Kinesiology Exam Questions
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Say a person of 86 kg stands on a single leg. Please indicate the reaction force:
-843.66 N
Person #1 provides a force of 100 N in the negative direction while person #3 provides a force of 200 N in the positive direction. Please indicate the magnitude of the resulting force and its direction:
+100 N to the right (positive direction)
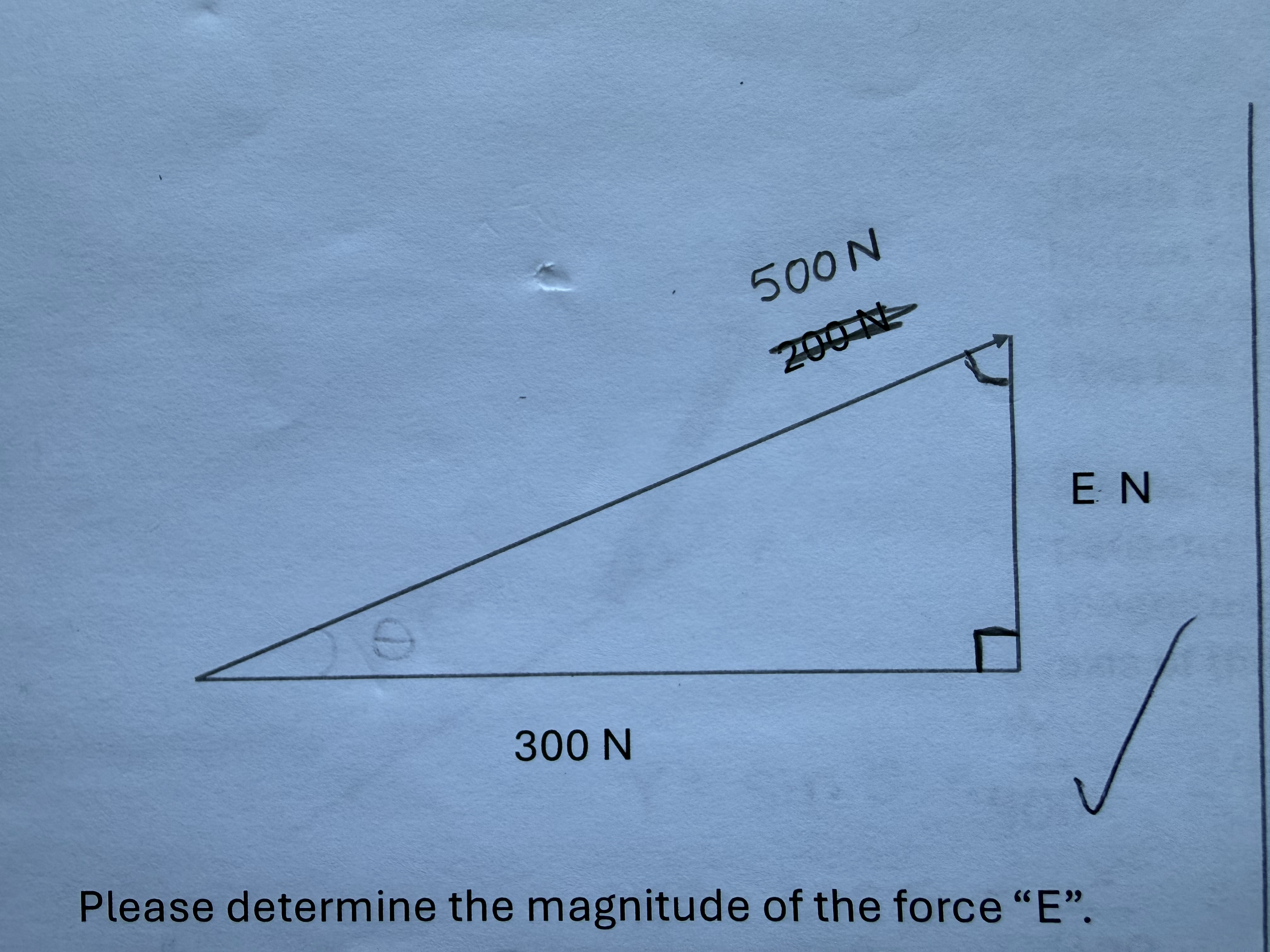
400 N
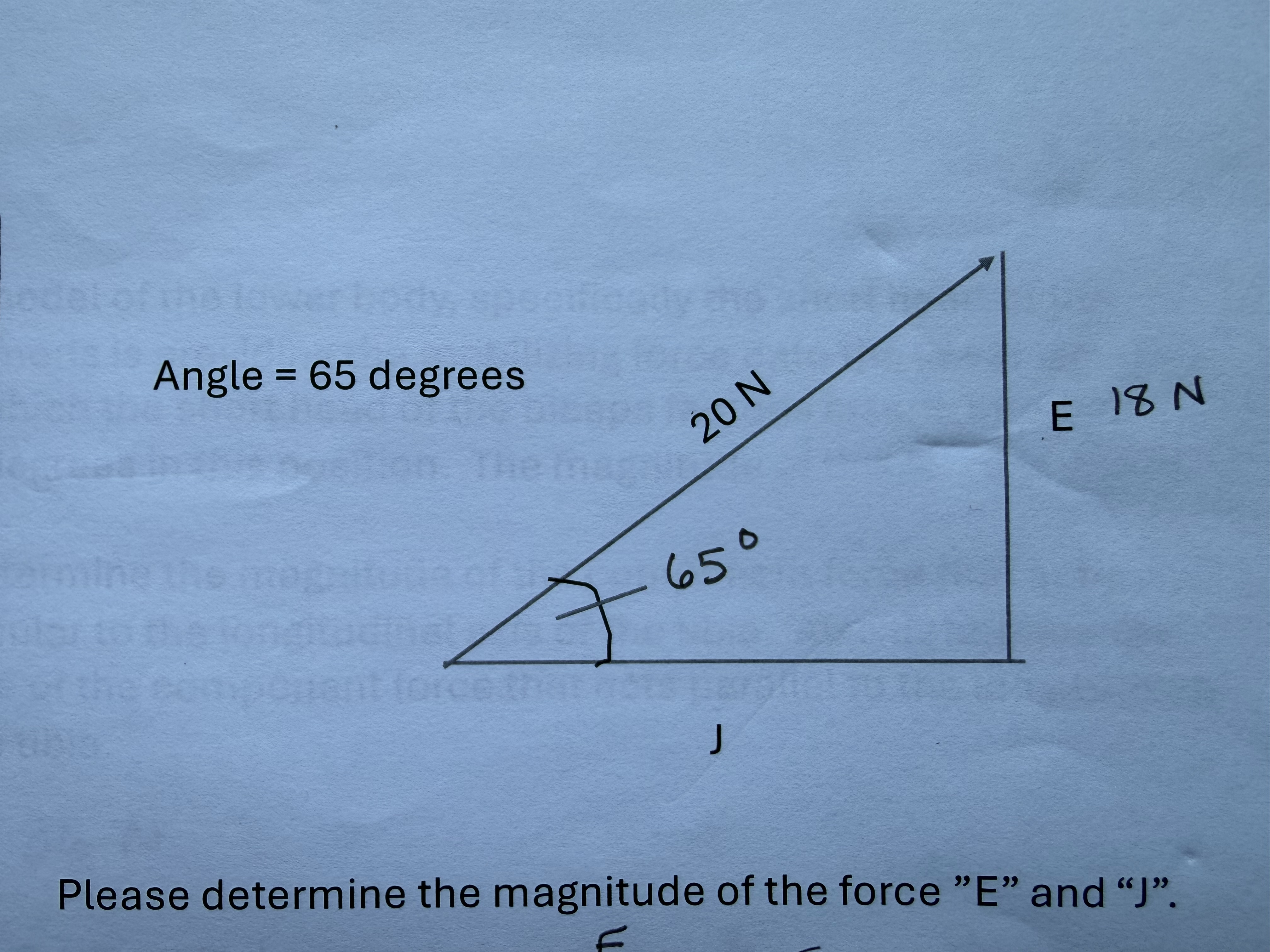
E = 18.13 N
J = 8.45 N

Perpendicular Force = 34.86 N
Parallel Force = 398.48 N
Bob has a mass of 120 kg. What is his weight in Newtons?
-1176 N
What is the magnitude of the normal force acting on Bob?
+1176 N
Assume that for a moment Bob has a mass of 120 kg’s and his walking motion produces a 100 N force that acts within the + direction. The static coefficient of friction is 0.5.
Provide the magnitude of force necessary for his weight bearing foot to begin moving in the (-) direction:
-588 N
Given that Bob produces a force in the (+) direction that is 100 N, did Bob produce enough force for his weight-bearing foot to “slip” (move in the (-) direction)?
No
Bob is now hanging stationary in all directions from “still rings.” He is 2m above the floor.
How much total force must his arms be placing on the still rings?
1176 N
Bob is now hanging stationary in all directions from “still rings.” He is 2m above the floor.
Now he increases the force produced within his arms by 50 N.
In which direction will his body move?
Up
What is the equation for acceleration?
a = change in velocity / change in time
Vinitial = 0m/s
Vfinal = ?
Time initial = 0 sec
Time final = 0.64 sec
Bob is now hanging stationary in all directions from “still rings.” He is 2m above the floor.
Find Bob’s downward velocity at the end of the 2m drop from the still rings.
-3.125 m/s
Bob (120kg) releases the still rings and is free falling. At a point in time Bob’s kinetic energy is calculated to be 15 J.
Please calculate Bob’s velocity at the point his kinetic energy is 15 J.
Equation given: KE = 1/2mv²
0.5 m/s
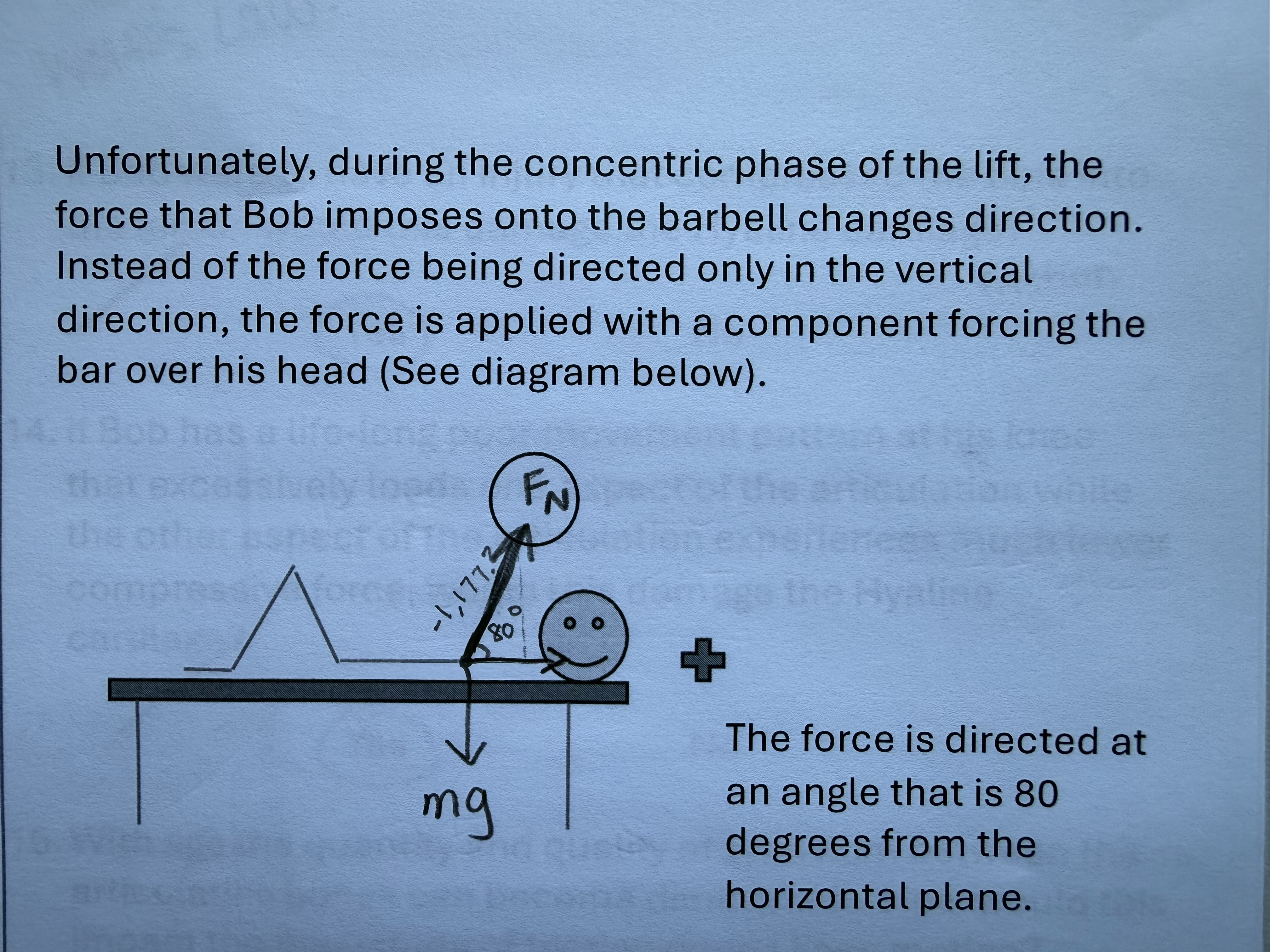
Bob moves to the strength room to do some bench press work. Currently he’s working with 120 kg. On the eccentric phase Bob produces a force that is -1177.2 N. The vertical displacement of the barbell is 0.35m.
Please determine the quantity of work that Bob performed in this one repetition:
-412.02 J
Determine the force that is acting in the (+) horizontal direction
+204 N
Why is it important for the articulating bones to have firm and smooth surfaces between them?
To lessen the amount of friction between the articulation bones.
If Bob were to have an injury that compressed the tibia into the femur, would this damage the Hyaline cartilage?
Yes
If Bob has a life-long poor movement pattern at his knee that excessively loads one aspect of the articulation while the other aspect of the articulation experiences much lower compressive force, would this damage the Hyaline cartilage?
Yes
With age the quality and quantity of synovium between the articulation bones can become diminished. How would this impact the magitude of friction during knee motion?
Increase
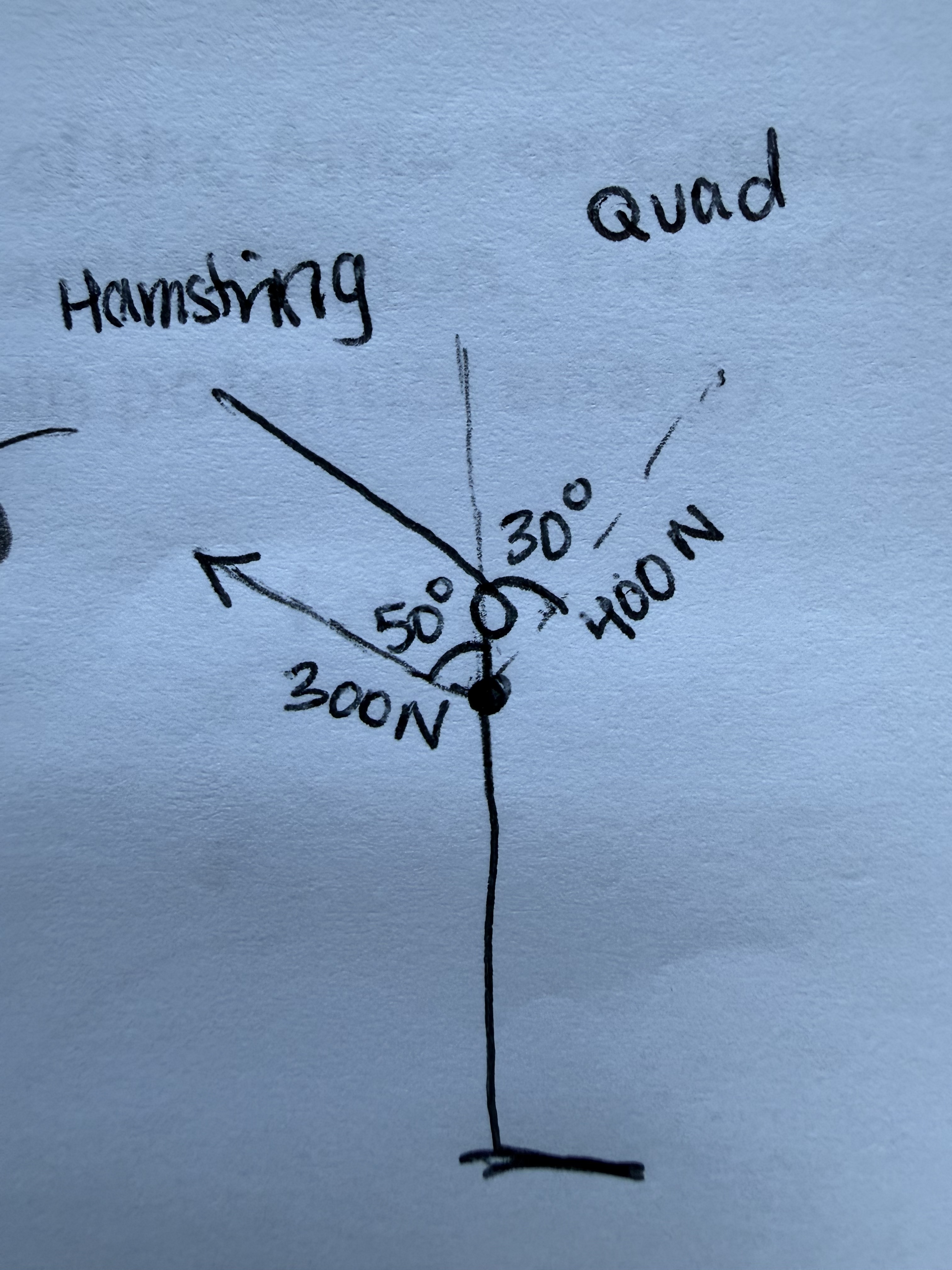
Bob sticks the landing!
What is his anterior displacement force?
200 N
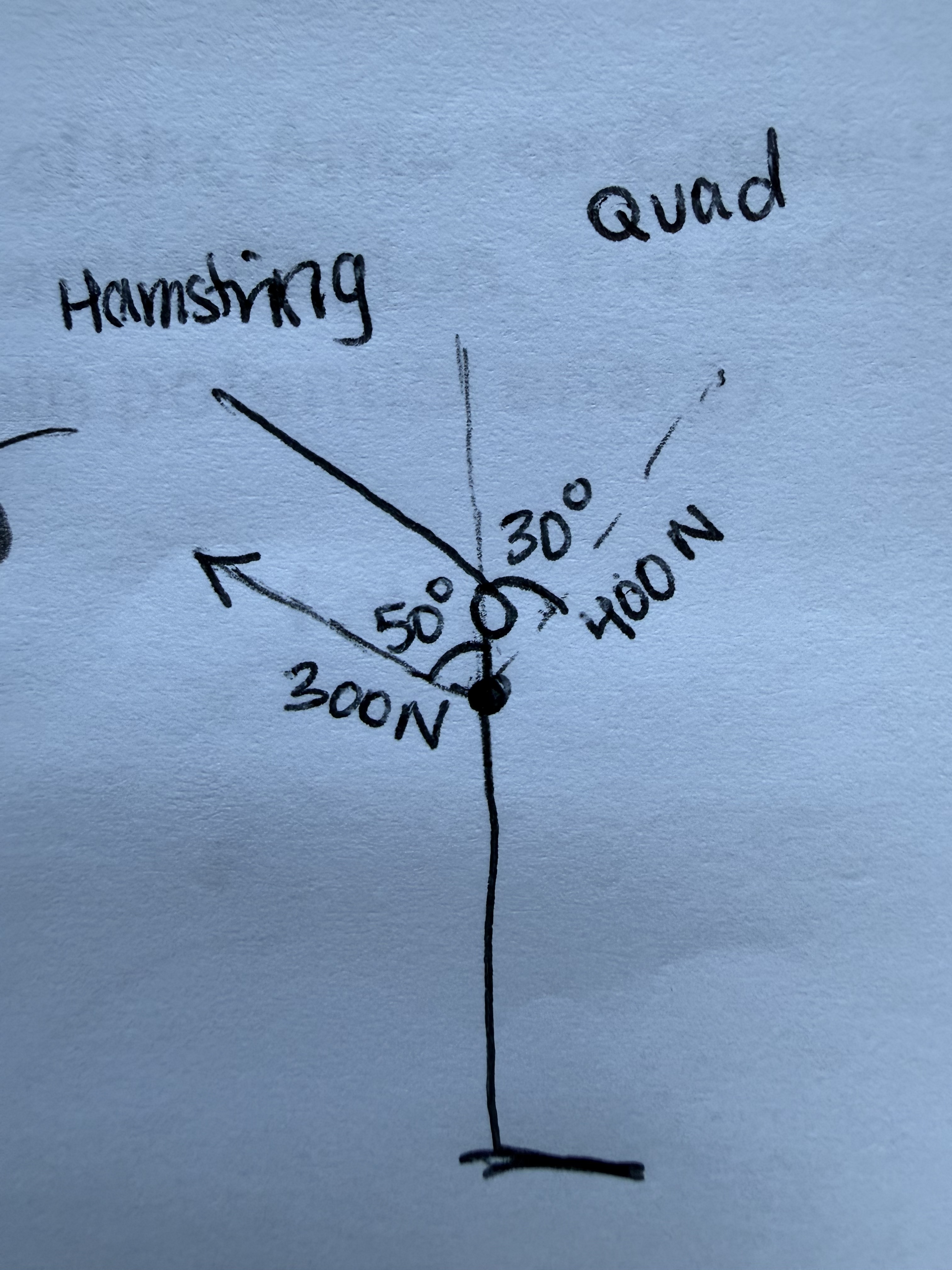
Bob sticks the landing!
What is his posterior displacement force?
229.81 N
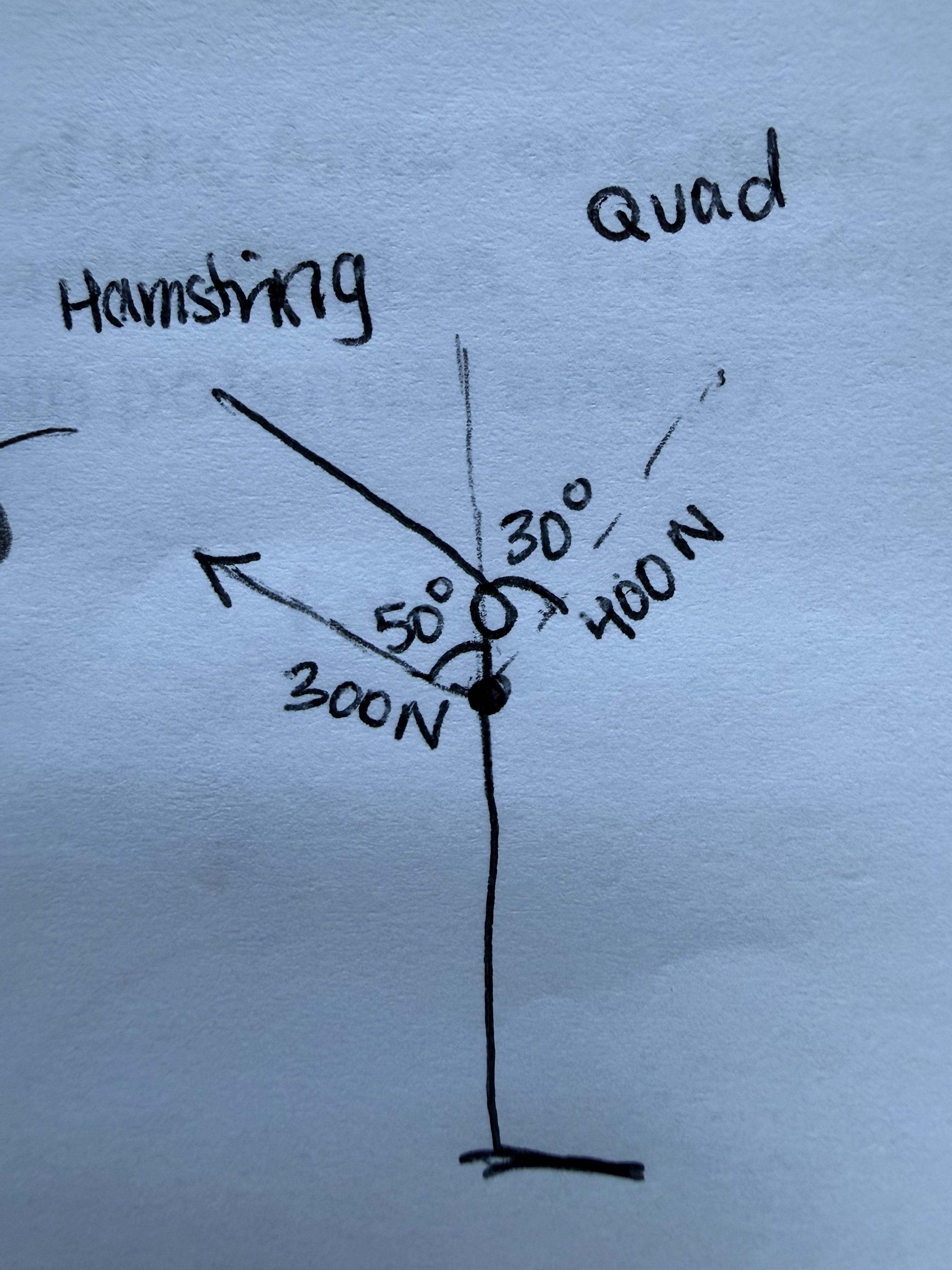
The net force acting within the sagittal plane about the frontal axis is?
29.81 N
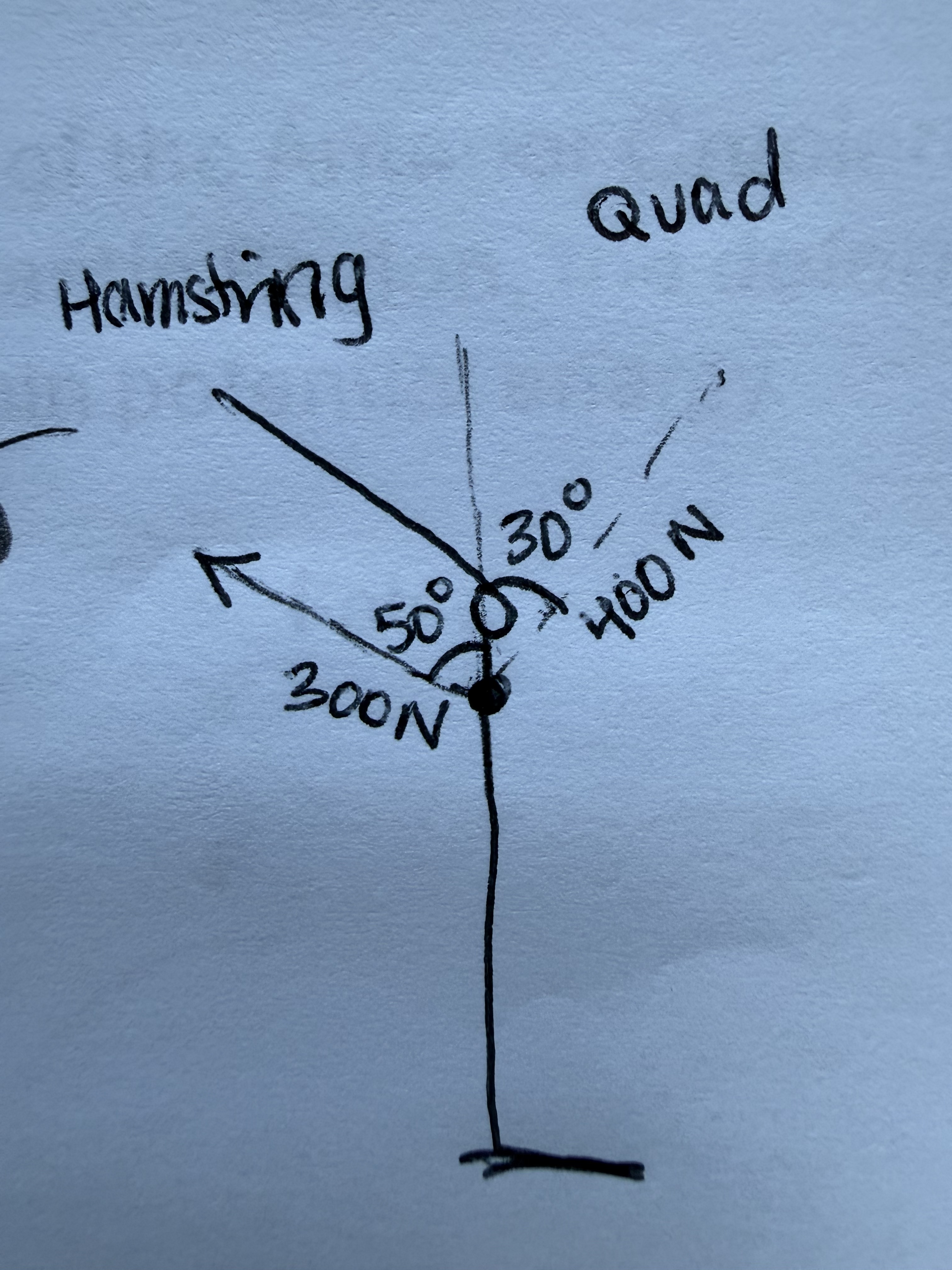
Given the information provided to you, do you have concern for the ACL?
No
What is the function of the anterior cruciate ligament?
To prevent excessive anterior translation of the tibia relative to the femur
Assuming the deformation of the ACL remains within the Elastic Region the deformation of the ligament represents the strain potential energy.
True
Did the anterior cruciate reconstructed subjects demonstrate bilateral force production symmetry when compared to the individuals who did not have this surgery?
No
Bob is performing a counter jump exercise. Remember his mass is 120 kgs. During the concentric phase of the jump and while his feet remain on the floor, the vertical displacement of his body is +75 m.
What is the quantity of work accomplished?
882 J
Say Bob work 882 J. He accomplished this work in 0.25 seconds. What is the quantity of power that Bob produces?
3528 Watts
Say Bob goes a distance of 0.75m in 0.25 seconds. What is the average velocity of the upward movement? Remember velocity at the initiation of the concentric phase is 0 m/s
3 m/s
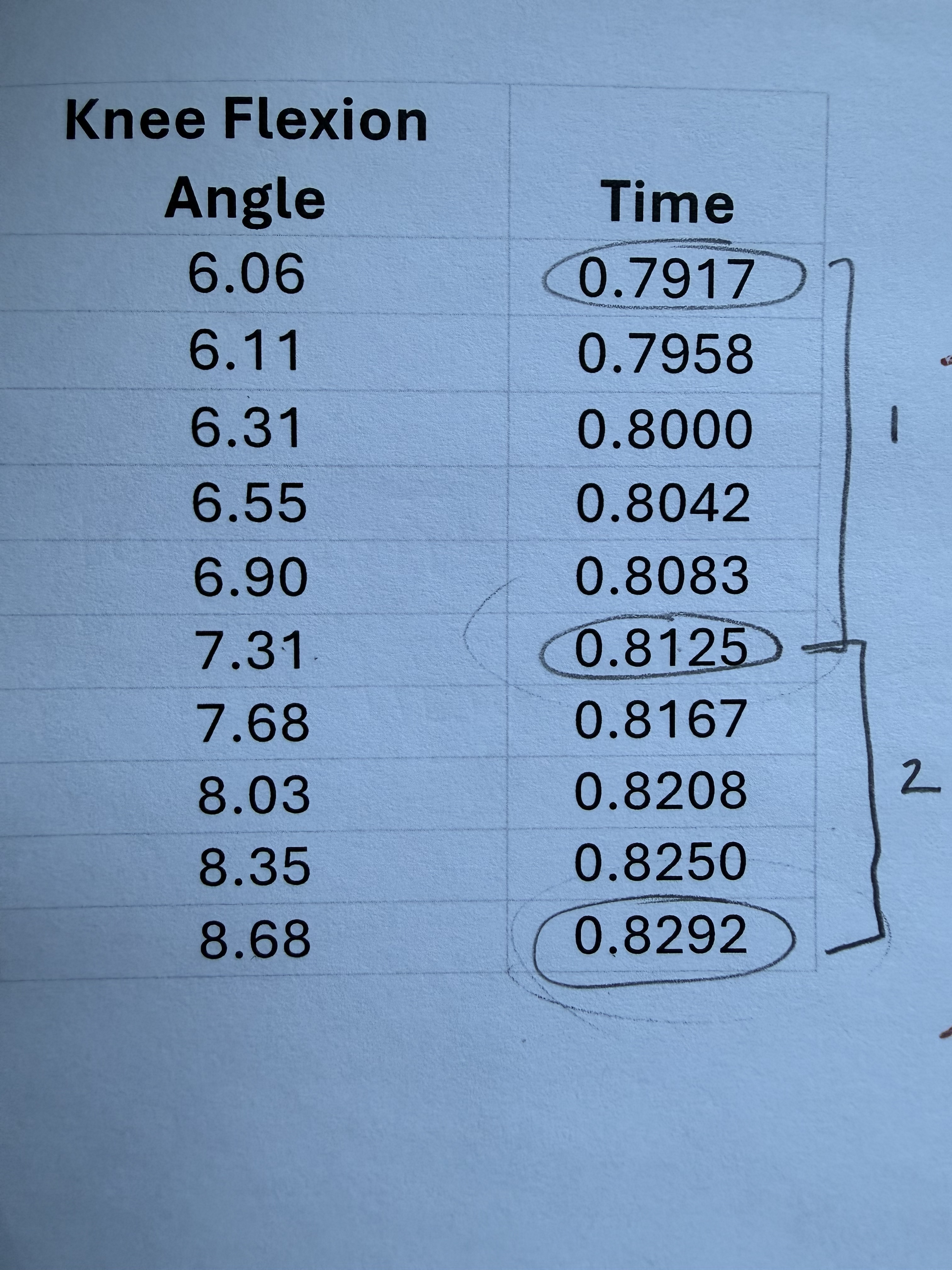
For the time period between 0.7917 and 0.8125 seconds.
What is the average velocity of knee flexion?
60.10 degrees/sec
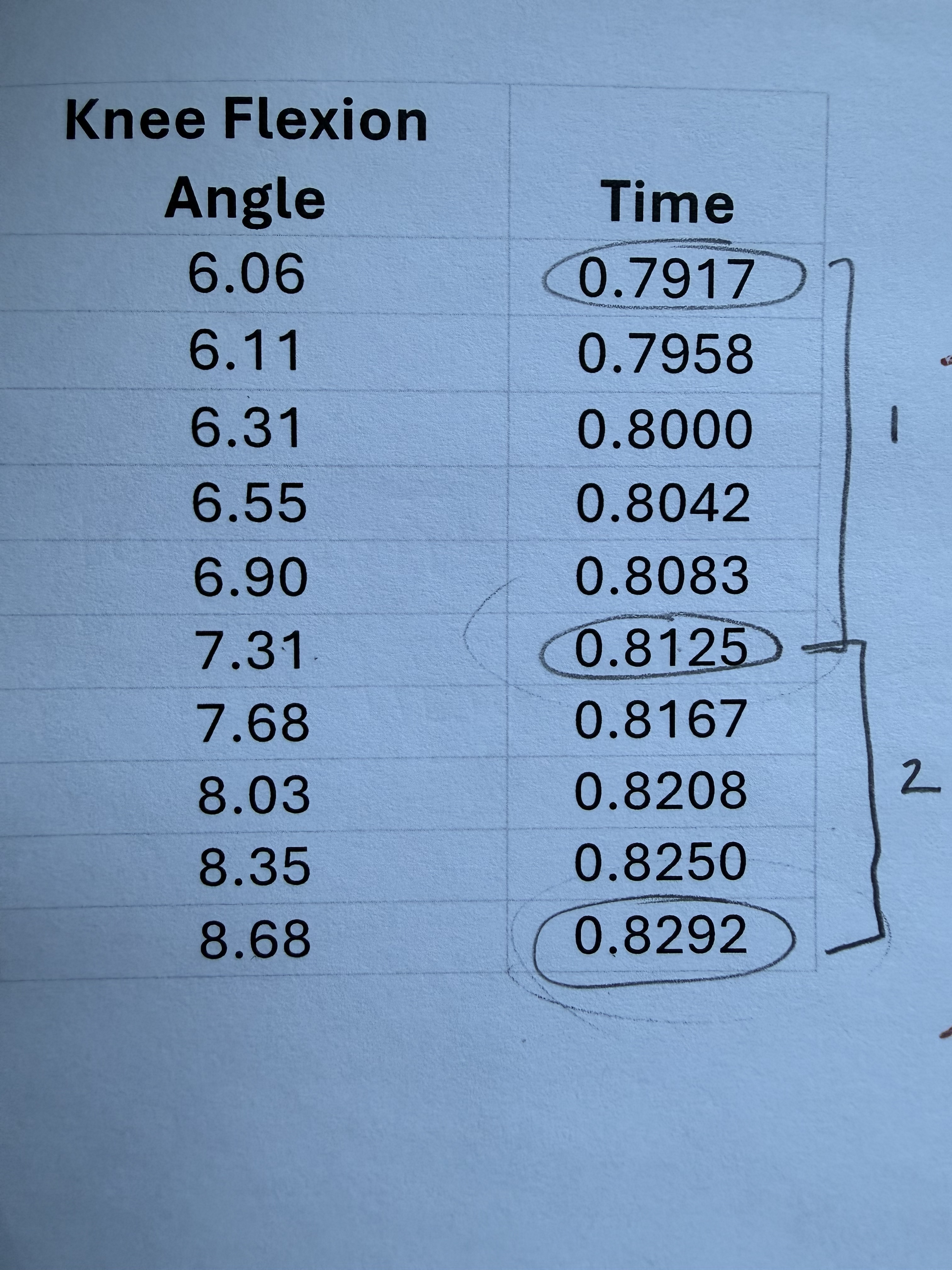
For the time period between 0.8125 and 0.8292 seconds.
What is the average velocity of knee flexion?
82.04 degrees/sec
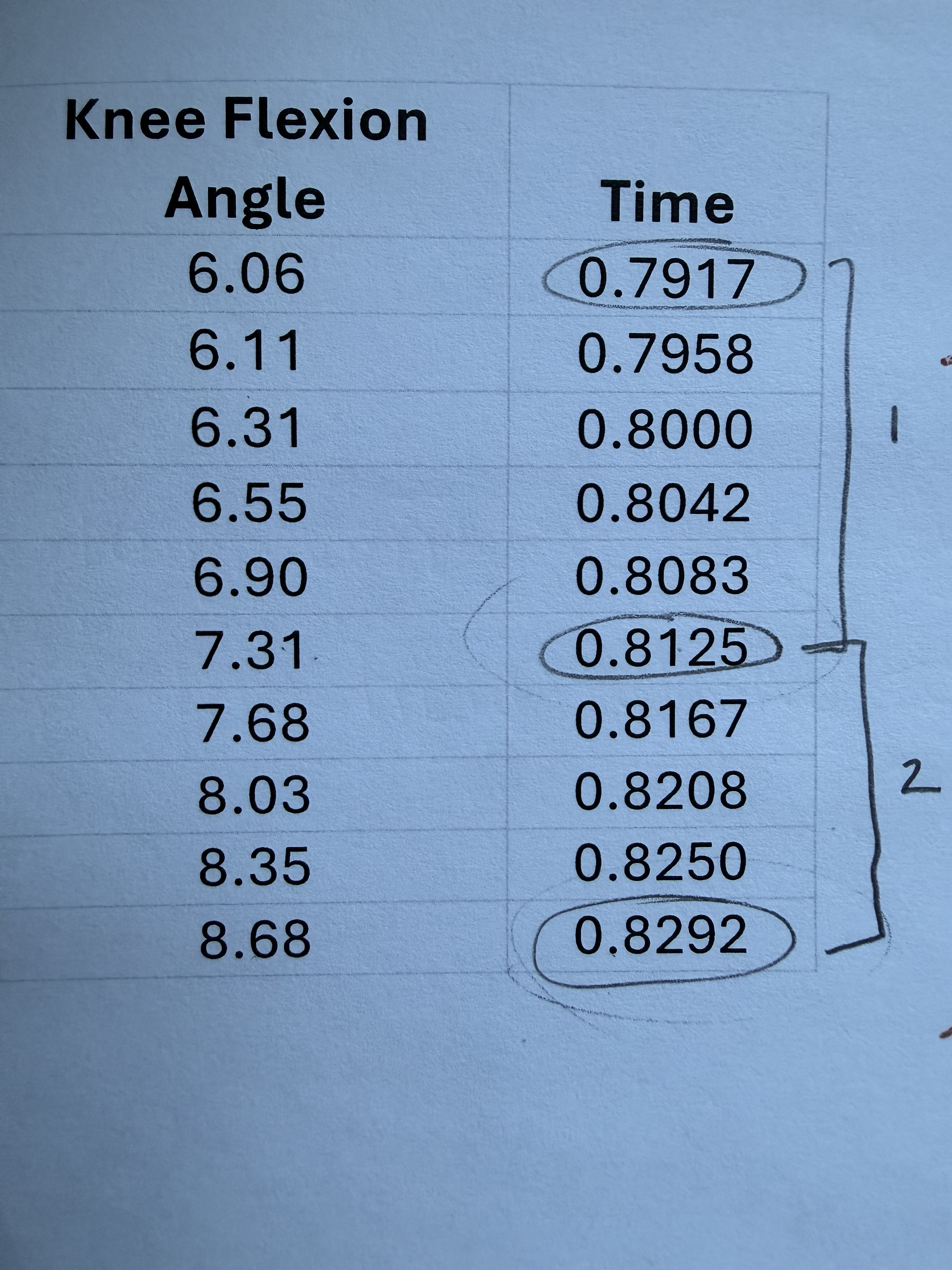
Say the two velocity values are 60.10 degrees/s and 82.04 degrees/s
What is the average acceleration that occurs from the end of the first time interval and the end of the second?
1313.77 degrees/sec²
Uniplanar motion within the frontal plane around the anterior posterior axis of rotation is associated with which two angular directions at the ankle?
Inversion/Eversion
Flexion of the foot is defined as…
Motion in the sagittal plane about the frontal axis of rotation such that the angle formed by anterior aspects of the articulating bone decreases
Uniplanar motion within the transverse plane around the longitudinal axis of rotation is associated with which two angular directions at the ankle?
Internal Rotation / External Rotation
Within the ankle we will find true uniplanar motion occur
False
A push up exercise is an example of a closed kinetic chain of the upper extremity.
True, because this exercise places the distal aspect of the upper extremity on a stable platform
Pronation of the foot & ankle in an open kinetic chain includes which motions?
Flexion of the foot
External rotation of the calcaneus & talus
Eversion of the calcaneus
Extension of the foot
Inversion of the calcaneus
What additional motion would complete the requirement for open kinetic chain supination?
Internal rotation of the calcaneus & talus
What are the motions associated with closed kinetic chain pronation?
Talus & tibia internal rotation
Talus extension
Calcaneus eversion
Your patient explains that they injured their ankle during a fall in which they experienced excessive foot extension, inversion of their heel bone, while twisting their foot into internal rotation. This mechanism of injury would be classified as a _?
Supination mechanism
Most in vivo studies that have examined the correlations between the integrity of the plantar fascia and long plantar ligament with the collapse of the medial longitudinal arch yields results that are…
damage to the plantar fascia and long plantar ligament have conflicting and inconclusive association with the quality of the medial longitudinal arch
Which of the following statements are an accurate characterization of the study’s hypothesis?
Drastic collapse of the longitudinal arch of the foot under the body weight condition only occurs with both the plantar fascia and long plantar ligament are completely torn
Which one prevents a drop in navicular height more? Long plantar ligament or plantar fascia?
plantar fascia
Say the ankle joint can bear a force five times body weight during a normal walking stance. Assume 66 kg individual. What is the magnitude of the ground reaction force in N?
+3234 N
Assuming this person has a functioning medial longitudinal arch, what do you expect the magnitude of the ground reaction force to be as it moves into the tibia?
less
Pes cavus is associated with which tri-planar motion of the ankle?
Supination
In a closed kinetic chain of the lower extremity supination is associated with which motions?
Talus & tibia external rotation
Talus flexion
Calcaneus inversion
What is the compartment of the lower leg that will facilitate the motion of foot flexion?
anterior
What are the two muscles that are found within the lateral compartment of the lower leg?
Fibularis longus
Fibularis brevis
What is the compartment of the lower leg that will facilitate the motion of eversion?
lateral
What is a muscle that is found within the posterior superficial compartment of the lower leg?
Soleus
Which of the following muscles will facilitate inversion?
posterior tibialis
Which of the following muscles will elevate the medial longitudinal arch?
anterior tibialis
A significant increase in the navicular drop test is associated with which motion?
excessive pronation
Assume you need to provide an orthotic in order to correct for your patient’s excessive pronation. How will you posture the foot it form the mold?
talar neutral
When you properly posture the foot & ankle to form the orthotic mold for your patient, you raise and lower the medial longitudinal arch until you can palpate the talus on the lateral aspect.
false
When considering movement at the sternoclavicular articulation, which bone is considered to be the more stable bone?
Manubrium
Within the transverse plane about the longitudinal axis of rotation, the motion occurring at the sternoclavicular articulation is…
Protraction / Retraction
Within the frontal plane the clavicle has a ______ shape.
Convex
Given that the angular motion occurring at the sternoclavicular articulation is elevation, in which direction will the proximal aspect of the clavicle glide?
Inferior
Given that the angular motion ocurring at the sternoclavicular articulation is protraction, in which direction will the proximal aspect of the clavicle glide?
Anterior
Which of the following ligamentous static stabilizers will prevent excess depression of the clavicle?
Interclavicular ligament
During sternoclavicular retraction, which ligament will prevent the associated excessive linear glide of the clavicle?
Anterior sternoclavicular ligament
Does the sternoclavicular articulation have an articular capsule?
Yes
What type of connective tissue forms articular capsule?
dense irregular
Which type of boney architecture does the acromioclavicular articulation have?
Neither, both the clavicle and the scapula have a flat shape
Within the transverse plane about the longitudinal axis of rotation, the scapula will move in the following direction
External / Internal Rotation
Within the frontal plane about the anterior posterior axis of rotation, the scapula will move in the following direction
Upward / Downward rotation
Within the sagittal plane about the frontal axis of rotation, the scapula will move in the following direction
Anterior / Posterior tilt
This ligament that augments the stability of the acromioclavicular articulation has collagen fiber that are all oriented horizontal to the surface
Acromioclavicular ligament
The force acting on the scapula that is attributed to a 10 kg arm.
98.1 N acting to move the scapula in the inferior direction
Assuming your arm is not moving in the superior or inferior direction, What is the magnitude of the force that the scapula must be applying to the clavicle?
98.1 N acting to move the scapula in the superior direction
The force the scapula applies to the clavicle will move through which of the following ligaments?
Acromioclavicular ligament
Trapezoid ligament
Conoid ligament
An injury (sprain) that involves all of the ligaments that support the acromioclavicular articulation will result in movement of which bone?
Scapula in the downward direction
Which of the following muscles will provide for the upward rotation motion of the scapula?
Superior Trapezius
Serratus Anterior
Inferior Trapezius
A dislocated “shoulder” refers to an injury that sacrifices the stability of which articulation?
Glenohumeral articulation
Which of the following uniplanar motions of the scapula will facilitate the superior spin of the clavicle?
Posterior tip
As the scapula experiences any triplanar motion that involves the uniplanar motion (posterior tip), the _____ ligaments pulls downward and forward on the inferior aspect of the clavicle. This explains the superior spin of the clavicle.
Acromioclavicular ligament
Coracoclavicular ligament
A high magnitude “seperated sholder” will not negatively alter the superior spin of the clavicle.
false
Contraction of the rhomboid major muscle will cause which motion of the scapula within the frontal plane about the anterior posterior axis of rotation
Downward rotation
Flexion of the humerus will cause which motion of the clavicle?
Retraction
Elevation
Superior spin
The shape of the glenoid fossa is…
Concave
The shape of the proximal humeral head is…
Convex
Assuming the humerus is the more mobile bone at the glenohumeral articulation. Assuming we abduct the humerus above the shoulder, what is the linear glide of the humerus?
Inferior
Movement at the glenohumeral articulation within the sagittal plane about the frontal axis of rotation is…
Flexion / Extension
Adduction of the humerus from 1 degree to 0 degree (against the side of your body) will result in an ______ linear glide of the proximal humeral head?
Lateral
The glenohumeral capsular ligament will prevent excessive motion within which plane?
Sagittal, frontal, transverse
Horizontal abduction of the humerus will be associated with which linear guide of the proximal humeral head?
Anterior
Which muscles will provide for adduction of the glenohumeral articulation?
Latissimus dorsi
Triceps brachii
Which ligamentous stabilizer of the glenohumeral articulation will prevent excessive inferior translation of the humerus relative to the glenoid fossa?
Inferior glenohumeral ligament
The function of the acromioclavicular ligament is…
Prevent excessive inferior displacement of the scapula on the clavicle