Biology- Exam 2: Ch 4-7
1/234
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
235 Terms
cytoplasm
jelly-like substance that contains dissolved molecular building blocks (proteins, nucleic acids, ions, etc.)
organelle
structures that carry out specialized functions within the cell; most are surrounded by a membrance
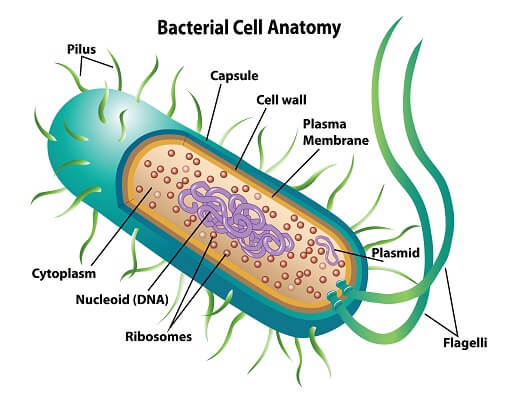
prokaryotic cell
(1) no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles
(2) dna is suspended in cytoplasm
(3) most are microscopic, single-celled organisms
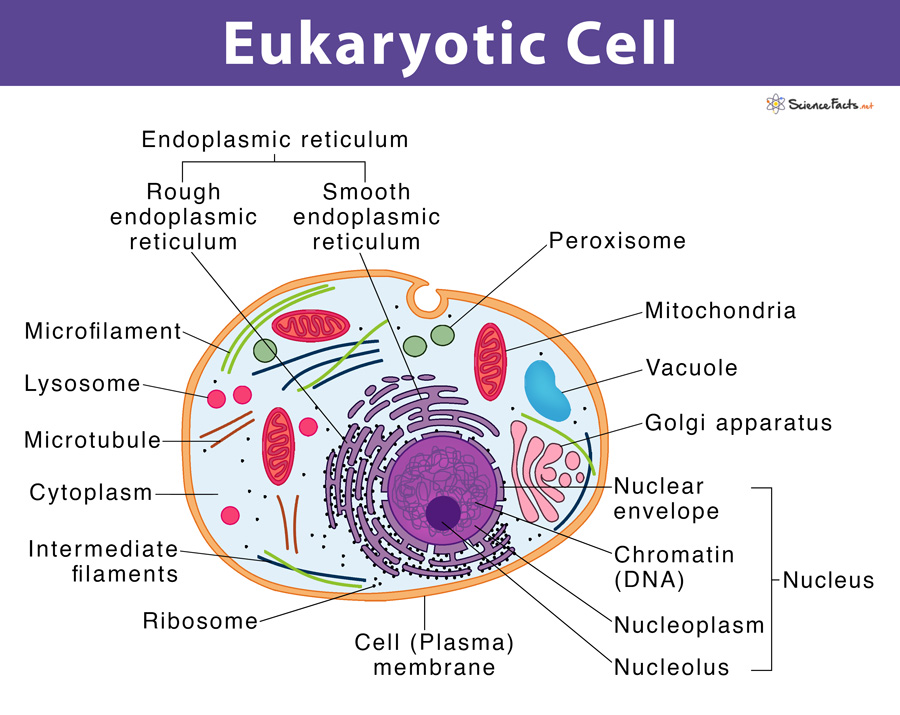
eukaryotic cell
(1) have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
(2) dna is enclosed in nucleus
(3) may be uni- or multicellular organisms
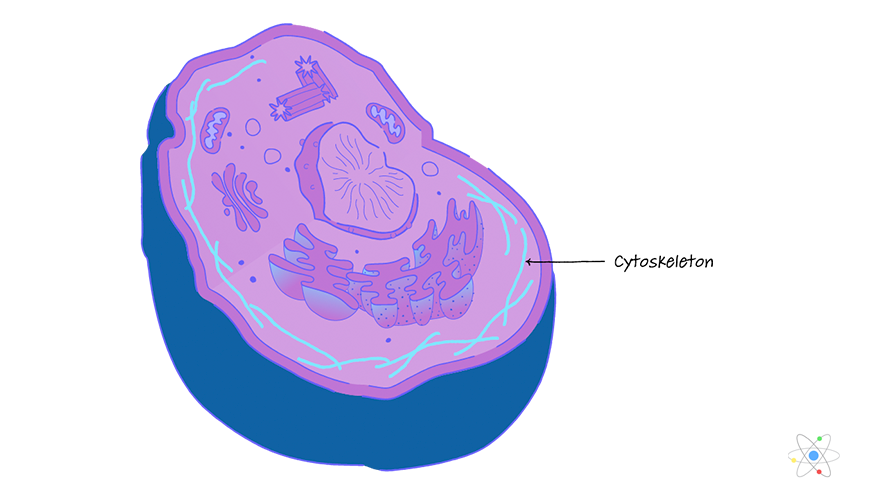
cytoskeleton
flexible network of proteins that provide structure to eukaryotic cells
actin filaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules
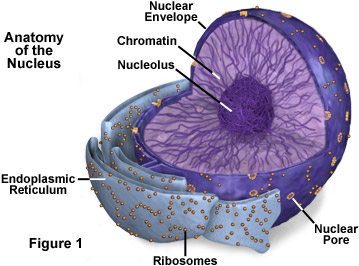
nucleus
storehouse for most of the genetic information in the cell
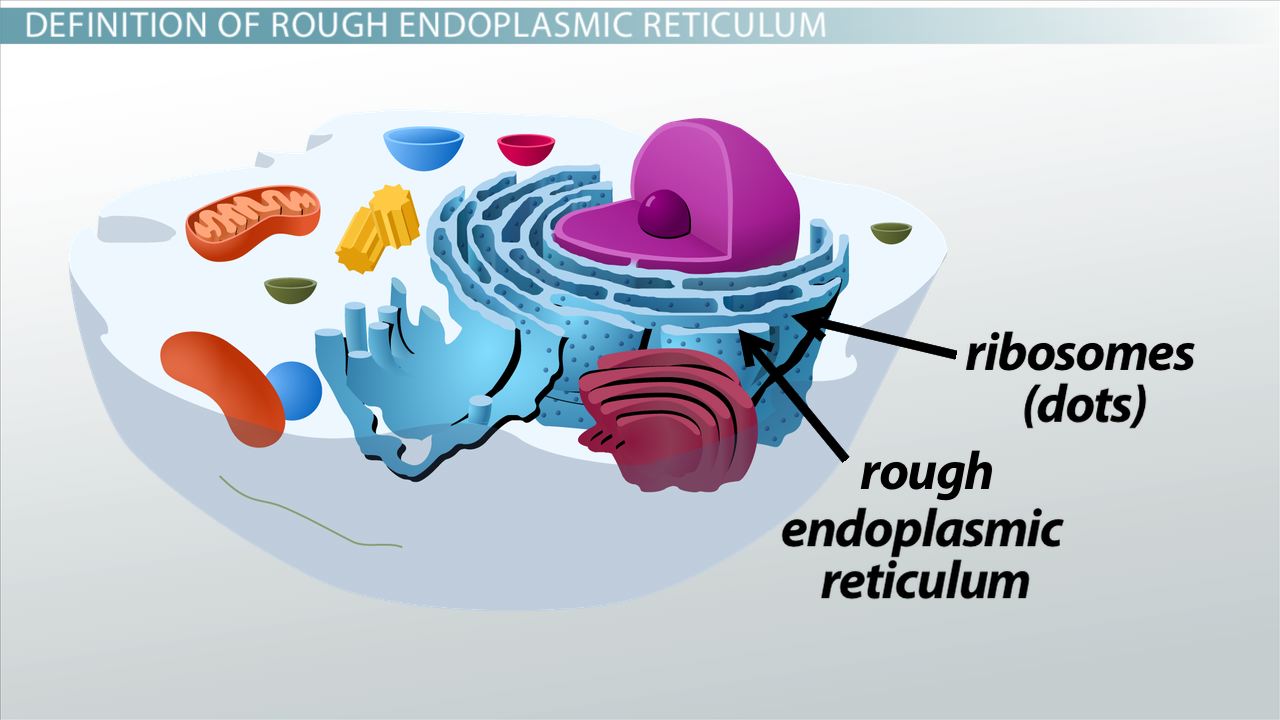
rough endoplasmic reticulum
interconnected network of thin, folded membranes that are studded with ribosomes; once a protein is produced, it moves into the lumen where it’s modified for folding and stability
synthesizes proteins
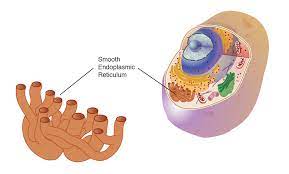
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
interconnect network of thin, folded membranes that are smooth (lack ribosomes) and produce lipids, as well as breaking down drugs, toxins, poisons, and alcohol
makes lipids
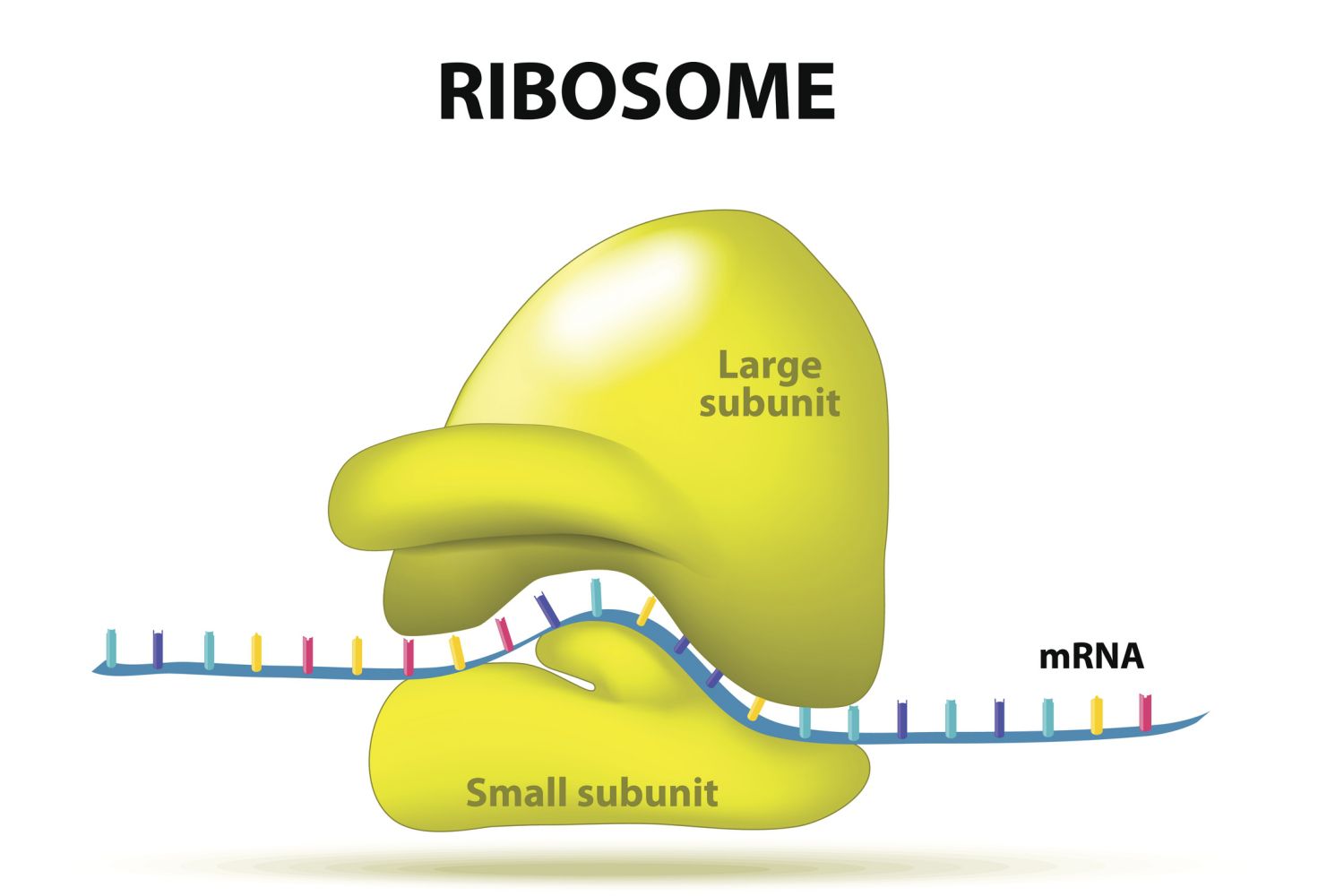
ribosome
site of and active participant in proteins synthesis (the linking of amino acids)
composed of rna and protein
non-membranous structure
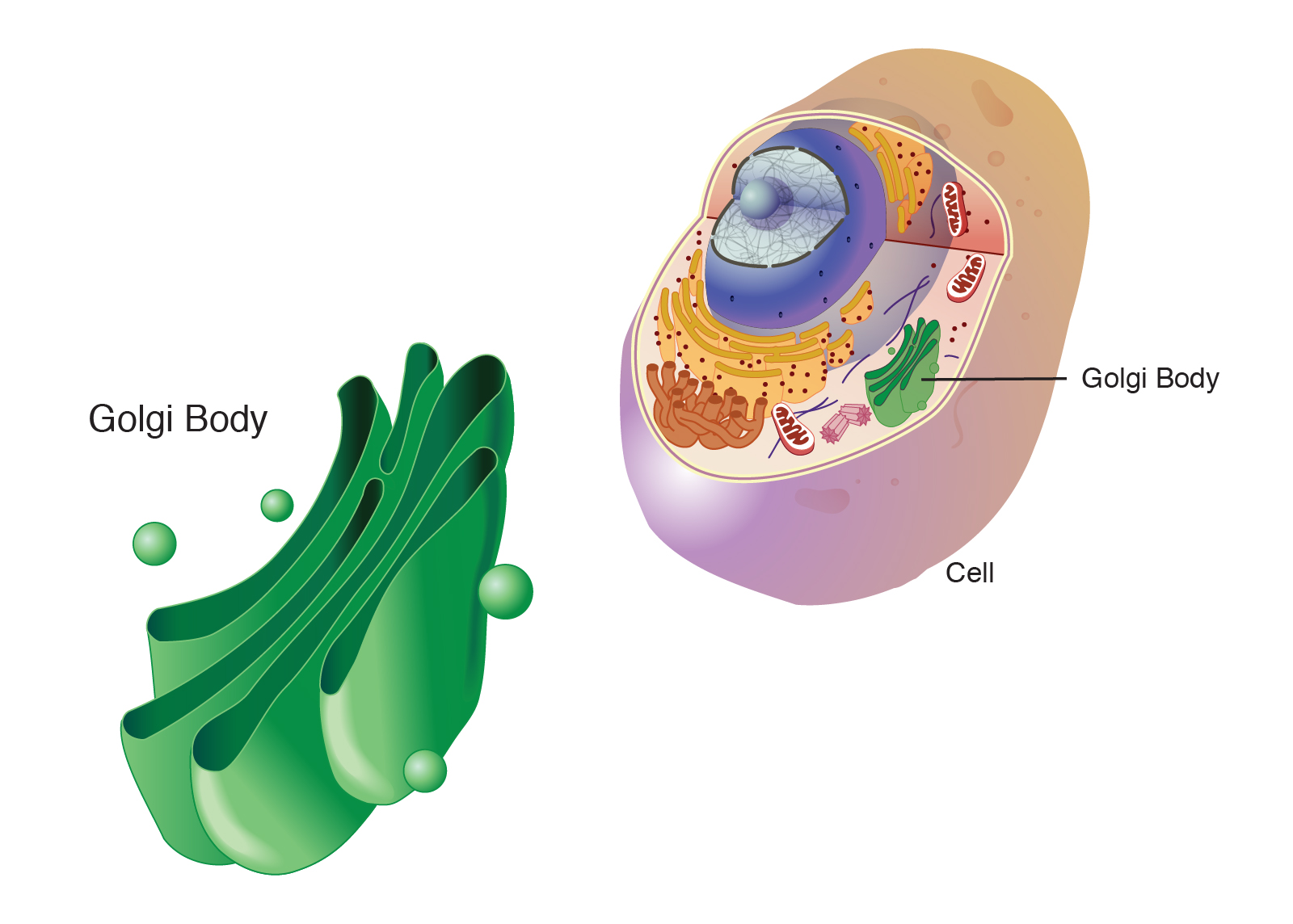
golgi apparatus
closely stacked layers of membrane-enclosed spaces that process, sort, and deliver proteins
packages and distributes proteins
vesicle
small, membrane-bound sacs that separate some material from the rest of the cytoplasm, transporting the materials from place to place within the cell
specializes in moving products into, out of, and within a cell
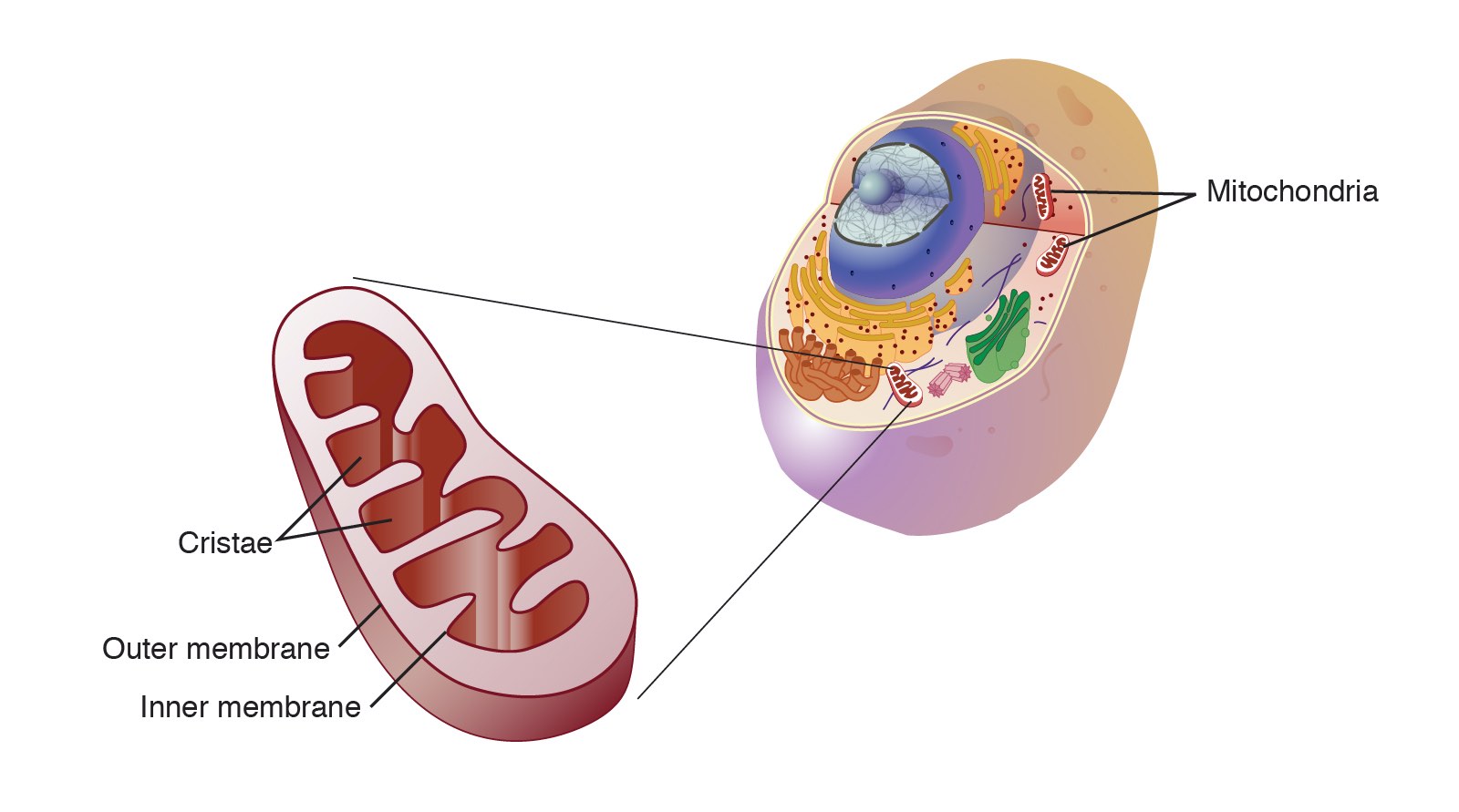
mitochondrion
bean-shaped and have two membranes; carries out series of chemical reactions that creates energy (ATP) for the cells from oxygen and sugar
participant in cellular respiration
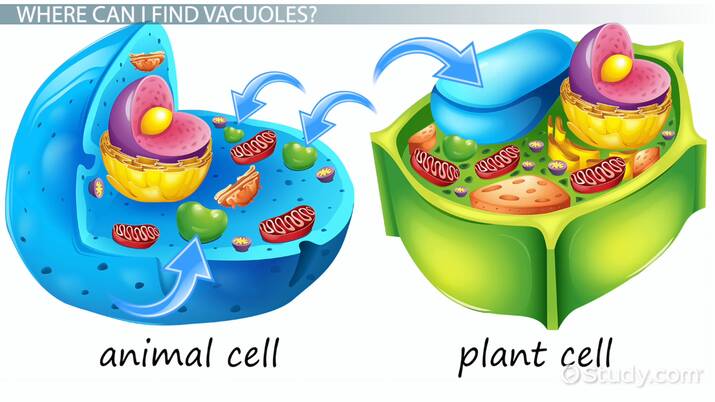
vacuole
a fluid-filled sac used for the storage of materials needed by the cell (water, food molecules, inorganic ions, enzymes, etc.)
central vacuole found in plant cells to equilibrate water diffusion with the environment
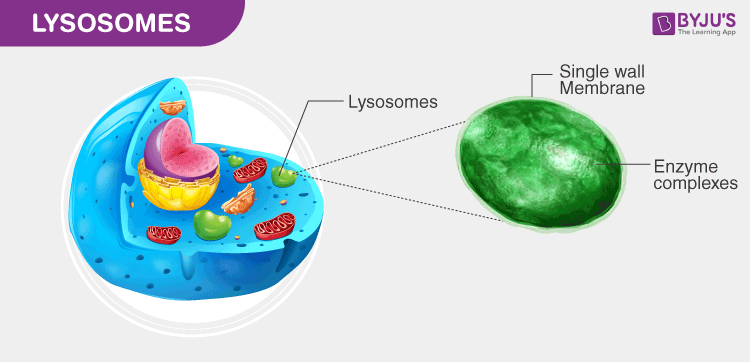
lysosome
membrane-bound organelle that contains digestive enzymes; ‘stomach’ of the cell
hydrolitic enzymes that break down waste
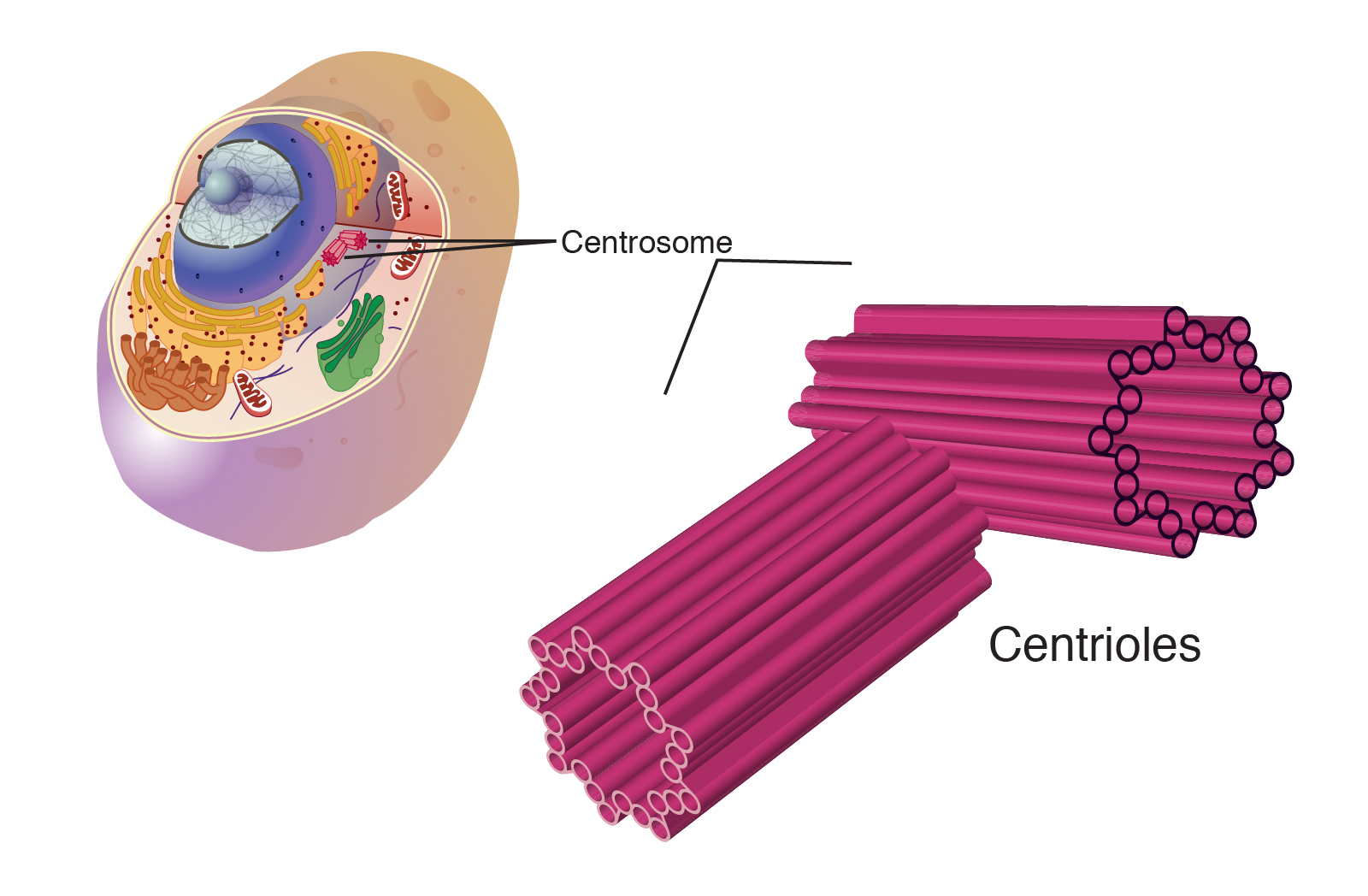
centrioles
cylinder-shaped organelles made of a set of nine triplets of microtubules; organize or ‘anchor’ microtubules
composed of microtubules
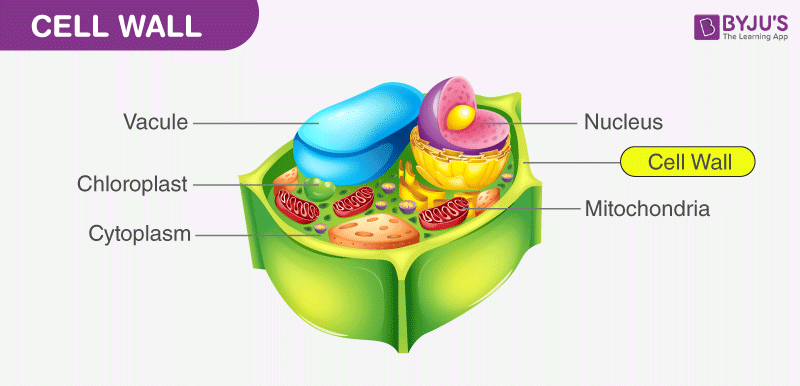
cell wall
rigid layer that gives protection, support, and shape to plant cells; made of the carbohydrate cellulose
structural cellulose
present in plant cells
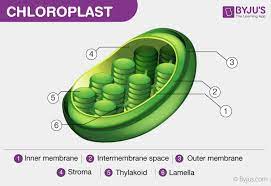
chloroplast
site of photosynthesis; highly compartmentalized, similar to mitochondria… have inner and outer membranes, as well as stacks of disc-shaped sacs within the inner membrane
chlorophyll, photosynthesis- converts CO2 and light and h20 to produce sugar and oxygen, double membranes
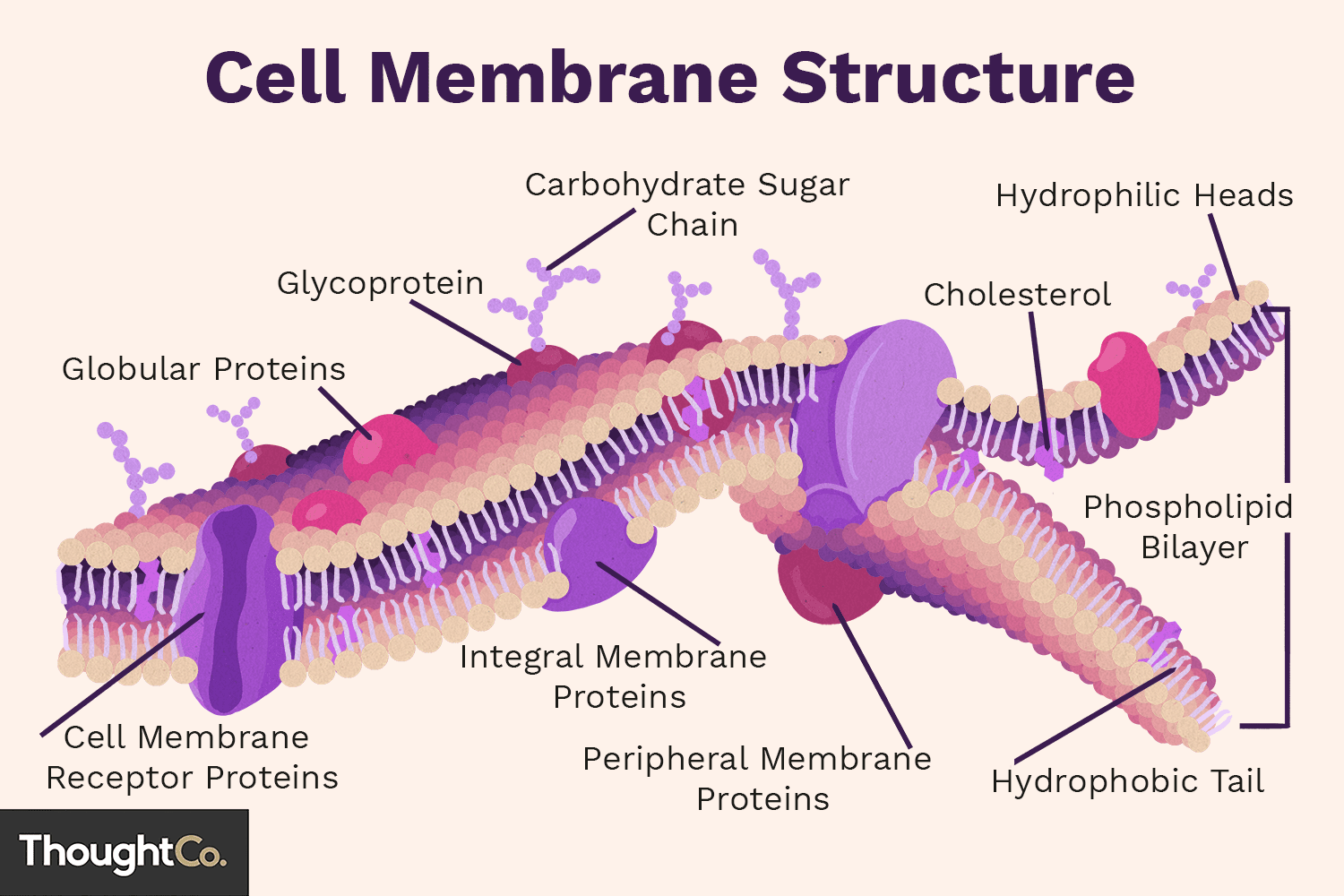
cell membrane
also known as plasma membrane; a phospholipid bilayer that separates intracellular space from extracellular space; controls passage of materials into and out of cell
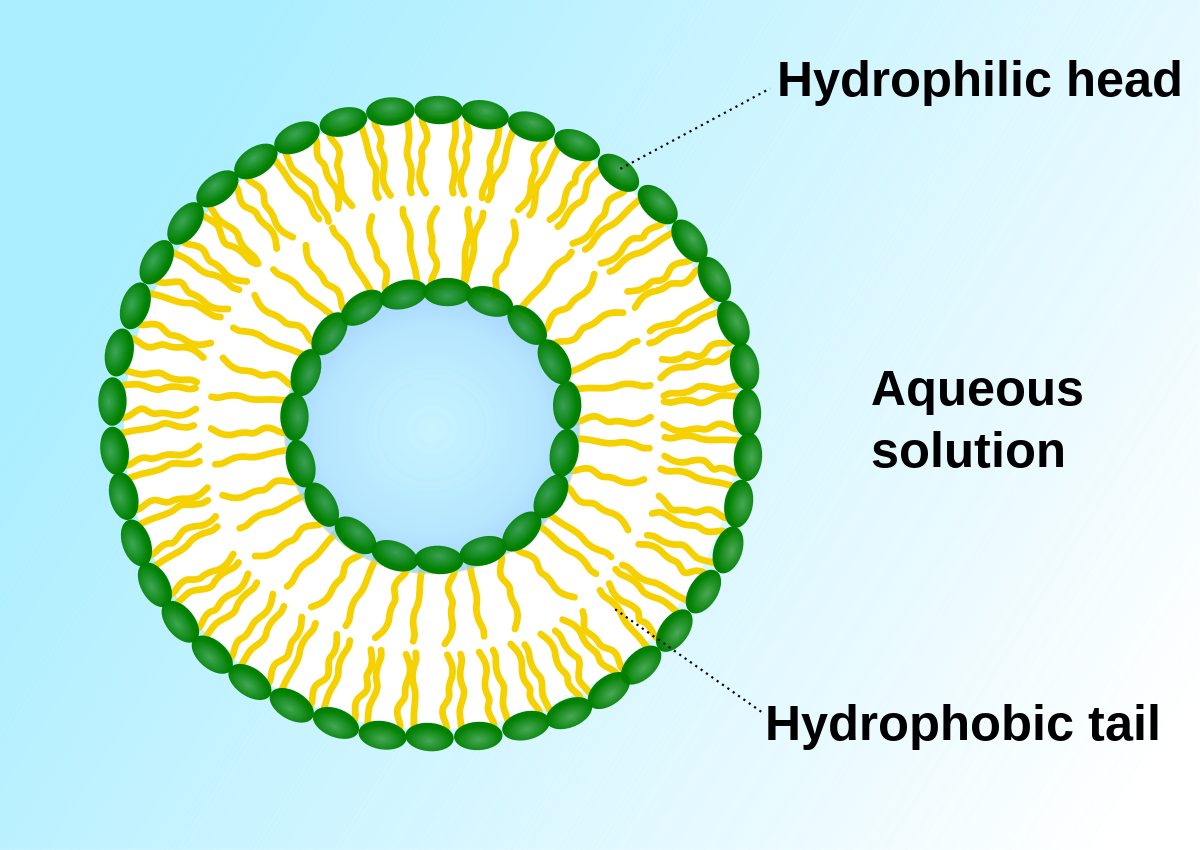
phospholipid
molecule composed of charged (polar) ‘head’ made of glycerol and phosphate group and a ‘tail’ made of two fatty acid tails that are non-polar
nucleoid
singular circle dna
nucleoplasm
fluid inside the nucleus
chromosomes
dna and protein- condensed visible with dye
chromatin
dna and protein- no condensed, invisible
nucleolus
produces ribosomes inside the nucleus
nuclear envelope
a double membrane that surrounds the nucleus in the cell
bound ribsomes
ribosomes attached to rough er
Monomer for dna/rna
nucleotides
a _______ ____ is a polymer of nucleotide monomers
nucleic acid
monomer for dna
deoxyribonucleotide
monomer for rna
ribonucleotides
phosphate group is bonded to _ carbon
5’
nitrogenous base is bonded to _ carbon
1’
nitrogenous base is the ________ group
variable group
nucleotides are composed of?
a phosphate group, a sugar, and nitrogenous base
dna is ______ stranded
double
rna is ______ stranded
single
what sugar group does rna have?
ribose
what sugar group does dna have?
deoxyribose
how do you tell the differentiate between the different sugars?
look at carbon 2’ for the difference
ribose has a ________ _____ attached to C 2’
hydroxyl group
deoxyribose has a ________ attached to C 2’
hydrogen
pyrimidines
Cytosine (C), Uracil (U) in rna, Thymine (T) in dna
purines
Guanine (G) + Adenine (A)
purines are ______ than pyrimidines
larger
how do you read dna/rna strands?
5’ —> 3’
the strand grows from the _ end
3’
which carbon bonds with a phosphate group?
carbon 3’
the condensation bond that occurs when joining a phosphate group forms a…
phosphodiester linkage (bond)
dna grows ____-________ to eachother
anti-parallel
what would be the anti-parallel pairing to 5’ ATTGGC 3’?
3’ TAACCG 5’
the phosphate + sugar bases are the outer piece of the dna molecule or “backbone”
true
dna has a overall electronegativity due to?
the phosphates; polar covalent bonds
dna is hydrophillic and has high solubility
true
the double helix is a _________ structure
secondary
________ bonds hold/ join the inner or “nitrogenous” groups
hydrogen bonds
G-C rich code would be stronger than a A-T rich code since G-C rich code would have a higher amount of hydrogen bonds
true
Adenine (A) and Thymine (T) / Uracil (U) can form how many hydrogen bonds?
2 hydrogen bonds
Cytosine (C) and Guanine (G) can form how many hydrogen bonds?
3 hydrogen bonds
How is the dna molecule stabilized?
hydrophobic interactions in the interior and hydrogen bonding between base pairs
what is the function of dna?
can store and transmit biological information; the information is required for the growth and reproduction of all cells
an rna secondary structure consists of a ____ and ____
loop (single stranded loop) and stem (double helix)
considered a hairpin structure
rna is shortlived in the cell; it can come and leave the nucleus.
true
rna tertiary structure
folds to form distinctive three-dimensional shapes
rna quaternary structure
associations between severall molecules
rna is structurally, chemically, and functionally intermediate between dna and proteins
true
rna function
information containing molecule and is capable of self-replication
can function as a catalytic molecule
-ribozymes are enzyme-like rnas
Enzymes that break down DNA perform hydrolysis reactions of the covalent bonds that join nucleotides together. What would happen to DNA molecules treated with these enzymes?
The phosphodiester linkages of the DNA backbone would be broken.
Consider the DNA nucleotide sequence ATCGGATCGA. What does this sequence best represent?
The primary structure of DNA
DNA double helices are soluble in water. How do these physical properties reflect the chemical structure of the DNA molecule?
The charged phosphate groups and sugars of DNA are hydrophilic.
If radiactively tagged 14C-labeled uracil is added to the growth medium of cells, what macromolecule(s) will be labeled?
RNA
If a double-stranded DNA sample was composed of 10 percent thymine, what would be the percentage of guanine?
40
A section of one DNA strand has the sequence ACCGAGGTT. What is sequence of the complimentary strand?
TGGCTCCAA
Nucleic acids are polymers made up of which of the following monomers?
Nucleotides
what nitrogenous base will form complementary base pair with uracil in RNA synthesis?
Adenine
Which bond holds together deoxyribose and the phosphate of a nucleotide?
covalent
Two complimentary strands of DNA are held together by ____________.
hydrogen bonds
A young scientist studying the Herpes virus infection wants to make a cream to kill the Herpes viruses in the cold sore. Her cream contains an enzyme that breaks the phosphodiester bonds between the nucleic acid monomers.
She tries it on herself. The results showed that the cold sore disappeared! But her lip is not healing. Which of the following statements can explain this result?
The cream also disrupted the covalent bonds between the monomer of her lip cells’ nucleic acids
What is the monomer of a carbohydrate?
monosaccharides
where is the carbonyl group in an aldose?
end of carbon chain
where is the carbonyl group in a ketose?
middle of carbon chain
what are isomers?
same formula with a different arrangement of atoms in the molecule and different properties
what is an example of isomers?
glucose (C-OH is pointed up) and galactose (C-OH is pointed down)
Triose
3 carbons
Pentose
5 carbons
Hexose
6 carbons
Example of a triose sugar
glyceraldehyde
example of a pentose sugar
ribose
sugars tend to form ring structures in aqueous solutions
true
alpha molecule
C-OH bond is pointed downwards
beta molecule
C-OH bond is pointed upwards
what causes a ring structure to form?
oxygen from the 5-carbon bonds to the 1-carbon
What is the bonding point of a ring structure?
C = O (carbon double bonded to oxygen)
The simplest polysaccharides are disaccharides because…
they’re comprised of two monosaccharides monomers
polysaccharides or complex carbohydrates are _________ of monosaccharides monomers
polymers
a polysaccharide is comprised _+ monosaccharides
3
what is a glycosidic linkage(bond)?
when a condensation reaction occurs between two hydroxyl (OH) groups; a covalent bond
alpha glycosidic linkage
C-O-C bond is pointed downwards
beta glycosidic linkage
C-O-C bond is pointed upwards
carbohydrates are full of _________ ______ and later converted to actual atp molecules
potential energy
plants store sugar as ______
starch