P2- Energy Transfer by heating
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
1
New cards
What is a conductor ?
a material that allows energy to move easily through it
2
New cards
What is an insulator ?
a material that doesn't allow energy to move easily through it
3
New cards
Describe what happens to the particles when energy is transferred by conduction in a metal.
The particles gain kinetic energy
From this kinetic energy, particles vibrate faster
The vibrating particles transfer energy to neighboring particles in the metal through collision until the whole metal is heated
From this kinetic energy, particles vibrate faster
The vibrating particles transfer energy to neighboring particles in the metal through collision until the whole metal is heated
4
New cards
Name 3 insulators ?
Glass, wood and plastic
5
New cards
Name 3 conductors?
Steel, Aluminium and Copper
6
New cards
Why does conduction occur in solids rather than in gases/liquids?
Conduction occurs in solids rather than in liquids/gases because the particles are more closely packed together than in comparison to liquids and gases that have particles that move freely.
7
New cards
Define thermal conductivity?
the measurement of how well a material conducts heat ( the ability to conduct heat )
8
New cards
The higher the thermal conductivity of a material, the higher _______
The higher the rate of energy transfer by conduction across material
9
New cards
Which material has a lower thermal conductivity : glass or metal
Glass, insulators have a low thermal conductivity
10
New cards
3 Factors that affect the rate of energy transfer by conduction?
thickness of material
the thermal conductivity
the temperature difference across the material
the thermal conductivity
the temperature difference across the material
11
New cards
2 ways to reduce energy transfers? (unwanted heat loss) ?
using a thick material
using a material with a low thermal conductivity that can trap air ( insulator )
using a material with a low thermal conductivity that can trap air ( insulator )
12
New cards
Define Specific heat capacity?
The specific heat capacity of a substance is the amount of energy it takes to increase the temperature of 1kg of the substance by 1degree C
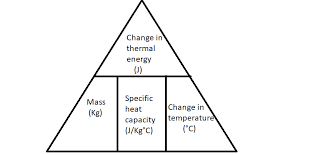
13
New cards
Which material has a lower thermal conductivity ? Non metals or metals?
Non metals, low thermal conductivity = high specific heat capacity ( more energy required to increase temperature 1kg of substance by 1 degree)
14
New cards
What is the difference between thermal energy and temperature?
Thermal is the sum of the kinetic energy of particles in an object and is measured in Joules
Temperature is the measure of the average kinetic energy of particles and it is measured in Degrees
Temperature is the measure of the average kinetic energy of particles and it is measured in Degrees
15
New cards
Why does an iceberg have higher thermal energy than a matchstick?
An iceberg has a larger sum of the kinetic energy of particles than a matchstick therefore icebergs have higher thermal energy than matchsticks.
16
New cards
How much thermal energy does a 2 kg steel block (c = 450 J/kg°C) lose when it cools from 300°C to 20°C?
252000 J
17
New cards
How hot does a 3.5 kg brick get if it’s heated from 20°C by 20,000 J (20 kJ)? SHC=840
26.8 C
18
New cards
If the temperature of a material increases, the increase in temperature depends (3):
mass of material
type of material
amount energy input into material
type of material
amount energy input into material
19
New cards
Why is it better to have a window made of two layers of glass with a layer of air trapped between them?
Both glass and air are insulators because they have low thermal conductivities.
The layer of air has the lowest thermal conductivity which reduces overall thermal conductivity. This makes it harder for energy to leave the window
The layer of air has the lowest thermal conductivity which reduces overall thermal conductivity. This makes it harder for energy to leave the window
20
New cards
Why is loft insulation so effective?
It traps air which helps to reduce heat lost from the home
21
New cards
The walls of houses are often built out of brick with an inner and an outer layer; there is a gap between the layers. Sometimes this gap is filled with a solid insulating material such as foam. Why is the foam effective in reducing heat loss?
The insulating material ( foam) as it has a lower thermal conductivity than the air it replaces
22
New cards
What happens to a material when it is heated up ( talk about particles and kinetic energy)?
When a material is heated up, the particles gain kinetic energy and start moving faster. This results in an increase in temperature and the material getting hotter
23
New cards
What colour surfaces are the best emitters of infrared radiation ?
Matt Black surfaces
24
New cards
What colour surfaces are the best reflectors of infrared radiation?
Shiny Silver surfaces
25
New cards
All objects emit radiation however, the hotter the object is the more___
infrared radiation it emits and the visible light
26
New cards
Both wavelength and intensity of radiation depend on____
the temperature of the object
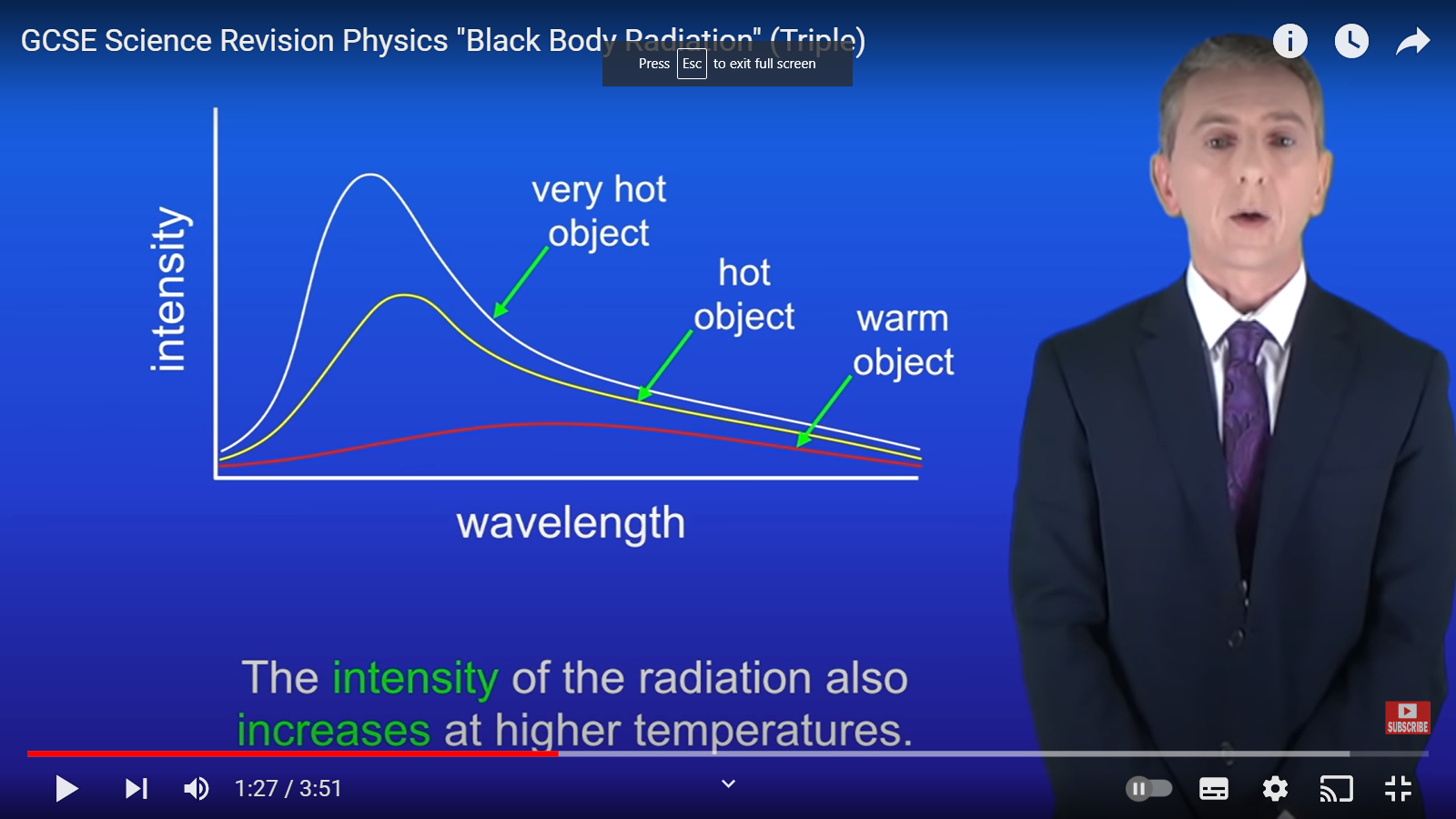
27
New cards
Which wavelengths are the hottest?
Short wave lengths
28
New cards
What properties does a perfect black body have?
Perfect black bodies absorbs all infrared radiation
It also emits all the radiation
doesn't reflect or transmit radiation
It also emits all the radiation
doesn't reflect or transmit radiation
29
New cards
What happens to the temperature of a body that absorbs and emits infrared radiation at the same rate?
It remains constant
30
New cards
What happens to the temperature of a body that absorbs infrared radiation faster than it emits?
It increases
31
New cards
What gases in the atmosphere change the balance of infrared radiation absorbed and emitted by the Earth?
greenhouses
32
New cards
Factors affecting the earths temperature?
concentration of greenhouse gases
infrared radiation absorbed by earths surface/atmosphere
infrared radiation emitted by earths surface/atmosphere
infrared radiation absorbed by earths surface/atmosphere
infrared radiation emitted by earths surface/atmosphere
33
New cards
Explain. in terms of particles, how evaporation causes the cooling of water?
Particles gain kinetic energy and speed up
The fastest particles escape through then surface of the water
the remaining particles decrease in energy
This means the total thermal energy is decreased therefore the temperature decreases too
The fastest particles escape through then surface of the water
the remaining particles decrease in energy
This means the total thermal energy is decreased therefore the temperature decreases too
34
New cards
How do greenhouse gases keep the earth warm?
Infrared radiation from the sun warms the earth ground. The ground then emits long-wavelength infrared radiation. Greenhouse gases absorb it and then emit into the earths surface.
35
New cards
The specific heat capacity of aluminium block is 913 J per kg per °C and its temperature is increased by 10 °C. 4565 J of energy is transferred. Calculate the mass of the aluminium block.
500g
36
New cards
Why are data logs better than glass temperature
more precise/sensitive
reduces instruments random error
reduces instruments random error