ANSC 3080 pt 3 reflex arcs
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
somatic is
reflex (skeletal muscle)
what is a reflex
involuntary, unvarying response
an automatic or unconscious response of effectors organs muscle of gland to a stimulus
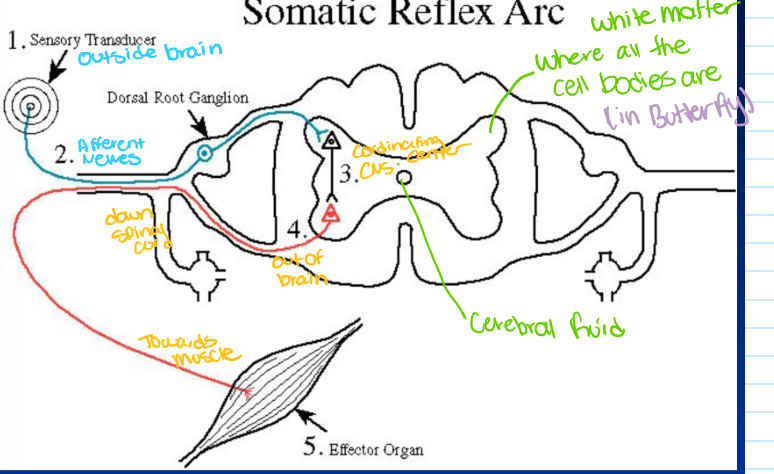
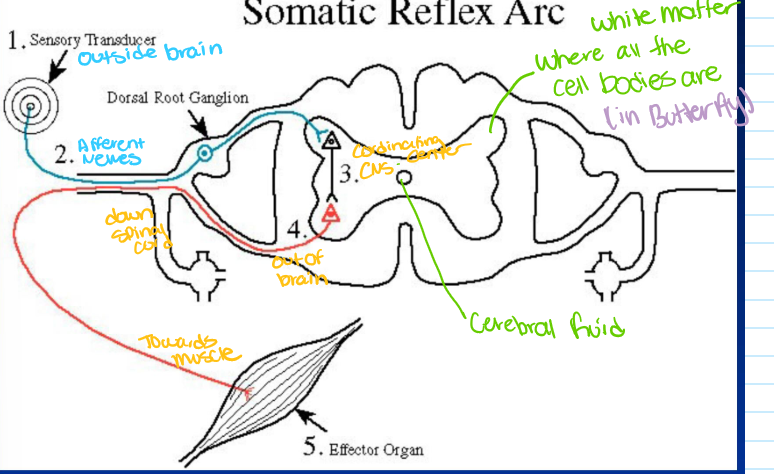
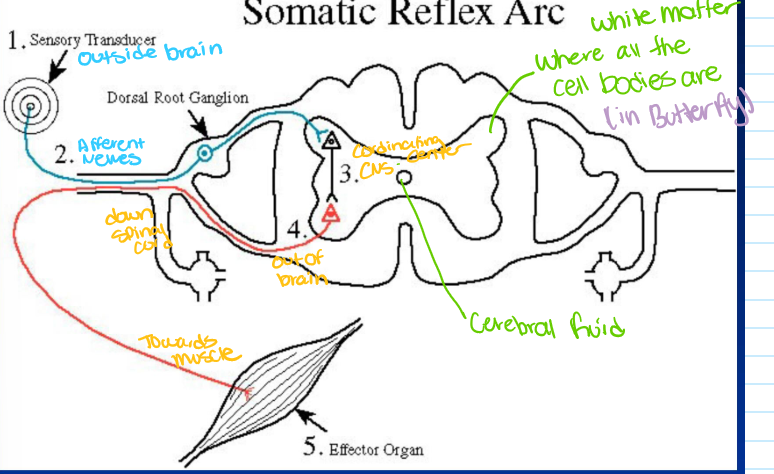
what are the 5 fundamental components of a reflex arc
sensory cells/ receptors
sensory nerve fibers
coordinating center
motor nerve fibers
effectors (muscle or gland cells
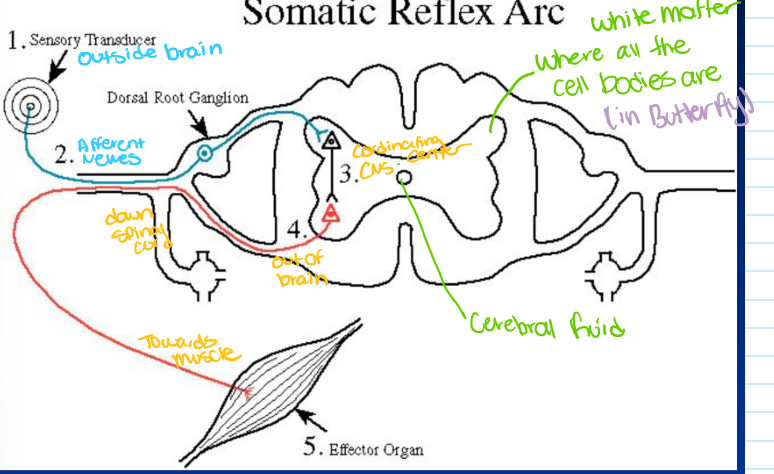
somatic (skeletal muscle) reflex arcs pt 1
receptors
transduce the environmental energy
skin- heat, cold, pressure
muscle (spindle)- stretch
tendon (Golgi)- tension
converts energy into action potentials
frequency of AP proportional to intensity of energy transduced (frequency coding)- enables CNS to detect intensity
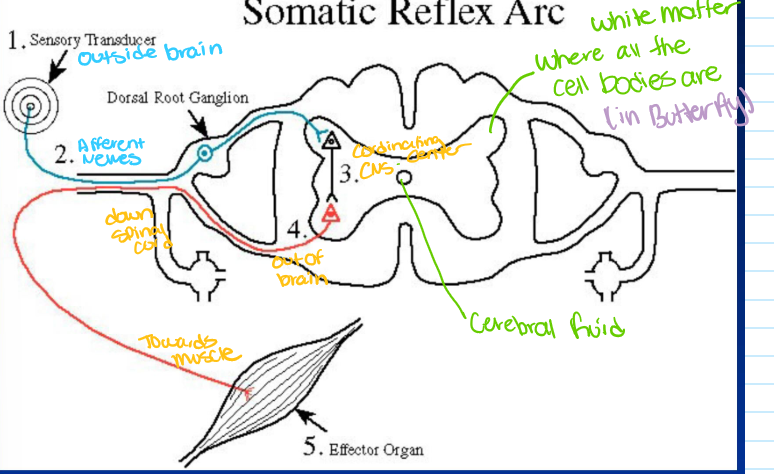
somatic (skeletal muscle) reflex arcs pt 2
sensory (afferent) nerve
conduct AP from the receptor
cell body in ganglion outside of spinal cord
enter spinal cord via dorsal root
somatic (skeletal muscle) reflex arcs pt 3
coordinating center= CNS synapses
monosynaptic (muscle spindle reflex)
multisynaptic ( elaborate reflexes)
somatic (skeletal muscle) reflex arcs pt 4
motor (efferent) nerve
carries AP from CNS to target (effectors) organs
via ventral roots
cell body within CNS
somatic (skeletal muscle) reflex arcs pt 5
target organ response
skeletal muscle (knee jerk)
multiple targets (scratching)
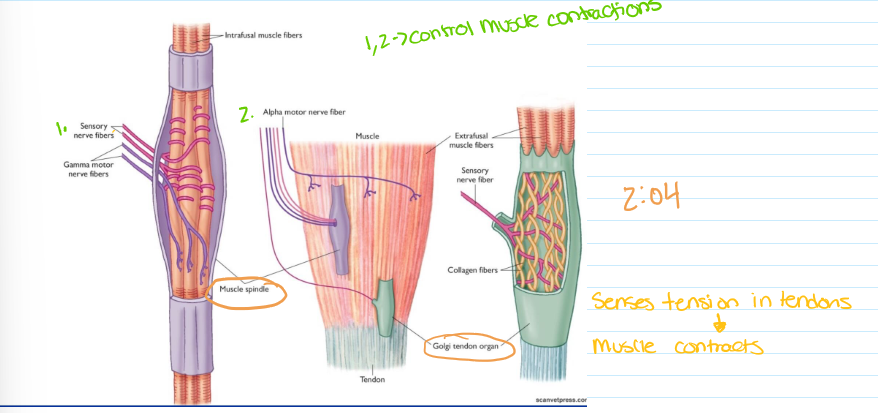
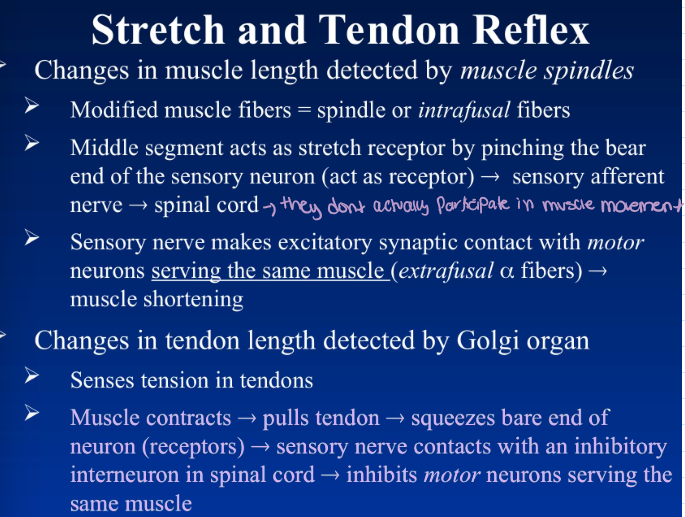
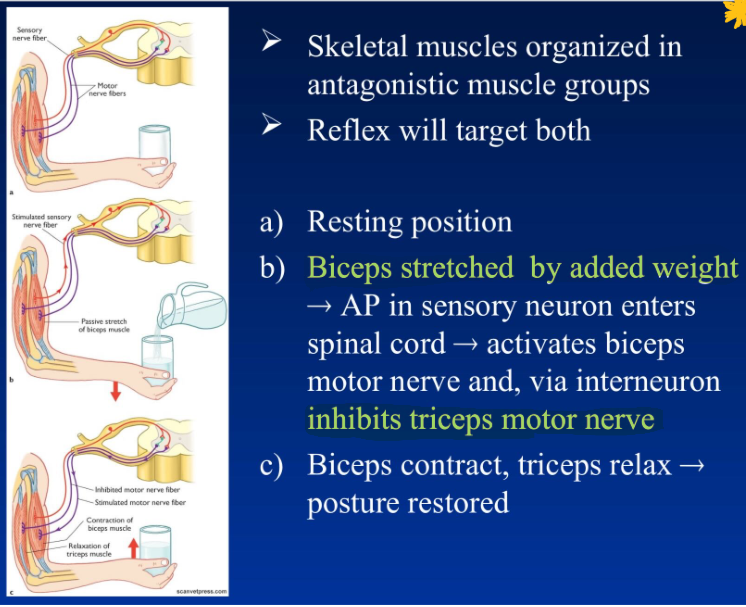
stretch and tendon reflex
changes in muscle length detected by muscle spindles