lecture 32: vision (CNS processing & cortical representation)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
1
New cards
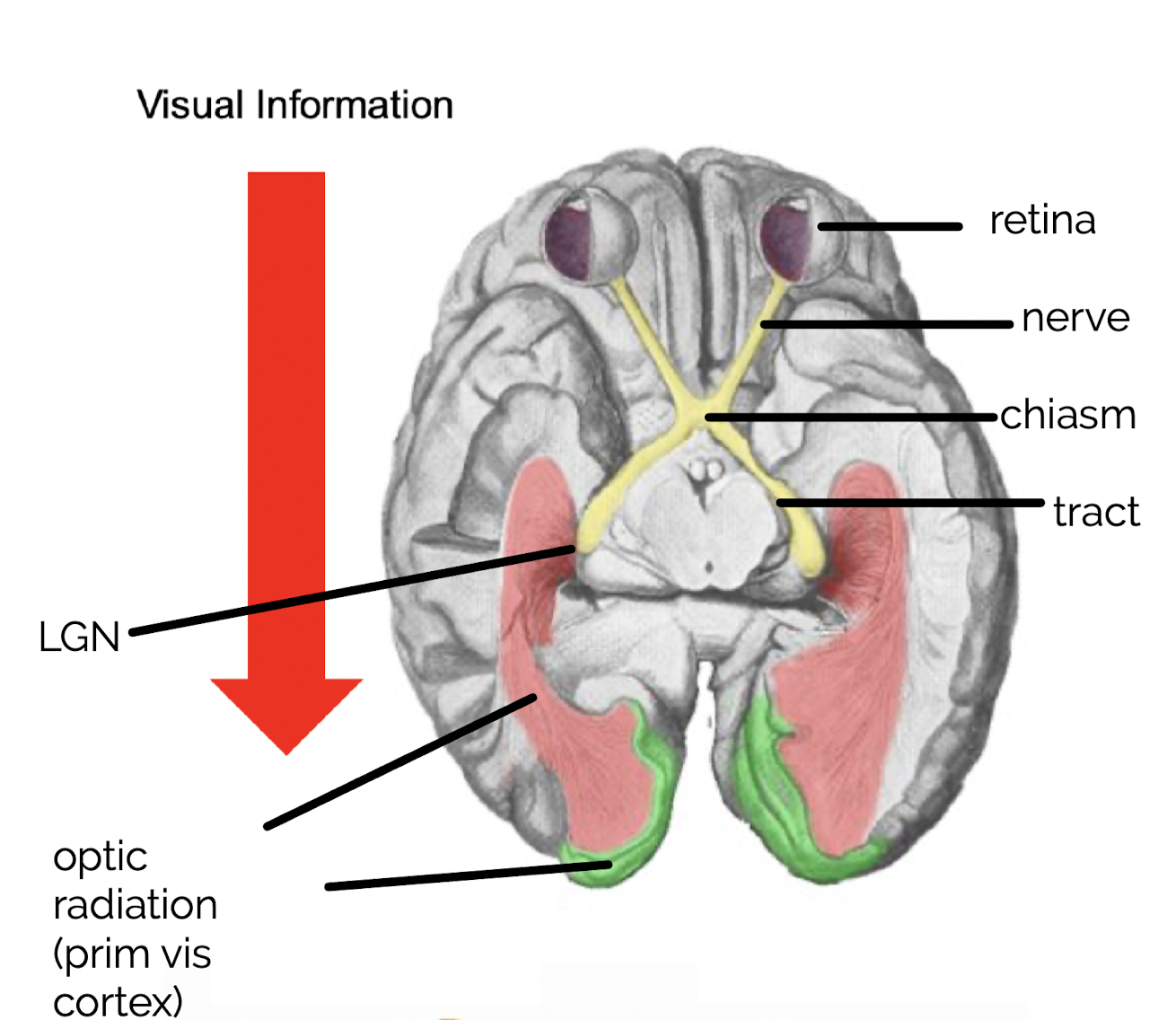
what are some of the key functional anatomical structures involved in the visual pathway?
* optic nerve
* optic tract
* optic chiasm
* LGN
* visual cortexes (V1-V5)
* optic tract
* optic chiasm
* LGN
* visual cortexes (V1-V5)
2
New cards
what is the optic radiation ?
large white matter tract which joins the thalamus to the primary visual cortex (V1)
3
New cards
where do fibres cross over in the visual pathway?
optic chiasm
4
New cards
when does the optic nerve become the optic tract?
after the optic chiasm
5
New cards
describe the nomenclature of the visual fields
* superior
* inferior
* temporal
* nasal
* inferior
* temporal
* nasal
6
New cards
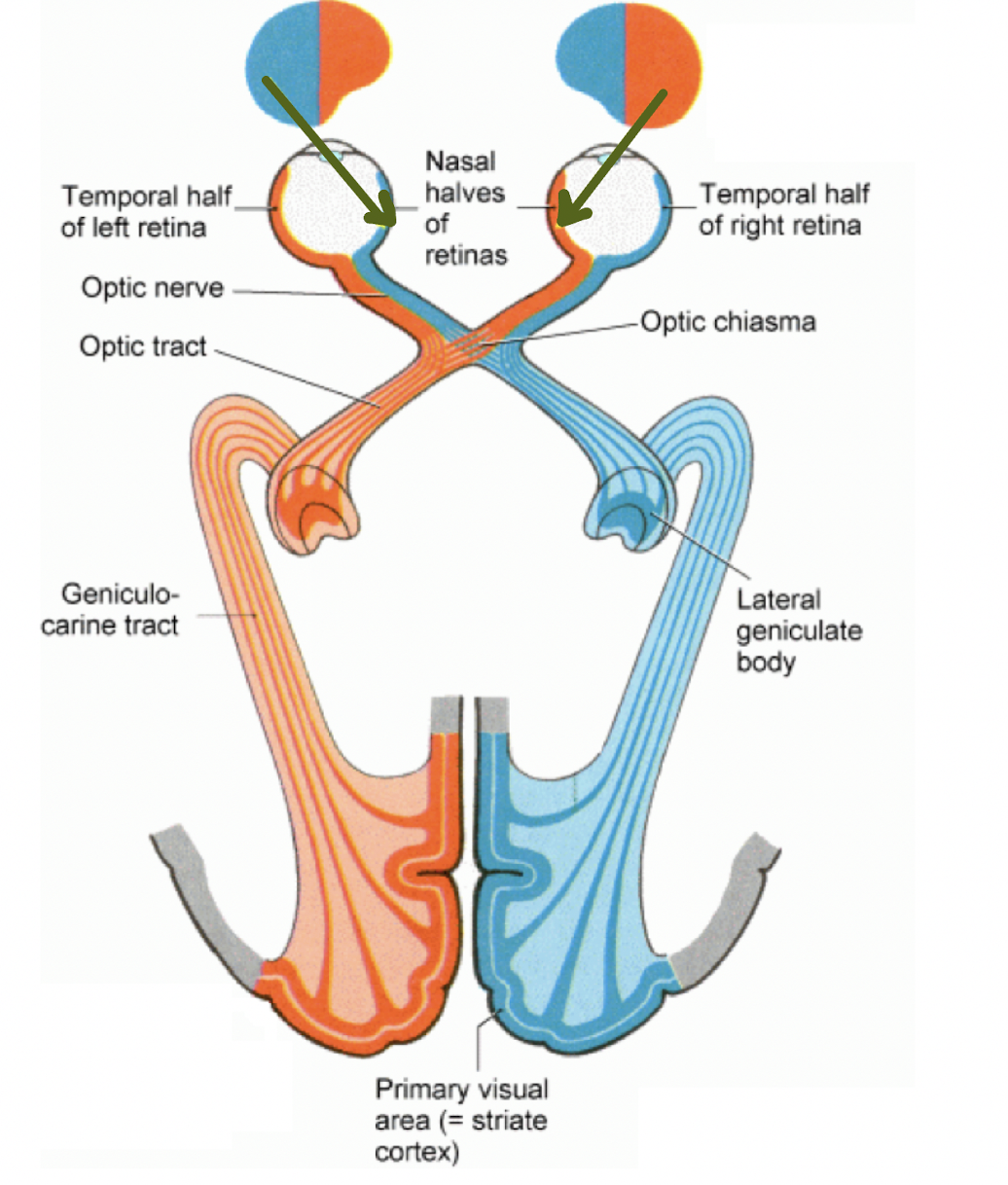
what is the pathway of information from the retina → V1?
1. retina
2. optic nerve
3. optic chiasm (where fibres cross over)
4. LGN
5. striate cortex (V1)
7
New cards
T/F: in the LGN, info the from the L & R eyes is kept segregated in diff layers
true
8
New cards
how many layers does the LGN have?
6
9
New cards
which layers does ipsilateral info go through from the LGN?
2, 3, 5
10
New cards
which layers does contralateral info go through from the LGN?
1, 4, 6
11
New cards
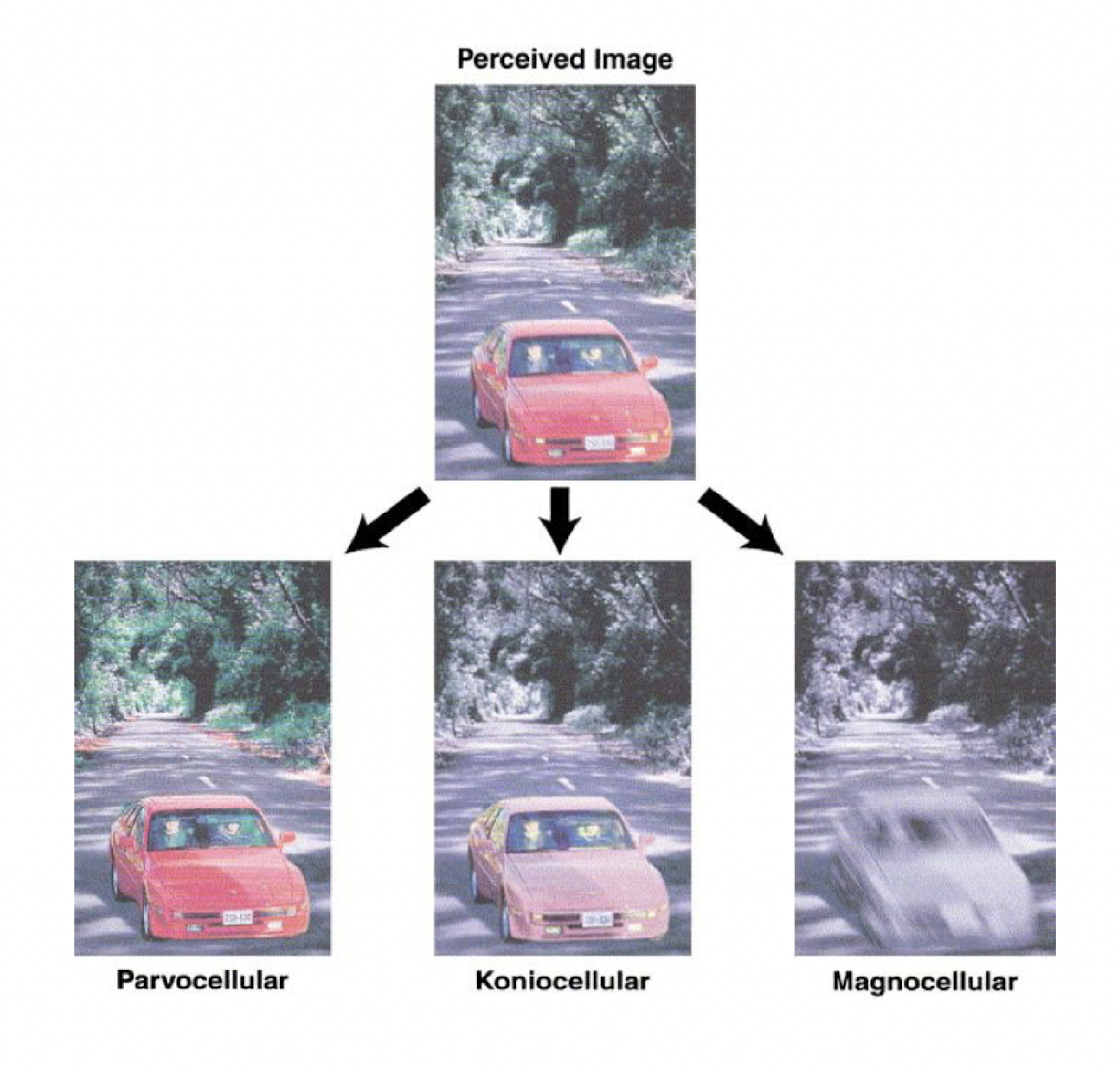
what types of cellular layers does the LGN have in it?
1. magnocellular
2. parvocellular
3. koniocellular
12
New cards
respectively, what do the M, P, & K layers channel info on?
M = motion
P = fine res & colour
K = we don’t really know, but perhaps involved in blue/yellow light, motion, & eye movements
P = fine res & colour
K = we don’t really know, but perhaps involved in blue/yellow light, motion, & eye movements
13
New cards
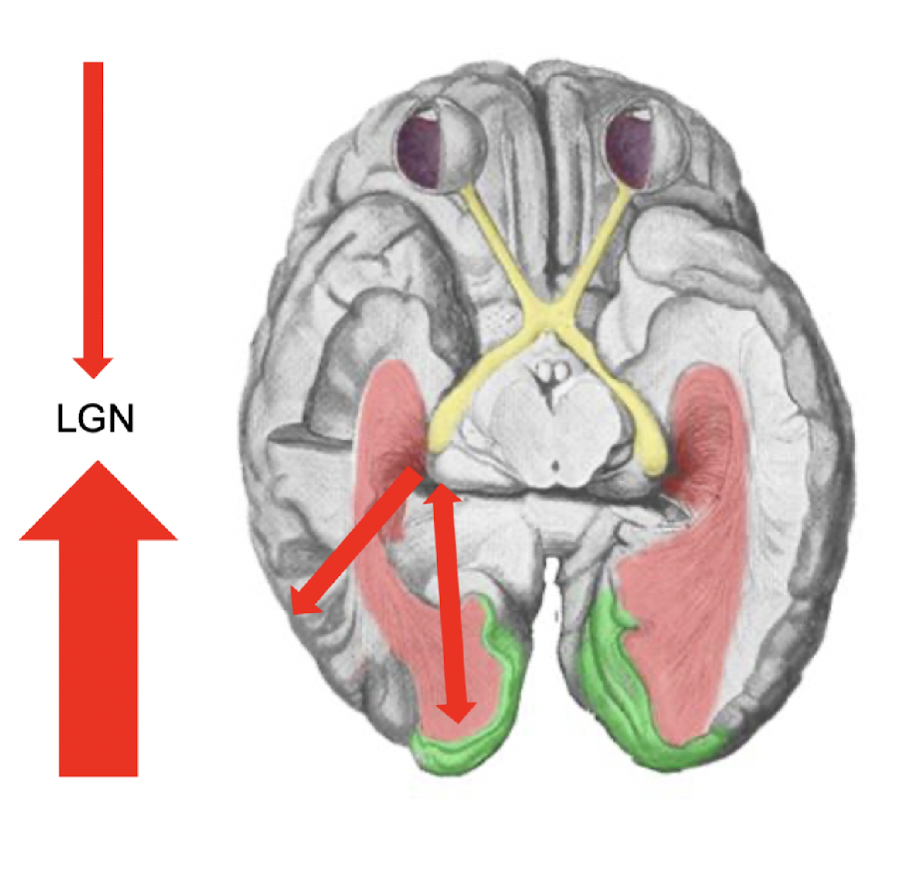
which is the dominant flow of direction in the LGN?
backwards
14
New cards
T/F: there is ONLY serial flow of info to brain, no parallel inputs enter V1
false, from LGN onwards, there are parallel inputs into V1
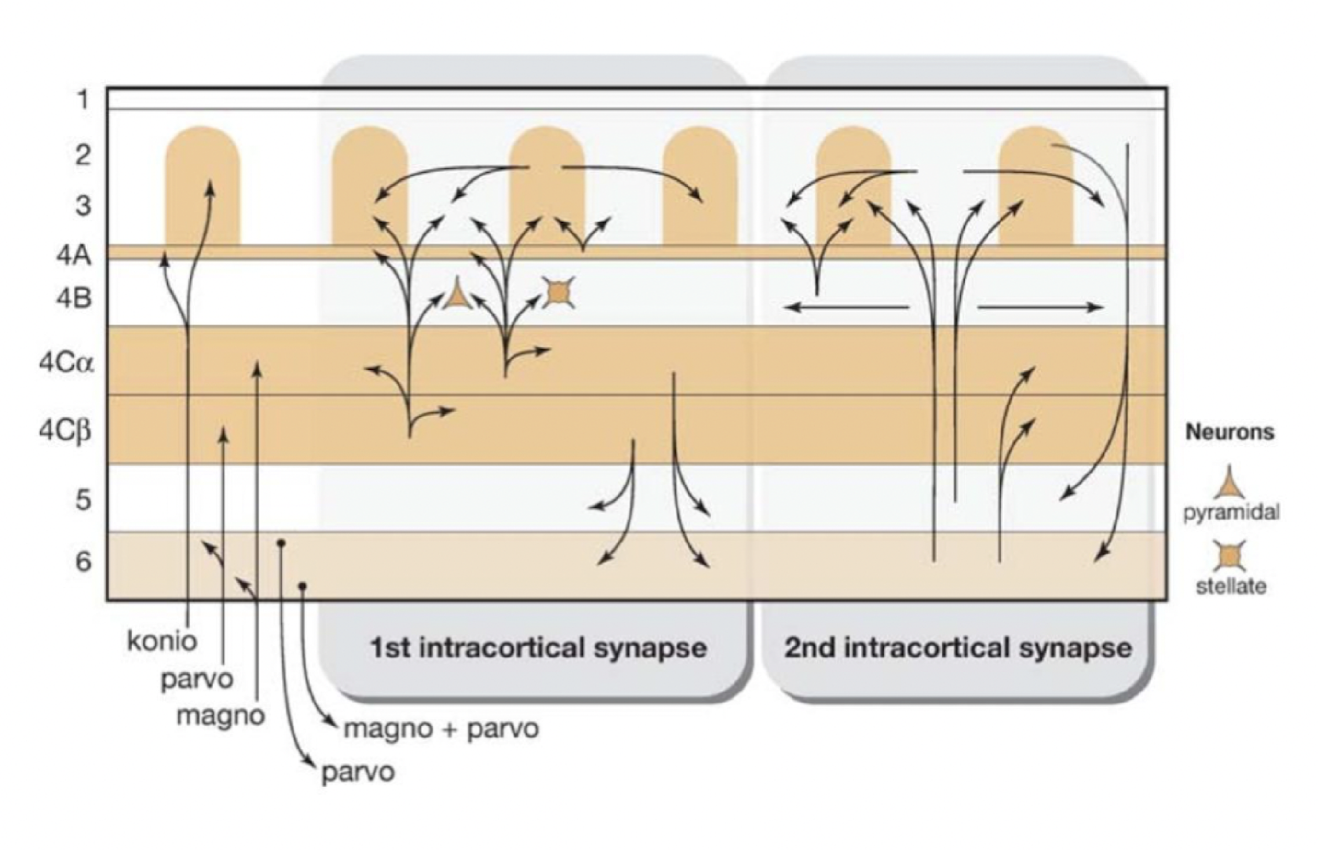
15
New cards
T/F: channels combine once entering brain as fibres mix from park, magno, and konio cellular inputs
true
16
New cards
T/F: in V1, L & R eye info is STILL kept segregated. diff neighbouring chunks of V1 layers only recieve info L OR R eye
true
17
New cards
what is functional specialisation?
what the area does best, not that it does only that
18
New cards
describe functional specialisation in visual maps
V1-V5; each region is specialised for a diff aspect of vision
e.g. V4 = specialised for colour
V5 = specialised for motion
FFA = feasible face area = specialised for facial recognition
e.g. V4 = specialised for colour
V5 = specialised for motion
FFA = feasible face area = specialised for facial recognition
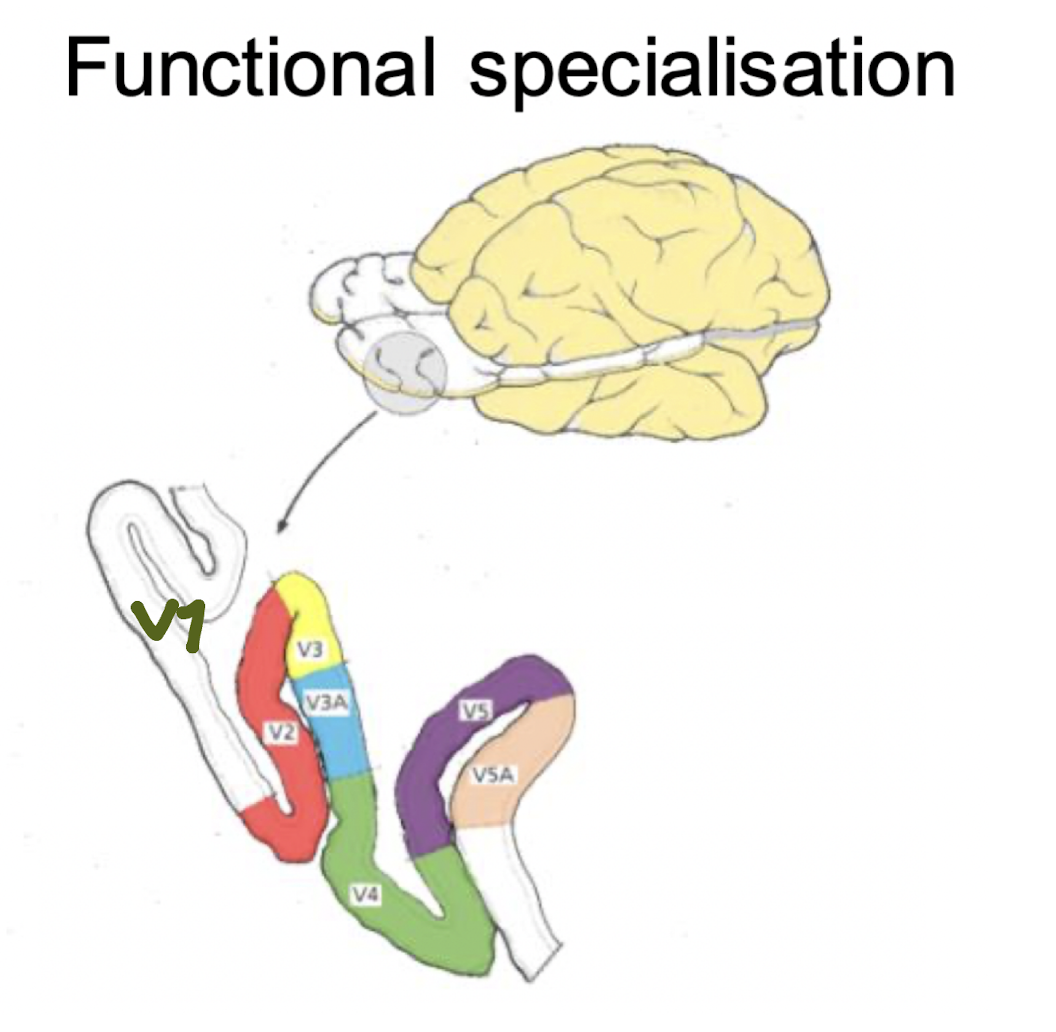
19
New cards
what streams of information exist for specialised info, and what info do they convey?
**ventral** = specialised info going down temporal lobe; linked to what an object in the REAL WORLD might be
**dorsal** = specialised info going parietal lobe; linked to info on WHERE objects are
**dorsal** = specialised info going parietal lobe; linked to info on WHERE objects are
20
New cards
T/F: there are complex connections in feed fwd, feed back, and parallel pathways as well as short circuits and routes
true