Gastrointestinal Pathology and Physical Therapy Implications
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
What are common signs and symptoms of GI disease?
Nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, anorexia-cachexia, constipation, dysphagia, heartburn/indigestion, abdominal pain (mechanical, inflammatory, referred), and GI bleeding.
What are some rehabilitation considerations for patients with GI disease?
Constipation due to inactivity or opioid medications, impaired bowel function with neurological conditions, nausea and vomiting in chemotherapy patients, and the potential for GI symptoms to affect participation in physical therapy.
What is dysphagia and what can cause it?
Dysphagia is difficulty swallowing, which can be caused by neurologic conditions, trauma, mechanical obstruction (intrinsic or extrinsic), or as a side effect of medication.
What are the PT implications for patients with dysphagia?
Aspiration precautions and referral to a speech-language pathologist (SLP) as needed.
What are the risks associated with fluid and electrolyte imbalance in GI disease?
Increased risk for postural hypotension and other signs of imbalances.
What role does exercise play in the management of GI disease?
Exercise can increase motility of the GI tract and assist with postural interventions for swallowing difficulties.
What types of referred pain are associated with GI conditions?
T/L pain may indicate an acute ulcer, while left shoulder pain can be associated with stomach ulcers or diverticular disease.
What age-related changes can affect the GI system?
Increased risk of tooth decay, decreased taste buds, altered sense of smell, difficulty chewing/swallowing, slower absorption of nutrients, and changes to the gut microbiome.
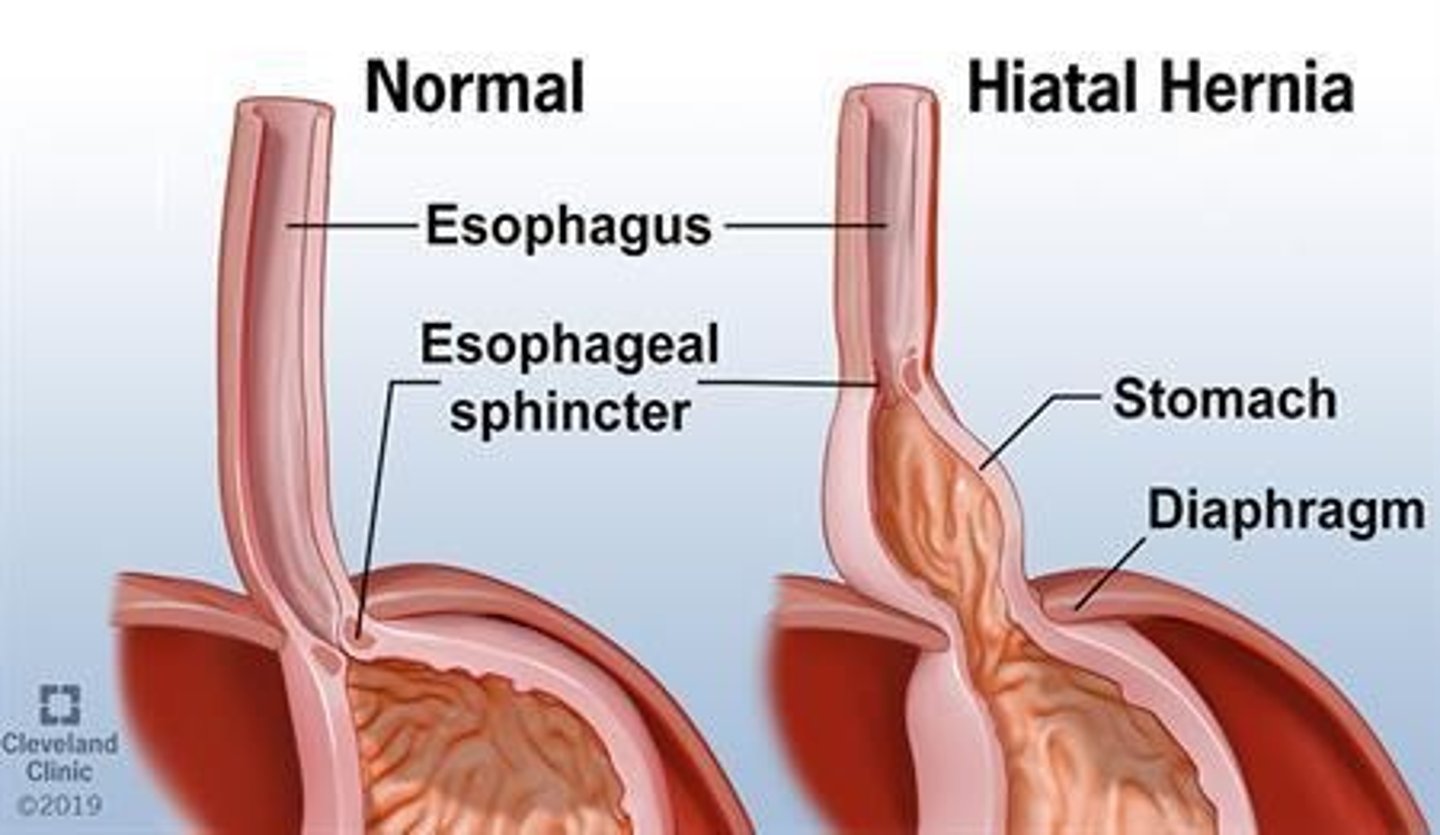
What is a hiatal hernia and what are its symptoms?
A hiatal hernia occurs when the stomach comes through the diaphragm into the thoracic cavity, causing symptoms such as heartburn or reflux.
What are the treatment options for hiatal hernia?
Proton pump inhibitors to treat symptoms, along with patient education to eliminate alcohol, quit smoking, lose weight, and reduce stress.
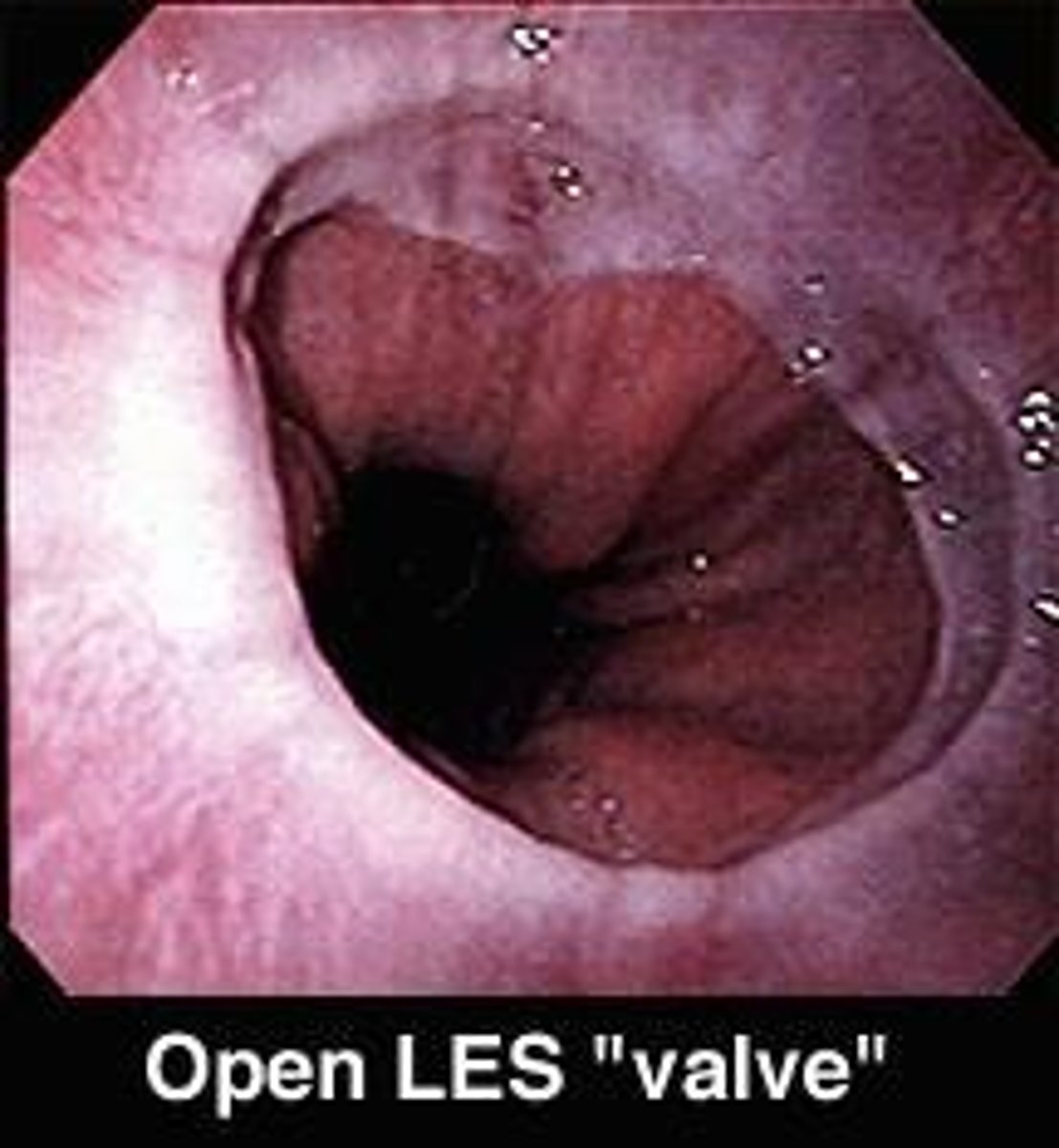
What is Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)?
GERD is a condition characterized by lower esophageal sphincter malfunction, allowing gastric contents to flow backward into the esophagus.
What is the potential association between H. pylori and GERD?
There may or may not be an association between H. pylori infections and GERD.
What are some common GI symptoms that can affect physical therapy participation?
GI symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain can make patients uncomfortable and impact their ability to participate in physical therapy.
What are the implications of constipation in patients with GI disease?
Constipation can result from inactivity or the use of opioid medications, and physical therapy can assist in its treatment.
What are the implications of aging on the GI system?
Problems can start before age 50, with common issues including constipation, incontinence, and diverticular disease.
What factors can increase intraabdominal pressure leading to hiatal hernia?
Factors include obesity, pregnancy, heavy lifting, and straining during bowel movements.
What are the PT implications when treating patients with GERD?
Avoid placing the patient flat in supine and avoid the Valsalva maneuver.
What is anorexia-cachexia?
Anorexia-cachexia is a syndrome characterized by weight loss, muscle wasting, and decreased appetite, often seen in chronic illnesses.
What is the significance of recognizing GI symptoms in physical therapy?
Recognizing GI symptoms is crucial as they can indicate underlying conditions that may affect treatment and patient safety.
What are some intrinsic and extrinsic causes of mechanical obstruction leading to dysphagia?
Intrinsic causes may include tumors or strictures, while extrinsic causes may involve compression from surrounding structures.
What are the implications of neurological changes on the GI system?
Neurological changes can impair bowel function and contribute to various GI disorders.
What are common food triggers for GERD?
Chocolate, coffee, and alcohol.
What are some clinical manifestations of GERD?
Heartburn, belching, dysphagia, nausea, vomiting, and painful swallowing.
How can body position affect GERD symptoms?
Laying flat can worsen symptoms; sleeping on the left side and elevating the head of the bed (HOB) can help.
What are some lifestyle modifications to manage GERD?
Smaller meals, weight loss, smoking cessation, and exercise.
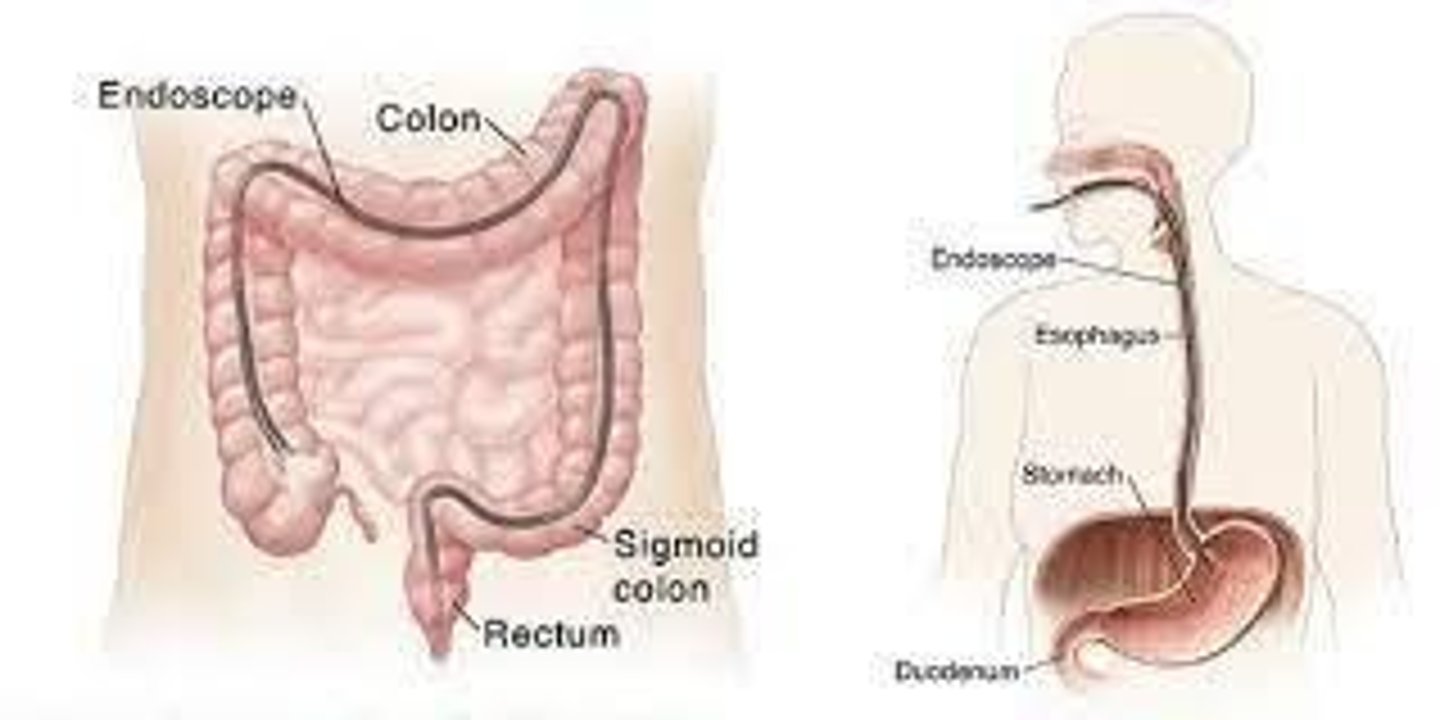
What is the role of endoscopy in GERD?
It is used for diagnosis.
What medications are commonly used to treat GERD?
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs), H2 receptor blockers, and antacids.
What are the potential side effects of long-term use of PPIs?
Increased fracture risk, acid rebound when discontinued, and potential for C. difficile infection.
What are H2 receptor blockers and their purpose?
Medications that block histamine receptors to reduce gastric secretion, treating GERD.
Name some examples of H2 receptor blockers.
Cimetidine (Tagamet), Famotidine (Pepcid), Nizatidine (Axid), Ranitidine (Zantac).
What are antacids and their potential side effects?
Medications that neutralize stomach acid; can cause constipation or diarrhea depending on composition.
What is the significance of esophageal varices in patients with cirrhosis?
They are fragile, dilated veins in the lower esophagus that can rupture and cause significant bleeding.
What is Peptic Ulcer Disease?
Erosion or ulceration of the stomach or duodenum, with duodenal ulcers being the most common.
What are some risk factors for Peptic Ulcer Disease?
NSAID usage and infection with H. pylori.
What is the implication of exercise for patients with GERD?
Exercise can help with weight loss and strengthen the esophageal sphincter.
What should be avoided to prevent worsening of esophageal varices?
Avoid Valsalva maneuver.
What is the role of Reglan (Metoclopramide) in GERD treatment?
It stimulates upper GI motility and may help treat GERD.
What are the adverse effects of Metoclopramide?
Restlessness, drowsiness, fatigue, and potential Parkinsonian-like effects.
What are the implications of long-term medication use for GERD?
Risk of osteoporosis and electrolyte imbalances.
How can surgery be involved in the treatment of GERD?
Surgery may be considered for severe cases that do not respond to other treatments.
What is the importance of patient education in managing GERD?
Educating patients about lifestyle changes, medication adherence, and symptom management is crucial.
What is the relationship between obesity and GERD?
Obesity increases the risk of GERD due to increased abdominal pressure.
What are some common causes of Peptic Ulcer Disease?
H. pylori infections, Crohn disease, cancer, viral infections, psychological stress, and diet.
What are the symptoms of Peptic Ulcer Disease?
Epigastric pain, abdominal cramping, heartburn, indigestion, chest pain, nausea and vomiting, melena (dark stool), fatigue, and weight loss.
What should physical therapists monitor in patients with Peptic Ulcer Disease?
Signs of bleeding and referred pain, including back pain, mid thoracic pain, and right shoulder pain.
How can exercise impact patients with Peptic Ulcer Disease?
Exercise can assist in decreasing gastrointestinal bleeding.
What is a common malabsorptive disorder mentioned in the notes?
Celiac disease.
What are some symptoms of malabsorptive disorders?
Diarrhea, bloating, weight loss, gastrointestinal pain, depression, failure to thrive, delayed puberty, bone pain, and multisystem involvement.
What nutritional deficiencies are associated with malabsorptive disorders?
Iron and B12 deficiencies, which can lead to anemia, bruising, and hair loss.
What are the physical therapy implications for athletes with prolonged unexplained illness?
They should be screened for signs of malnutrition, including fatigue, weight loss, paresthesia, muscle weakness, and muscle wasting.
What risks are associated with malabsorptive disorders?
Increased risk for osteoporosis and pathological fractures.
What are some common opioid derivatives used as antidiarrheal agents?
Imodium (loperamide) is an example.
What is the mechanism of action for bismuth salicylate as an antidiarrheal agent?
It stimulates water and electrolyte absorption from the lower GI tract and may limit irritation of the intestinal lining.
What are the categories of laxatives used to treat constipation?
Fiber supplements, stool softeners, osmotic agents, lubricants, and stimulants.
What is the mechanism of action of fiber supplements?
They are bulk-forming agents that facilitate the passage of stool through the rectum.
What are the potential side effects of stool softeners?
Nausea, cramps, gastrointestinal irritation, and fluid and electrolyte imbalances.
How do osmotic agents work?
They cause water to be retained with the stool, increasing bowel movements and softening the stool.
What is the effect of stimulants on the intestines?
They induce contractions in the intestines to move stool through the colon.
What is chronic mesenteric ischemia?
A condition characterized by decreased blood supply to the intestines, often secondary to atherosclerosis.
What are the symptoms of acute mesenteric ischemia?
Abdominal pain progressing to nausea and vomiting, fever, mental status changes, and black pain.
What is the diagnostic method for mesenteric ischemia?
Diagnosis is typically via CT scan.
What are the two types of surgical approaches mentioned for abdominal surgery?
Laparoscopy (minimally invasive) and laparotomy (large incision).
How does the surgical approach affect physical therapy evaluation and treatment?
The approach can influence the rehabilitation process, recovery time, and specific therapeutic interventions.
What are the two main types of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)?
Crohn's disease (CD) and Ulcerative colitis (UC).
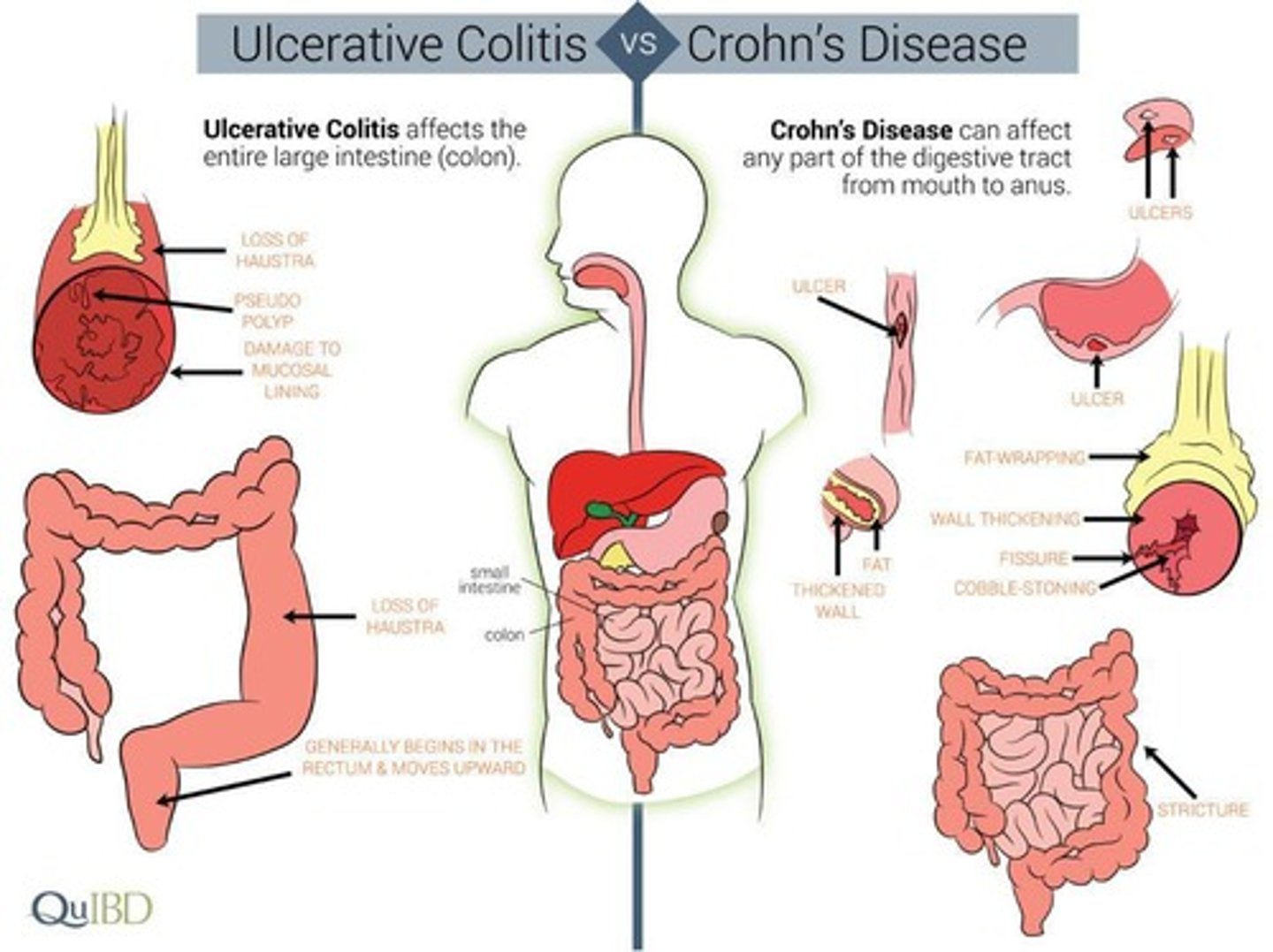
What part of the intestinal tract does Crohn's disease affect?
It can affect any part of the intestinal tract.
What part of the intestinal tract does Ulcerative colitis primarily affect?
It affects the colon mucosa.
What is a common symptom of both Crohn's disease and Ulcerative colitis?
Abdominal pain.
What are some symptoms specific to Crohn's disease?
Discontinuous attacks, fever, weight loss, bloody diarrhea, and up to 30 bowel movements a day.
What are some symptoms specific to Ulcerative colitis?
Diarrhea, malnutrition, weight loss, joint involvement, and extra-intestinal complications.
What is a significant risk factor for developing Diverticular Disease?
Low-fiber diets.
What are the two forms of Diverticular Disease?
Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis.
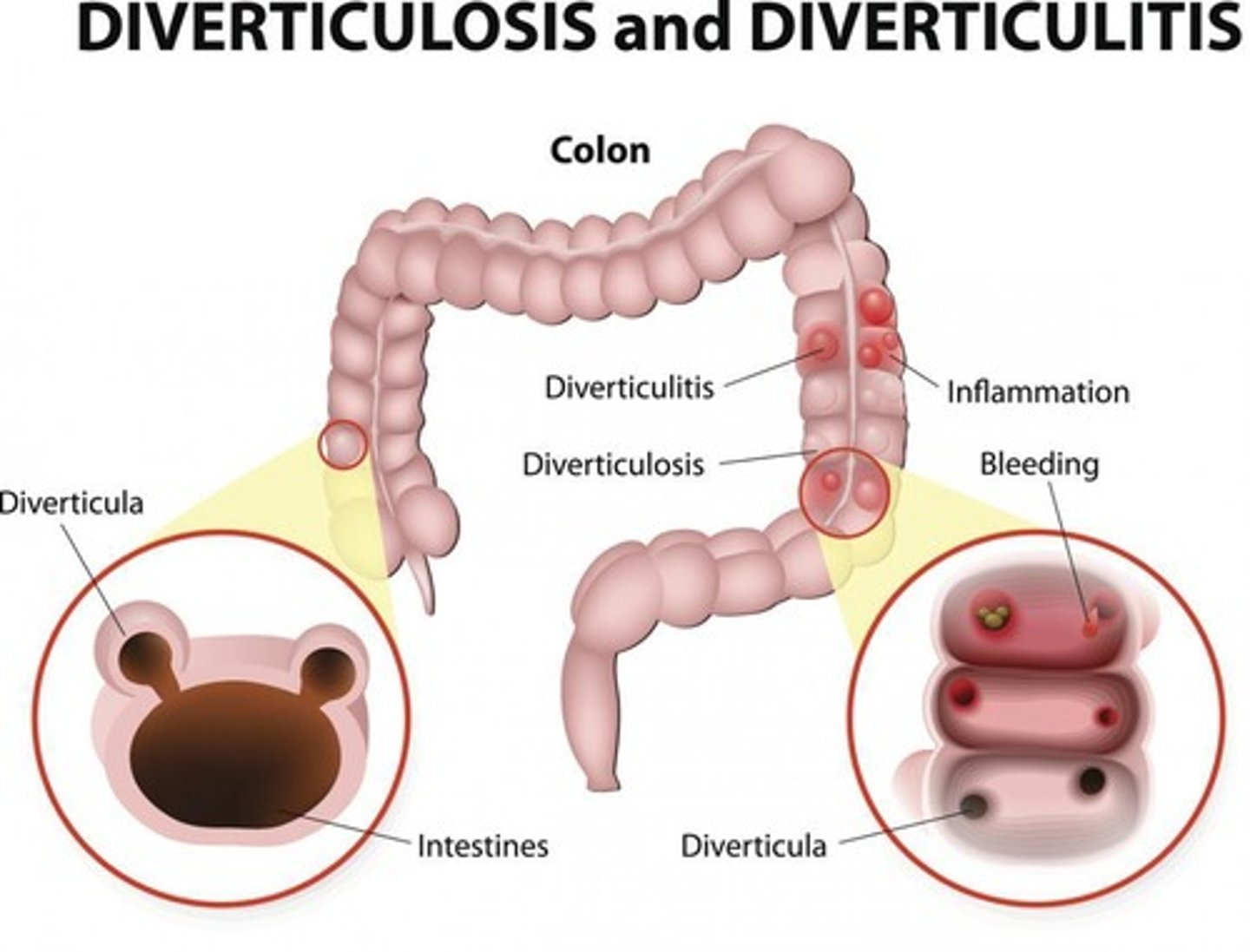
What are common symptoms of Diverticular Disease?
Left quadrant pain (increased with eating), fever, bowel changes, nausea, and vomiting.
What are some risk factors for colorectal cancer?
Age over 40, male gender, personal history of UC or CD, history of polyps, family history of colon cancer, obesity, and a diet low in fiber.
What is a common early warning sign of colorectal cancer?
Change in bowel habits.
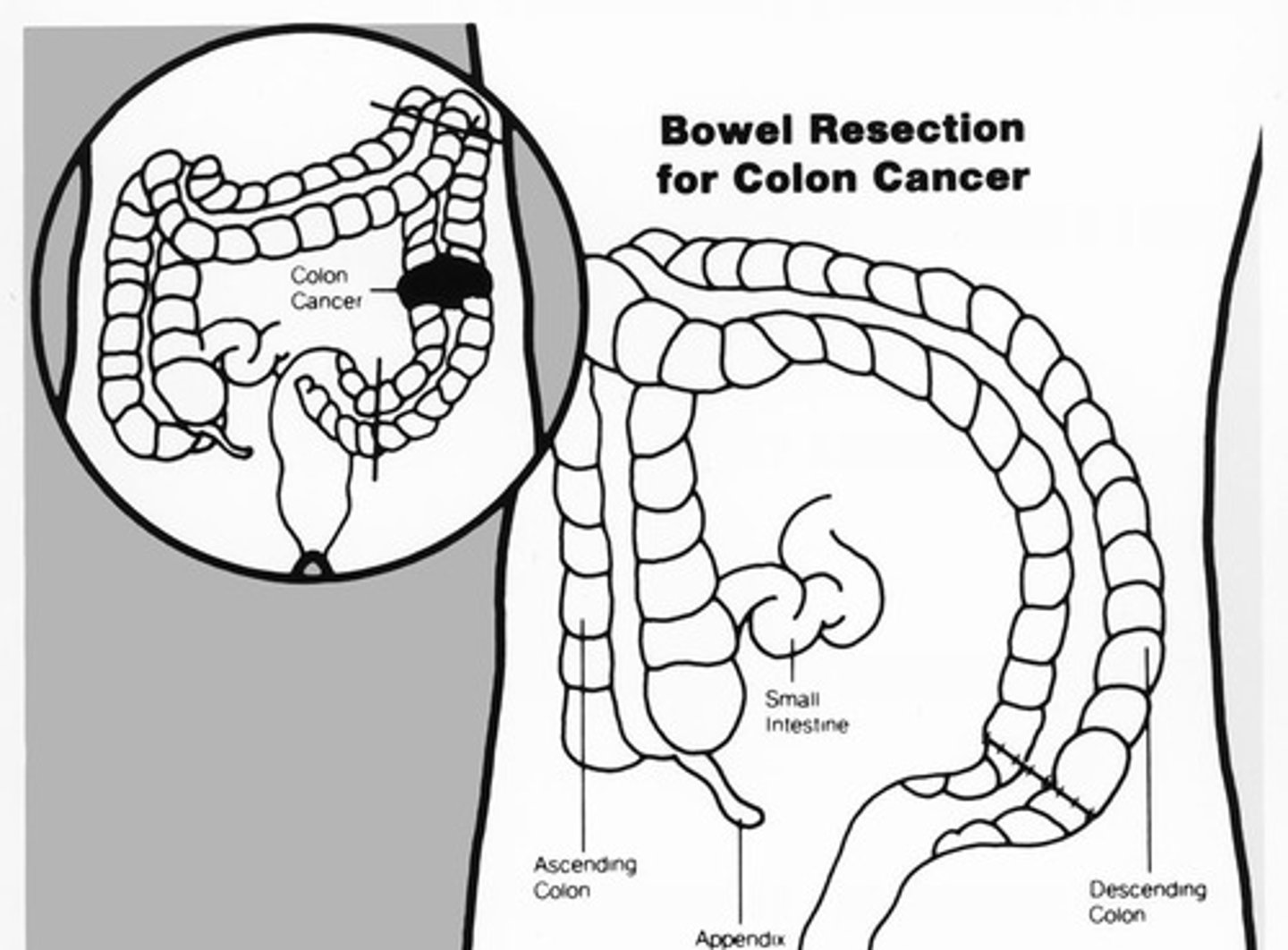
What does the staging of colorectal cancer include?
T (tumor), N (lymph nodes), and M (metastasis).
What is the treatment approach for colorectal cancer?
Surgical removal, bowel resection, tumor removal, lymph node removal, chemotherapy, and targeted biologic therapy.
What are some physical therapy implications for patients with IBD?
Musculoskeletal issues, referred pain to the back, signs of malnutrition and dehydration, and psychological issues.
What is a potential complication of corticosteroid use in IBD patients?
Osteoporosis.
What are some signs that may indicate the need for medical referral in physical therapy for patients with back pain?
Fever and significant changes in bowel habits.
What is the significance of screening for colorectal cancer in patients aged 45 to 75?
Encourages early detection and prevention.
What are the implications of lymphedema risk with lymph node removal in colon cancer patients?
Increased risk of swelling and complications post-surgery.
What is the role of physical activity in managing Diverticular Disease?
Physical activity is protective and can help manage symptoms.
What should be monitored in patients with a history of IBD regarding nutrition?
Signs of malnutrition and dehydration.
What are some potential constitutional symptoms to inquire about in patients with unexplained pain?
Weight loss, blood in stools, and changes in bowel movements.
What is the relationship between obesity and Diverticular Disease?
Obesity is a risk factor for developing Diverticular Disease.
What is the typical age range for diagnosis of Crohn's disease?
Ages 15-40.
What are the potential complications of colorectal cancer?
Obstruction, bleeding, perforation, anemia, ascites, and metastases.