Animal Nutrition Exam 1
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
Digestive System
______:
The portal for nutrients to gain access to the circulatory system.
Food stuffs are broken down to very simple molecules → resulting surgars, amino acids, fatty acids etc. are then transported across the GI tract lining into the bloodstream.
Absorption
Digestion → ______
Digestive System
Specific feedstuffs animals can utilize is dependent on the type of _______ they possess.
Monogastrics
3 Classifications of GI Systems
_________
1 stomach
Chickens
Pigs
Turkeys
Dogs
Cats
Ruminants
3 Classifications of GI Systems
______
1 compartamentalized stomach with FOUR compartments
Cattle
Goats
Sheep
Deer
Giraffes
Buffalo
Bison

Hind Gut Fermentors
3 Classifications of GI Systems
______
Horses
Rabbits
Ostrich

Mouth
The starting point that begins the digestive process

Select their food
The beaks of chickens are trimmed so they cannot do what?

Lips
Mouth: ______
Grab food
Select/nitpicking types of foods

Domestic Animals
Selection of Food
Good for wild animals to avoid dangers with limited resources
Bad for _________ as we value their nutrition, these animals have formulated diets and we don’t want them to select.

Selection of Food
Ways to prevent the ________
Kibble/Pellets → make it difficult for animals to sort.
Trim beaks
Add Molasses/something animals like
Total Mixed Ration (TMR)
Chop/make particles smaller
Add water to avoid the selecting out of dustry foods.

Tongue
Mouth: Tongue and Teeth
_______: used for grasping food, mixing, and swallowing.

Teeth
Mouth: Tongue and Teeth
_____: Tear and chew the feed into smaller particles that may be swallowed
Bite
_____ effects how an animal grabs food and eats.
Salivary Glands
Mouth: _________
IMPORTANT FOR DIGESTION
Excrete saliva, which serves many purposes:
Water to mositen food
Mucin to lubricate for swallowing
Bicarbonates to buffer acids
Enzyme amylase to break down carbs
pH
Saliva Buffer Acids
especially important for ruminants.
Stabilize ____
Important because they prevent ulcers (too much acid), damaged teeth, sustain microbes → microbiome needed for digestion (changes in pH kills the microbes)
*Cows cannot digest cellulose (grass) → need microbes
Small
Enzyme Amylase - In Saliva (breaks down carbs)
Chemical digestion in the mouth is not that important because food does not stay in the mouth long enough for enzymes to do anything.
Retention time for food in the mouth is ________
Less than 10% of chemical digestion.
Esophagus
_______- doesn’t do much for digestion
The hollow muscular tube that leads from the mouth to the opening of the stomach.
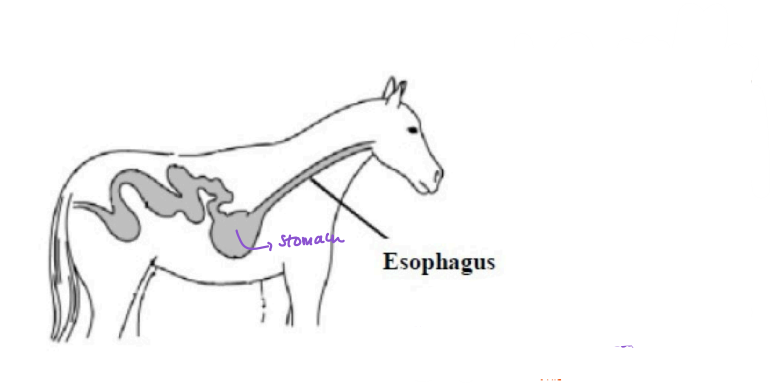
Sphincters
Horses cannot throw up because their _______are too strong → horses had to run on a full stomach, the one’s that stopped to throw up were eaten.
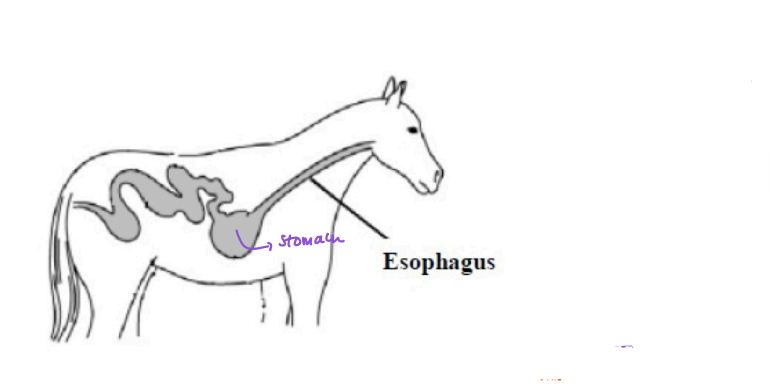
Stomach
______
A hollow tube that contracts and relaxes to integrate digetsive juices with the food causing it to breakdown.
Small Intestine
The place when most digestion occurs ~ stays here longer than in the stomach.
Small Intestine
The next organ in the digestive system that is controlled by a sphincter muscle that helps move food into and through the tract.
Made of 3 Segments
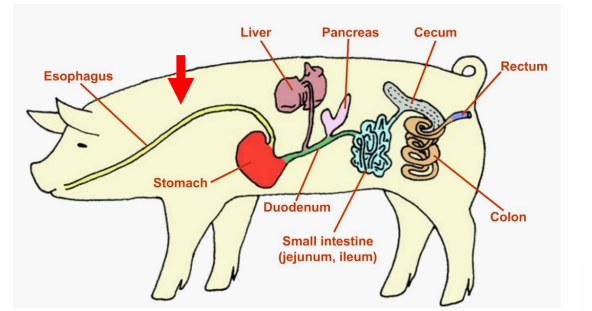
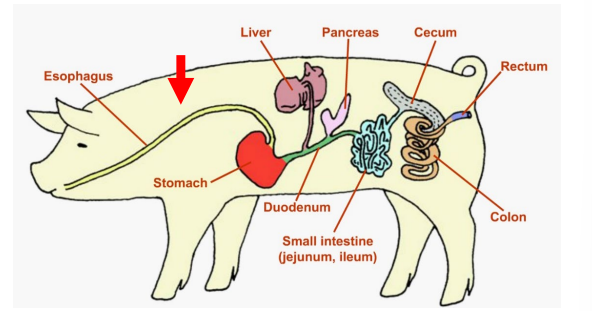
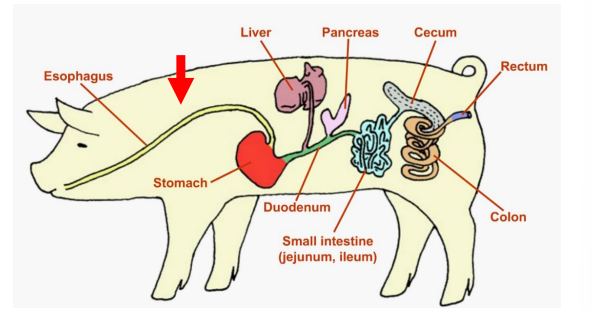
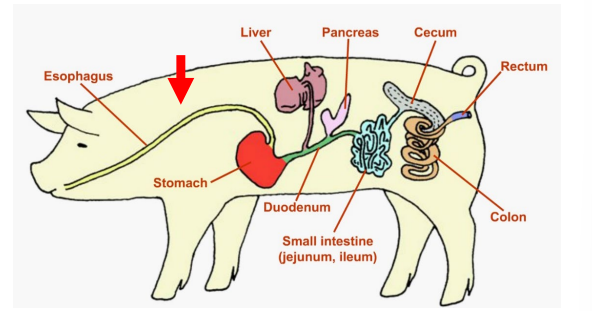
Duodenum
Jejunum
Ileum
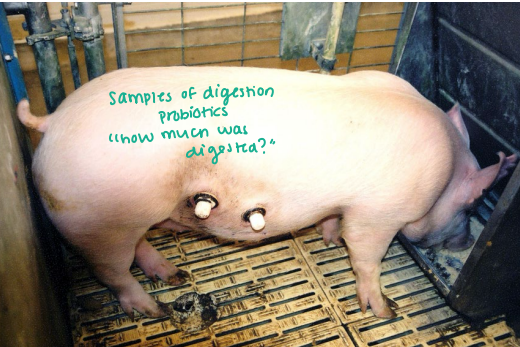
Cannulated Pig
_______
Pig must be in good condition or else the data is invalid
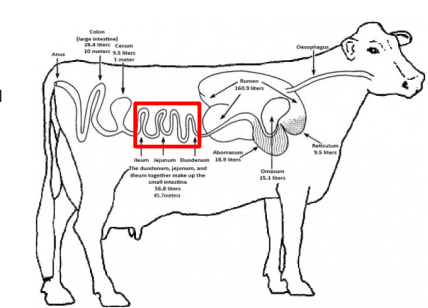
Duodenum
Segments of the Small Intestine
_______
First Segment
Uses secretions from the pancreas and intestinal wall to break down proteins, strarches and fats.
Jejunum and Ileum
Segments of the Small Intestine
___________
Second and third segements
Where ABSORPTION occurs
Absorption is the process which nutrients are passed from the intestine into the bloodstream
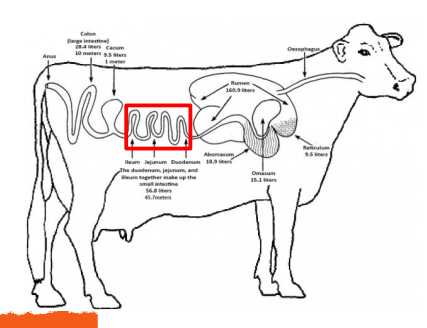
Absorption
_________- the process which nutrients are passed from the intestine into the bloodstream
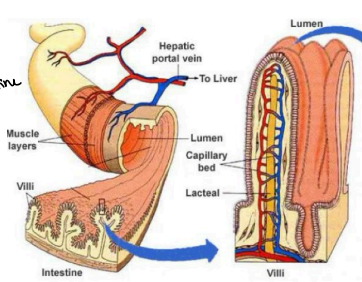
Villi
Walls of Jejunum and Ileum
______: small fingerlike projections that protrude from the epithelial lining of the intestinal wall.
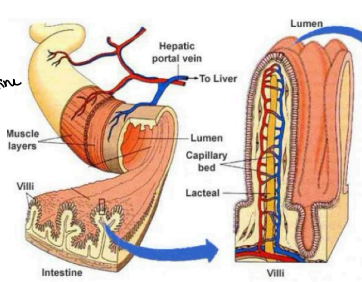
Entherocytes
Walls of Jejunum and Ileum - Villi
_________: specialized cells for absorption in the small intestine
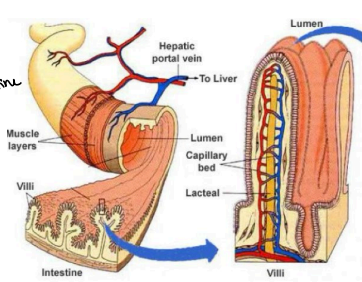
Blood Vessels
Walls of Jejunum and Ileum - Villi
Connected to ______ to allow nutrients to circulate in the blood.
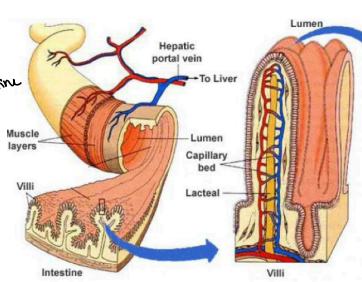
Surface Area
Walls of Jejunum and Ileum - Villi
Increases ______ for absorption
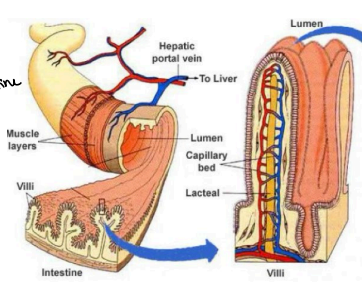
Semi-permeable membrane
Walls of Jejunum and Ileum - Villi
Absorbs nutrients through a _____________, these particles can pass through by a process called DIFFUSION
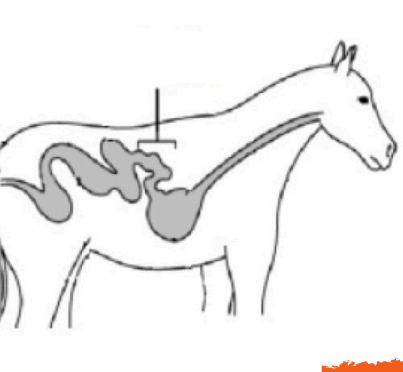
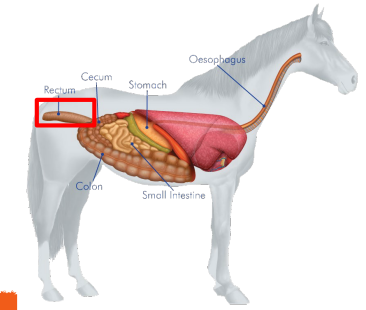
Large Intestine
The last organ of the digestive system, which mostly absorbs WATER and conatins two segments
Cecum
Colon
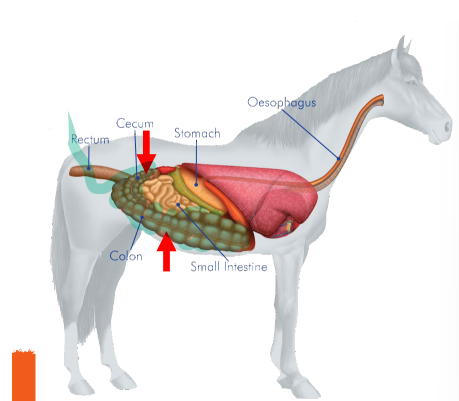
Cecum
Segments of the Large Intestine (absorbs water)
_______
Fibrous food such as hay and grass is broken down into usable nutrients
Comparable to the appendix in humans
Large in horses - hind gut fermentors
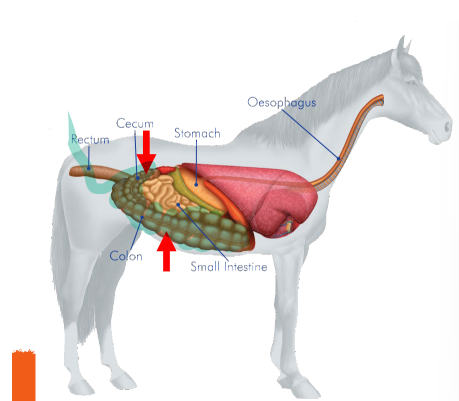
Colon
Segments of the Large Intestine (absorbs water)
_______
Provides a storage space for waste from the digestive process and is the largest part of the large intestine
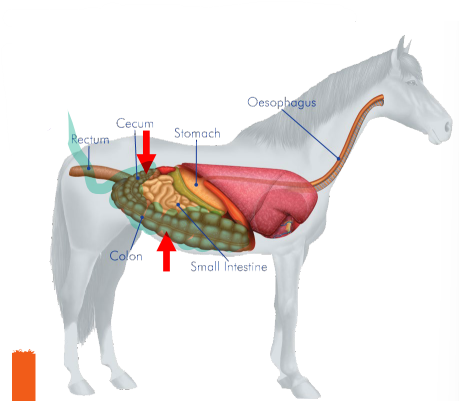
Rectum
Large Intestine - _____
The terminal end of the large inestine and the entire digestive tract.
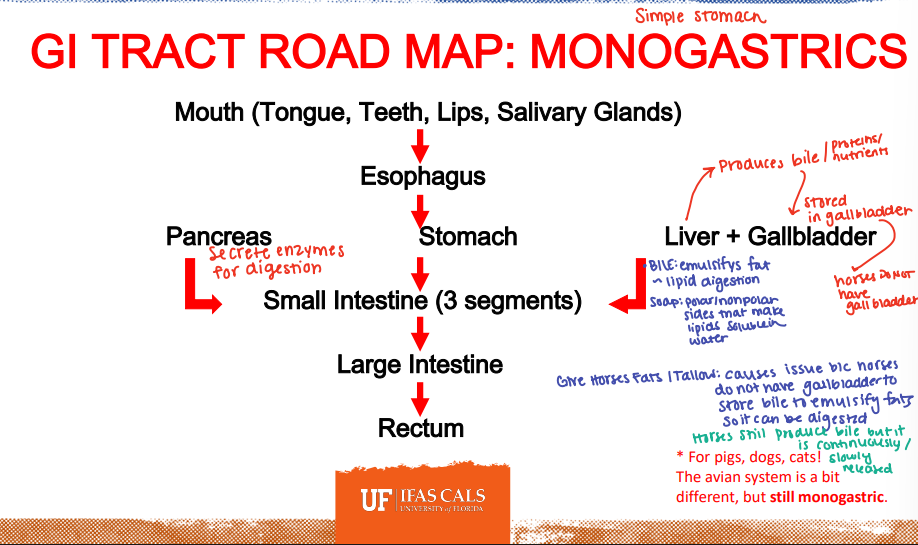
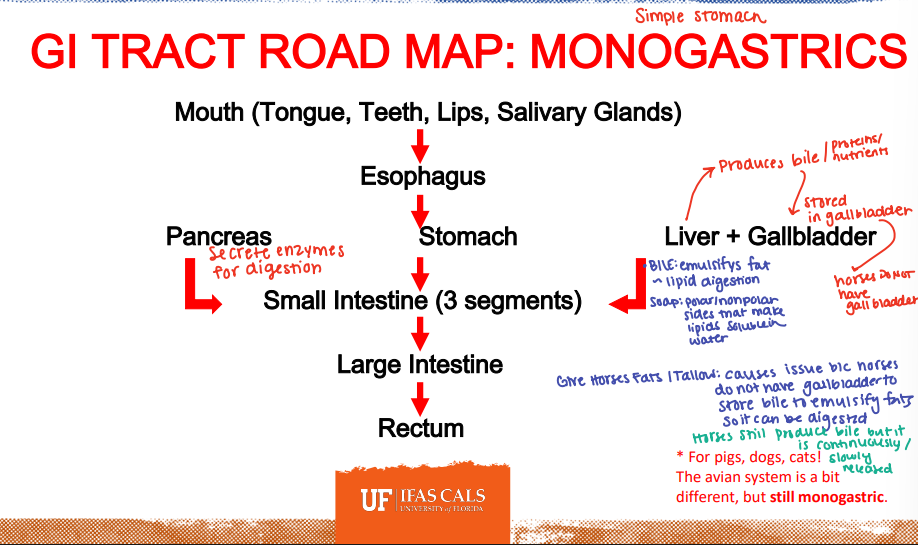
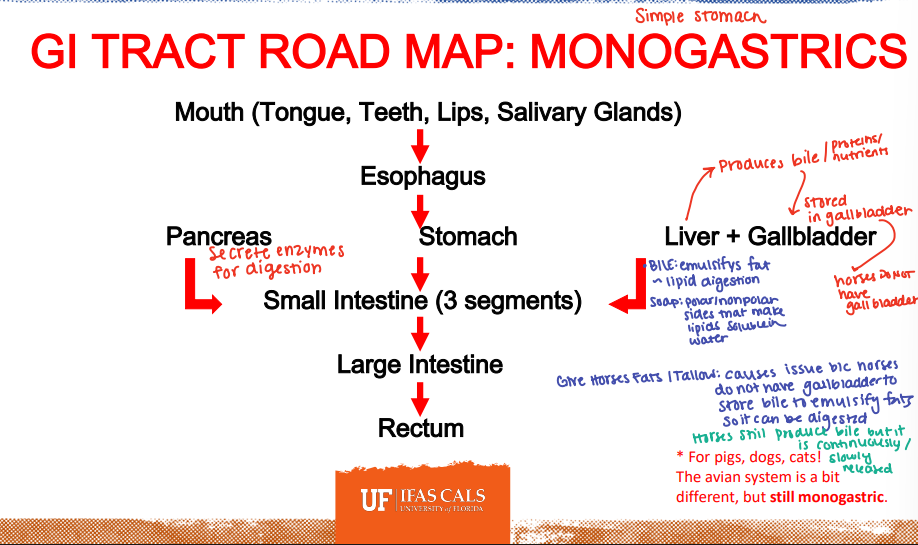
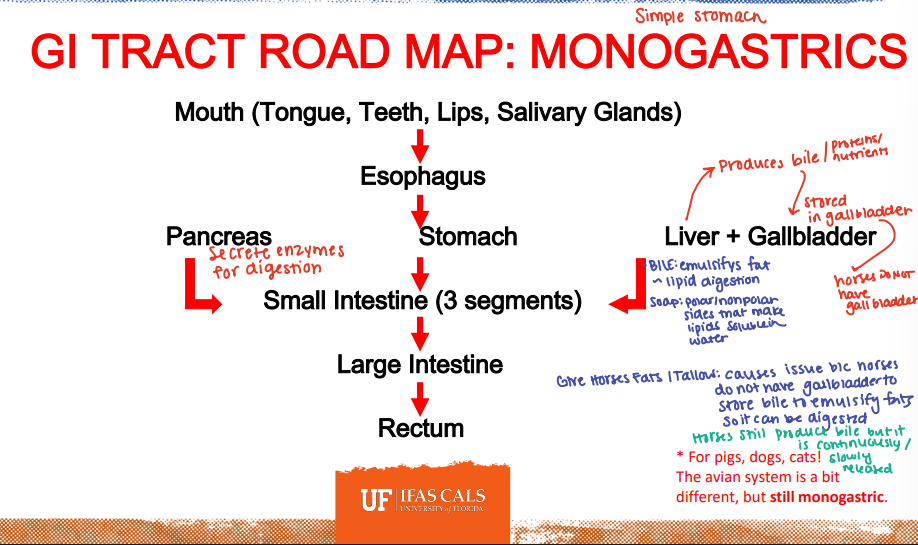
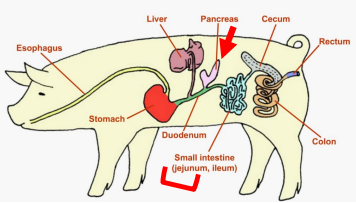
GI Road Map: Monogastrics
Pancreas
GI Road Map: Monogastrics
________: Secretes enzymes for digestion
Liver
GI Road Map: Monogastrics
_______: Produces bile (proteins/nutrients) → that bile is stored in the gall bladder.
*Horses do not have a gall bladder
Bile
GI Road Map: Monogastrics
_______: emulsifies fat/lipid digestion
Fats/Tallow
You should not give horses _______:
Causes issues because horses DO NOT have a gallbladder to store bile to emulsify large quantities of fats so it can be digested.
*Horses still produce bile but it is continously/slowly released.
Simple
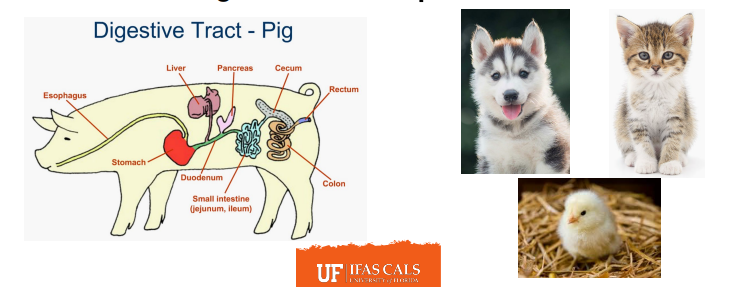
Monogastrics: Pigs, Dogs, Cats
Monogastric = 1 “_____” stomach
Digestion
_______: the chemical/physical/mechanical breakdown of macronutrients into micronutrients
Mouth/Teeth
Monogastrics: Pigs, Dogs, Cats
Mechanical digestion begins in the _______ unless the animal eats really fast
Chewing
Monogastrics: Pigs, Dogs, Cats
MOUTH
Mechanical breakdown of foodstuffs by _____ (reduces particle size, increases surface area for enzyme action)
Amylase
Monogastrics: Pigs, Dogs, Cats
MOUTH
Saliva added as a lubricant and, in some species, contains _____ to begin starch digestion
Amino Acids
Proteins → Peptides → _________ (what is actually digested)
Esophagus
Monogastrics: Pigs, Dogs, Cats
______
Tube connecting the mouth to the stomach
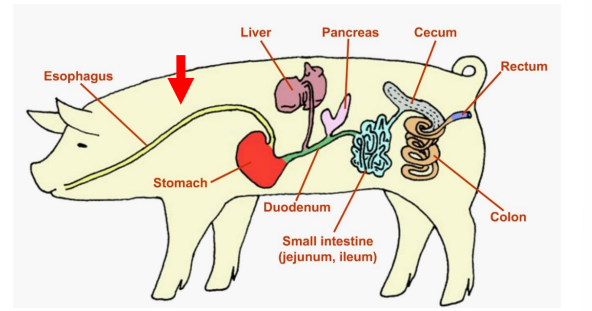
Stomach
Monogastrics: Pigs, Dogs, Cats
______
Produces acid and enzymes
Enzymatic digestion of protein begins
Food stuffs reduced to liquid form
Protases
In the stomach of a monogastric, what are the enzymes for digestion called?
Small Intestine
In monogastrics, most chemical digestion occurs in the ______
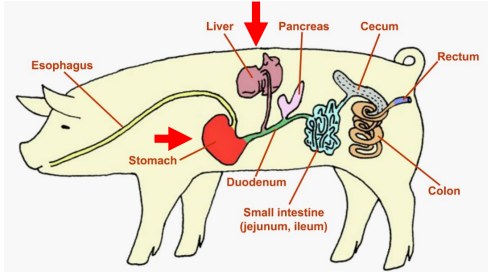
Liver
Monogastrics: Pigs, Dogs, Cats
________
Center of metabolic actvity in the body
Major role: provide bile salts to the small intestine for fat digestion and absorption
Gall Bladder
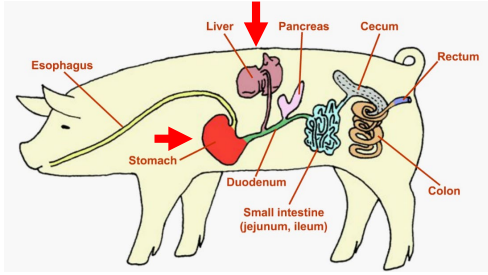
Monogastrics: Pigs, Dogs, Cats
______
Small pouch under the liver
Stores Bile
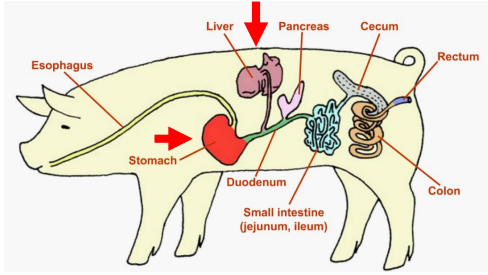
Pancreas
Monogastrics: Pigs, Dogs, Cats
______
Provides a mixture of digestive enzymes to the small intestine to help in digestion of fats, carbohydrates, and proteins.
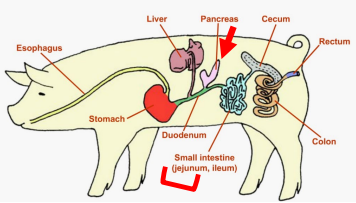
Small Intestine
Monogastrics: Pigs, Dogs, Cats
_______ (Place of chemical digestion and absorption)
3 Segments → Duodenum, Jejunum, Ileum.
Site of final stages of chemical enzymatic digestion
Where almost all nutrients are absorbed
Beak (Mouth)
Monogastrics: Avian
_____
Used for grabbing food and important to feed something ground up.
No lips, no teeth, no chewing.
Esophagus
Monogastrics: Avian
______: tube connecting the mouth to the crop.
Crop
Monogastrics: Avian
_____: pouch where food is SOAKED, softened, and stored (very little digestion)
Outer-pocketing of the esophagus
Proventriculus
Monogastric: Avian
________
True stomach for birds
First significant amount of digestive juices added like HCl
Physical breakdown of food hasn’t begun yet
Gizzard
Monogastrics: Avian
_______ (GRIND)
Muscular organ used to grind and break up food
Stones or grit found here to help with the break up process
Act like teeth for oher monogastrics

Small Intestine
Ceca
Large Intestine
Monogastrics: Avian
____
____
____
all have the same function
Cloaca
Monogastrics: Avian
______
Digestive and renal (urinary) system waste exits here
Urine and feces are excreted together
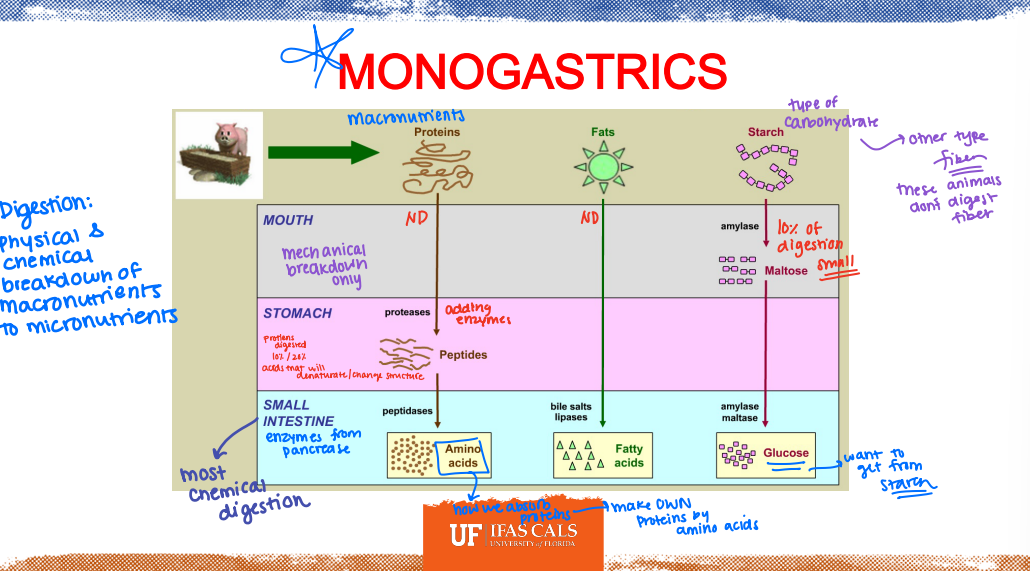
Review
Review
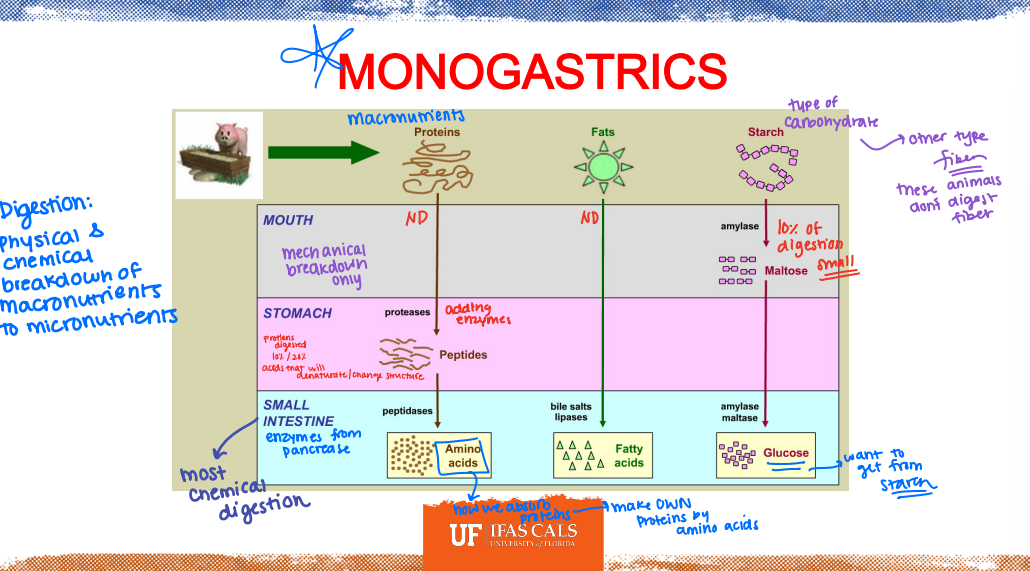
Review
Review
Complex
Ruminants = A “____” stomach
Ruminants
Examples of ______
Cattle
Sheep
Buffalo
Deer
Giraffe
Antelope
Goat
Moose
Elk
Llamas
Alpacas
Bison
Cud
Characteristics of Ruminants
Chewing ___
Dental Pad
Characteristics of Ruminants
No upper front teeth
Instead, they have a ______ that works with the lower front teeth (incisors) in tearing off feedstuff
*Tongue grab and lascerate food with dental pad

Enzymes
Characteristics of Ruminants
Saliva does not contain ____
But they produce it in large quantities
Bicarbonates
Although ruminant saliva does not contain enzymes it does contain ______ which is important to all animals as it helps control pH in the stomach and keep the microbe population alive in the stomach.
Ruminate
The Bicarbonates in saliva are extra important for ruminates because they _____ (come back up → redcues particle size and produces more saliva) more of this means more saliva → important to keep bacteria in stomach alive
Monogastrics
Ruminants
*Mouth, esophagus, liver, panceras, gall bladder, small intestine, and large intestine have functions similar to _____
Ruminants
____ eat as much as they can → sit and ruminate for hours → prey animals need to eat as much as they can while they have food source: hide and have time to ruminate.
Stomach
Ruminants
_________
Structure and function is the main difference between ruminants and monogastrics
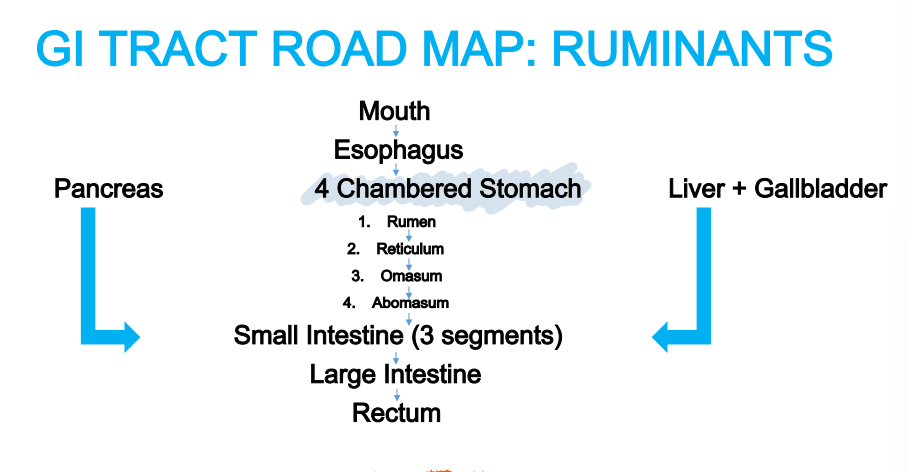
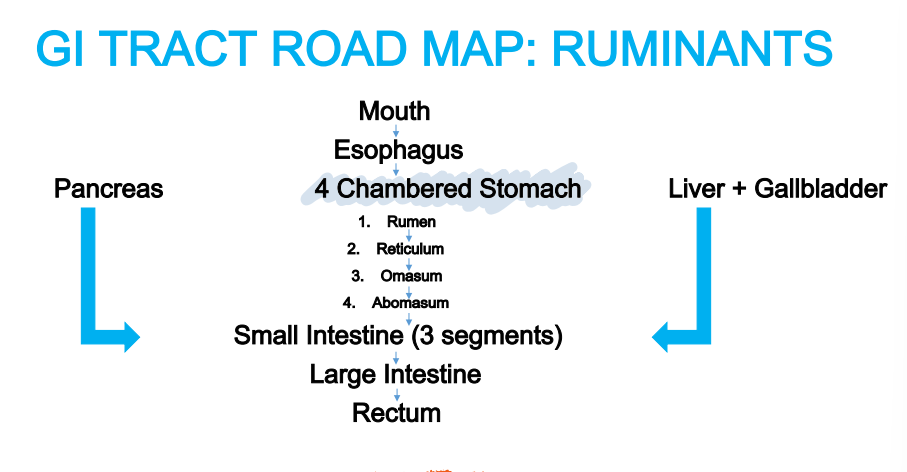
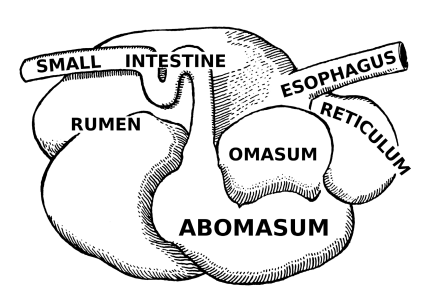
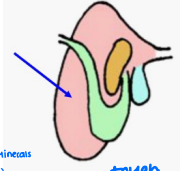
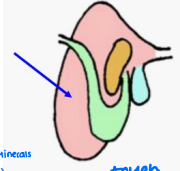
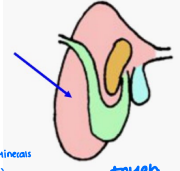
Multi-compartmented: rumen, reticulum, omasum, abomasum → microbes in rumen can tolerate large variations in pH
Rumen
Four Compartments of the Stomach - Ruminants
______: Paunch
Reticulum
Four Compartments of the Stomach - Ruminants
_____: Honeycomb
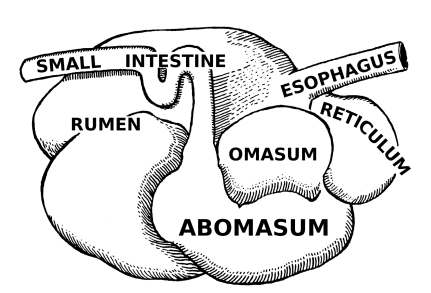
Omasum
Four Compartments of the Stomach - Ruminants
______: Book pages or the “Butcher’s Bible”
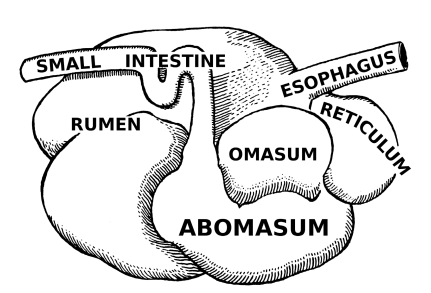
Abomasum
Four Compartments of the Stomach - Ruminants
________: True or glandular
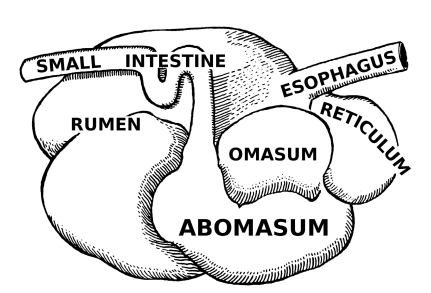
Cud Chewers
Ruminants are often called “________”
Rumen
Ruminants
______
Large anaerobic fermentation vat
Food is soaked, mixed, and fermented by bacteria
Contains finger-like projections called papillae that absorb nutrients through the wall into the bloodstream to provide energy
“Shag carpet” appearance
Saturated with gases and in constant motion
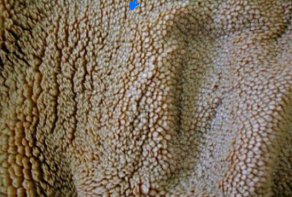
Rumen
____ absorbs
Water
Ammonia
Some Vitamins and Minerals
Some Acids
Volatile Fatty Acids
Contractions
Ruminants
Rumen
______ occur at a rate of 43 per minute
Purpose: mix contents, aid in eructations of gases, move fluid and fermented feedstuffs into the omasum
Microorganisms
Ruminants
Rumen
Houses ________ → highly concentrated: grow bacteria and digest them in the small intestine
Protozoa - 100,000 per gram of rumen fluid
Bacteria + Fungi - 100 million per gram of rumen fluid
Fats
____ = High Energy
Volatile Fatty Acids
Microbial Protein
Vitamin B + K Complexes
VFA’s are also absorbed and produced in the rumen
Ruminants
Rumen
Microorganisms digest roughages to make
_________
_________
_________
____ are also absrobed in the rumen
Volatile Fatty Acids (VFA’s)
In the Rumen of ruminants, microbes ferment carbohydrates, _____ are produced as a by-product.
Where they are Absorbed in the rumen and travel to the liver where ATP is produced.
Microbial protein
The ruminant protein supply comes from _______
Cellulose
Ruminants
Advantages of Microbial Digestion
______ digestion via microbial fermentation
This is a fiberous carbohydrate - many glucose together
Humans cannot digest cellulose
This is how horses digest it in the large intestine
Vitamin B
Ruminants
Advantages of Microbial Digestion
Microbial synthesis of _____
Abomasum
Ruminants
Advantages of Microbial Digestion
Microbial protein formation in the rumen (digested in the _____)
Non-Protein Nitrogen
Ruminants
Advantages of Microbial Digestion
Ability to use ______ (NPN) → urea: commonly used as fertilizer and to make amino acids
Compound that is not a protein but contains nitrogen
Energy Fermentation
Ruminants
Disadvantages of Microbial Digestion
_______ lost (heat loss = 5-6% gross energy)
Gas
Ruminants
Disadvantages of Microbial Digestion
____ production (methane production = 6-8% of gross energy)
*Burping
modification
Ruminants
Disadvantages of Microbial Digestion
Microbial ____of dietary nutrients
Cheap Proteins
Ruminiants Microbial Modifcation of Nutrients
Good for when you are feeding _____: as the microbes modify and make their own proteins necessary for the body
Good formulated diet
Ruminants Microbial Modifcation of Nutrients
Not good when you are feeding a _________ → microbes get first dibs
May want to use a slow release feed: coat/protect the nutriens in fats, so it can be digested in the small intestine but not the rumen so microbes cannot access it
Glucose
Ruminants
Disadvantages of Microbial Digestion
____ shortage
Low Blood Sugar → Cellulose is low on the glucose index and a low digesting carb meaning it does not reach the blood stream vey fast.
Ruminants don’t get sugar highs
Glucosenogenesis
Becuase microbial digestion leads to a glucose shortage in ruminants, and ruminants need glucose to make milk ruminants carry out ________, which is the making of glucose out of something that is not a carbohydrate (ex: protein)
CO2
Ruminants
End Products of Ruminal Fermentation
(80%) ____ - Green house gas and energy loss for the animal (belching → burping)
*Most common
CH4
Ruminants
End Products of Ruminal Fermentation
(20%) ____- Green house gas and energy loss for the animal (belching → burping)
Volatile Fatty Acids
Ruminants
End Products of Ruminal Fermentation
_____ - drives the pH down, therefore saliva (buffer → bicarbonates) is more important than in non-ruminants. - Acids that drive pH down, mild acids → we produce HCl in stomach ~ much stronger