Anatomy and Physiology: Skeleton Vocab
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Practice these terms, learn how to identify the different parts of a skeleton
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
epiphysis
rounded end of a long bone
articular cartilage
smooth surface that covers the epiphysis
diaphysis
the middle shaft of the bone
ossicles
three bones of the middle ear
hyoid bone
attachment point for the tongue and does not directly articulate with any other bone
sacrum
made of the five vertebrae that fuse during early adulthood (towards the end of the vertebral column)
coccyx (tailbone)
the remnant of a vertebral tail
Atlas (C1)
first bone in vertebral column; have two large articular that form joints with other bones; wider
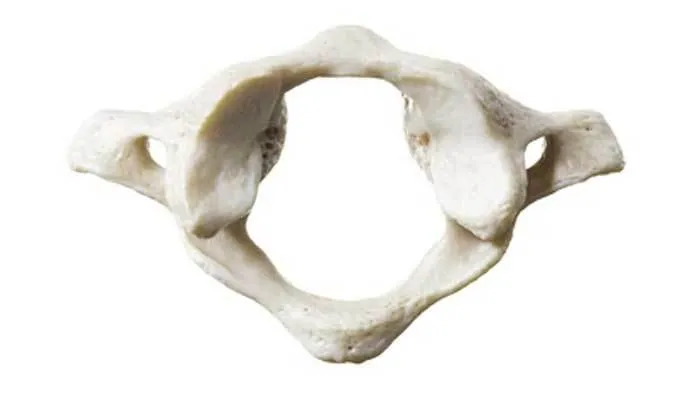
Axis (C2)
second bone in vertebral column; tooth like dens that create a rotation point for that atlas
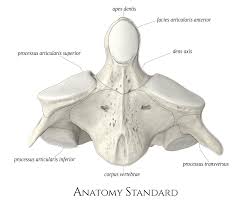
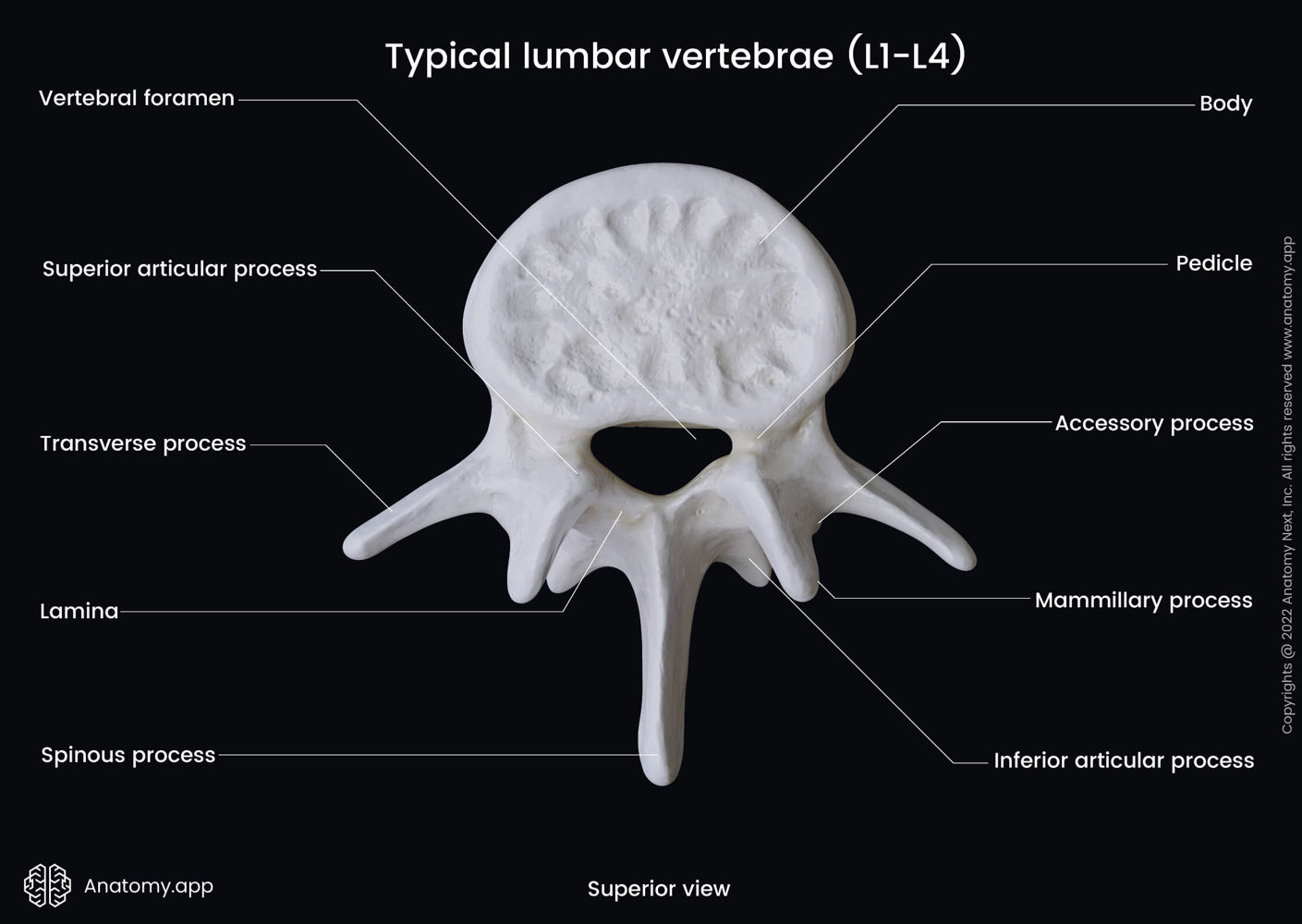
spinous process
bony projection from the back of a vertebrae
vertebral foramen
central opening in each vertebra that allows spinal cord to pass through
vertebral body
thick, cylinderal, front part of the vertebral
transverse process
small bony projection that extends from either side of each vertebra
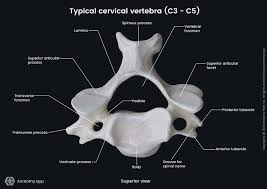
cervical vertebrae
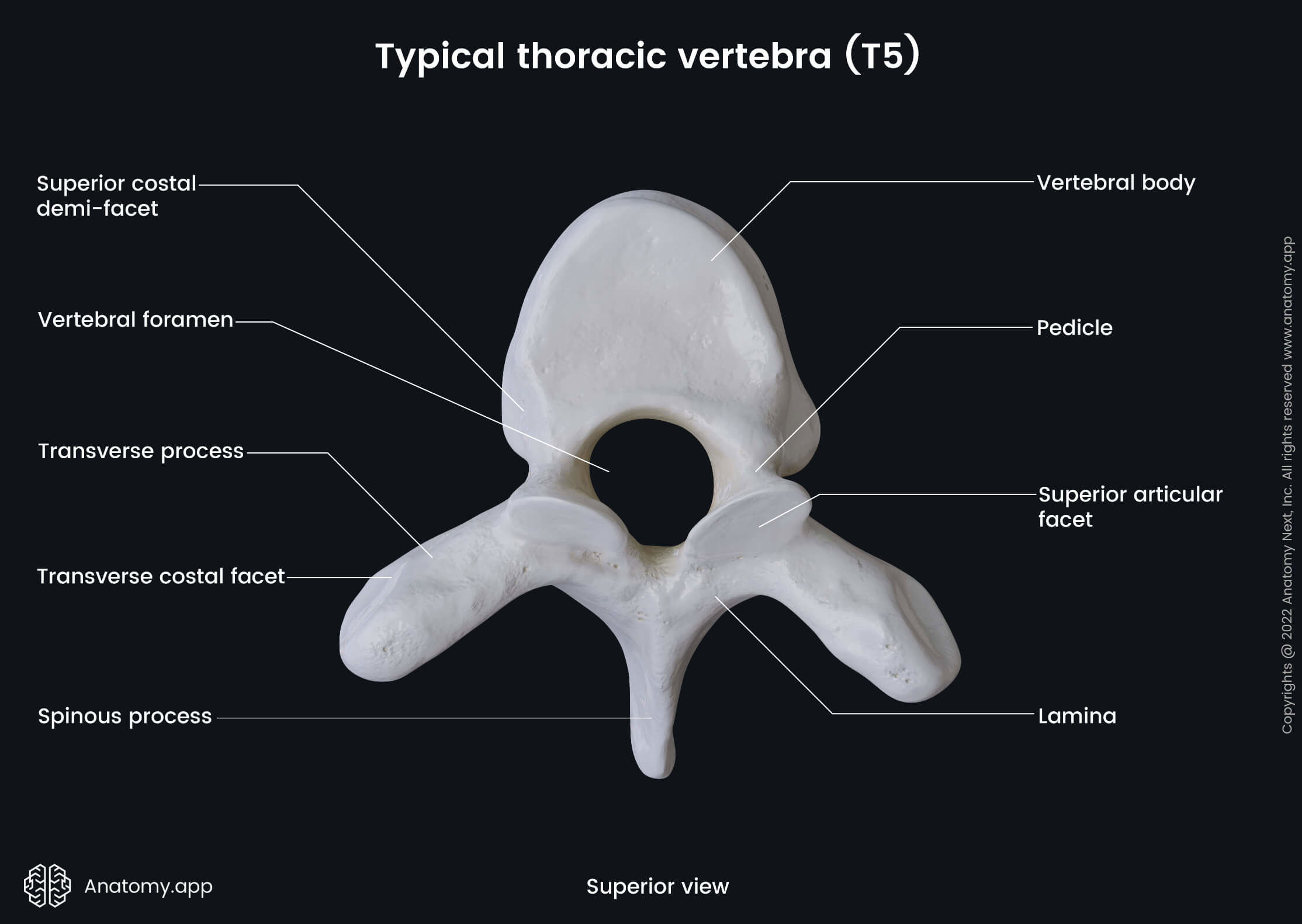
thoracic vertebrae
lumbar vertebrae
fibrous joints
immovable, dense connective tissue, cranial sutures
cartilaginous joints
limited movement, fibro or hyaline cartilage, vertebral discs
synovial joints
free movement, fluid-filled cavity, knee, elbow, and fingers