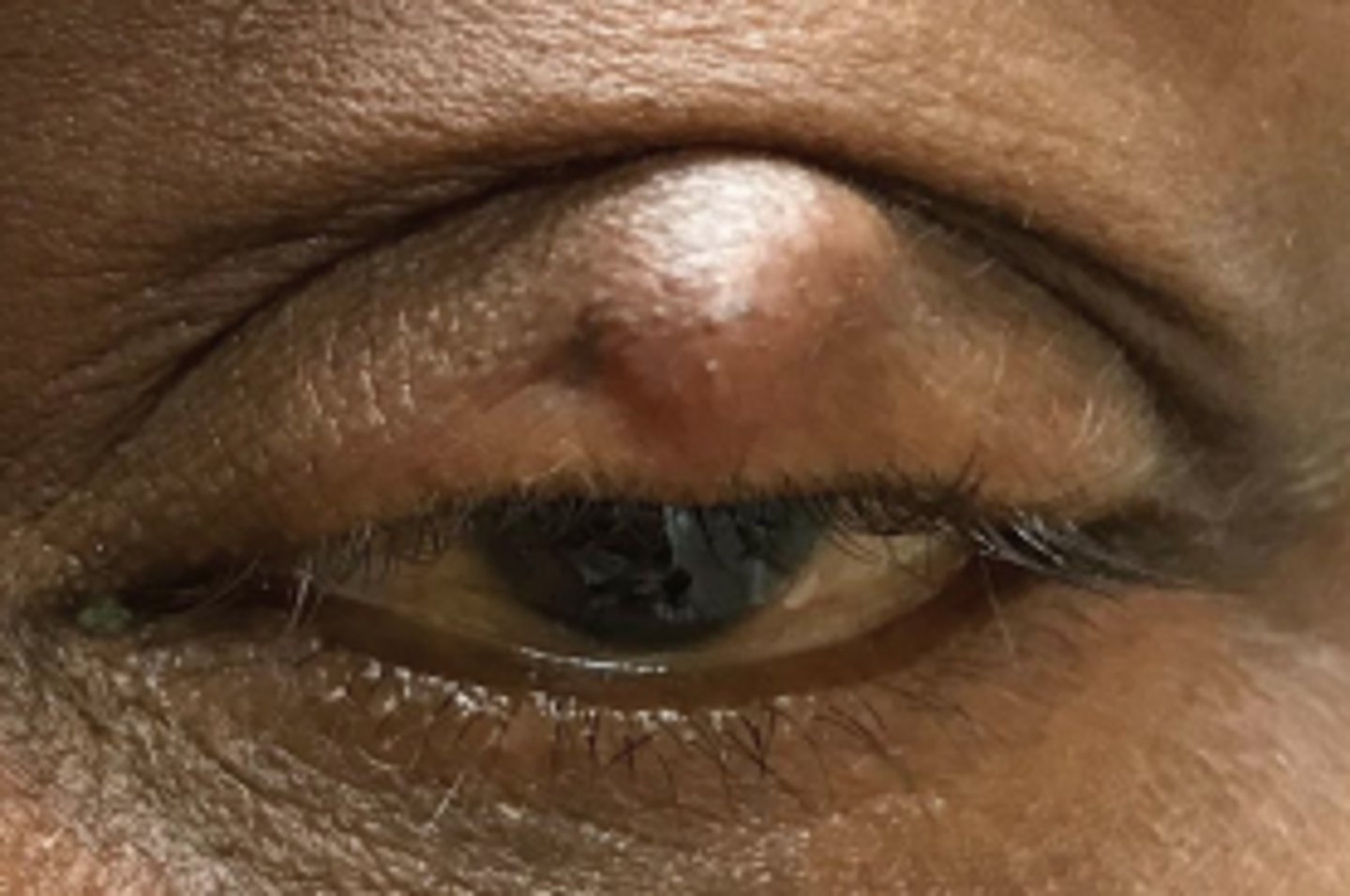
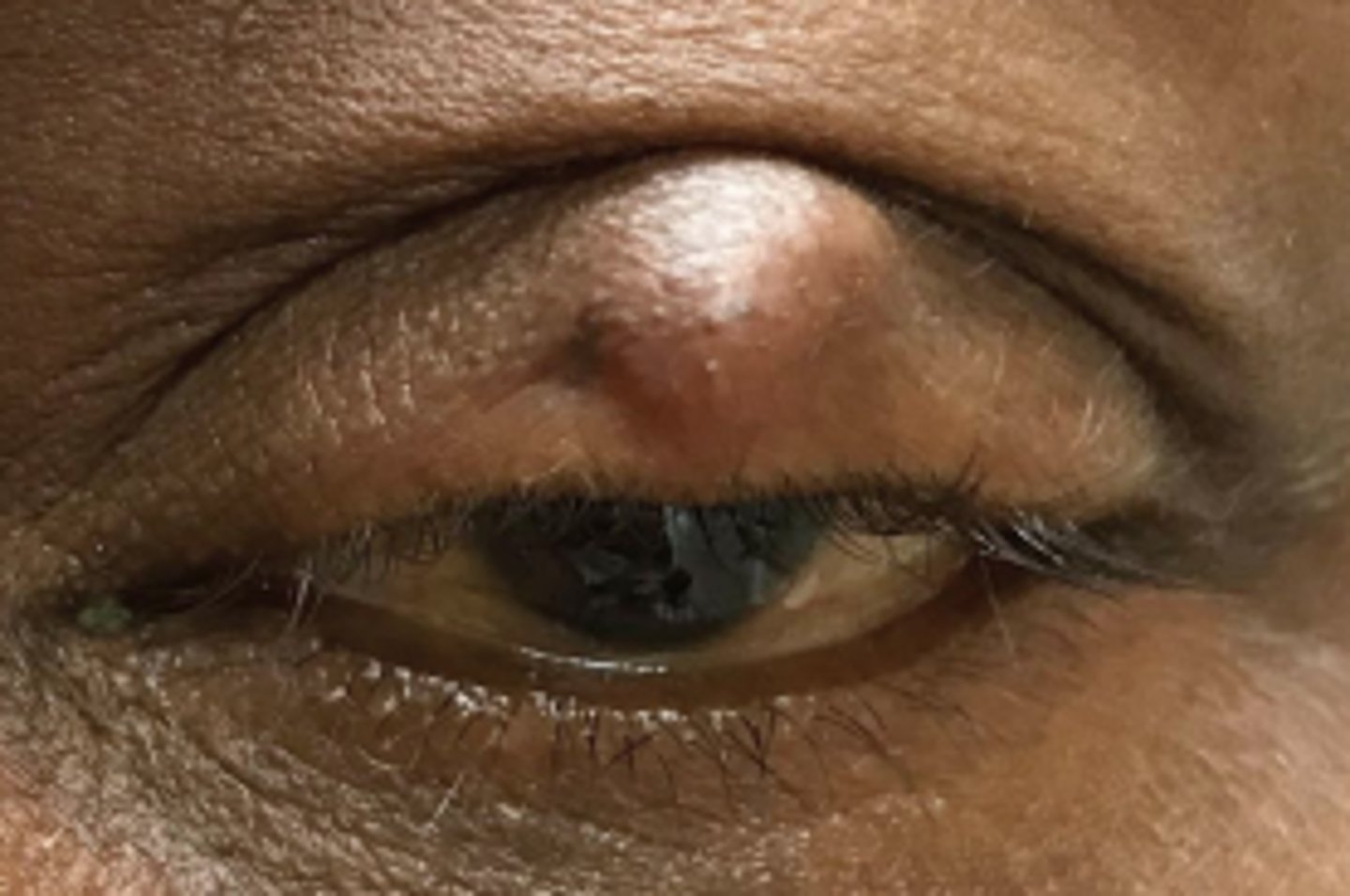
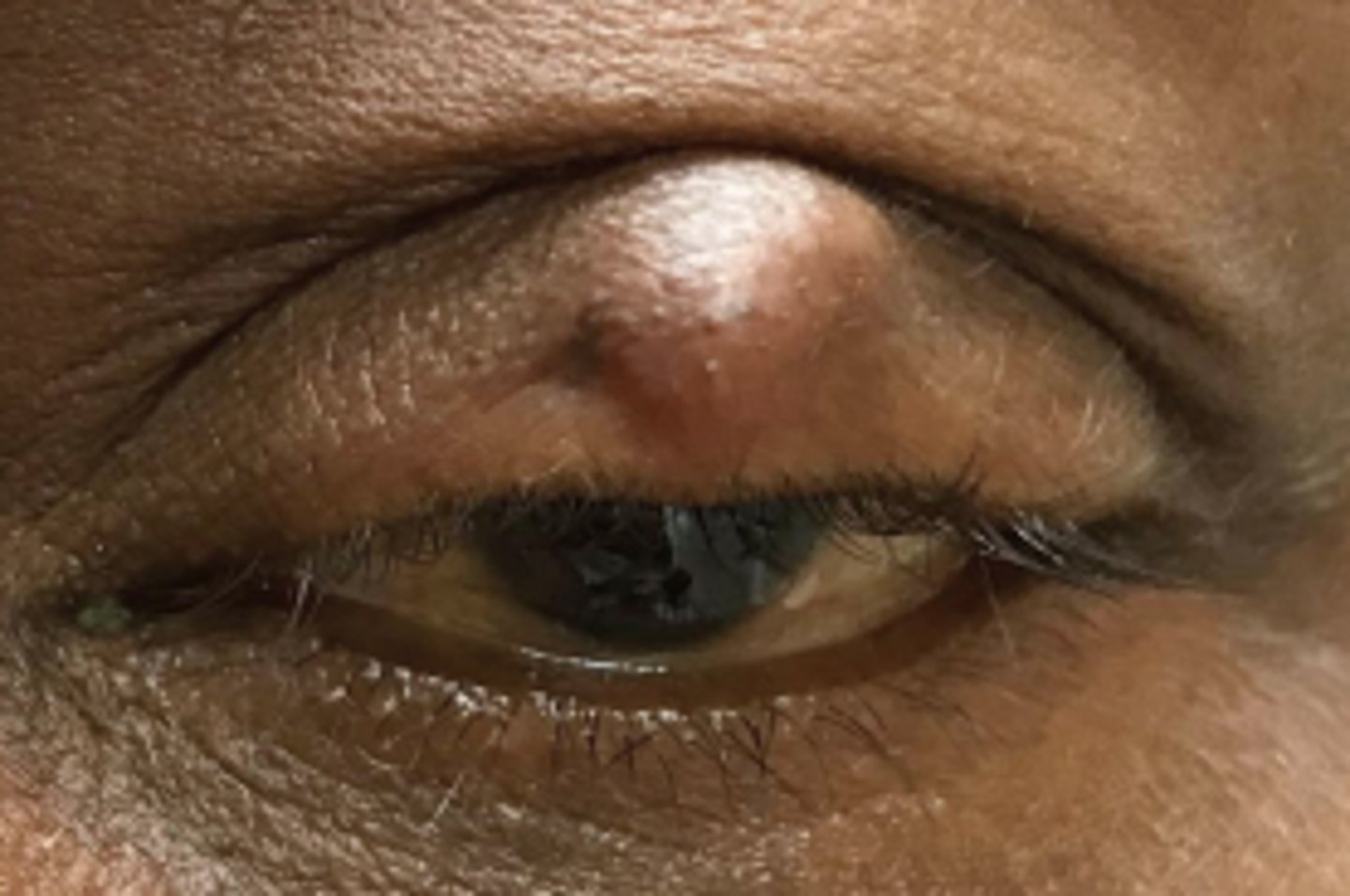
What is a chalazion?
obstruction and inflammation of a sebaceous gland = lipogranuloma, either...
anterior = Zeis Gland (sebaceous cyst)
interior = Meibomian gland
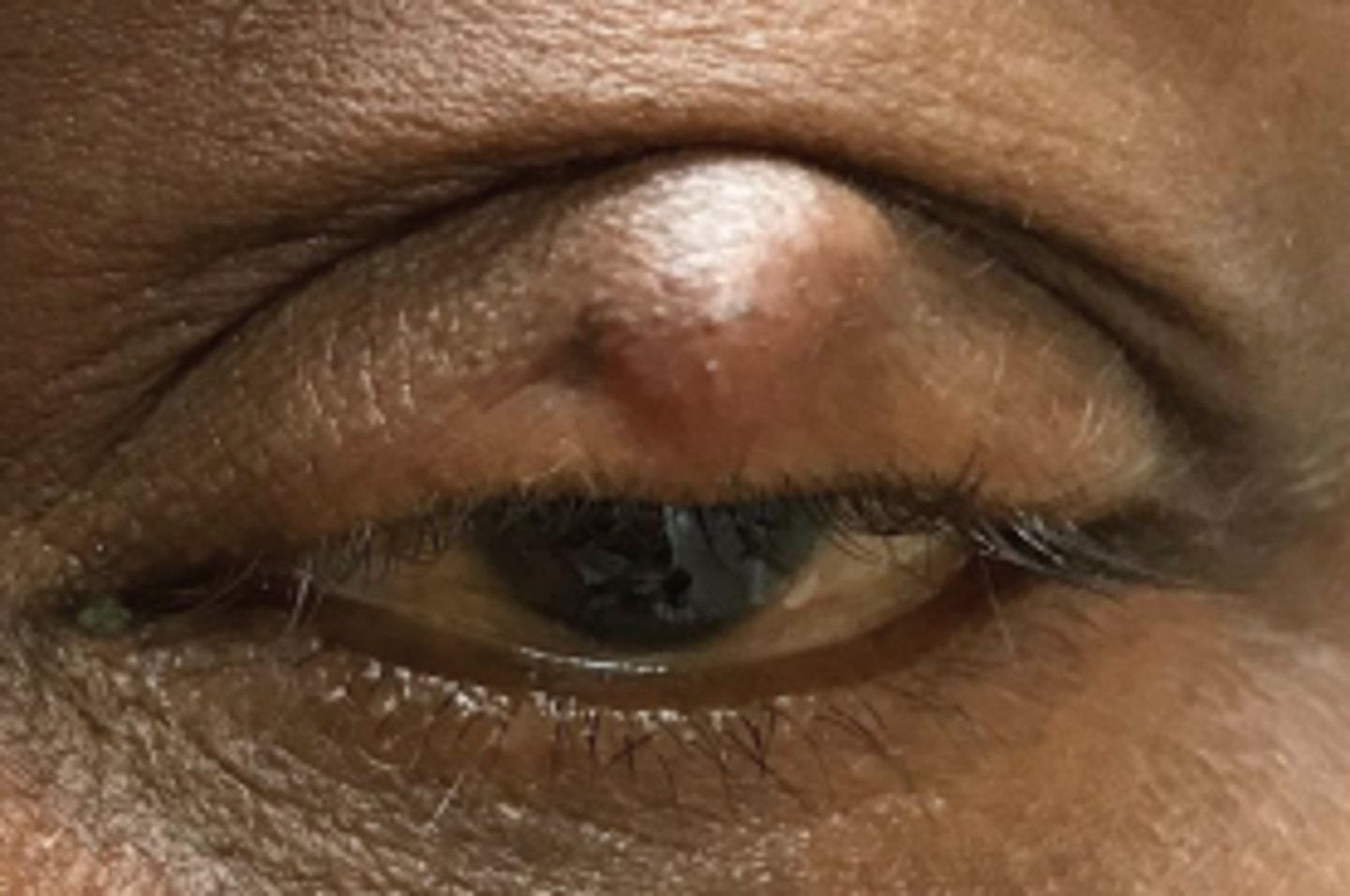
What is the histopathology behind a chalazion?
lipid products escape gland to surrounding tissue = granulomatous inflam = mononuclear phagocyte response = increased macrophage, epithelioid cells, multinucleated giant cell response = empty spaces with surrounding epithelioid and foamy multinucleated cells
What are some S/S of chalazion?
slowly progressing, relatively painless bump, especially in UL
+/- recurrence
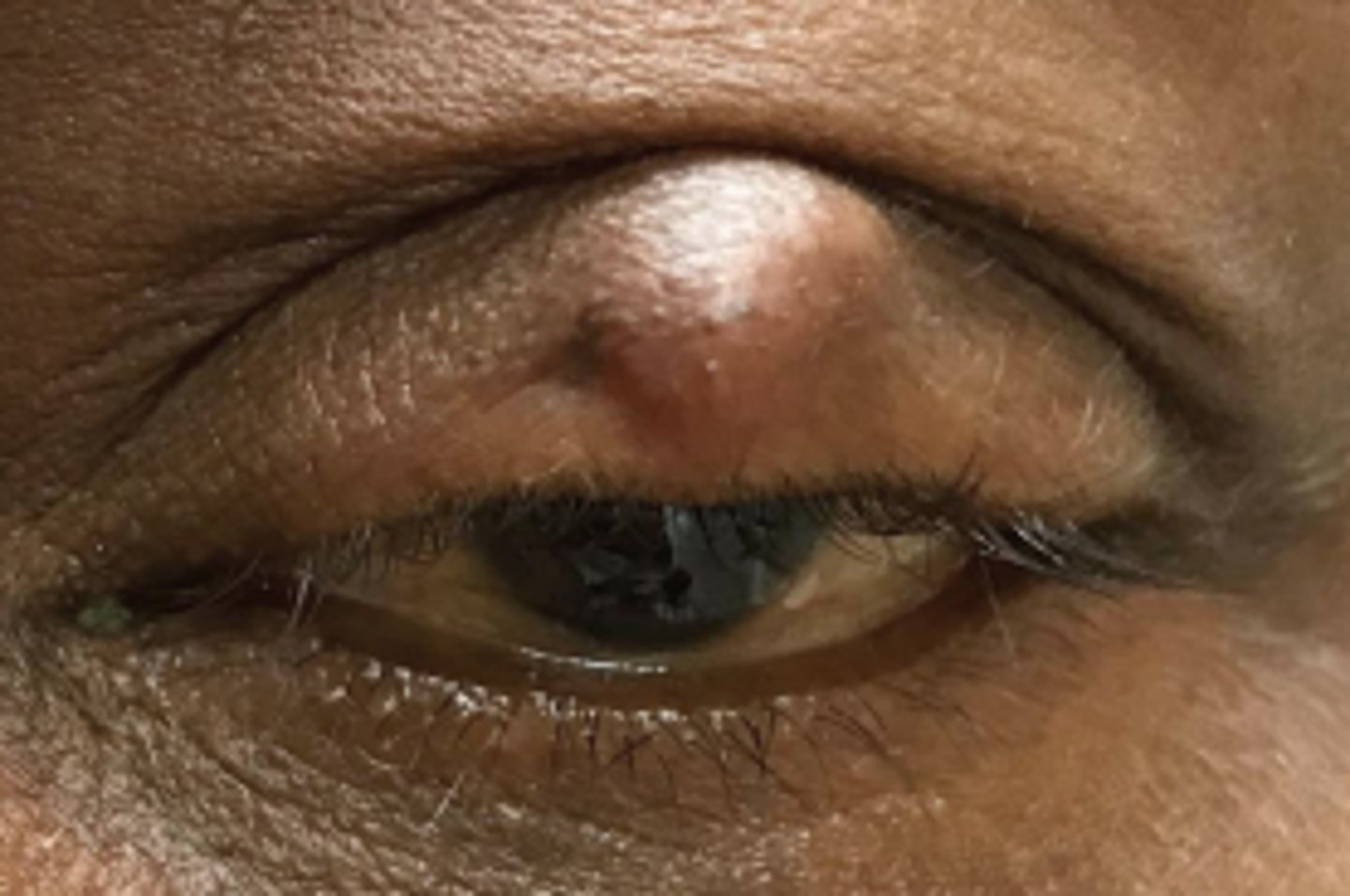
What are some risk factors/associations with chalazion?
adults (age 30+)
chronic blepharitis (lash debris, capped glands)
rosacea
hormonal factors
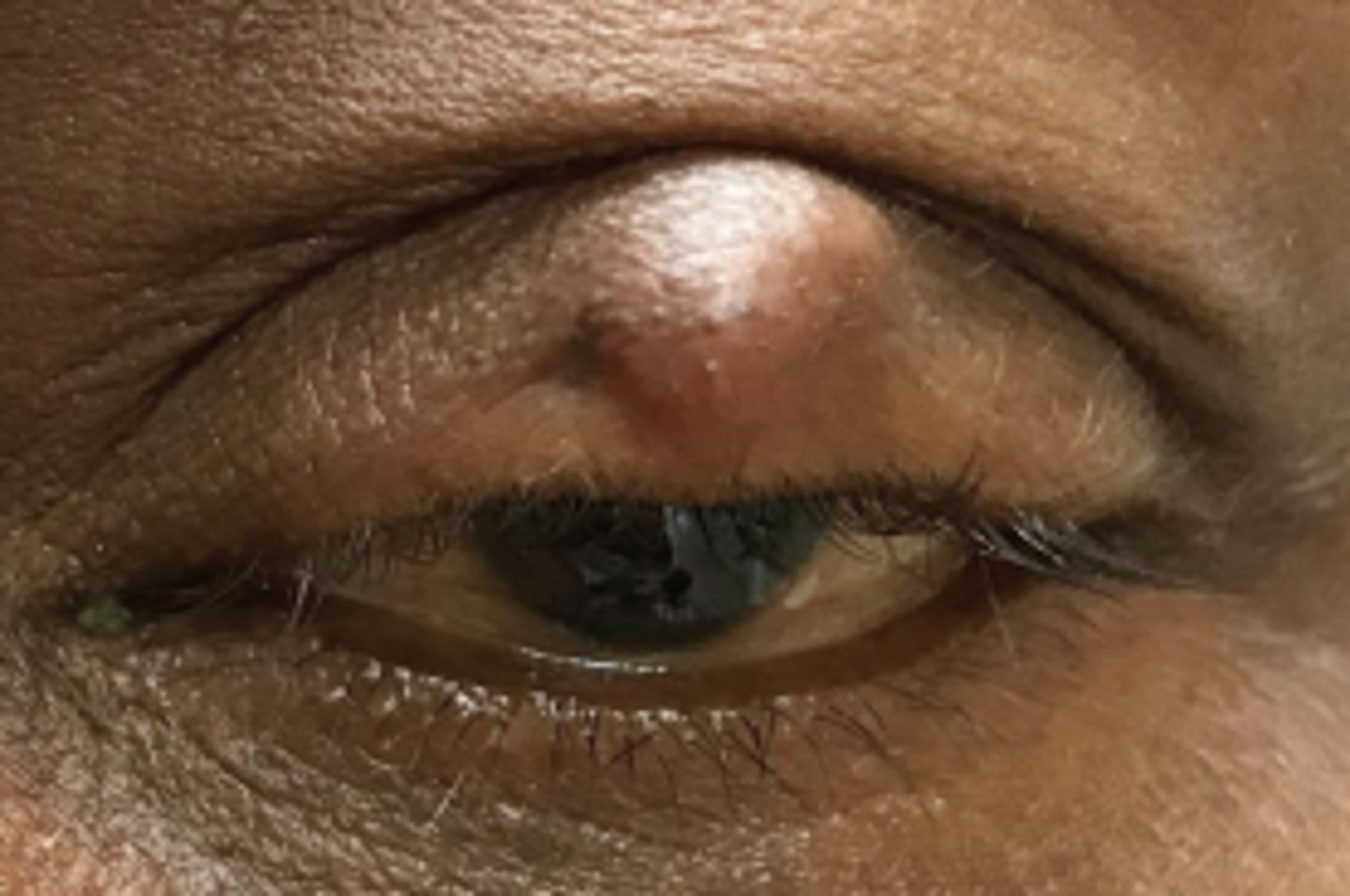
What are some tx options for chalazion?
warm compresses QID
intralesional steroid injection typically 0.2 cc Kenalog 40mg/mL
incision & curettage
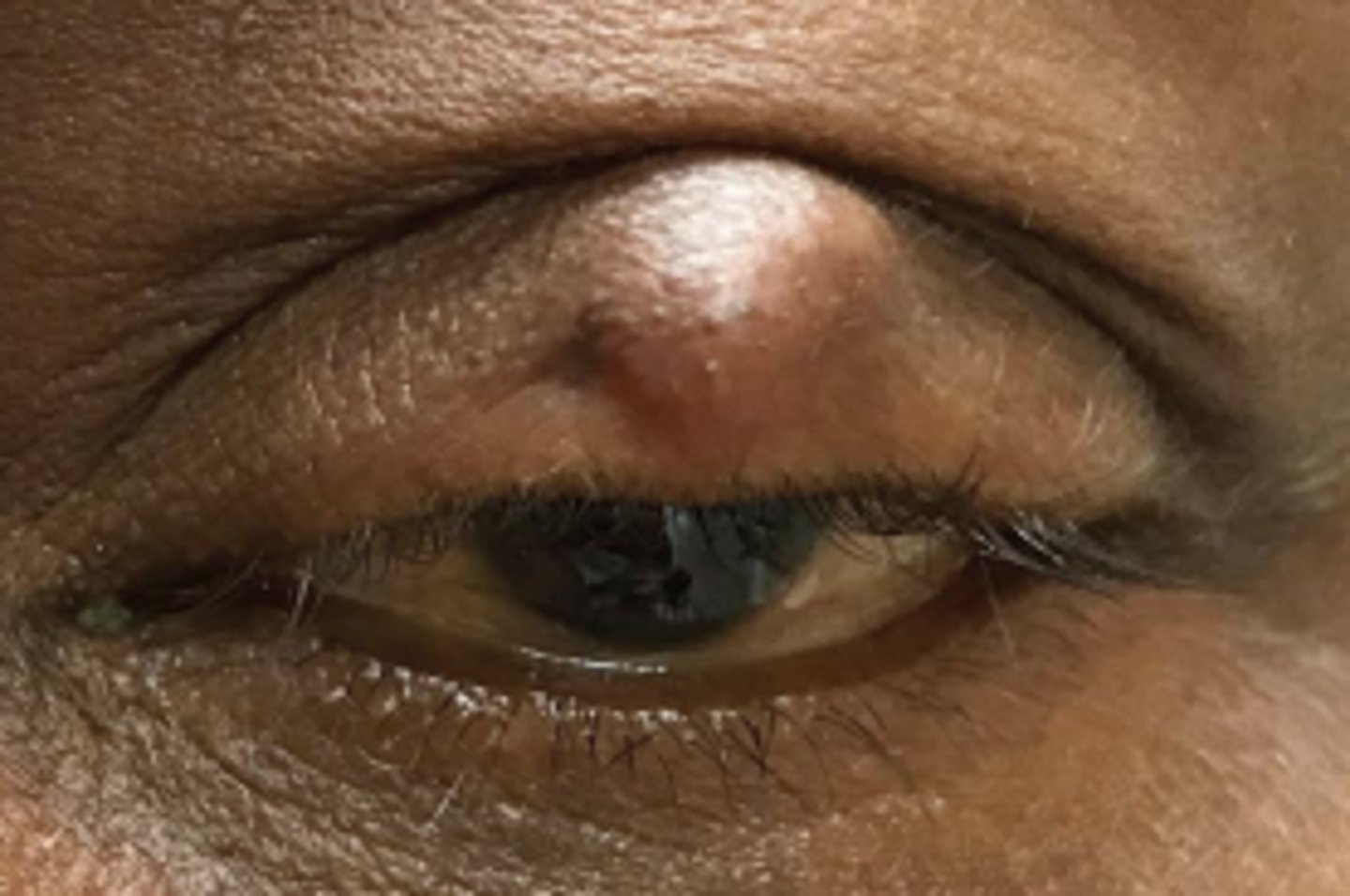
What are 3 complications of steroid injection for chalazion tx?
skin depigmentation
microembolization = retinal/choroidal infarct
fat atrophy
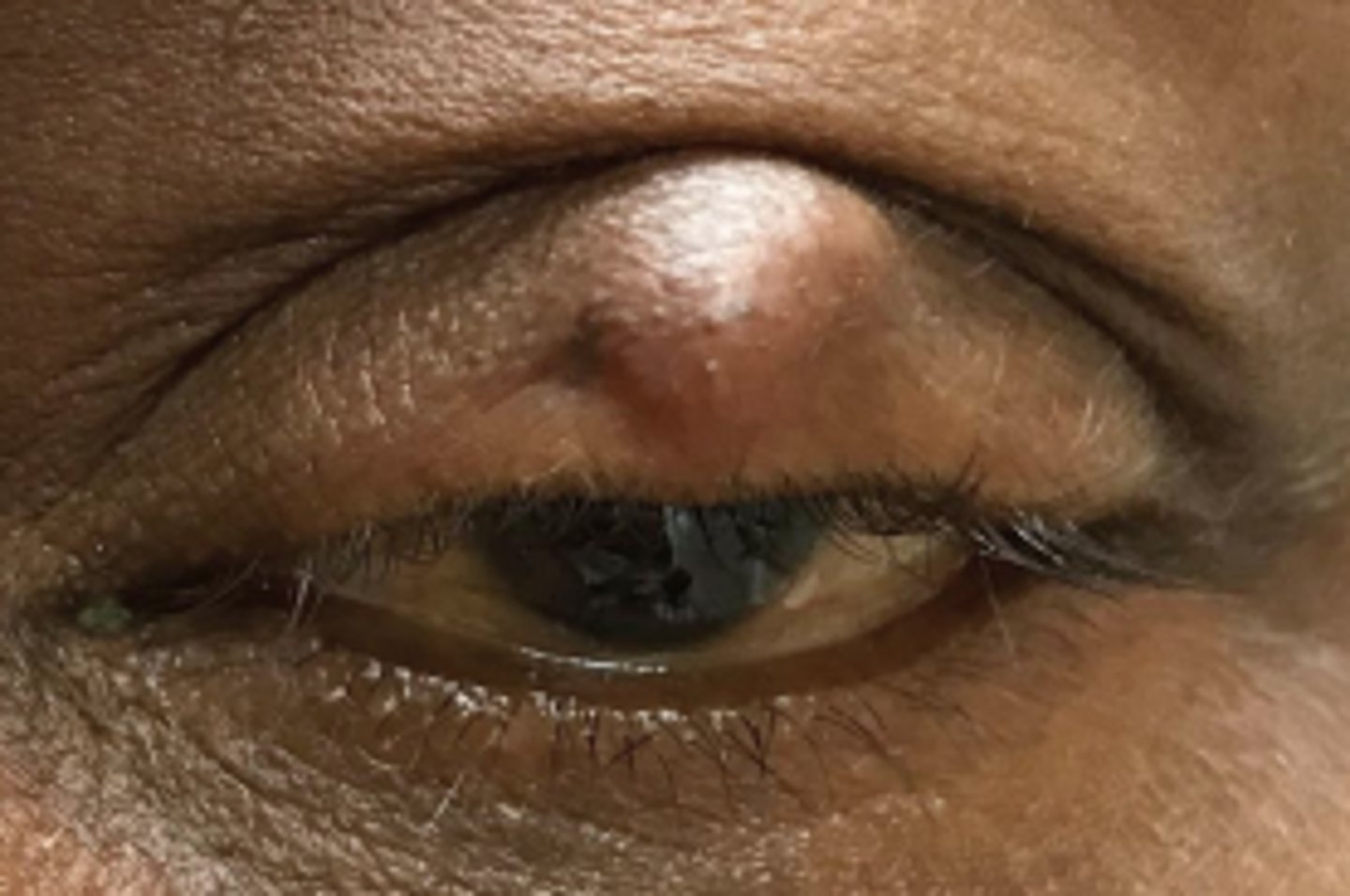
When compared to intralesional injection and hot compresses, how effective is chalazion I&C?
I&C shows greater size reduction and resolution
I&C has less recurrence
BUT more pain and inconvienience with I&C
What is the rule of 6 in terms of success of chalazion intralesional steroid?
if the chalazion is <6mm size and present for <6 months, then there is a 60% chance it will respond to intralesional steroid injection
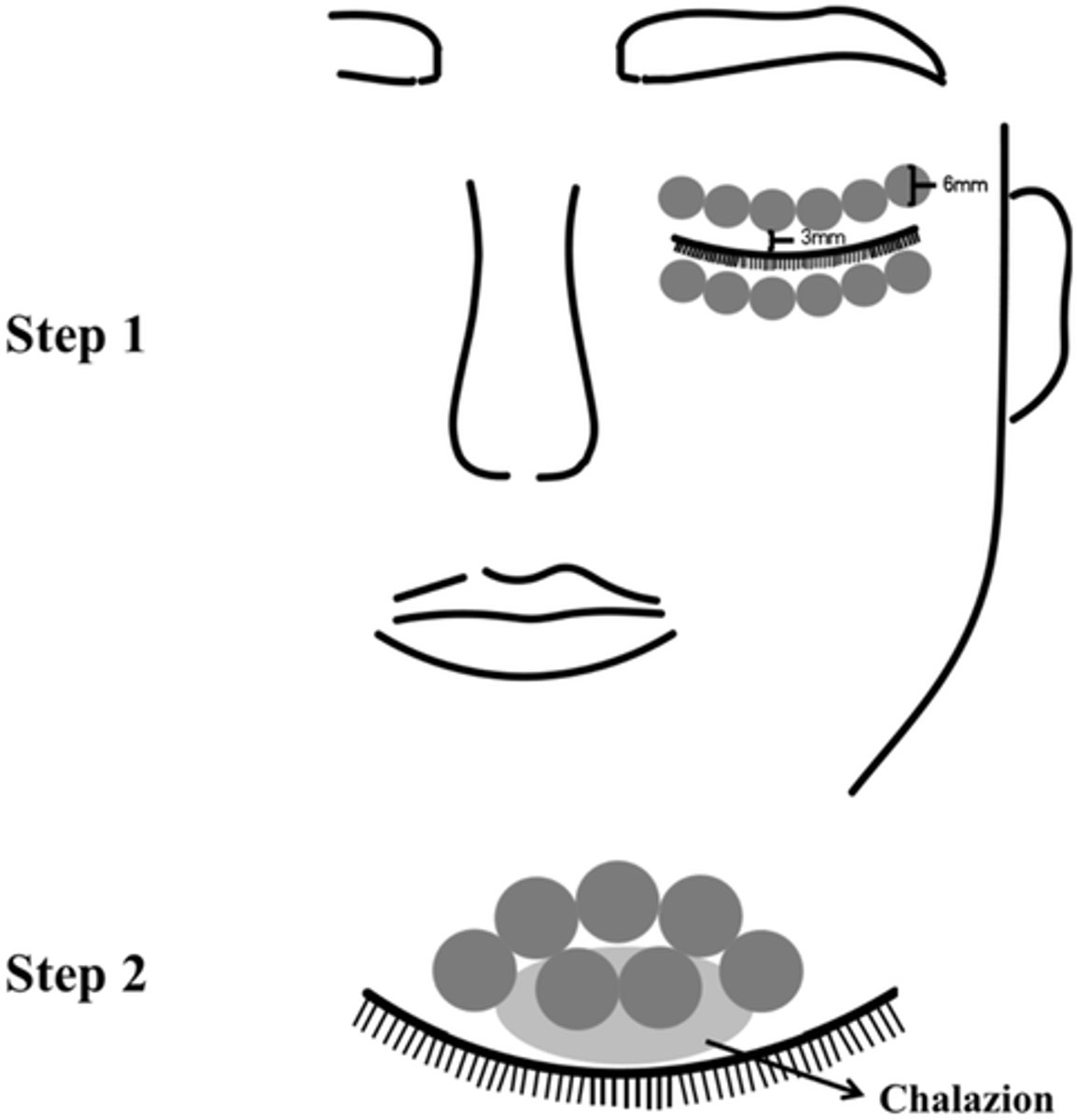
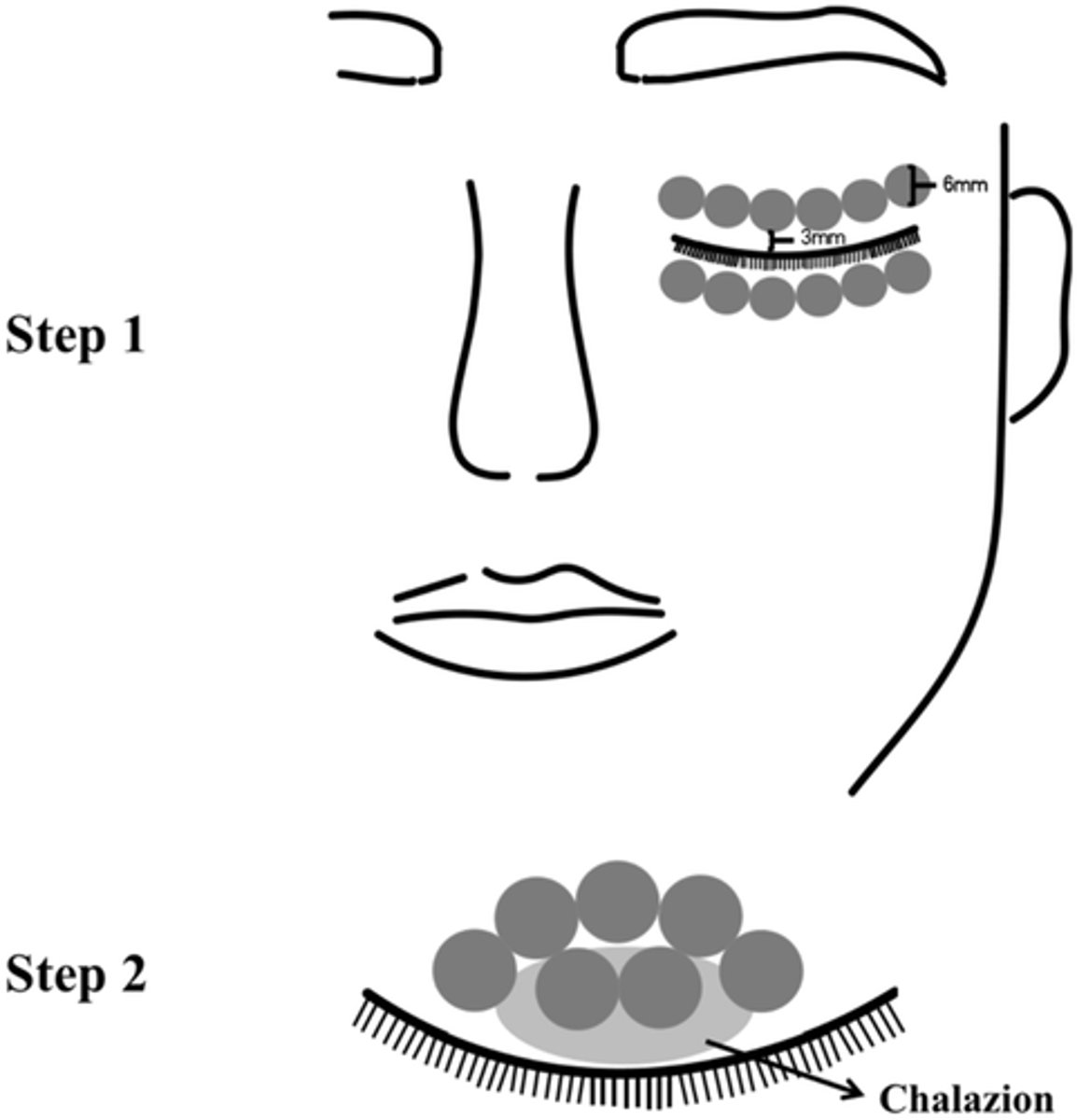
What is a new form of tx for chalazion?
IPL = normal dry eye area tx AND small applicator tip directly to the lesion with longer exposure (15min) and lower intensity
What are the 3 MOA's of IPL in treating chalazion?
antimicrobial effect
anti-inflammatory effect
kills demodex = targets melanin-like chromophore in backbone, also inhibits reproduction
What is a sebaceous cyst?
occluded gland of Zeis = sebum-filled opaque yellow lesion near lid margin
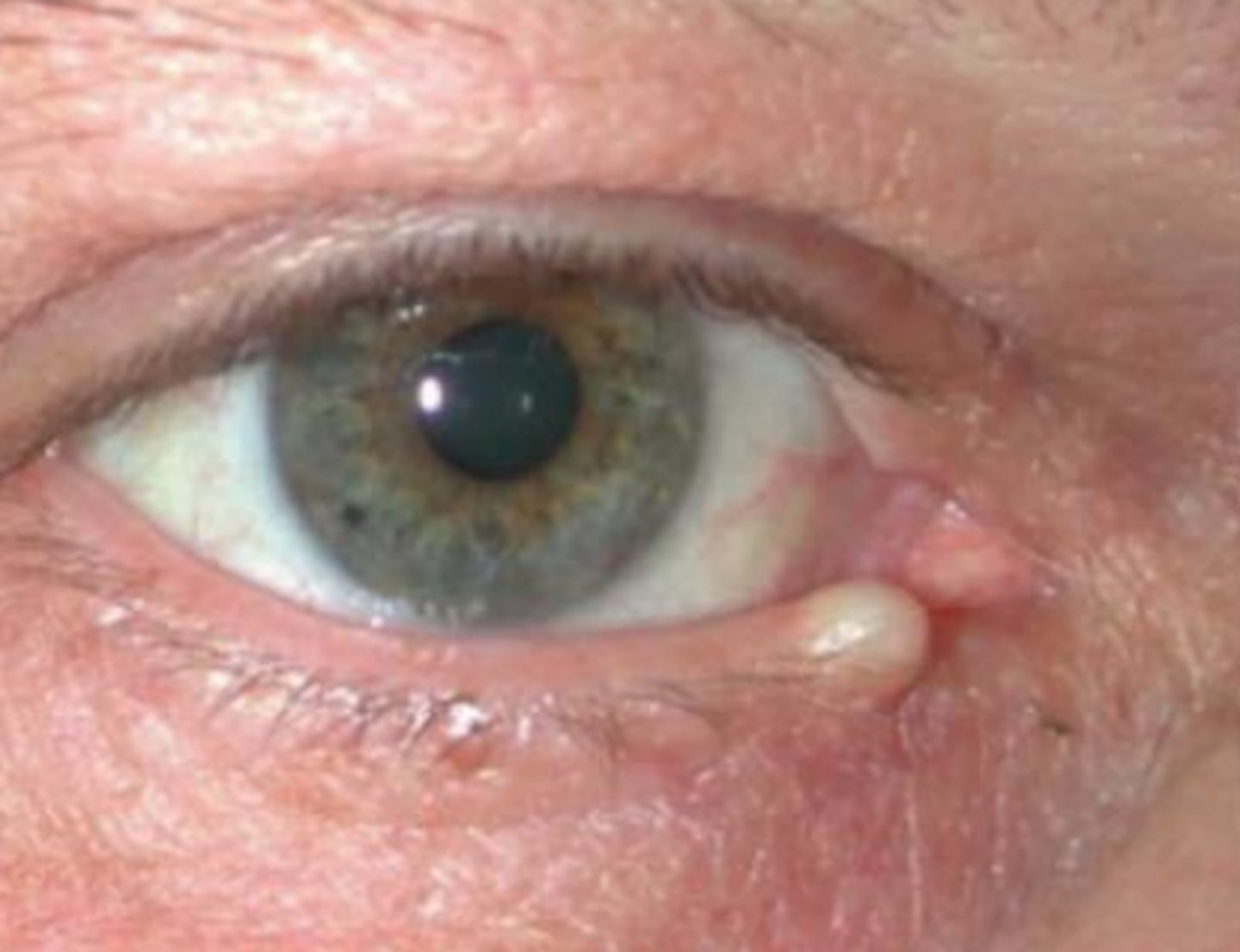
What is a hydrocystoma?
blockage of Glands of Moll (eccrine/apocrine sweat glands) = superficial, translucent, firm dome-shaped of clear fluid
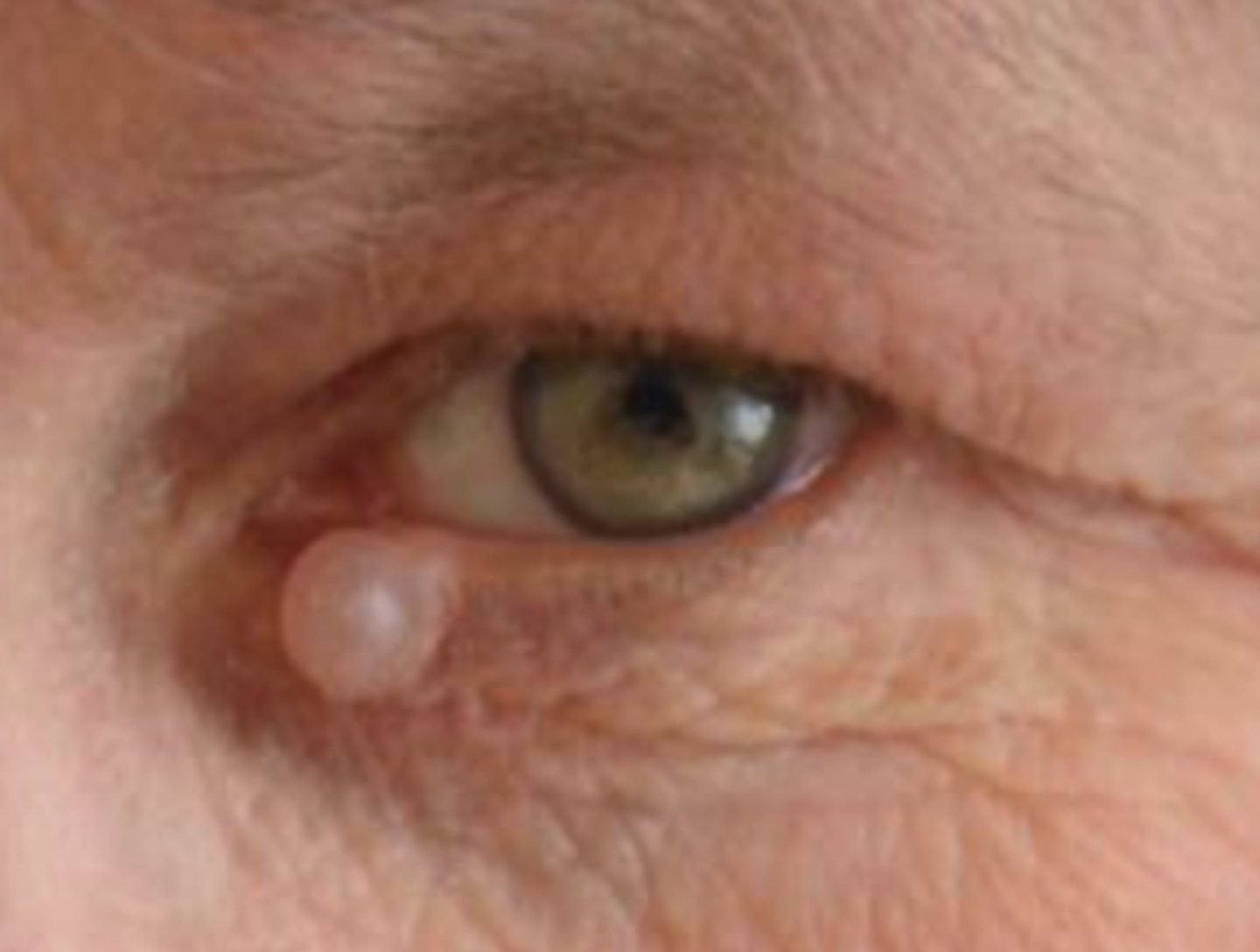
What is an epidermal inclusion cyst?
firm, over-proliferation of epithelial cells entrapped in the dermis = stratified squamous epithelium shell and keratinized core
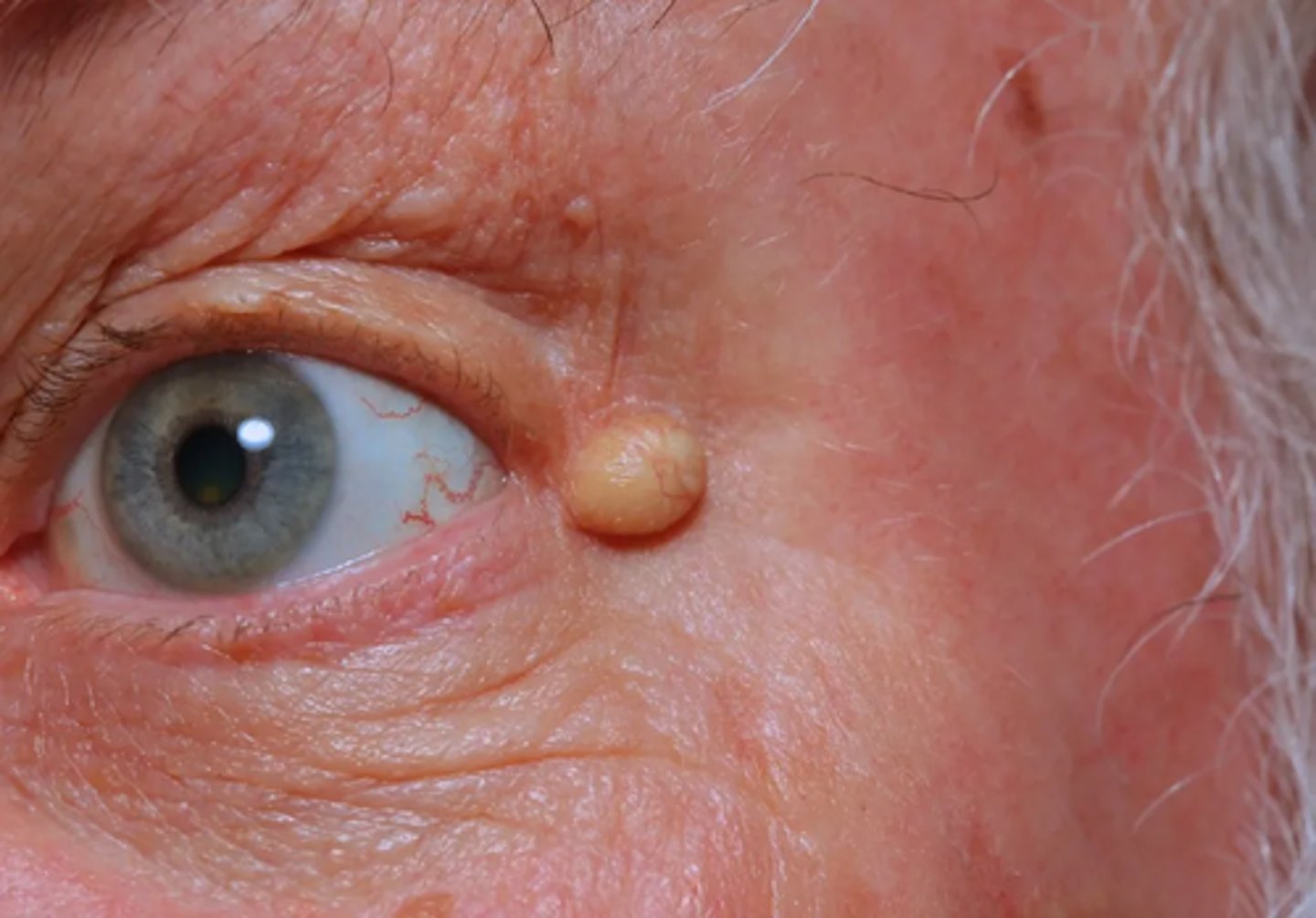
What is a syringoma?
comma-shaped gland = adenoma of intraepidermal eccrine duct = translcent yellow/flesh coloured waxy papule on LL
What are some risk factors for syringoma?
women >>> men, esp during menstruation and contraceptive
adolescence and continue through reproductive years
Down's syndrome
Japanese
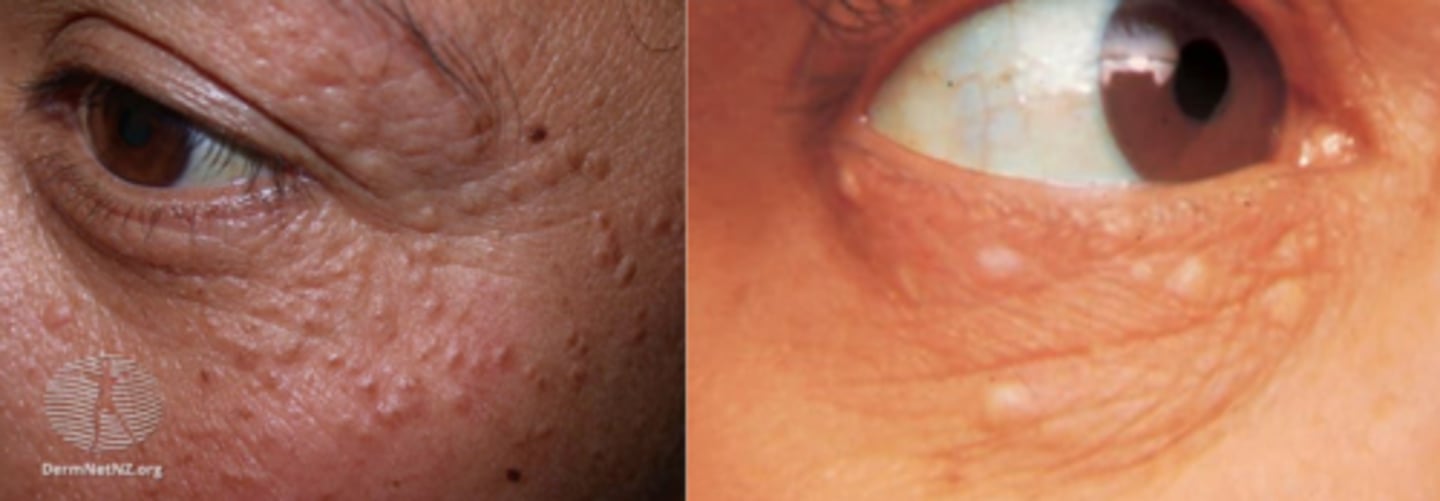
Why are syringoma difficult to treat?
originates in deep dermis tissue
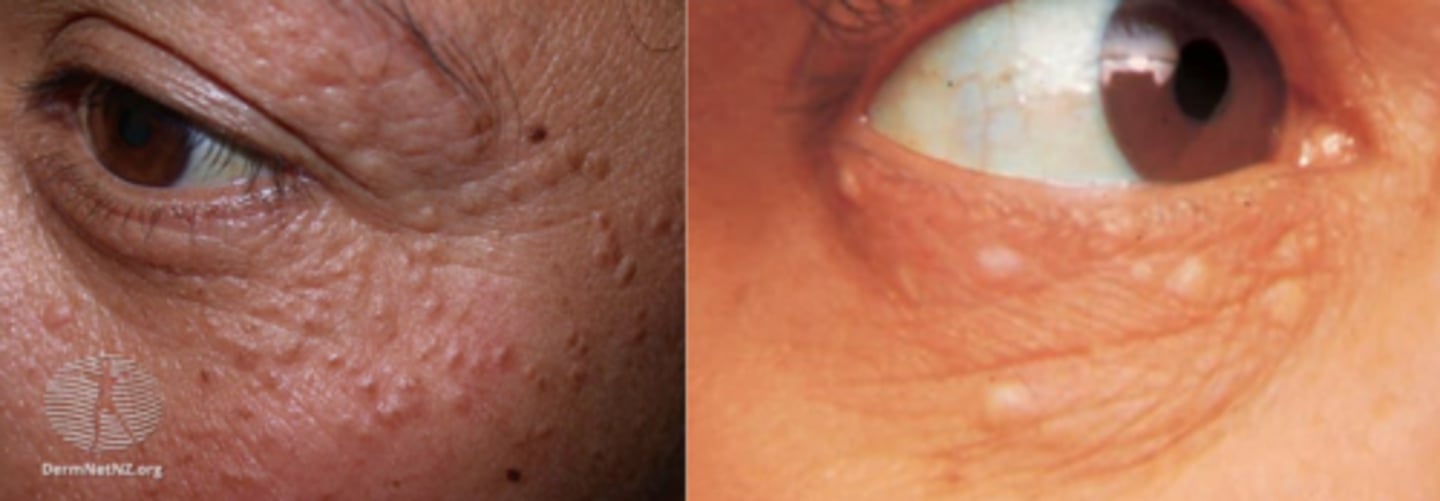
What is the tx for syringoma?
shave excision = high risk of scar
chemical peel = bichloracetic acid or tretinoin
electrocautery/RF
CO2 or Er:YAG laser = least scar potential
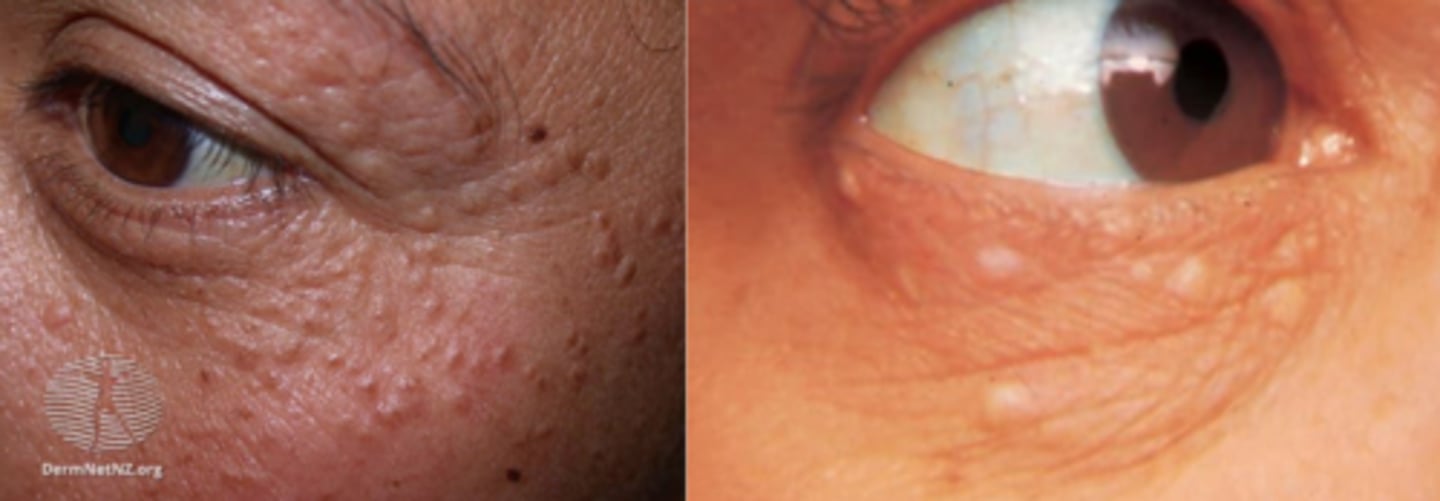
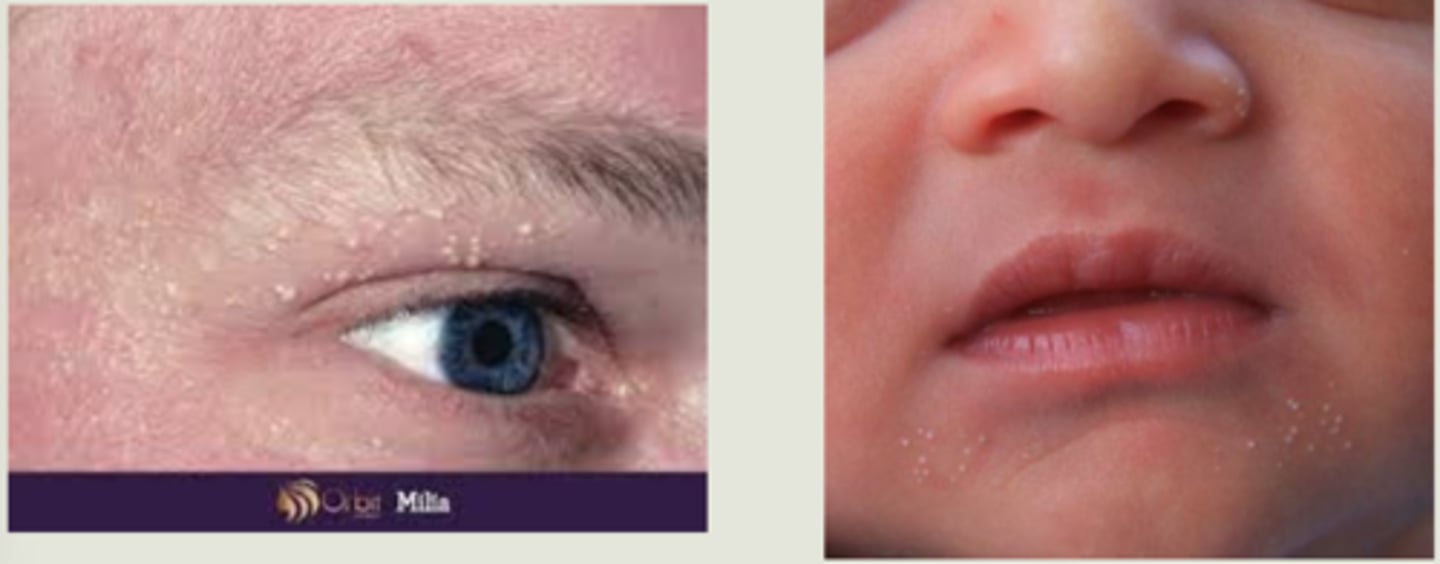
What are milia?
superficial white bumps = external layers of stratified squamous epithelium with keratin core
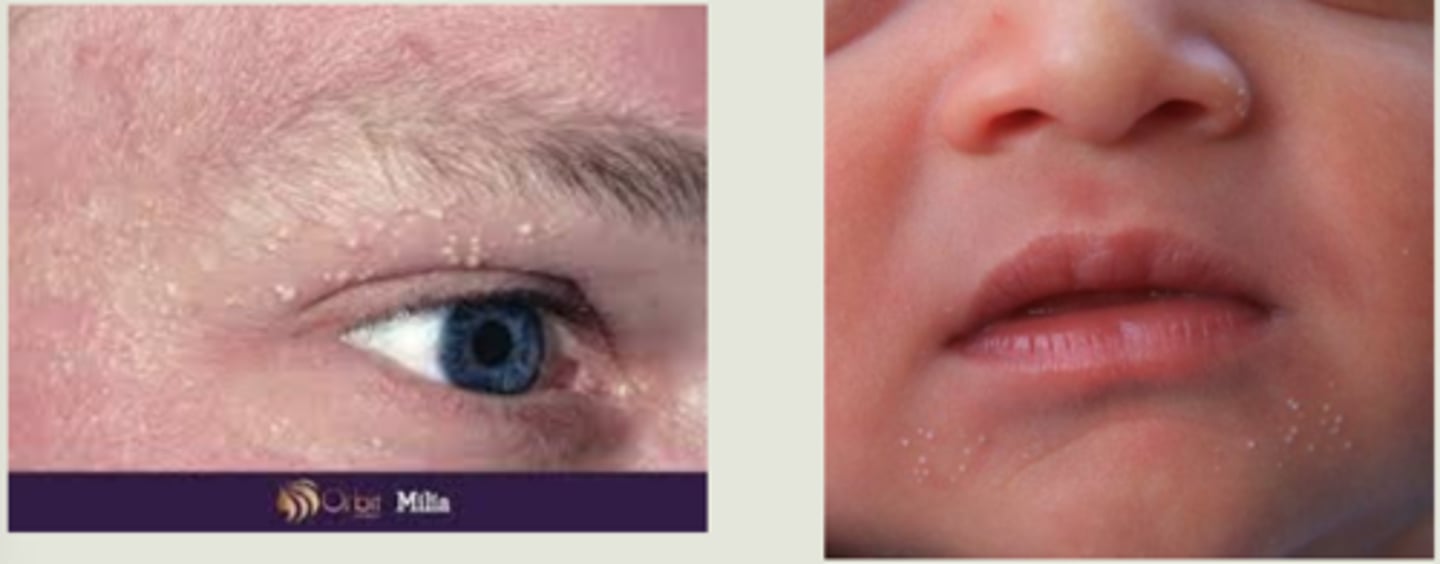
What are primary vs secondary milia?
primary = cysts of pilosebaceous unit of the vellus hair follicle
secondary = entraped material in eccrine grlands, etc.
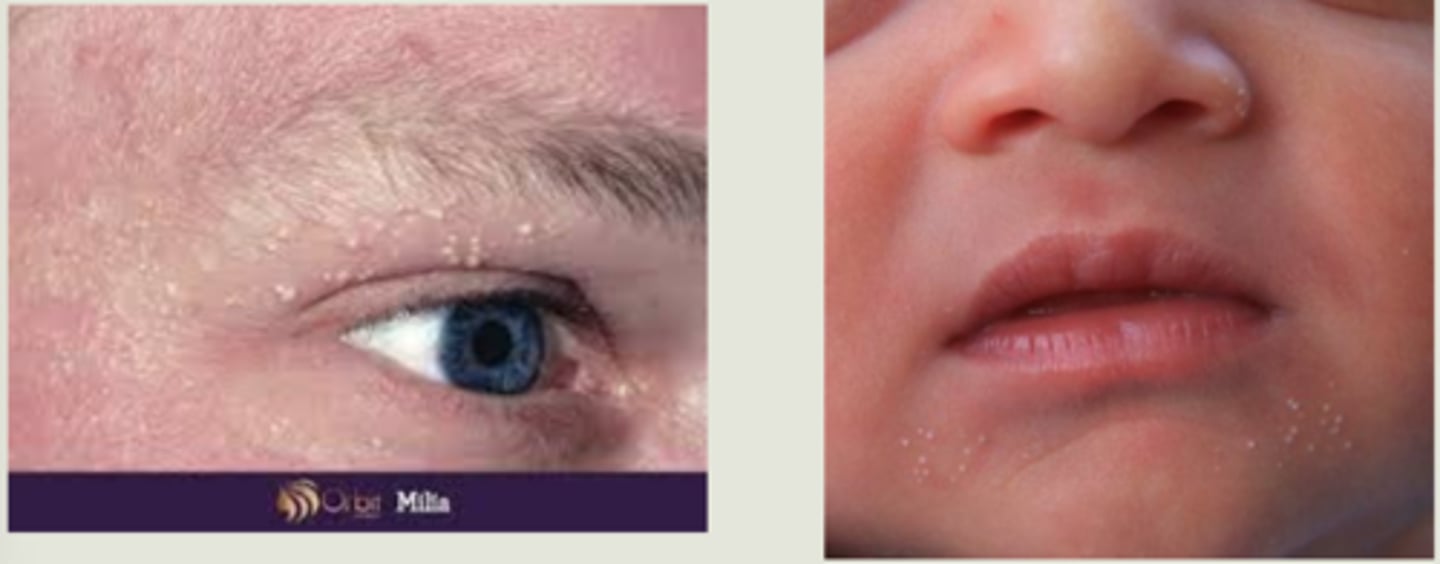
What are some risk factors for developing milia?
sun damage
LT topical steroid cream
skin creams/makeup
babies (primary)
What is molluscum contagiosum?
infectious pox virus = intracytoplasmic molluscum bodies form in epithelial cells where virus replicates = multiple small flesh-coloured, waxy papules with umbilicated center that continues to release virus
+/- follicular conjunctivitis
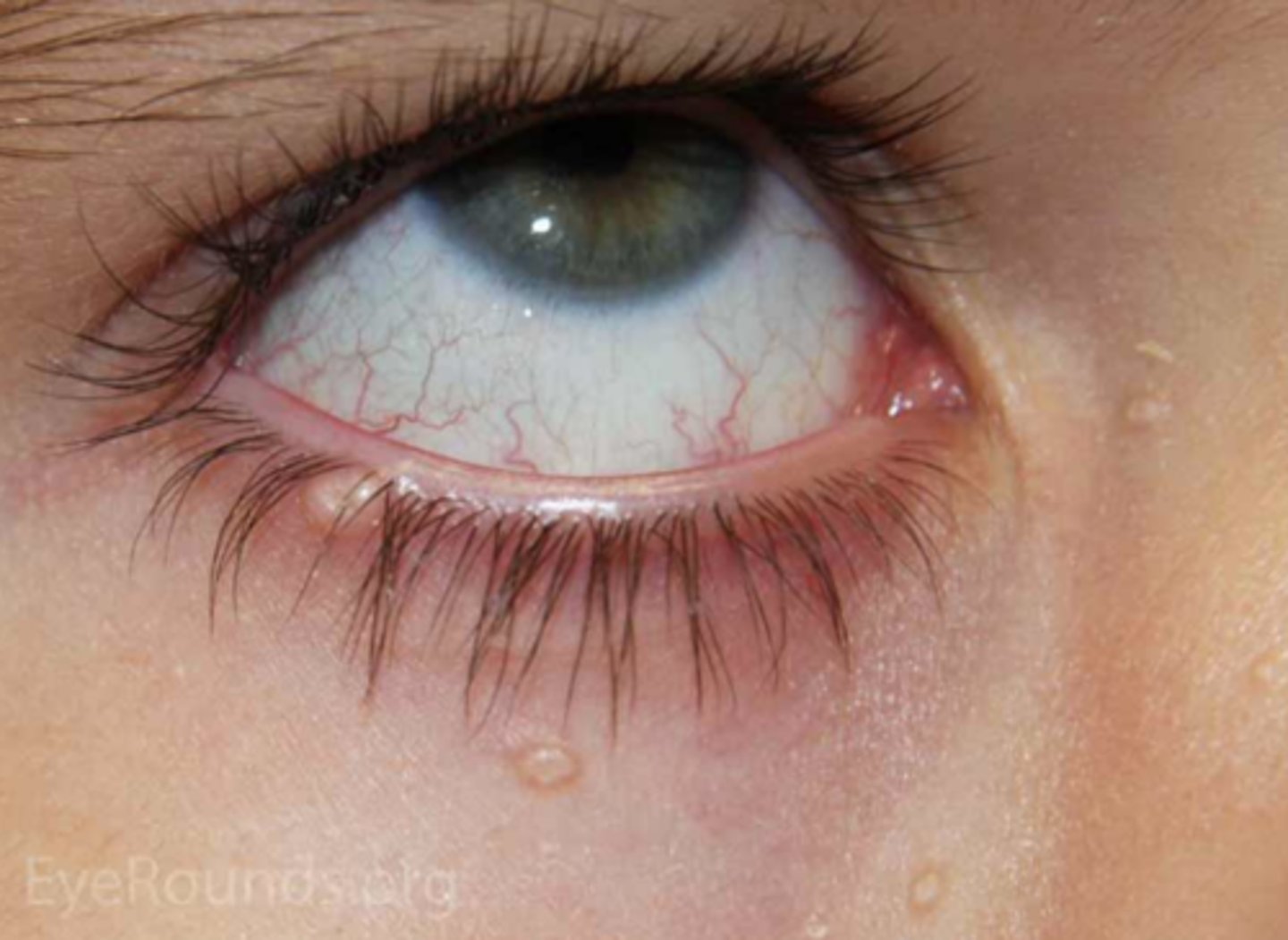
What 2 populations is molluscum contagiosum more common in?
young kids
immunocompromised
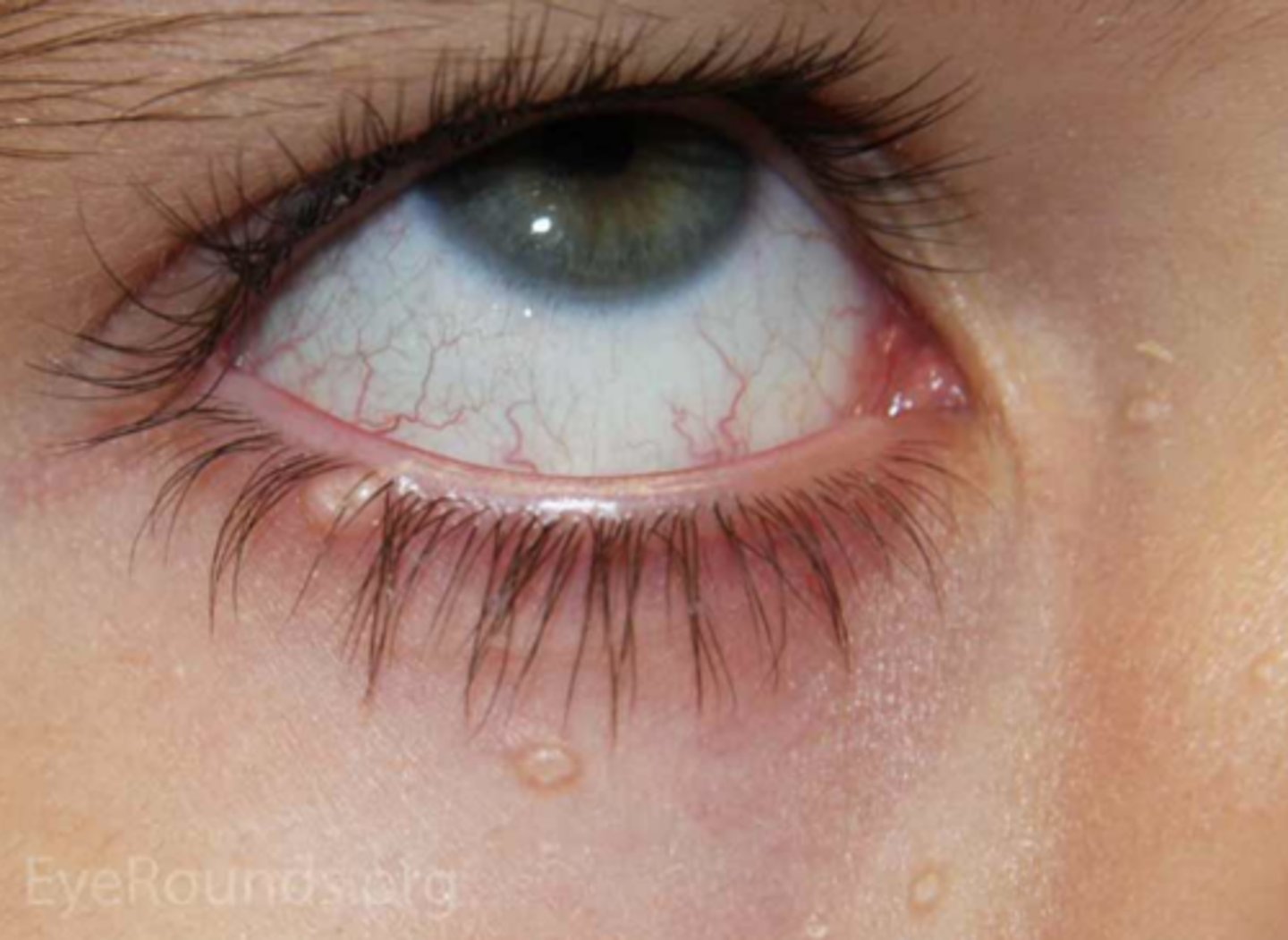
What are some tx for molluscum contagiosum?
may resolve on it's own
excision
curettage
electrodessication
cryotherapy
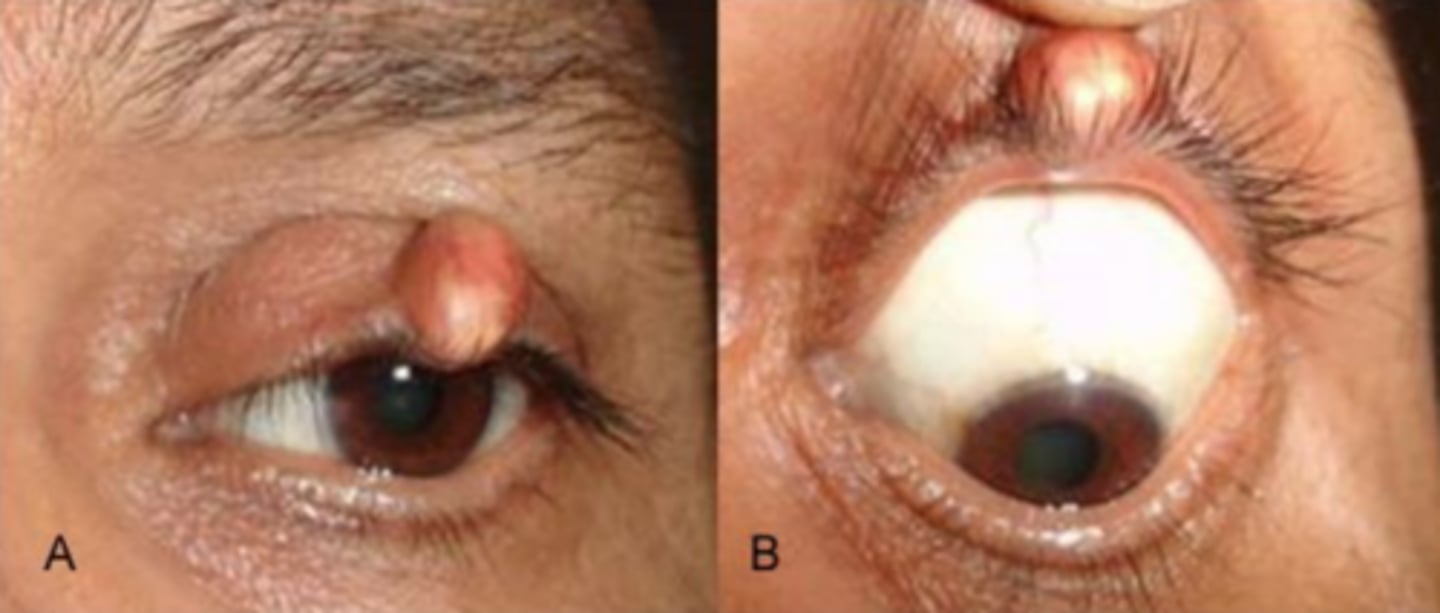
What is pilomatricoma?
calcium deposition = granulomatous response = slow growing, hard, benign tumor of lash hair bulb = typically reddish surround with whiteish calcium nodules
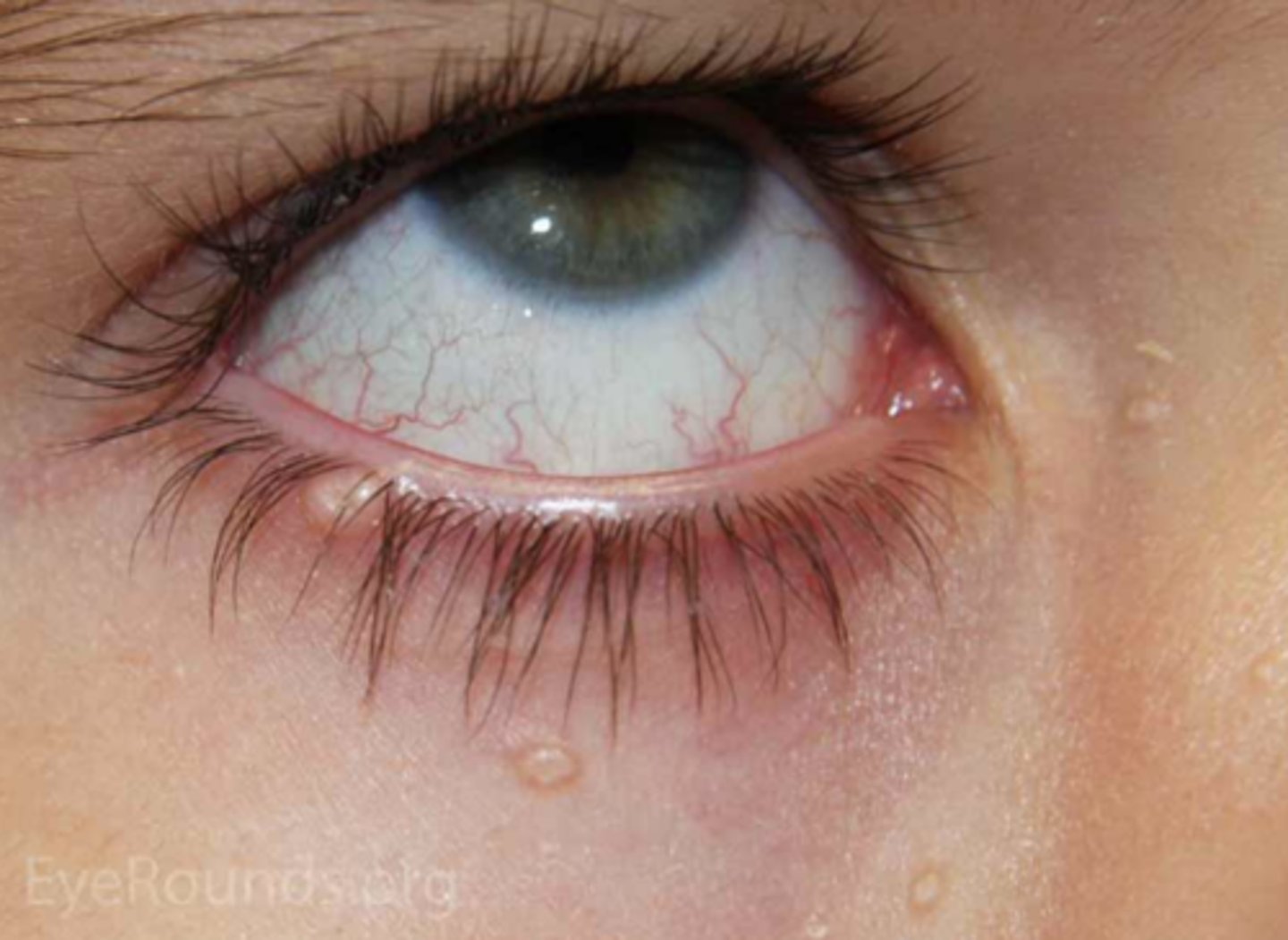
What is a conj inclusion cyst?
displaced conj epithelial cells form a cystic cavity = thin-walled cyst is filled with seroud fluid
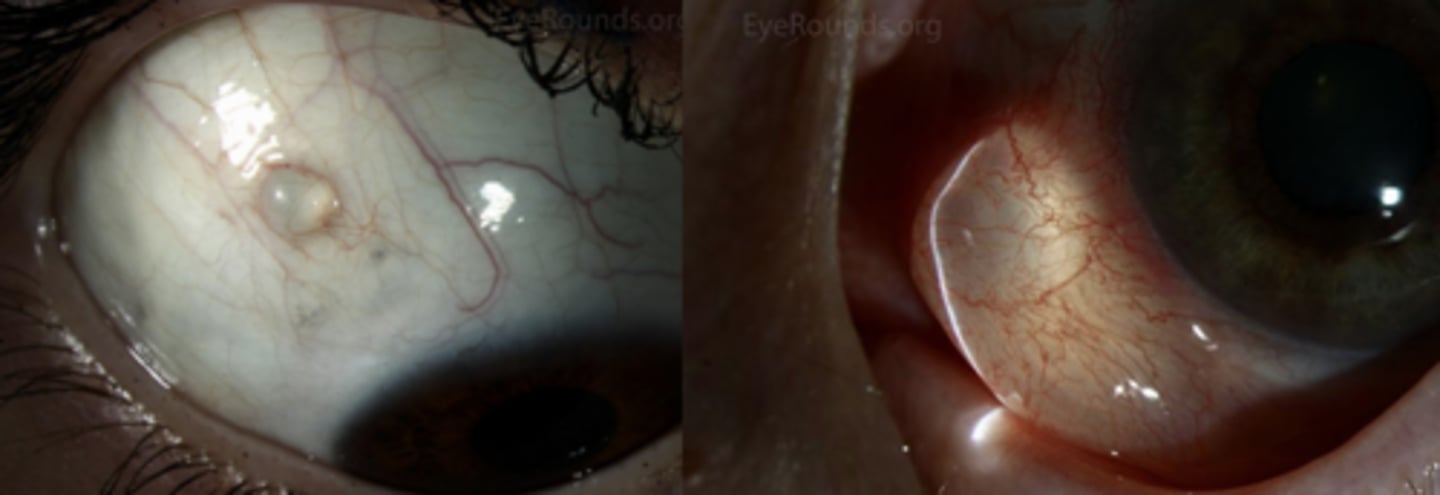
What are some potential causes of conj inclusion cysts?
trauma
inflammation
lymphangiectasia = poor lymphatic drainage, dilated lymphatic vessel
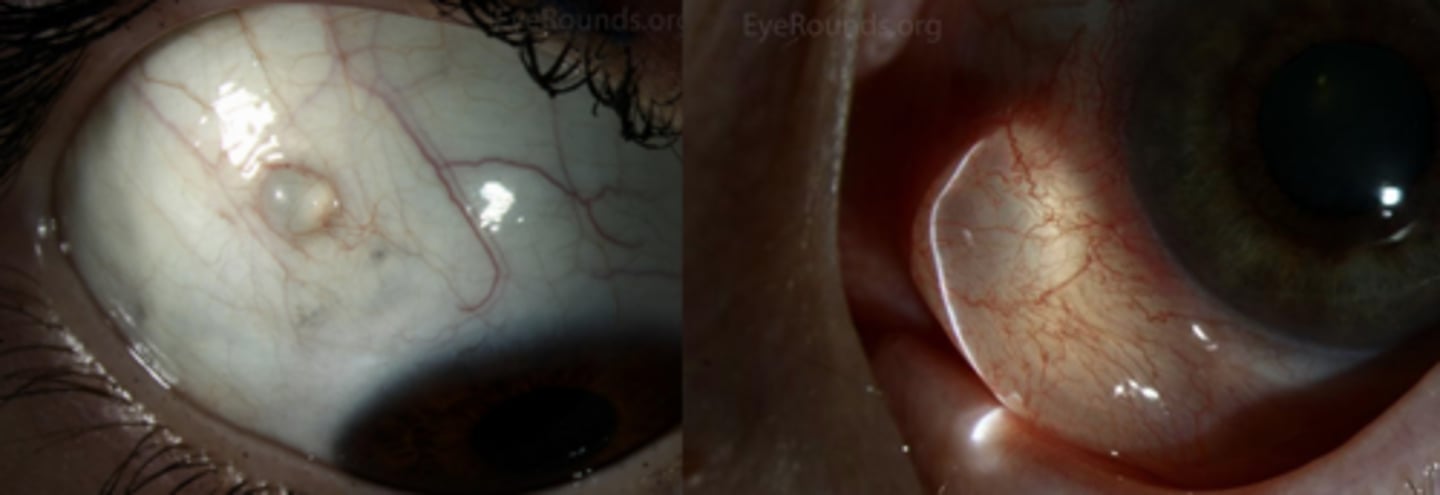
What are some tx options for conj inclusion cysts?
self-resolving as blinking helps fluid move along
excision
alcohol
cryo
CO2 laser
What is a neoplasm/tumor?
non-specific, enlarged, abnormal mass of cells BUT not necessarily cancer!
What is a malignancy?
cancerous lesion w/ potential to spread
What is an adenoma?
benign neoplasm pertaining to gland tissue
What is a papilloma?
benign neoplasm pertaining to epithelial tissue
What is a carcinoma?
malignant neoplasm pertaining to epithelial tissue
What is a hamartoma?
tumor made up of cells that are normal for that area
What is a choristoma?
tumor made up of cells that are NOT normal for that area
What is an ulceration?
loss of epithelial tissue
What is hyperkeratosis?
excess keratin = scaly, waxy appearance
What is an induration?
swelling, redness
What is a macule/plaque?
flat lesion, with plaque being larger than macule
What is a papule/nodule?
circular, well-circumscribed bumps, with a nodule being larger than a papule
What are the ABCDE's of describing skin lesions?
A = asymmetry = benign lesions tend to be more symmetric
B = borders of the lesion = benign lesion tend to have regular borders
C = colour = changes in color, inconsistent color can be concern for malignancy
D = diameter = larger lesions (> 5mm) give concern for malignancy
E = evolution or elevation = how has it changed in color, bleeding, crusting, change in tissue composition, etc.
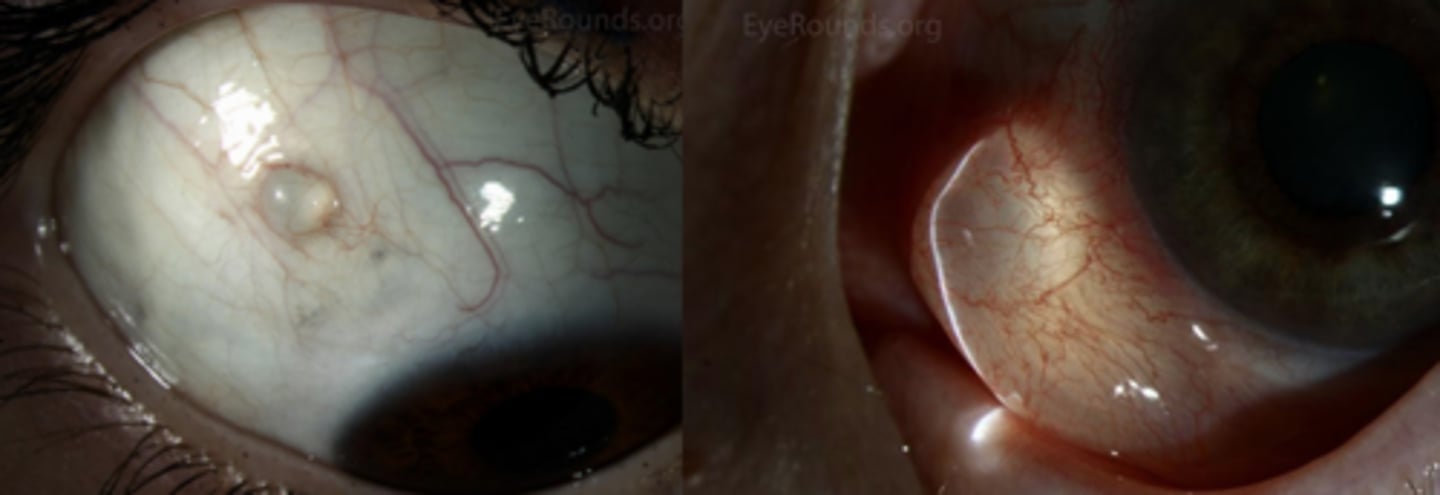
What is the most common epithelial tumor of the eyelid?
squamous papilloma
What is a squamous papilloma?
over-growth of squamous epithelium = often pedunculated (on a stalk, skin tag) or may be sessile (flat)
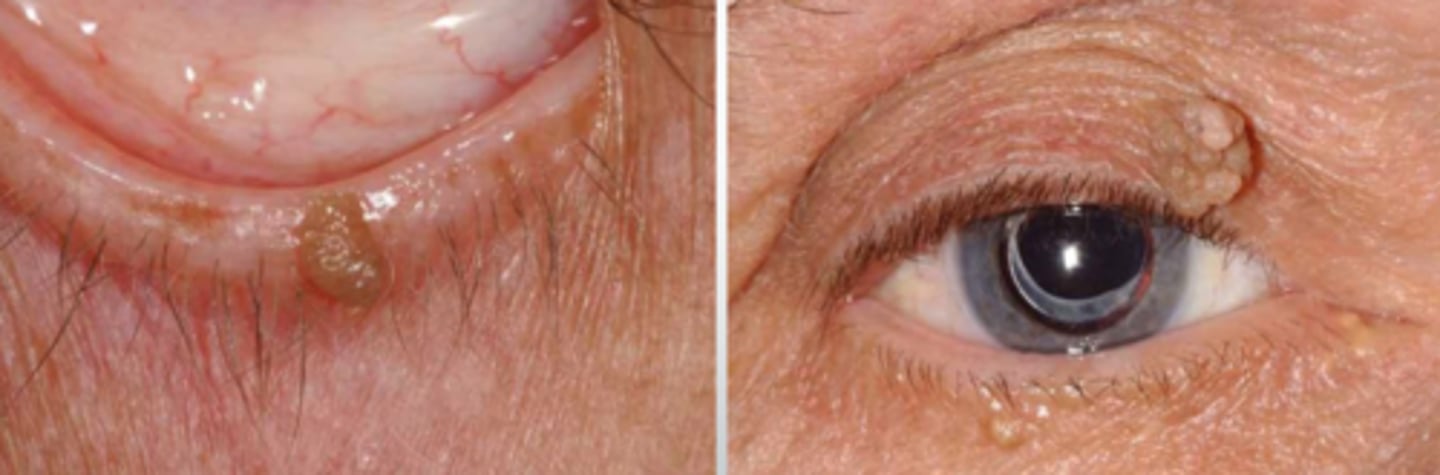
What typically causes a squamous papilloma?
low-risk types of HPV
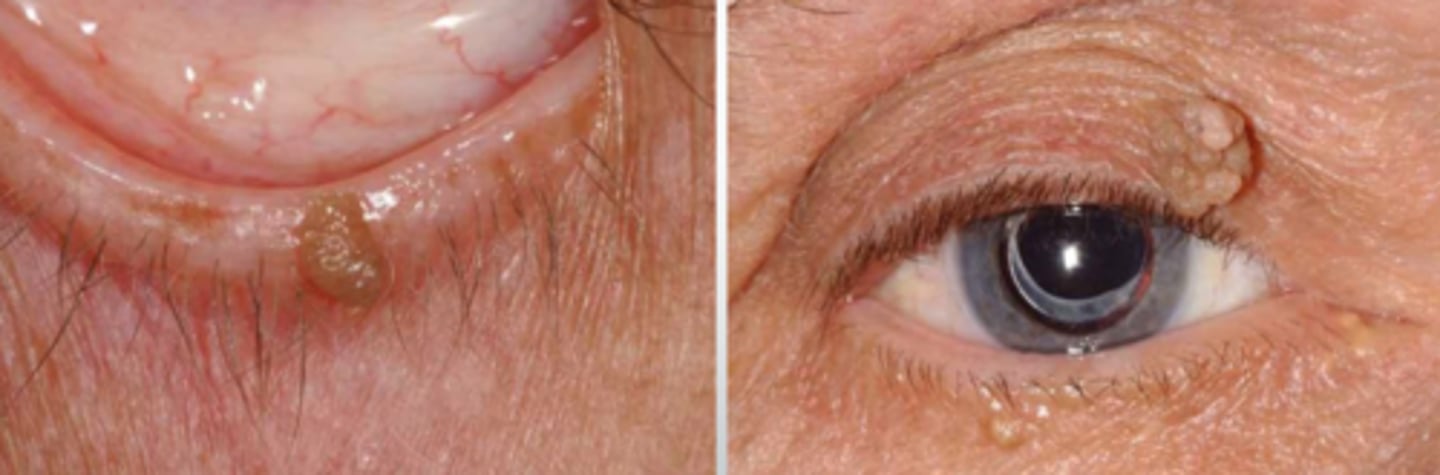
What are some associated risk factors for squamous papilloma?
middle aged-older adults
areas of skin rubbing
increased weight of pt
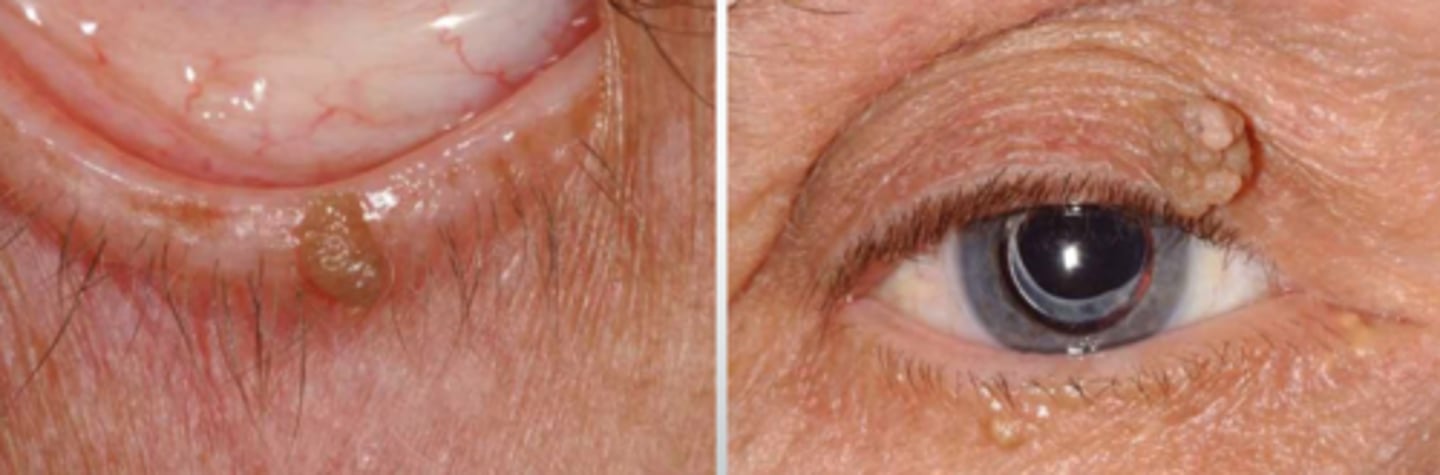
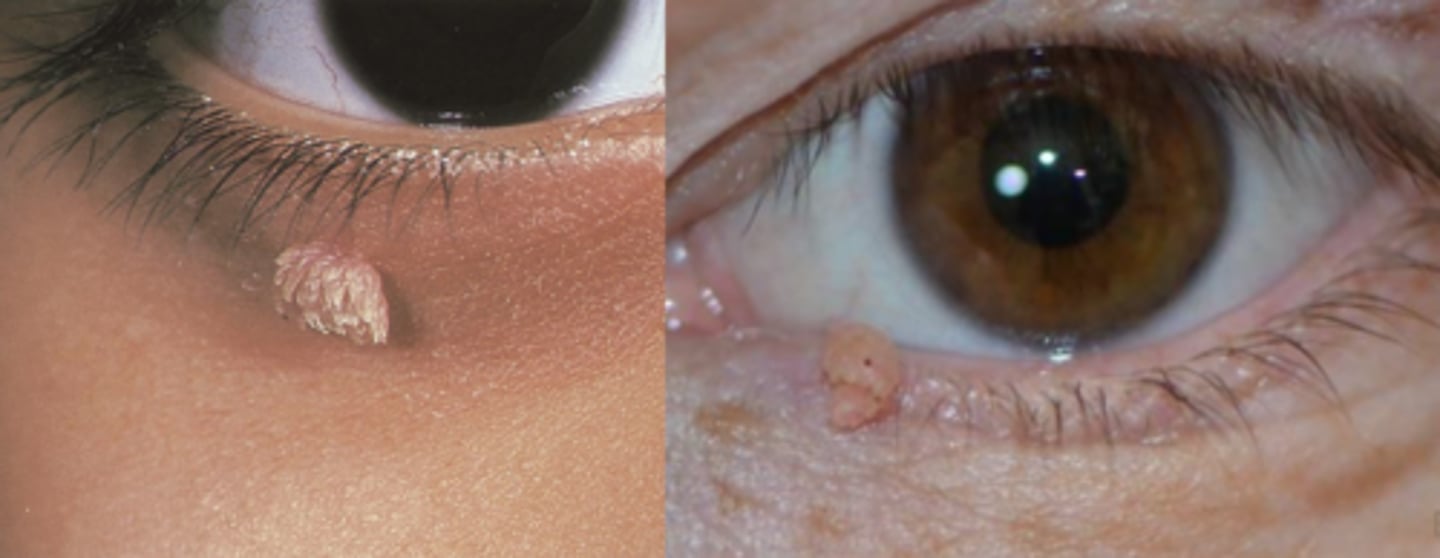
What is verruca vulgaris?
epidermal tissue wart, either plane (flat) or finger-like projections (filiform/digitate) = can increase in pigment and keratinization over time
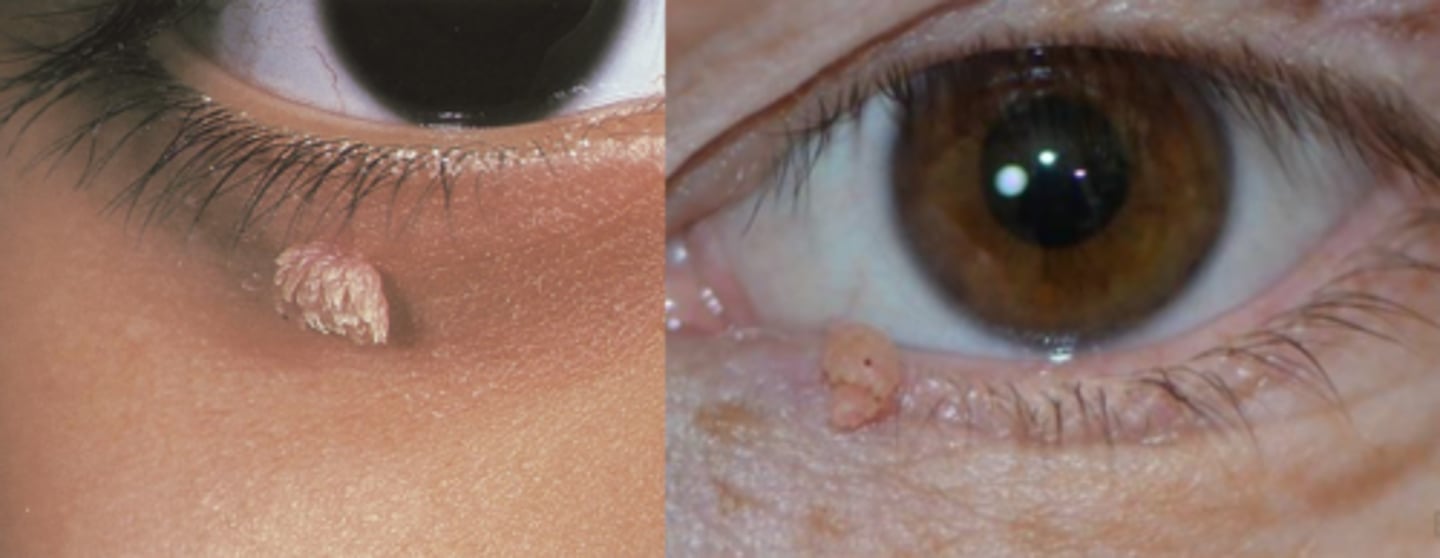
What typically causes a verruca vulgaris?
types VI or XI of HPV
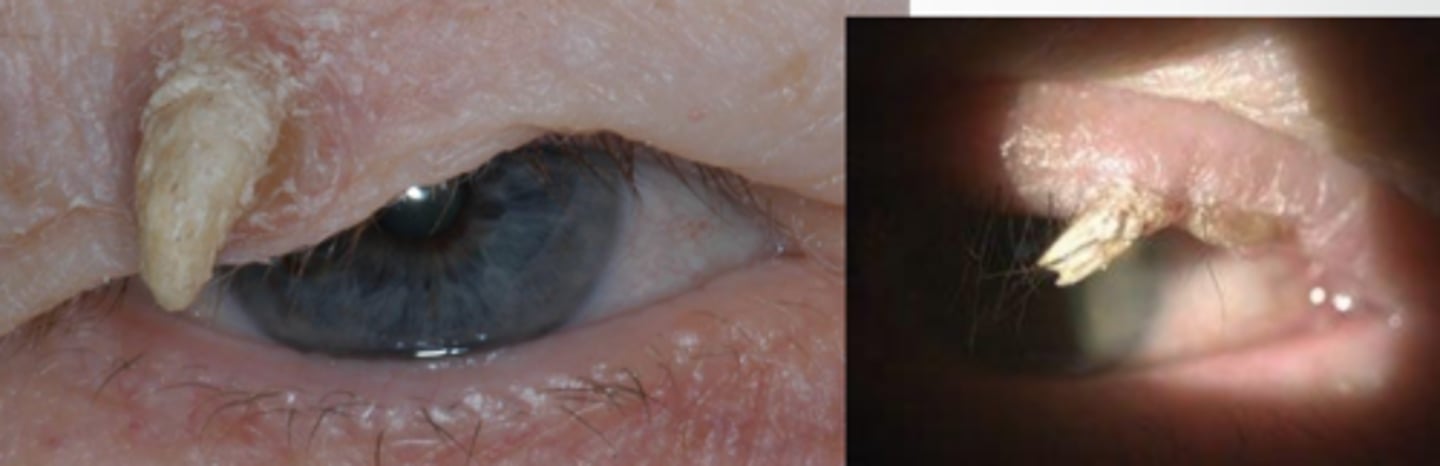
What is a cutaneous horn?
somewhat non-specific descriptor of hyperkeratinized, elongated growth seen in verruca, seborrheic keratosis, basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma
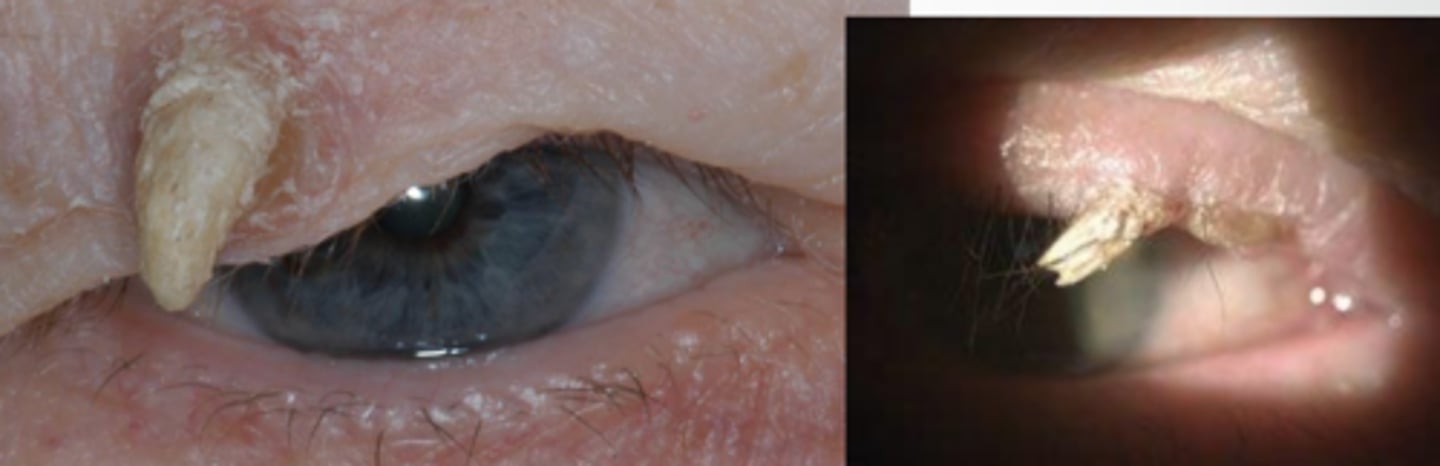
Aside from the usual excision like we use for other non-malignant lesions, what is an additional tx we should do for cutaneous horn?
send off for lab histophathology to determine underlying etiology (possible carcinoma)
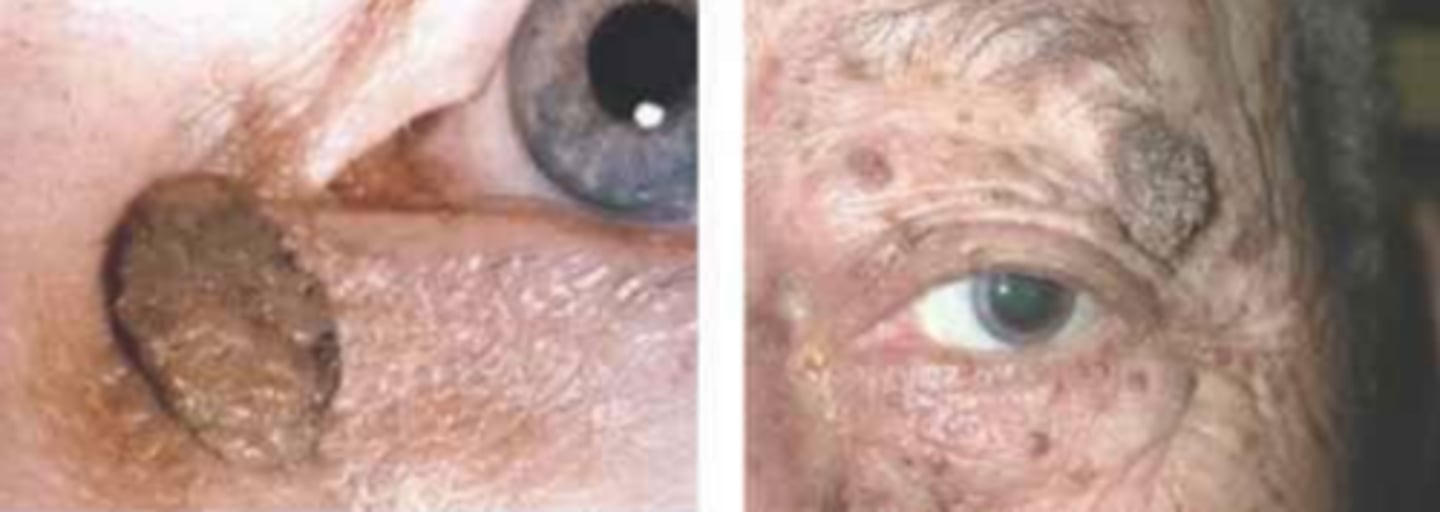
What is serborrheic keratosis?
basal epithelial cell tumor consisting of hyper-keratinized epithelium = well-demaracted, greasy, stuck-on appearance w/ slight elevation
What is dermatosis papulosa nigra?
acanthosis, papillomatosis, hyperkeratosis of epidermis = hyperpigmented, smooth papules 1-5mm size with 1-3mm elevation on cheeks, temples, forehead
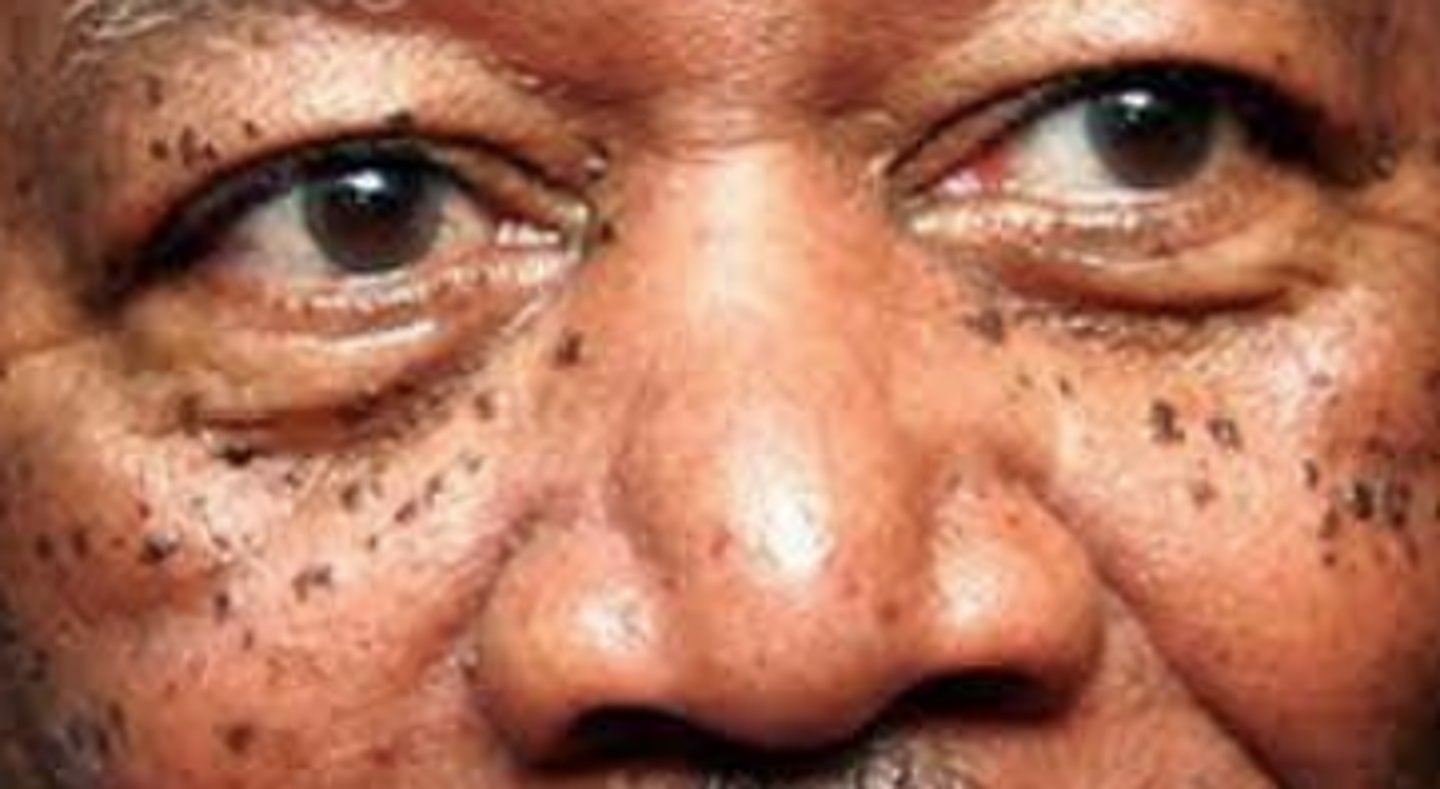
Who is dermatosis papulosa nigra most common in?
African or Asian descent
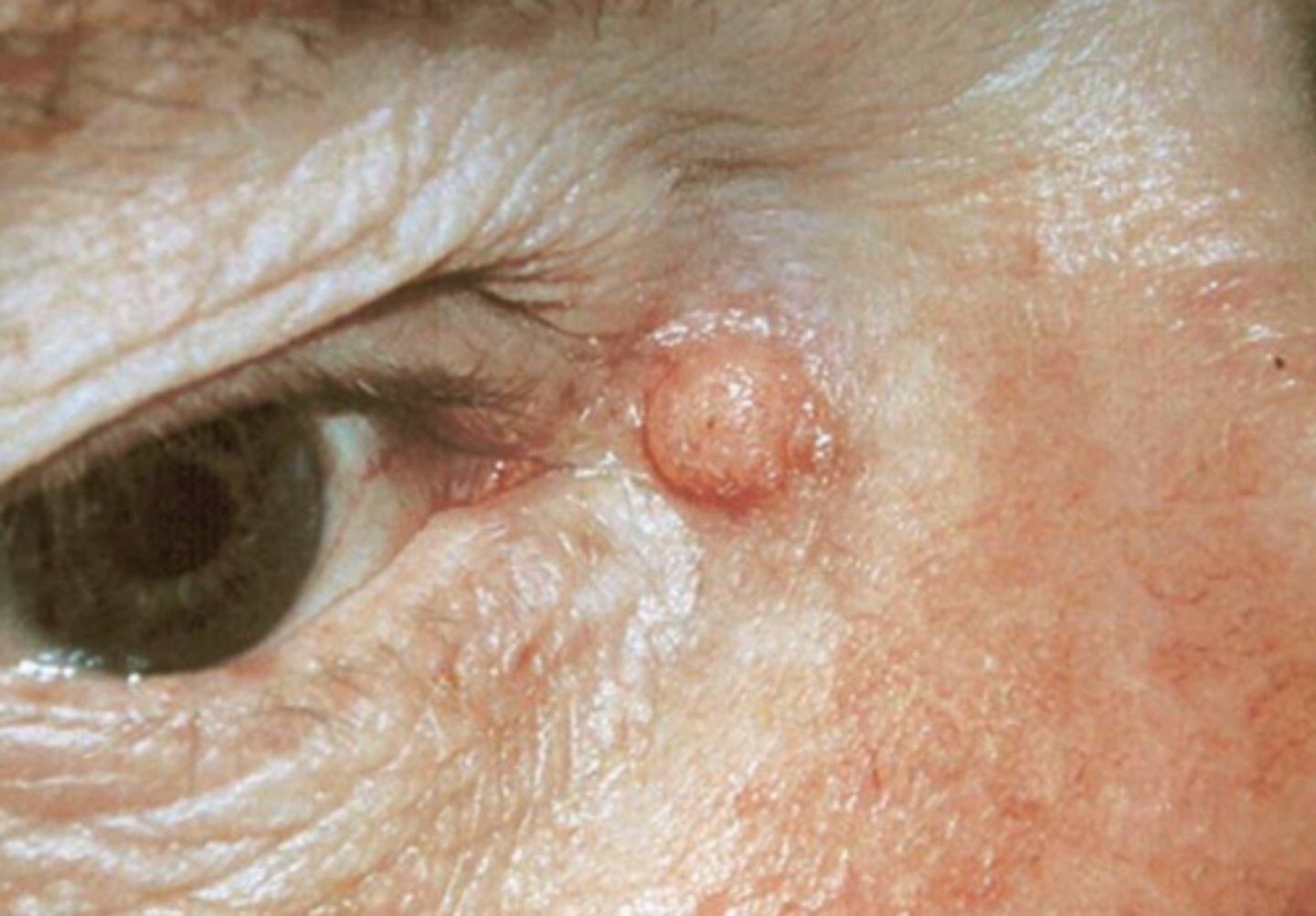
What causes xanthelasma?
macrophages take on excess lipid = foamy histiocytes in reticular dermis filled w/ intracellular fat deposits = dense yellow papules or plaques filled with cholesterol, UL > LL
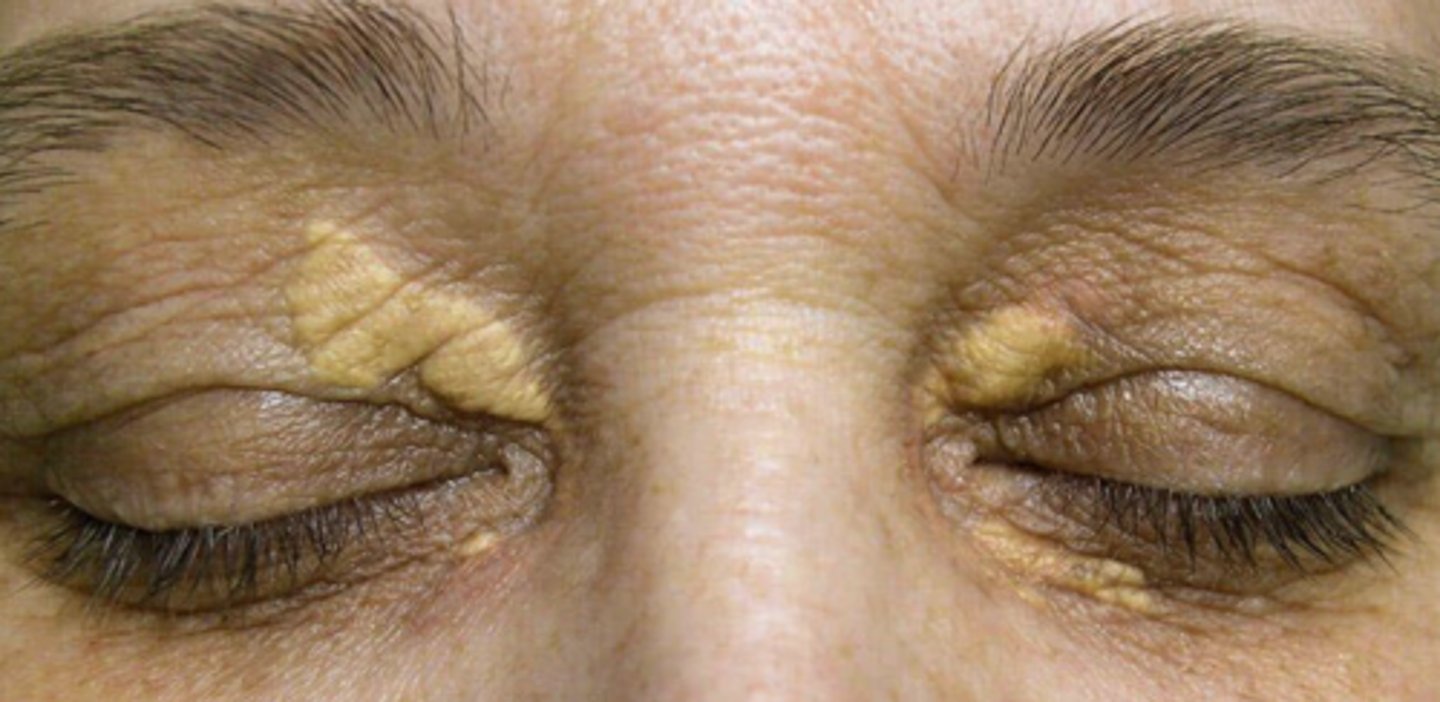
What is the tx for xanthelasma?
> age 50 = no tx needed
< age 50 = refer for hyperlipidemia testing
What is a capillary hemangioma?
elevated bight red (vascular) lesion that will blanch with pressure
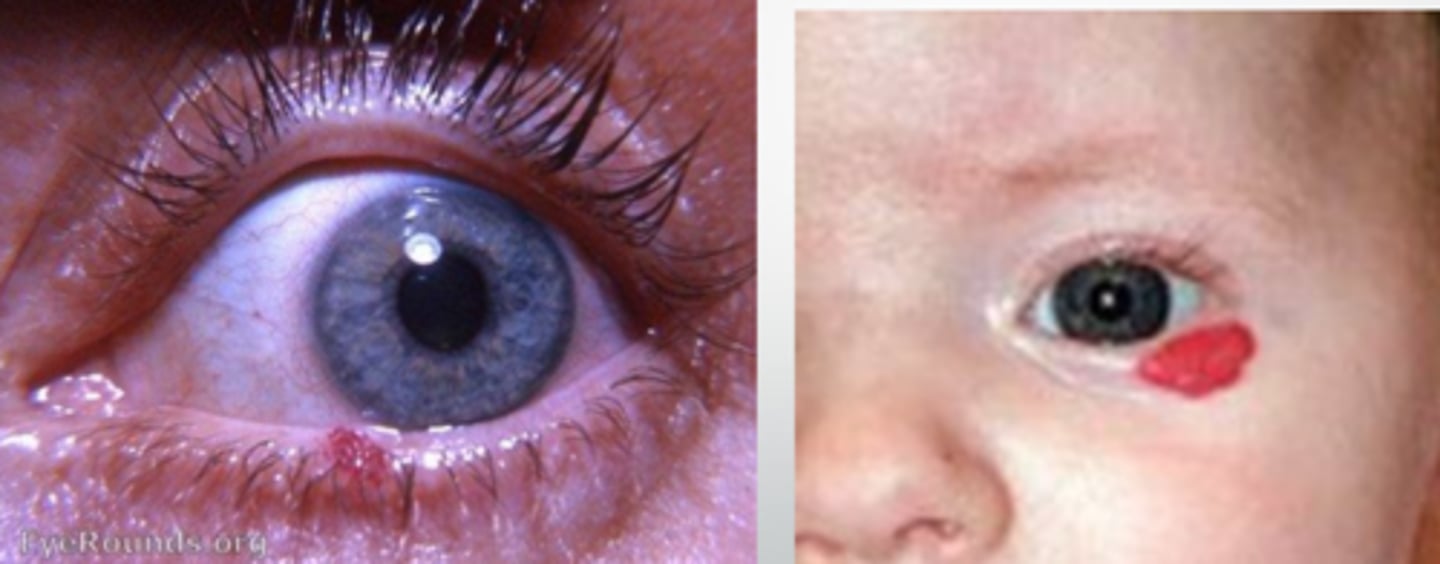
In what populations is capillary hemangioma more common?
infants
females >>> males
What are some tx options for capillary hemangioma?
self-resolving in 70% of pediatric cases
intralesional steroid
surgical excision w/ cautery
propranolol (oral)
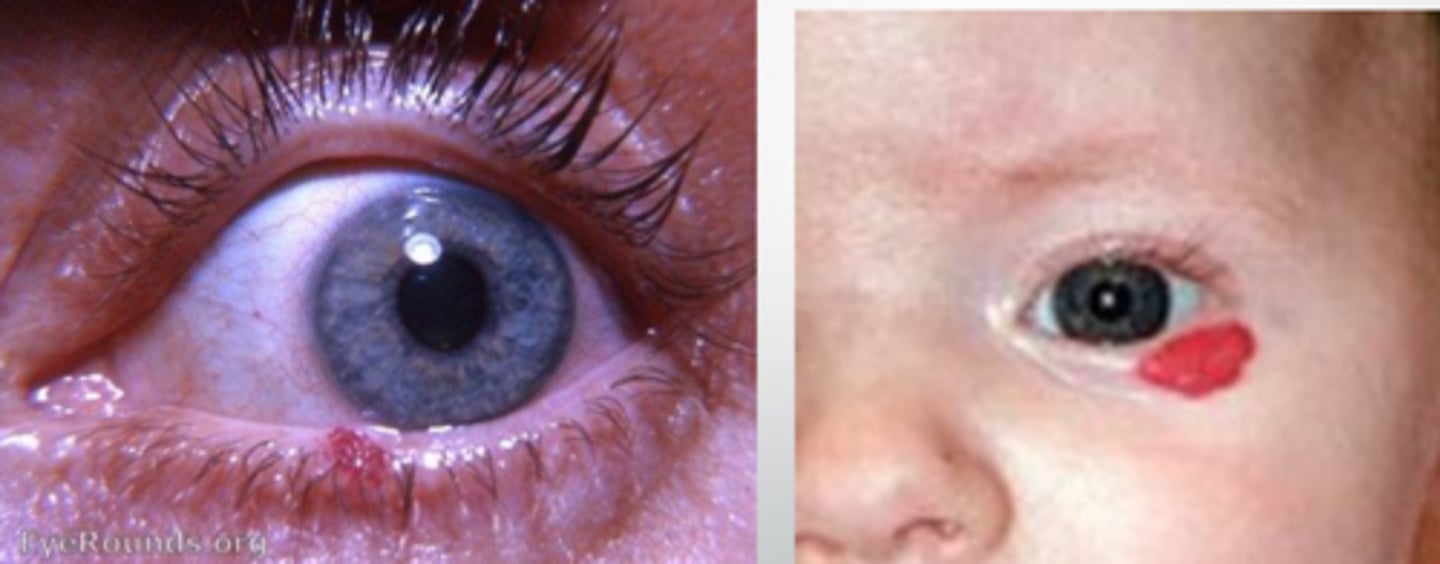
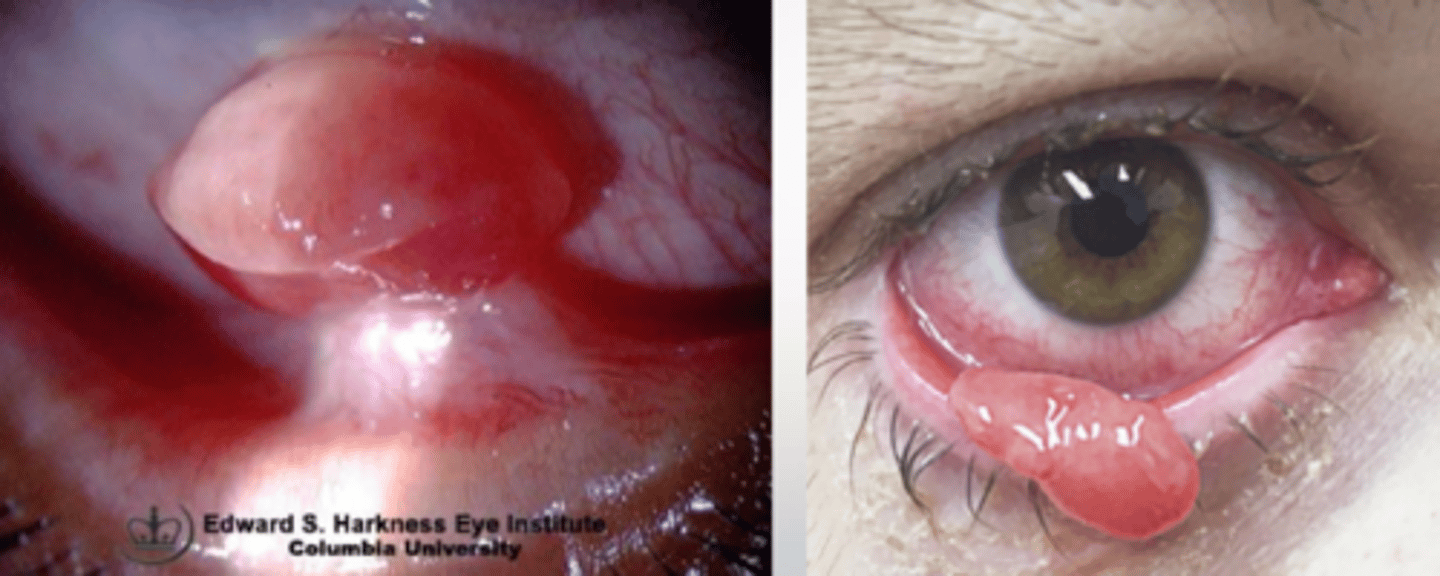
What is the most common vascular lesion of the conj/lids?
pyogenic granuloma
What is a pyogenic granuloma?
angiogenic dysregulation = overgrowth of capillary vascular tissue = bright red, lobulated, elevated vascular lesion of conjunctiva or skin (often pedunculated)
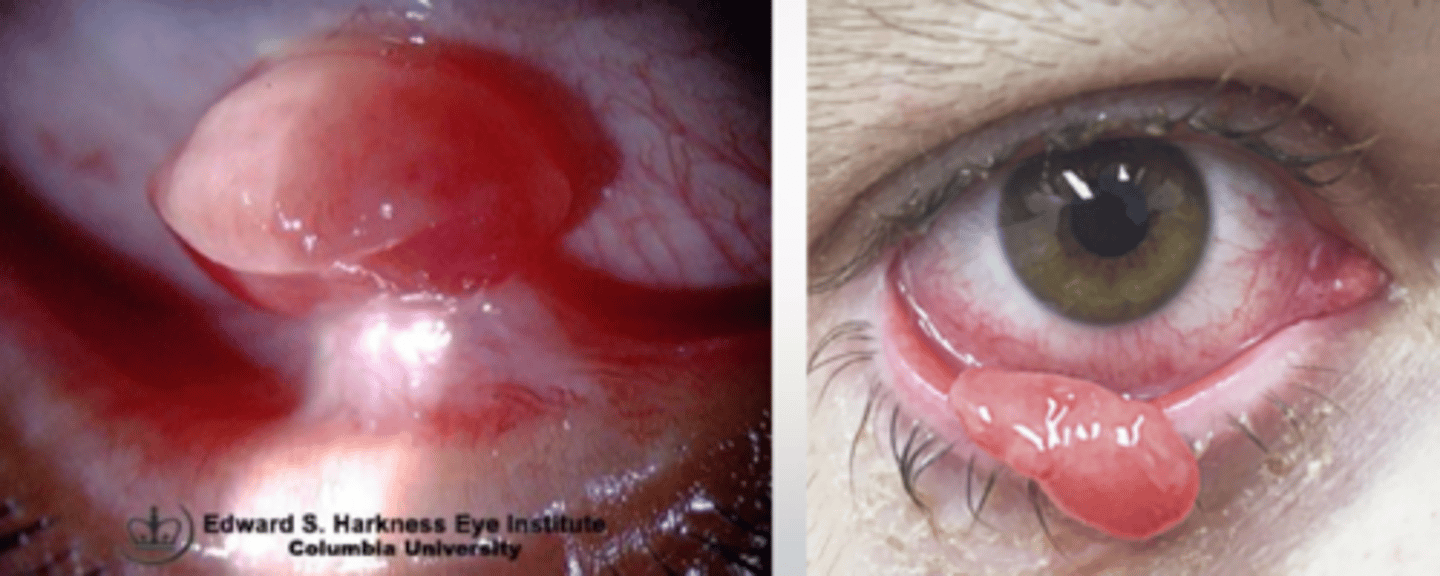
What are some typical causes of pyogenic granuloma?
trauma
post-surgery
chronic irritation
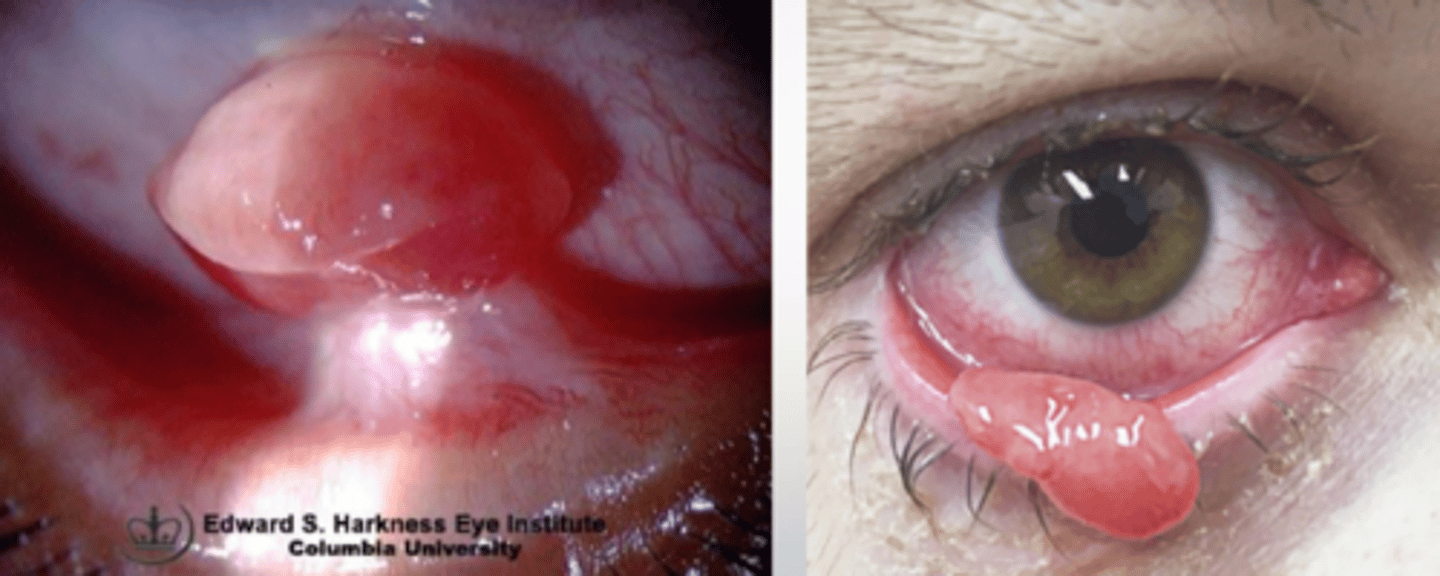
Pyogenic granuloma is a ________________, since the lesions is not pus-producing nore granulomatous.
misnomer
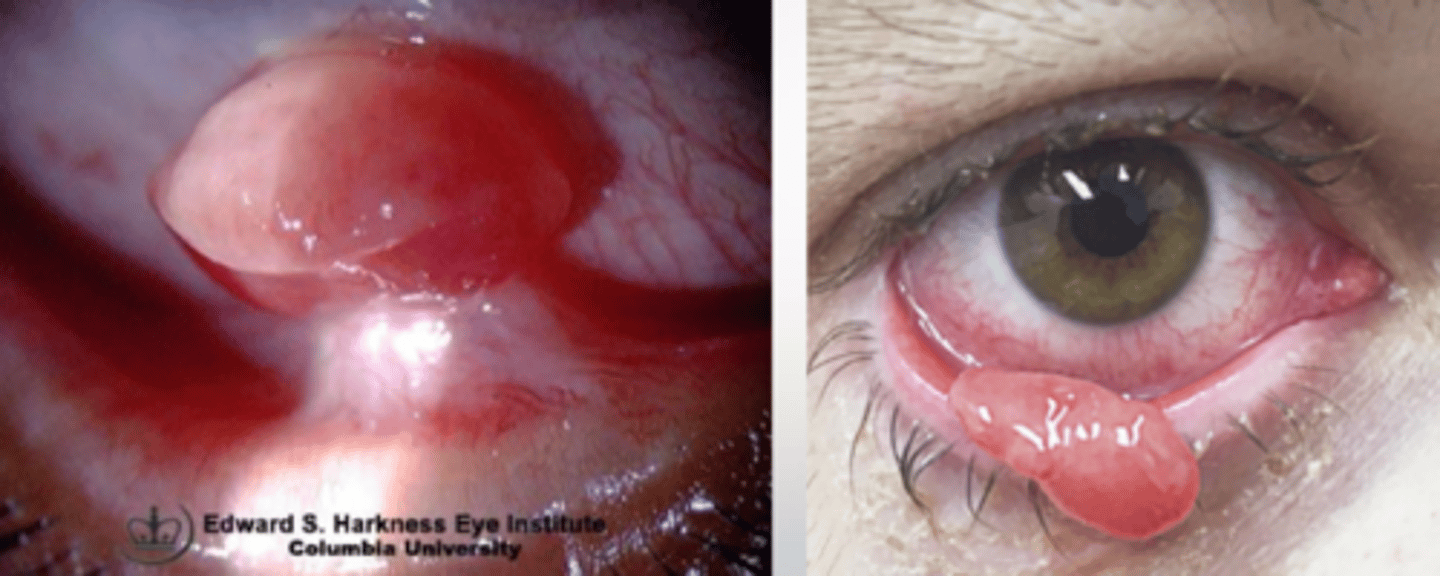
What are some tx options for a pyogenic granuloma?
topical steroid = prednisolone acetate QID x 10-14 days
beta blocker 0.5% topical BID x 3 weeks
excision
steroid injection