PHARM 331 Drug actions, effects, and etc
1/214
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
215 Terms
How diuretics work: Mechanism of action
Blockade of sodium and chloride reabsorption
•Site of action = Proximal tubule produces greatest diuresis
•Adverse effects = Hypovolemia (cause getting rid of fluids), Acid-base imbalance (solutes, K, Na), and Electrolyte imbalances
Classification of diuretics
•Loop: Furosemide (lasix…??? - last 6 hrs)
•Thiazide: Hydrochlorothiazide
•Osmotic: Mannitol
•Potassium-sparing: Two subcategories (rid of sodium only, the other diuretics get rid of sodium AND potassium )
•Aldosterone antagonists (spironolactone)
•Nonaldosterone antagonists (triamterene)
•Fifth group = Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (not common)
Loop Diuretics
•Furosemide (Lasix): Most frequently prescribed loop diuretic
•Mechanism of action = Acts on ascending loop of Henle to block reabsorption
•Pharmacokinetics = Rapid onset (PO 60 minutes; IV 5 minutes)
Cannot control urine
•Therapeutic uses = Pulmonary edema, Edematous states, Hypertension
Goal is to get of fluid for pressure to go down
Furosemide [Lasix]
•Adverse effects = Hyponatremia, hypochloremia, and dehydration
•Hypotension
•Loss of volume
•Relaxation of venous smooth muscle
•Hypokalemia
•Ototoxicity (rare) - hearing of the ears
Furosemide [Lasix] Drug interactions
•Digoxin when K+ levels are low
•Ototoxic drugs
•Potassium-sparing diuretics
•Other loop diuretics
Thiazides and Related Diuretics
•Effects similar to those of loop diuretics
Increase renal excretion of sodium, chloride, potassium, and water (monitor them, NGFAR, creatine levels)
Elevate levels of uric acid and glucose
•Maximum diuresis is considerably lower than with loop diuretics
•Not effective when urine flow is scant (unlike with loop diuretics)
Hydrochlorothiazide
•Most widely used
•Action: Early segment distal convoluted tubule
•Peaks in 4 to 6 hours
Therapeutic uses
Essential hypertension = majority of the population (HTN occurs typically occur from 8:00 am- 2:00 pm)
Edema
Hydrochlorothiazide Adverse Effects
•Hyponatremia, hypochloremia, and dehydration
•Hypotension
•Hypokalemia
•Ototoxicity
•Hyperglycemia- idea that resorption in kidneys and reabsorb glucose
•Hyperuricemia - if someone has gout, the meds led to it
•Effects on lipid levels
•Use in pregnancy and lactation
•Impact on lipids, calcium, and magnesium (make sure to monitor them)
Hydrochlorothiazide drug interctions
•Digoxin
•Augments effects of hypertensive medications
•Lithium
•NSAIDs may blunt diuretic effect with chronic use
•Can be combined with ototoxic agents without increased risk of hearing loss
Potassium-Sparing Diuretics
•Useful responses
Modest increase in urine production
Substantial decrease in potassium excretion
•Rarely used alone for therapy
•Aldosterone antagonist
Spironolactone
•Nonaldosterone antagonists
Triamterene
Amiloride
Spironolactone [Aldactone]
Mechanism of action
•Blocks aldosterone in the distal nephron
•Retention of potassium
•Increased excretion of sodium
Therapeutic uses
•Hypertension
•Edematous states
•Heart failure (decreases mortality in severe failure)
Adverse effects
•Hyperkalemia
•Endocrine effects
Spironolactone [Aldactone] interactions
•Thiazide and loop diuretics = worry of hypovolemia leads to hypotension which leads to orthostatic which leads to fall, which we don’t want for pts. DONT USE MULTIPLE DURETIC AT ONCE.
•Agents that raise potassium levels
Triamterene [Dyrenium]
Mechanism of action
•Disrupts sodium-potassium exchange in the distal nephron
•Direct inhibitor of the exchange mechanism
•Decreases sodium reuptake
•Inhibits ion transport
Therapeutic uses
•Hypertension
•Edema
Adverse effects
•Hyperkalemia
•Leg cramps
•Nausea
•Vomiting
•Dizziness
•Blood dyscrasias (rare)
Amiloride [Midamor]
Mechanism of action
•Blocks sodium-potassium exchange in the distal nephron
Therapeutic use
•Counteract potassium loss caused by more powerful diuretics
Adverse effects
•Hyperkalemia
Drug interactions
•ACE inhibitors; other drugs with hyperkalemia
Osmotic Diuretic
•Mannitol [Osmitrol]
Promotes diuresis by creating osmotic force within lumen of the nephron
•Pharmacokinetics
Drug must be given parenterally
•Therapeutic uses
Prophylaxis of renal failure
Reduction of intracranial pressure
Reduction of intraocular pressure
Mannitol [Osmitrol]
•Adverse effects
Edema
Precipitate heart failure
Precipitate pulmonary edema
ACE Inhibitors
•Reduce levels of angiotensin II
•Increase levels of bradykinin (causes coughing frfr, dry cough, not the phlegm, give Angiotensin blocker)
Retains K+
ACE Inhibitors Pharmacokinetics
Ends in -pril= means ACE inhibitors
Nearly all orally. The only exception is enalaprilat (the active form of enalapril), which is given intravenously (IV) with FOOD
Therapeutic uses
•Hypertension
•Heart failure
•Myocardial infarction (MI)
•Diabetic and nondiabetic nephropathy
•Prevention of MI, stroke, and death in patients at high cardiovascular risk
ACE Inhibitors adverse effects
•First-dose hypotension
•Fetal injury
•Cough
•Angioedema
ACE inhibitors can cause angioedema, a potentially life-threatening reaction. If patients report edema of the tongue, lips, or eyes, emergency care should be sought immediately. The patient must never take ACE inhibitors again.
•Hyperkalemia
•Renal failure
•Neutropenia = low WBC
ACE Inhibitors drug interactions
•Diuretics
•Antihypertensive agents
•Drugs that raise potassium levels
•Lithium
•Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Preparations, dosage, and administration
•Except for enalaprilat, all ACE inhibitors are administered orally
•All are available in single-drug formulations
•Except for captopril and moexipril, all oral formulations may be administered without regard to meals
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers
•Block access of angiotensin II
•Cause dilation of arterioles and veins
•Prevent angiotensin II from inducing pathologic changes in cardiac structure
•Reduce excretion of potassium
•Decrease release of aldosterone
•Increase renal excretion of sodium and water
•Do not inhibit kinase II
•Do not increase levels of bradykinin
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers therapuetic uses/adverse effects
•Hypertension, heart failure, myocardial infarction
•Diabetic nephropathy
•Patient unable to tolerate ACE inhibitors: Protection against MI, stroke, and death from cardiovascular (CV) causes in high-risk patients
•May prevent development of diabetic retinopathy
•New data show that ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) are not effective for primary prevention of nephropathy in normotensive diabetic patients
Potassium levels will increase with usage of ARB.
Adverse effects
•Angioedema
•Fetal harm
•Renal failure
•ARBs do not promote accumulation of bradykinin in the lung and therefore have a lower instance of cough
Direct Renin Inhibitors
•Ex: Aliskiren [Tekturna]
•Binds tightly with renin and inhibits the cleavage of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I
Side effects
Angioedema, cough, GI effects, hyperkalemia, fetal injury, and death
Aldosterone Antagonists
•Eplerenone [Inspra]
Mechanism of action
Selective blockade of aldosterone receptors
•Therapeutic uses
Hypertension
Heart failure
•Pharmacokinetics
Absorption is not affected by food
•Adverse effects
Hyperkalemia
•Drug interactions
Inhibitors of CYP3A4 -> 80%
Drugs that raise potassium levels
Use with caution when combined with lithium
Spironolactone [Aldactone]
Mechanism of action
Blocks aldosterone receptors
Binds with receptors for other steroid hormones
Therapeutic uses
Hypertension
Heart failure
Adverse effects
Hyperkalemia
Gynecomastia
Menstrual irregularities
Impotence
Hirsutism
Deepening of the voice
Calcium Channel Blockers
Physiologic functions and consequences of blockade - In blood vessels, calcium entry causes vasoconstriction; calcium channel blockade, therefore, causes vasodilation.
•In the heart, calcium entry increases the heart rate, atrioventricular conduction, and myocardial contractility; therefore, calcium channel blockade has the opposite effects.
Calcium Channel Blockers types
Calcium channel blockers: Classification and sites of action
Verapamil and diltiazem: Agents that act on vascular smooth muscle (VSM) and the heart
Dihydropyridines: Agents that act mainly on vascular smooth muscle or BP (not arrhythmia)
Calcium Channel Blockers hemodynamic effects
•Blockade at peripheral arterioles
-Reduces arterial pressure
•Blockade at arteries and arterioles of heart
-Increases coronary perfusion
•Blockade at SA node
-Reduces heart rate
•Blockade at AV node (most important)
-Decreases AV nodal conduction
•Blockade in the myocardium
-Decreases force of contraction
Verapamil
Therapeutic uses
•Angina pectoris
Vasospastic angina and angina of effort
•Essential hypertension
Second-line agent after thiazide diuretics
•Cardiac dysrhythmias
Atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation, paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia
•Migraine (vasodilation/constriction in the brain, some cases only if everything else fails)
Adverse effects
•Constipation
Most common complaint
Results from blockade of calcium channels in smooth muscle of the intestine
•Especially severe for older adults
•Can be decreased by increasing dietary fiber and fluids
Dizziness
Facial flushing (common)
Headache (common)
Edema of ankles and feet (not that common with Verapamil)
Gingival hyperplasia
Heart block
Verapamil Drug interactions, toxicty, and management
•Digoxin - increases contractility of heart
•Beta-adrenergic blocking agents
Work of the heart
Toxicity
•Severe hypotension
•Bradycardia and AV block
•Ventricular tachydysrhythmias
•Treatment = Gastric lavage and activated charcoal
Management
IV verapamil for dysrhythmias can cause severe cardiovascular effects
Blood pressure and ECG should be monitored
Resuscitation equipment should be kept immediately available
Diltiazem
CCB
•Actions and uses
Blocks calcium channels in the heart and blood vessels (similar to verapamil)
•Lowers blood pressure
Arteriolar dilation
Direct suppressant/reflex cardiac stimulation = Little net effect on the heart
Therapeutic uses
•Angina pectoris
•Hypertension
•Cardiac dysrhythmias
•Atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation, paroxysmal tachycardia
Diltiazem adverse effects and interactions
•Similar to verapamil, except for less constipation
•Dizziness
•Flushing
•Headache
•Edema of ankles and feet
•Exacerbates bradycardia, sick sinus syndrome, heart failure, second- or third-degree heart block
Drug interactions
•Digoxin
•Beta-adrenergic blocking agents
Dihydropyridines
Agents that act mainly on vascular smooth muscle
•Nifedipine [Adalat, Nifedical, Nifediac, Procardia]
-Pine= dihydropyridines
Significant blockade of calcium channels in blood vessels
Minimal blockade of calcium channels in the heart
Similar to verapamil in some respects and quite different in others
Nifedipine
-Shell with two holes (one for gastric juice and other for med with shell, shells could be seen in feces after dispelling, medicine was absorbed but not the shell.
•Vasodilation by blocking calcium channels
•Blocks in vascular smooth muscle, relaxation
•Very little blockade of heart calcium (Ca) channels
•Cannot be used to treat dysrhythmias
•Less likely than verapamil to exacerbate preexisting cardiac disorders
Direct Effects
Limited to blockade of Ca channels invascular smooth muscle (VSM)
•No direct suppressant effects on:
•Automaticity, AV conduction, or contractile force
Indirect effects
•Lowered blood pressure (BP) activates baroreceptor reflex
•Primarily with immediate release versus sustained release
Vasodilation by blocking calcium channels
Nifedipine uses and adverse effects
CCB
Angina pectoris
Hypertension
Investigational basis: To relieve migraine headache and to suppress preterm labor
Adverse effects
•Flushing
•Dizziness
•Headache
•Peripheral edema (common in high doses)
•Gingival hyperplasia
•Chronic eczematous rash in older patients
•Reflex tachycardia
•Increases cardiac oxygen demand
•Can increase pain in angina patients
•Can be combined with a beta blocker for prevention of reflex tachycardia
Note: Beta blockers decrease the adverse cardiac effects of nifedipine but can intensify the adverse cardiac effects of verapamil and diltiazem
Other Dihydropyridines
•Seven other dihydropyridines available
•All similar to nifedipine
•Produce greater blockade of Ca channels in the VSM than in the heart
Nicardipine, amlodipine, isradipine, felodipine, nimodipine (common in US), nisoldipine, and clevidipine
*Verapamil and diltiazem are contraindicated for patients with severe hypotension, sick sinus syndrome (in the absence of electronic pacing), and second-degree or third-degree AV block. Use with caution in patients with heart failure or liver impairment and in patients taking digoxin or beta blockers
Digoxin
The combination of digoxin with verapamil or diltiazem increases the risk of partial or complete AV block.
Monitor for indications of impaired AV conduction (missed beats, slowed ventricular rate).
•Verapamil (and possibly diltiazem) can increase plasma levels of digoxin. Digoxin dosage should be reduced.
Also used to treat supraventricular dysrhythmias (inactive against ventricular dysrhythmias)
Suppresses dysrhythmias by decreasing conduction through AV node and automaticity in the SA node
interval may be shortened
Digoxin [Lanoxin]
Effects
Positive inotropic action on the heart
Increases force of ventricular contraction
Increases myocardial contractility
Relationship of potassium to inotropic action
Potassium levels must be kept in normal physiologic range
Hemodynamic benefits
Increased cardiac output
Decreased sympathetic tone
Increased urine production
Decreased renin release
Digoxin [Lanoxin] other effects
Neurohormonal benefits
Modulates the activity of the neurohormonal system
Suppresses renin release in the kidney
Decreases sympathetic outflow from the CNS
Increases sensitivity of cardiac baroreceptors
Electrical effects
Alters electrical properties of the heart
Increases firing rate of vagal fibers
Increases responsiveness of sinoatrial (SA) node to acetylcholine = Very active in arrhythmias (HTN, congestive HF)
Digoxin [Lanoxin] adverse effects
Cardiac dysrhythmias
Predisposing factors
Hypokalemia
Elevated digoxin level
Narrow therapeutic range
Heart disease
Diagnosing digoxin-induced dysrhythmias
Managing digoxin-induced dysrhythmias
Noncardiac adverse effects
Anorexia, nausea, vomiting, fatigue
Measures to reduce adverse effects
Education
*Cardiotoxicity
Digoxin [Lanoxin] drug interactions
changes the concentration of K+ (EKG, K+ levels)
Diuretics
ACE inhibitors and ARBs
Sympathomimetics
Quinidine
Verapamil
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Distributed widely and crosses placenta
Eliminated primarily by renal excretion
Half-life about 1.5 days -> blood work after 3 Half lives so times days by 3
Ex: 1.5 * 3 Levels changes every 5 days (steady state and dosages depend on Half-life)
If pt needs certain meds, may need loading dose (not CHF), injects
*Some metabolize livers or kidneys so monitor where it metabolizes then the heart
Beta Blockers
•Concurrent use of a beta blocker with verapamil or diltiazem can cause bradycardia, AV block, or heart failure.
Monitor closely for cardiac suppression.
Administer intravenous verapamil and beta blockers several hours apart.
Beta blockers intention and adverse effects
With careful control of dosage, can improve patient’s status
Protect from excessive sympathetic stimulation
Protect against dysrhythmias
Adverse effects
Fluid retention or worsening of HF
Fatigue
Hypotension -> heart pumping less
Bradycardia or heart block
Grapefruit Juice (pulp)
can raise levels of verapamil and diltiazem, although new evidence reveals this is less than originally thought. Nevertheless, toxicity may result. Advise patients that it may be prudent to minimize grapefruit juice consumption.
One cup is okay but still unsure cause Americans do not drink the can ones (what they study for the interactions)
TELL THEM NO!!!!!!!!!!
Managing Acute Toxicity of Dihrdopyridines
Remove unabsorbed drug with gastric lavage followed by activated charcoal.
Give IV calcium to help counteract excessive vasodilation and reduced myocardial contractility.
To raise blood pressure, give IV norepinephrine. IV fluids and placing the patient in modified Trendelenburg position can also help.
Bradycardia and AV block can be reversed with atropine and glucagon. If these are inadequate, electronic pacing may be required.
Vasodilators patho
•Can be produced with a variety of drugs
•Some act primarily on veins or arterioles; others act on both types of vessels
•Wide variety of therapeutic applications
Basic Concepts in Vasodilator Pharmacology
•Selectivity of vasodilatory effects
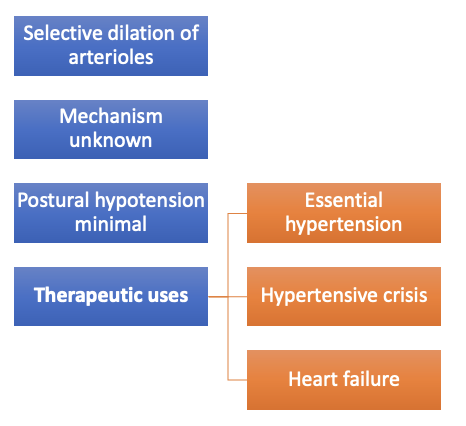
•Selective dilation of arterioles
- Hydralazine (vasodilator)
•Selective dilation of veins
- Nitroglycerin (vasodilator)
Adverse effect is headaches if pt leave the patch on after 10 hrs
•Dilation of arterioles and veins
-Prazosin
Vasodilators uses and adverse effects
•Essential hypertension
•Hypertensive crisis
•Angina pectoris
•Heart failure
•Myocardial infarction
•Pheochromocytoma
•Peripheral vascular disease
•Pulmonary arterial hypertension
•Production of controlled hypotension during surgery
Adverse effects related to vasodilation
•Postural hypotension
•Teach patients about symptoms of hypotension (lightheadedness, dizziness) and advise them to sit or lie down if these occur. Avoid abrupt transitions from a supine or seated position to an upright position.
•Reflex tachycardia
-Expansion of blood volume
Hydralazine Uses
Give it more than once a day, 3x a day (compliance is hard)
Adverse effects
•Reflex tachycardia
•Increased blood volume
•Systemic lupus erythematosus–like syndrome (rare)
•Headache, dizziness, weakness, and fatigue
Drug interactions
•Other antihypertensive agents
•Avoid excessive hypotension
•Combined with beta blocker to protect against reflex tachycardia and with diuretics to prevent sodium and water retention and expansion of blood volume
Minoxidil (grew hair)
Selective dilation of arterioles
•More intense dilation than hydralazine, but causes more severe adverse reactions
•Used for severe hypertension unresponsive to safer drugs
Adverse effects
•Reflex tachycardia
•Sodium and water retention
•Hypertrichosis
•Pericardial effusion
•Other
Sodium Nitroprusside [Nitropress]
•Fastest-acting antihypertensive agent
•Causes venous and arteriolar dilation
•Administration: IV infusion
•Onset: Immediate (BP returns to pretreatment level in minutes when stopped)
• Only Used for hypertensive emergencies
Adverse effects
•Excessive hypotension
•Cyanide poisoning -> you become a smurf (stop med, slowing the drip)
•Thiocyanate toxicity
Drugs for Hypertensive Emergencies
•Sodium nitroprusside (remember SMURF) - inject
•Fenoldopam
•Labetalol - inject
•Diazoxide
•Clevidipine
Drugs for Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy
Chronic hypertension and pregnancy
•ACE inhibitors, ARBs, and DRIs are contraindicated during pregnancy
•Most other antihypertensives can be continued during pregnancy
Preeclampsia and eclampsia
•Hydralazine
•Magnesium sulfate (anticonvulsant)
Classes of antihypertensive drugs
Diuretics
Thiazide diuretics
Loop diuretics
Potassium-sparing diuretics
Sympatholytics (antiadrenergic drugs)
Beta-adrenergic blockers
Alpha1 blockers
Alpha/beta blockers: Carvedilol and labetalol
Centrally acting alpha1 agonists
Adrenergic neuron blockers
•Direct-acting vasodilators: Hydralazine and minoxidil
•Calcium channel blockers
Drugs that suppress RAAS
ACE inhibitors best used for HTN
Angiotensin II receptor blockers
Aldosterone antagonists
Direct renin inhibitors: Type 2 diabetes mellitus precautions
Ivabradine (Corlanor)
For use in patients with stable, symptomatic heart failure with:
LVEF <35% Left ventricle ejection fraction
Sinus rhythm -> fix the dysrhythmia
Heart rate > 70 BPM
*Can be used for patients who have a contraindication to beta blocker use
Digoxin and Cardiac Glycosides
Positive inotropic actions
Increase myocardial contractile force
Alter electrical activity of the heart -> need K+ levels to be in normal limits (need K+ to be over 3.5 or else will have digoxin toxicity)
Nausea (is first) is adverse affect, visionary disorders (yellow hallo)
ALWAYS THINK OF POTASSIUM LEVELS WHEN PT HAS MUSCLE WEAKNESS
Favorably affect neurohormonal systems
Inotropic Agents
Sympathomimetics
Dopamine [Intropin]
Catecholamine
Activates beta1-adrenergic receptors in the heart, kidney, and blood vessels
Increases heart rate
Dilates renal blood vessels
Activates alpha1 receptors - does not block the receptors, causes constriction, enhancing the effects which makes the receptors better
Inotropic Agents Pt2
Dobutamine
Synthetic catecholamine
Selective activation of beta1-adrenergic receptors
Phosphodiesterase inhibitors
Milrinone [Primacor]
Inodilator: Increases myocardial contractility and promotes vasodilation
Reserved for patients with severe reduction in cardiac output resulting in decreased organ perfusion
Arrhythmias, myocardial ischemia
Vasodilators
Isosorbide dinitrate plus hydralazine
Cardiac (Digitalis) Glycosides
Digoxin [Lanoxin]
Class IA Agents
Quinidine
Effects on the heart
Blocks sodium channels
Slows impulse conduction
Delays repolarization
Blocks vagal input to the heart
Effects on the ECG
Widens the QRS complex
Prolongs the QT interval
Class 1A Agent uses and effects
Therapeutic uses
Used for supraventricular and ventricular dysrhythmias
Adverse effects (Delentones are used for seizures, also could use for arrhythmias)
Diarrhea
Cinchonism = overdose
Cardiotoxicity
Arterial embolism
Alpha-adrenergic blockade, resulting in hypotension
Hypersensitivity reactions
Drug interactions
Digoxin
Class IB Agents
Lidocaine [Xylocaine] for pain
Effects on the heart and ECG
Blocks cardiac sodium channels
Slows conduction in the atria, ventricles, and His-Purkinje system
Reduces automaticity in the ventricles and His-Purkinje system
Accelerates repolarization
Adverse effects
CNS effects
Drowsiness
Confusion
Paresthesias
Class IC Agents
Block cardiac sodium channels
Delay ventricular repolarization
All class IC agents can exacerbate existing dysrhythmias and create new ones
Two class IC agents
Flecainide
Propafenone
Class II: Beta Blockers ( ends with -ol)
Beta-adrenergic blocking agents
Only four approved for treating dysrhythmias, not for CHF
Propranolol
Acebutolol
Esmolol
Sotalol
Propranolol (non-selective BB)
Effects on the heart and ECG
Decreased automaticity of the SA node (vasoconstriction, broncho, reduced gkycogenolysis)
Decreased velocity of conduction through the AV node
Decreased myocardial contractility
Suppress secretion of renin
Therapeutic use
Dysrhythmias caused by excessive sympathetic stimulation
Supraventricular tachydysrhythmias
HTN, angina pectopris, MI
Adverse effects
Heart failure
Heart block
Sinus arrest
Rebound cardiac excitation → withdraw slowly over 1-2 weeks
Hypotension -> flushing (pts cannot handle constipation)
Bronchospasm (in asthma patients)
Beta 2 -> will be blocked due to the blocked receptors of B1 and 2
Propranolol (non-selective BB) warnings
Severe allergy
Diabetes → block early recognition of insulin induced hypoglycemia
Exacerbate heart failure, AV heart block, sinus bradycardia, asthma, and bronchospasm → beware of CCB
Metoprolol
Second gen selective BB 1 but high doses also Beta 2
reduces heart rate, force of contraction, and conduction velocity through the AV node
HTN, Angina pectoris, HF, and MI
Safe with asthma patients or allergic reactions
Adverse effects
bradycardia, reduced cardiac output, AV heart block, and rebound cardiac excitation after abrupt withdrawal
HF
Class III: Potassium Channel Blockers
Amiodarone [Pacerone]
Therapeutic use
For life-threatening ventricular dysrhythmias only
Recurrent ventricular fibrillation
Recurrent hemodynamically unstable ventricular tachycardia
Effects on the heart and ECG
Reduced automaticity in the SA node
Reduced contractility
Reduced conduction velocity
QRS widening
Prolongation of the PR and QT intervals
Potassium Channel Blockers adverse effects
Adverse effects
Protracted half-life
Pulmonary toxicity
Cardiotoxicity (big no no)
Thyroid toxicity (big no no)
Liver toxicity
Ophthalmic effects
Toxicity in pregnancy and breast-feeding
Dermatologic toxicity
Drug interactions (increases levels)
Quinidine
Procainamide
Phenytoin
Digoxin
Diltiazem
Warfarin
Cyclosporine
Lovastatin, simvastatin, atorvastatin
May have to reduce the dosages of these meds
Other factors on K+ channel blockers
Amiodarone levels can be increased by grapefruit juice and by inhibitors of CYP3A4. Toxicity can result.
Amiodarone levels can be reduced by cholestyramine (which decreases amiodarone absorption) and by agents that induce CYP3A4 (eg, St. John’s wort, rifampin).
The risk of severe dysrhythmias is increased by diuretics (because they can reduce levels of potassium and magnesium) and by drugs that prolong the QT interval, of which there are many
Combining amiodarone with a beta blocker, verapamil, or diltiazem can lead to excessive slowing of the heart rate
Muscle weakness -> think about K+ levels
Class IV: Calcium Channel Blockers
Verapamil [Calan, Verelan] and diltiazem [Cardizem, Tiazac]
Reduce SA nodal automaticity
Delay AV nodal conduction
Reduce myocardial contractility
Therapeutic uses
Slow ventricular rate (atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter)
Terminate SVT caused by an AV nodal reentrant circuit
Adverse effects
Bradycardia
Heart block
Heart failure
Hypotension
Peripheral edema
Constipation
Can elevate digoxin levels
Increased risk when combined with a beta blocker = same effect so risk of arrhythmia unless pt is not at risk
Propranolol -> you see trouble
Adenosine [Adenocard]
Other Antidysrhythmic Drug
Effects on the heart and ECG
Decreases automaticity in the SA node
Slows conduction through the AV node
Prolongs PR interval
Therapeutic use: Termination of paroxysmal SVT
Adverse effects
Sinus bradycardia
Dyspnea
Hypotension
Facial flushing
Chest discomfort
Drug interactions
Methylxanthines
Dipyridamole
HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors (Statins)
NUMBER 1
Most effective drugs for lowering LDL (plaque stability)
Reduction of LDL cholesterol
Elevation of HDL cholesterol
Reduction of triglyceride levels
Nonlipid beneficial cardiovascular actions
Promote plaque stability
Suppress production of thrombin
HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors (Statins) uses and actions
Mechanism of cholesterol reduction
Clinical trials
Therapeutic uses
Hypercholesterolemia
Primary and secondary prevention of CV events
Post-MI therapy
Diabetes
Potential uses
Beneficial actions
Reduction of LDL cholesterol
Elevation of HDL cholesterol
Reduction of triglyceride levels
Nonlipid beneficial cardiovascular actions
*May affect glucose levels
HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors (Statins) adverse effects
Common
Headache
Rash
Memory loss (not really)
disturbances
Rare
Myopathy/rhabdomyolysis (Major for some pts, dark urine, extremities pain,) -> considered an allergy (not really, more adverse effect) -> if they have a reaction to one, they will have reaction to everyone
Hepatotoxicity- have to monitor liver enzyme, AST, ALT
ANATERONE?= levels go higher -> toxicity
New-onset diabetes
HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors (Statins) drug interactions and dosing
Drug interactions
Most other lipid-lowering drugs (except bile-acid sequestrants)
Drugs that inhibit CYP3A4
Use in pregnancy
Dosing: Once daily in the evening
Endogenous cholesterol synthesis increases during the night
Statins have greatest impact when given in the evening, works at night since Cholesterol is made at night
Long Half-life = duration is long so if you take it in the morning it will work at night too expect avortastin and overostatin
Bile-Acid Sequestrants
Previously were first-line drugs (bile- acid was the reason why its not first line anymore, pulls cholesterol out)
Now primarily used as adjuncts to statins
Cholestyramine
Colestipol
Colesevelam
Newest and better-tolerated drug
Does not decrease uptake of fat-soluble vitamins (as other bile sequestrants do)
Does not significantly reduce the absorption of statins, warfarin, digoxin, and most other drugs studied
Reduces LDL cholesterol
Increases VLDL levels in some patients
Mechanism of action
Increases LDL receptors on hepatocytes
Prevents reabsorption of bile acids
Therapeutic use
Reduces LDL cholesterol (in conjunction with modified diet and exercise)
Adverse effects
Constipation, need to take with food/water and 2 hrs after or before after other meds?
Ezetimibe
Mechanism of action and impact on plasma lipids
Inhibits cholesterol absorption
Therapeutic use
Reduces total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and apolipoprotein B
Approved for monotherapy and combined use with statins
Adverse effects
Myopathy
Rhabdomyolysis
Hepatitis
Pancreatitis
Thrombocytopenia
Drug interactions
Statins
Fibrates
Bile-acid sequestrants
Cyclosporine
Fibric Acid Derivatives (Fibrates)
Most effective drugs available for lowering TG levels
Can raise HDL cholesterol
Little or no effect on LDL cholesterol
Can increase the risk for bleeding in patients taking warfarin
Can increase the risk for rhabdomyolysis in patients taking statins
Three drugs in the United States
Gemfibrozil [Lopid]
Fenofibrate [Tricor, others]
Fenofibric acid [TriLipix]
Gemfibrozil
Effects on plasma lipoproteins
Decreases plasma TG content
Lowers VLDL levels
Can raise HDL cholesterol
Mechanism
Drug interactions
Displace warfarin from plasma albumin
Measure international normalized ratio (INR) frequently
Therapeutic uses
Reduces high levels of plasma triglycerides (VLDLs)
Treatment reserved for patients who have not responded to diet modification
Less effective than statins in reducing LDL
Can raise HDL (not approved for this use)
Adverse effects
Rashes
Gastrointestinal disturbances
Gallstones
Myopathy
Liver injury (hepatotoxic)
Used to Alter Plasma Lipid Levels
Fish oil
Lovaza (also fish oil)
Plant stanol and sterol esters
Cholestin
Drugs for Angina Pectoris
Three families of antianginal agents
Organic nitrates
Nitroglycerin - vasodilate
Beta blockers
Example: Metoprolol (Specific beta 1- calcium channel blocker)
Calcium channel blockers
Example: Verapamil
Ranolazine (vasodilate)
Newer drug with limited indications
Can be combined with other drugs
Organic Nitrates: Nitroglycerin actions and adverse effects
Stable and variant angina
Vasodilator
Acts directly on vascular smooth muscle (VSM) to promote vasodilation
Adverse effects
Headache (common)
Orthostatic hypotension (common)
Reflex tachycardia
Organic Nitrates: Nitroglycerin drug interactions
Drug interactions -other medications that cause hypertension
Hypotensive drugs
Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors
Beta blockers, verapamil, and diltiazem
Organic Nitrates: Nitroglycerin tolerance and uses
Can develop rapidly
Cross-tolerance to all other nitrates
minimize, use the lowest effective dose
Long-acting formulas: 8 drug-free hours per day, night take it off and put it on in morning
Therapeutic uses
Acute anginal therapy
Sustained anginal therapy
for perioperative control of blood pressure and treatment of heart failure with myocardial infarction (MI), unstable angina, and uncontrolled exacerbations of chronic angina
Isosorbide mononitrate and isosorbide dinitrate
Actions identical to those of nitroglycerin
Used for angina; taken orally
produce headache, hypotension, and reflex tachycardia
Propranolol, metoprolol actions and adverse effects
Betablockers
decrease cardiac O2 demand
Adverse effects
Bradycardia
Decreased atrioventricular (AV) conduction
Reduction of contractility
Asthmatic effects
Use with caution in patients with diabetes
Insomnia
Depression
Bizarre dreams
Verapamil, diltiazem, nifedipine uses and adverse effects
CCB
Block calcium channels in vascular smooth muscle
Used for stable and variant angina
Adverse effects
Dilation of peripheral arterioles
Reflex tachycardia
Hypotension
Beta blockers
Bradycardia
Heart failure
Heart block
Ranolazine
Belongs to first new class of antianginal agents approved in more than 25 years
Benefits are modest and greater in men than in women
Does not reduce heart rate, blood pressure, or vascular resistance
Can prolong QT interval; multiple drug interactions
Exact mechanism unknown
a first-line therapy; combine with first-line agents for inadequate response to other first-line medications for angina
Drugs for Thromboembolic Disorders
•Anticoagulants: Disrupt the coagulation cascade, thereby suppressing the production of fibrin
•Antiplatelets: Inhibit platelet aggregation
•Thrombolytics: Promote lysis of fibrin, causing dissolution of thrombi
Anticoagulants
Reduce the formation of fibrin
Pt are easy to bruise, will have all over due to slowing down of blood clotting
Two mechanisms of action
•Inhibit the synthesis of clotting factors, factor X and thrombin
•Inhibit the activity of clotting factors: factor Xa/thrombin
Heparin and Heparin Derivatives
•Heparin (unfractionated)- high risk for bleeding
Enhances antithrombin, factor Xa
Rapid-acting anticoagulant
Administered by injection only
•IV
Continuous and intermittent
•Deep subcutaneous (subQ)
Heparin (Unfractionated) uses
•Therapeutic uses
Acute cases
For bleeding (more common)
•Preferred anticoagulant during pregnancy and when rapid anticoagulation is required
•Pulmonary embolism (PE)
•Massive deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
•Open heart surgery
•Renal dialysis
•Low-dose therapy postoperatively
•Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
•Adjunct to thrombolytic therapy, MI
Heparin adverse effects + tests
•Hemorrhage, avoid antiplatelet drugs
Spinal/Epidural Hematoma
•Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) = development of antibodies, discontinue when platelet count falls
•Hypersensitivity reactions = due to contamination
Contraindicated
•Thrombocytopenia
•Uncontrollable bleeding
•DONT USE During and immediately after surgery of the eye, brain, or spinal cord
Antidote for overdose (OD): Protamine sulfate (1 unit per 100 units of heparin)
Check for Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT, normal is 40 sec but with med is 60-80 sec) every 4-6 hrs then once a day
Check for Anti-factor Xa Heaprin Assay = 0.3 - 0.7 IU/mL, measures heparin and its activity
Low-Molecular-Weight (LMW) Heparins
•Heparin preparations composed of molecules that are shorter than those found in unfractionated heparin
Less risk for bleeding, can give pt an injectable pen to do it themselves
Therapeutic uses
•Prevention of DVT after surgery
Including replacement of hip, knee
•Treatment of established DVT
•Prevention of ischemic complications
Patients with unstable angina, non–Q-wave myocardial infarction (MI), and ST-elevation MI (STEMI)
•Administered subQ
•Dosage based on body weight
•Antidote for toxicity: Protamine sulfate
•Does not require monitoring; can be given at home
LMW Heparins actions and uses
Inactivates factor Xa
First line for preventation of and DVT
Unstable angina, non-Q wave MI, STEMI
Administered subQ
LMW Heparins adverse effects
•Adverse effects and interactions
Bleeding (but less than with unfractionated heparin)
Immune-mediated thrombocytopenia
Severe neurologic injury for patients undergoing spinal puncture or spinal epidural anesthesia
Other LMW Heparins
•In the United States, two LMW heparins are available:
•Enoxaparin - DVT, PE, unstable angina, MI, STEMI
•Dalteparin
Fondaparinux
synthetic SC anticaogulant → selective inhibition of factor Xa and inactivation of thrombin
Uses = preventing DVT, acute PE/DVT (with warfarin)
Adverse effects = Bleeding, caution with moderal renal impairment, immune-mediated HIT
Warfarin: Oral Anticoagulant
•Oral anticoagulant with delayed onset
•Vitamin K antagonist - people ate green leafy vegetables (spinach, kale, broccoli) so it interfere with warfarin
•Blocks biosynthesis of factors VII, IX, and X and prothrombin
-6-8 hours for factor VII, Factor II is 72 hours(?)
Give it at night
Only give 5-10%, if more risk of bleeding
Warfarin Pharmacokinetics
Warfarin binds to albumin, the free bound warfarin is inactivated by CYP2C9 in the liver
Initial responses take 8-12 hrs to develop
When discontinued, coagulation remains for 2-5 days
Warfarin therapeutic uses
•Not useful in emergencies since it takes 6-8 hrs
•Long-term prophylaxis of thrombosis
Prevention of venous thrombosis and associated pulmonary embolism
Prevention of thromboembolism (in patients with prosthetic heart valves)
Prevention of thrombosis during atrial fibrillation
Monitoring treatment
•Prothrombin time (PT)
•International normalized ratio (INR) -Give for 3 days then monitor INR 1-2 weeks (point of care, mechanical value of 2.5-3.5 but for everyone else is 1-2)
Warfarin adverse effects and drug interactions
•Hemorrhage (vitamin K for toxicity), look at even vitamins and herbal products
•Fetal hemorrhage and teratogenesis from use during pregnancy
•Use during lactation
•Other adverse effects
Drug interactions
•Drugs that increase anticoagulant effects
•Drugs that promote bleeding
•Drugs that decrease anticoagulant effects
•Heparin
•Aspirin - inhibit platelets
•Acetaminophen