Chemical Kinetics [MOSTLY DONE]
1/145
Earn XP
Description and Tags
pretty much all of Chemical Kinetics for JEEM and IAT. I still need to go through NCERT for it but that will come in the future. Question mode: Flashcards only. Answer mode: Answer with definition. Good luck!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
146 Terms
What is the general formula for Rate of Reaction?
\text{rate}=\dfrac{\text{change in concentration of reactant or product}}{\text{time taken to change}}
What is the average amount of time taken by very fast / instantaneous reactions?
10^{-14} to 10^{-16} seconds
Is an ionic reaction an instantaneous reaction, moderate reaction, or very slow reaction?
instantaneous reaction
is a neutralisation reaction an instantaneous reaction, moderate reaction, or very slow reaction?
instantaneous reaction
is a precipitation reaction an instantaneous reaction, moderate reaction, or very slow reaction?
instantaneous reaction
Which sort of reaction (based on speed of reaction) is it possible to determine the rate of?
Moderate reactions
What is the average amount of time taken by moderate / slow reactions?
a few seconds to a few hours under given conditions
Is hydrolysis of ester an instantaneous reaction, moderate reaction, or very slow reaction?
moderate reaction
Is the decomposition of H_2O_2 an instantaneous reaction, moderate reaction, or very slow reaction?
moderate reaction.
What is the average time taken by very slow reactions?
days or months lol
Is rusting of iron an instantaneous reaction, moderate reaction, or very slow reaction?
very slow reaction
Is formation of coal an instantaneous reaction, moderate reaction, or very slow reaction?
very slow reaction
Is the reaction between H_2 and O_2 at room temperature an instantaneous reaction, moderate reaction, or very slow reaction?
very slow reaction.
What does a negative sign of the rate of reaction indicate?
The rate of reaction refers to the decreasing reactant concentration
What does a positive sign of the rate of reaction indicate?
The rate of reaction refers to the increasing product concentration.
What is the formula for average rate of reaction?

What is the formula for instantaneous rate of reaction, for a reaction A → B?

In a graph of concentration of reaction vs time, how would you calculate the instantaneous rate of reaction at any point?
By finding the slope of the graph at that point.
How is the instantaneous rate of reaction related to the average rate of reaction?
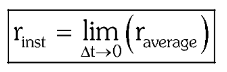
In a reaction m_1A+m_2B → n_1P+n_2Q,
What is the rate of disappearance of A?
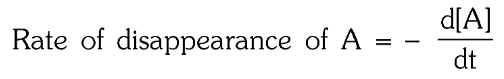
In a reaction m_1A+m_2B → n_1P+n_2Q,
What is the rate of disappearance of B?

In a reaction m_1A+m_2B → n_1P+n_2Q,
What is the rate of appearance of P?
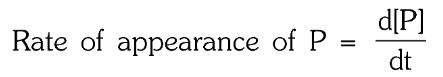
In a reaction m_1A+m_2B → n_1P+n_2Q,
What is the rate of appearance of Q?
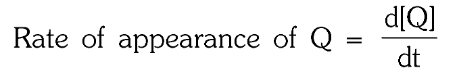
In a reaction m_1A+m_2B → n_1P+n_2Q,
What is the rate of reaction with respect to A?
Rate of reaction = -\dfrac{1}{m_1}\dfrac{d[A]}{dt}
In a reaction m_1A+m_2B → n_1P+n_2Q,
What is the rate of reaction with respect to B?
Rate of reaction = -\dfrac{1}{m_1}\dfrac{d[B]}{dt}
In a reaction m_1A+m_2B → n_1P+n_2Q,
What is the rate of reaction with respect to P?
Rate of reaction = \dfrac{1}{m_1}\dfrac{d[P]}{dt}
In a reaction m_1A+m_2B → n_1P+n_2Q,
What is the rate of reaction with respect to Q?
Rate of reaction = \dfrac{1}{m_1}\dfrac{d[Q]}{dt}
What is the unit of Rate of Reaction in terms of concentration?
mol\ L^{-1}\ time^{-1}
What is the unit of Rate of Reaction in terms of pressure?
atm\ time^{-1}
What is the Rate Law Expression?
The experimental expression which shows the relationship between the rate of reaction and the concentration of reactants.
What is the general form of a Rate Law Expression?
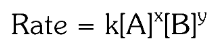
What is the rate constant?
It is the rate of reaction at unit concentration of reactants.
Does rate constant depend on the concentration of a reactant?
no
How does rate constant depend on temperature?
rate constant increases with increase in temperature
How does rate constant depend on the presence of a catalyst?
Increases in the presence of a positive catalyst, decreases in the presence of a negative catalyst.
What is the order of a reaction?
It is the sum of the powers of all concentrations of reactants in the Rate Law Expression
For the reaction aA + bB → product,
the rate law expression is r=k[A]^x[B]^y.
What is the order of reaction?
x+y
For the reaction aA + bB → product,
the rate law expression is r=k[A]^x[B]^y.
What is the order of reaction with respect to A?
x
For the reaction aA + bB → product,
the rate law expression is r=k[A]^x[B]^y.
What is the order of reaction with respect to B?
y
What is the unit of the rate constant in terms of concentration? (general form)
(mol\ L^{-1})^{1-n}\ sec^{-1}
where n is the order of the reaction.
What is the unit of rate constant in terms of pressure?
atm^{1-n}\ time^{-1}
What is an Elementary Reaction?
It is a reaction which takes place in a single step.
What is a Complex Reaction?
It is a reaction which takes place in multiple steps.
In which type of reaction (Simple/Complex) is an intermediate formed?
Complex
In which type of reaction (Simple/Complex) are the powers in the rate law expression equal to stoichiometric coefficients?
Simple
If a question doesn’t tell you whether a reaction is elementary or complex, what do you assume it is?
elementary
When given a complex reaction with its mechanism, how do you find the rate law expression for that reaction?
In a complex reaction every step of the mechanism is considered an elementary reaction, and for a complex reaction the rate is defined by the slowest step, known as the “rate-determining step”, or RDS.
First you would make a rate law expression for the RDS, and if that expression contains any intermediates, find those intermediates in terms of the reactants (with use of the other steps in the mechanism, as well as reaction constants).
What is the molecularity of an elementary reaction?
It is the number of molecules/atoms/ions of reactants of an elementary reaction?
Out of Order of reaction and Molecularity of reaction, which one is a theoretical quantity and which one is an experimental quantity?
Order → experimental
Molecularity → theoretical
How do you calculate molecularity of an elementary reaction?
Sum of stoichiometric coefficients of reactants.
What are the possible molecularities an elementary reaction could have?
1, 2, 3
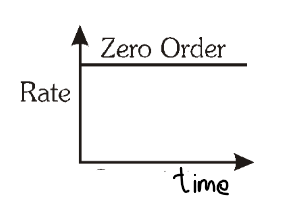
What is the significance of a Zero Order Reaction?
It is a reaction in which the rate of reaction is independent of the initial concentration of reactants.
What is the integrated rate law expression of a zero order reaction? (in terms of reactants)
[A]_t=[A]_0-kt
Where
[A]_t is the concentration of reactant A at time t
[A]_0 is the initial concentration of reactant A (t=0)
k is the rate constant of the reaction
t is time elapsed
What is the integrated rate law expression of a zero order reaction? (in terms of product)
x=kt
where
x is the concentration of the product
k is reaction constant
t is time elapsed
For a zero order reaction, how is the rate of reaction related to rate constant?
Rate of reaction is equal to rate constant.
r=k
For a zero order reaction, what is the graph of reactant concentration against time? What is the slope of the graph?
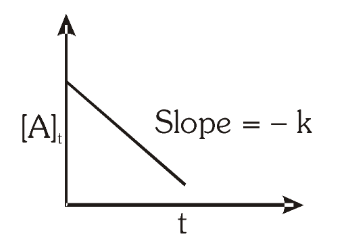
For a zero order reaction, what is the graph of product concentration against time? What is the slope of the graph?
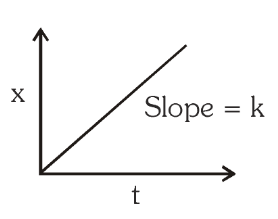
In a zero order reaction, what is the unit of the rate constant?
mol\ L^{-1}\ s^{-1}
(same as unit of rate of reaction)
For a zero order reaction, what is the graph of rate of reaction vs concentration of product/reactant?
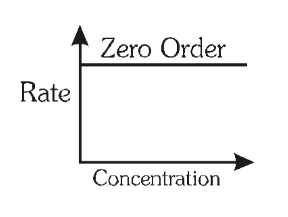
For a zero order reaction, what is the graph of rate of reaction vs time elapsed?
What is the “half life” of a reaction?
It is the time period in which half of the reactant is converted into product.
At half life of a reaction, t=t_{\frac12}. What is the relation between [A]_t and [A]_0?
[A]_t=\dfrac{[A]_0}{2}
For a zero order reaction, what is the formula for half-life of the reaction?
t_{\frac12}=\dfrac{[A]_0}{2k}
For a zero order reaction, What is the formula for Time For Completion of reaction?
t_{100}=\dfrac{[A]_0}{k}
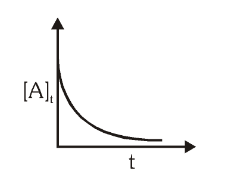
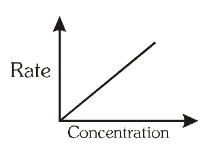
What is a First Order Reaction?
A reaction in which the rate of reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reaction.
Radioactive decay is a reaction of which order?
first order
Acidic hydrolysis of water is a reaction of which order?
first order
Decomposition reactions are of which order?
first order
What is the integrated rate law expression for first order reactions?
List all four
\ln [A]_t=\ln [A]_0-kt
[A]_t=[A]_0e^{-kt} (Wilhelmy equation)
kt=\ln\Bigg( \dfrac{[A]_0}{[A]_t}\Bigg)=\ln\Big(\dfrac{a}{a-x}\Big)
kt=2.303\log\Bigg( \dfrac{[A]_0}{[A]_t}\Bigg)=2.303\log\Big(\dfrac{a}{a-x}\Big)
For a first order reaction, what is the unit of rate constant?
time^{-1}
For a first order reaction, what is the graph for the natural log of concentration of reactant vs time? What is the slope?
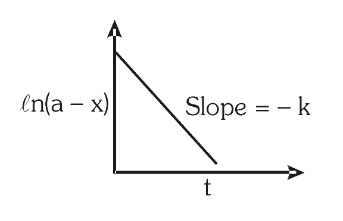
For a first order reaction, what is the graph for the concentration of reactant vs time?
For a first order reaction, what is the graph of rate of reaction vs concentration of reactant?
For a first order reaction, what is the formula for half-life of the reaction?
t_{\frac12}=\dfrac{\ln2}{k}
For a first order reaction, what is the graph of half-life vs the initial reactant concentration?
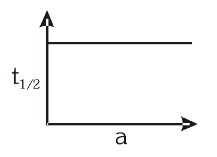
For a first order reaction, what is the total time for the completion of the reaction?
It is not defined, because yeah
In first order reactions, what is the formula for calculating the time period for x% completion of reaction?
t=\dfrac{2.303}{k}\log\Big(\dfrac{100}{100-x}\Big)
where
x is the percentage of completion
for a first order reaction, what is the formula to calculate the rate constant of the reaction, when given the concentrations of the reactant at two different time stamps, as well as the initial concentration?
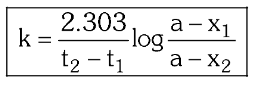
In a zero order reaction, an equal ____ of reactant will decompose in equal time.
In a first order reaction, an equal ____ of reactant will decompose in equal time.
(percentage, amount)
In a zero order reaction, an equal amount of reactant will decompose in equal time.
In a first order reaction, an equal percentage of reactant will decompose in equal time.
In second order reactions, what is the rate law expression?
\dfrac{1}{[A]_t}=\dfrac{1}{[A]_0}+kt
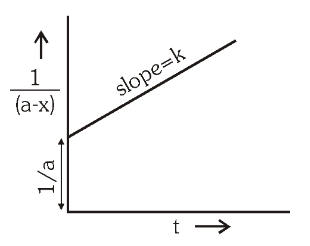
For second order reactions, what is the graph of \dfrac{1}{[A]_t} against time?
For second order reactions, what is the formula for half-life?
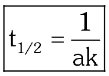
For second order reactions, what is the graph for half-life against initial concentration?
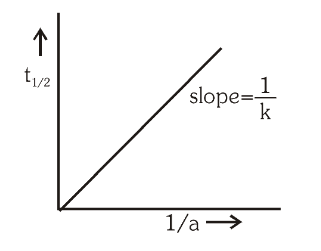
What is the General Integrated Rate Law for nth order reactions?
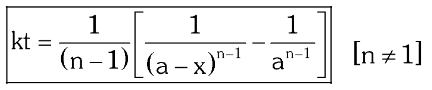
How do you derive the General Integrated Law for nth order reactions?
Integrate r=\dfrac{-d[A]}{dt}=k[A]^n
What is the general graph for \dfrac{1}{[A]_t^{n-1}}=\dfrac{1}{[A]_0^{n-1}}+kt(n-1) ?
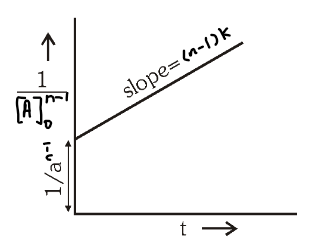
What is the general unit of rate constant?
\Big(\dfrac{mol}{L}\Big)^{1-n}\ sec^{-1}
What is a pseudo uni-molecular reaction?
A reaction in which the order of reaction is 1 but its molecularity is more than 1
Why is the acidic hydrolysis of ester a pseudo uni-molecular reaction?
Since H_2O is taken in excess, the concentration of H_2O does not change much during the reaction so even though the molecularity is 2, the concentration of H_2O does not affect the rate law expression.
What is the general formula for calculating the half-life of an nth order reaction?
t_{\frac12}=\dfrac{1}{k(n-1)}\Big(\dfrac{2^{n-1}-1}{a^{n-1}}\Big)
How is half-life related to the initial concentrations of reactions, for nth order reactions?
t_{\frac12}\propto \dfrac{1}{a^{n-1}}
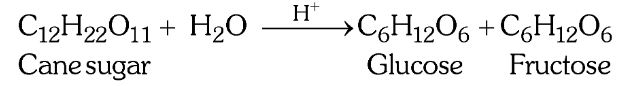
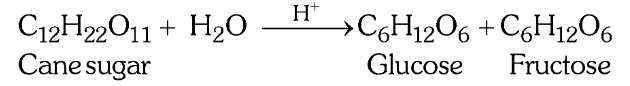
Why is the inversion of cane sugar a pseudo unimolecular reaction?
Since H_2O is taken in excess, the concentration of H_2O does not change much during the reaction so even though the molecularity is 2, the concentration of H_2O does not affect the rate law expression.

What is the order of this reaction?
What is the molecularity of this reaction?
1
2
What is the order of this reaction?
What is the molecularity of this reaction?
1
2
What is the rate law expression of this reaction?

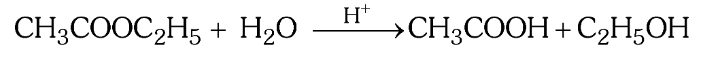
What is the rate law expression of this reaction?

What is the Initial Rate Method to determine the order of a reaction?
It works by taking ratios of different initial rates of a reaction by changing the cocentration of only one of the reactants while the concentration of the other reactants is kept constant.
What is the Half Life Method to determine the order of a reaction?
Calculating the order using two initial concentrations and their half life.
What is the formula for calculating the order of a reaction using the half lives of two different reactant concentrations?
\dfrac{(t_{\frac12})_1}{(t_{\frac12})_2}=\Big(\dfrac{([A]_0)_2}{([A]_0)_1}\Big)^{n-1}
What is the formula for calculating the order of a reaction using the initial concentration, the given concentration, and the number of half-lives during that interval?
[A]_t=\dfrac{[A]_0}{2^n}
Where n is the number of half-lives n that time interval during reaction (\dfrac{t_{\text{total}}}{t_{\frac12}}).