6.4.2 Blood glucose regulation
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Why is it important to maintain a stable blood glucose concentration?
maintain constant water potential
maintain constant concentration of respiratory substrate
What factors affect blood glucose concentration?
digestion of carbohydrates
exercise
Define glycogenesis
liver converts excess glucose into glycogen
Define glycogenolysis
liver hydrolyses glycogen into glucose
Define gluconeogenesis
liver synthesises gluocse from non-carbohydrate sources (amino acids, glycerol)
What are islets of Langerhans?
cells in the pancreas which detect blood glucose levels and release hormones
What is the role of alpha cells?
detect low glucose concentration
release glucagon
What is the role of beta cells?
detect high glucose concentration
release insulin
How insulin lowers blood glucose concentration?
binds to complementary receptors
(vesicles contaning glucose channel proteins fuse with cell membrame and increase permeability to glucose)
stimulated uptake (facilitated diffusion) of glucose by channel proteins
activates enzymes that catalyse glycogenesis
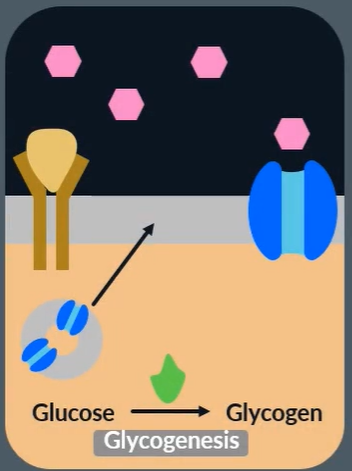
How does glucagon increase blood glucose concentration?
glucagon binds to complementary receptors (on liver cells)
activates enzymes which catalyse glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis
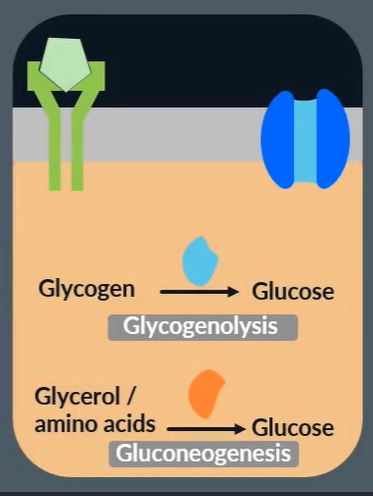
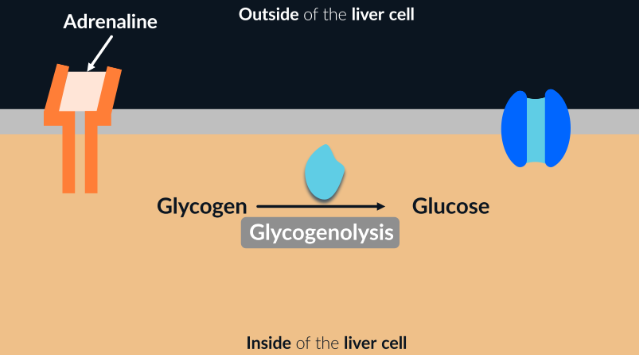
How does adrenaline increase blood glucose concentration?
adrenaline binds to complementary receptors in the liver cells
activates enzymes that catalyse glycogenolysis
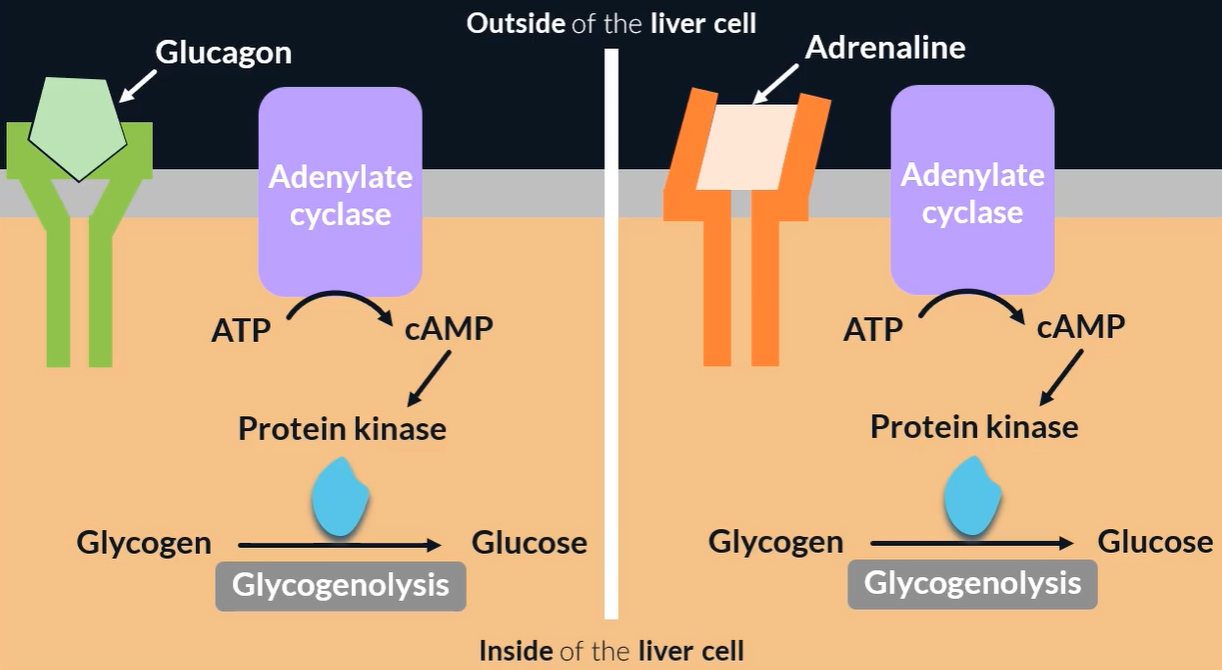
Explain the role of the second messenger model in glycogenolysis
hormone (primary messenger) binds to complementary receptor
causes adenyl cyclase (which undergoes conformational change) to be activated
catalyses conversion of ATP → cyclic AMP (secondary messenger)
cAMP activates enzyme protein kinase (which catalyses glycogenolysis)
What causes type 1 diabetes?
cannot produce insulin (e.g caused by autoimmune disease destroying beta cells)
How can you treat type 1 diabetes?
insulin injections
controlling diet (sugat intake)
What causes type 2 diabetes?
poor diet and obesity
glycoprotein receptors are damaged and lose responsiveness to insulin
How to treat type 2 diabetes?
regulating diet (e.g carb intake)
increasing exercise