Microbial Diversity
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Acellular Microbes
- also known as infectious particles.
- includes Prions and Viruses.
Cellular Microbes
- also called microorganisms
- Includes Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
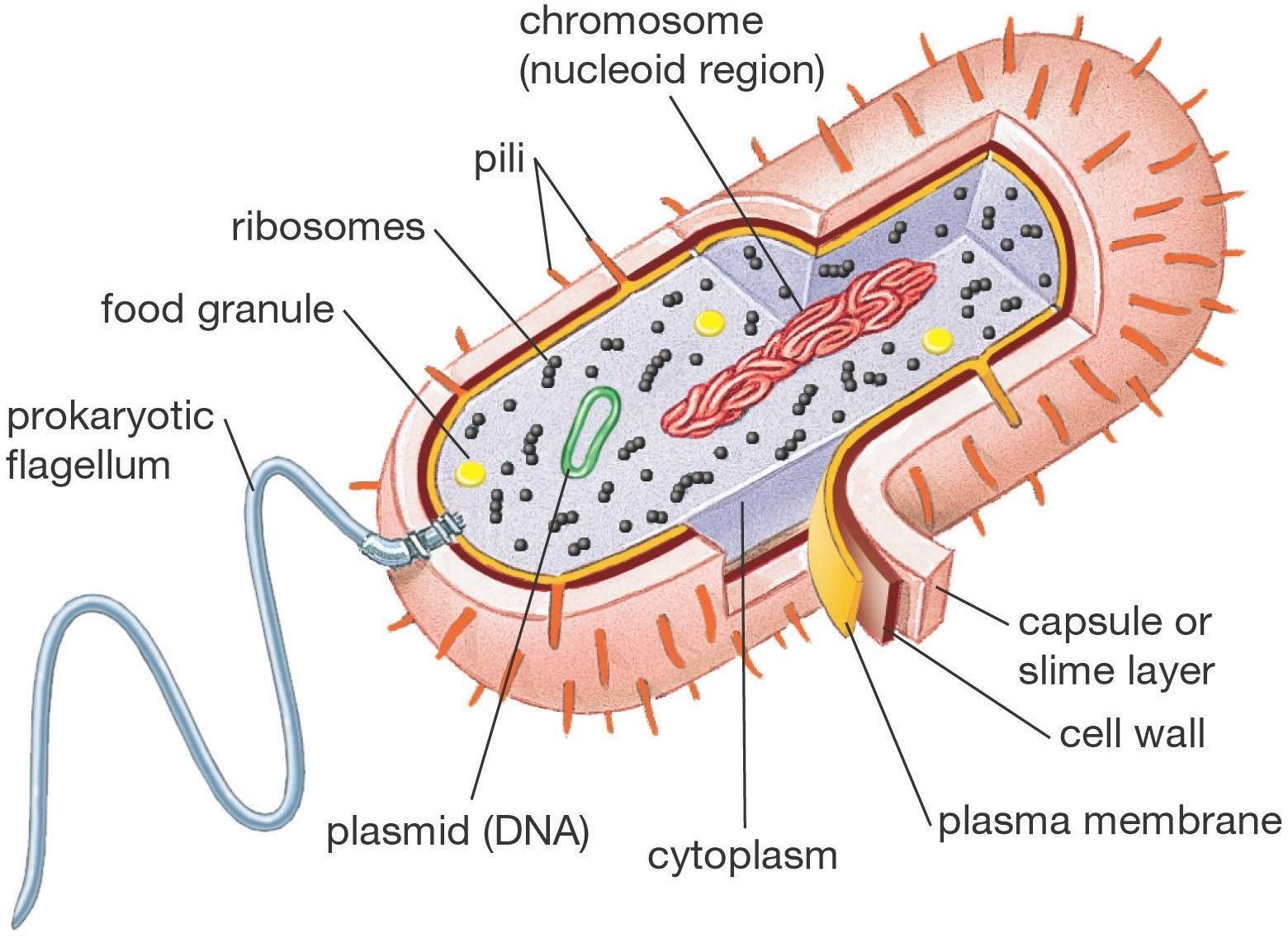
Prokaryotes
- organisms with cells that lack true nucleus.
- Includes Archaea and Bacteria
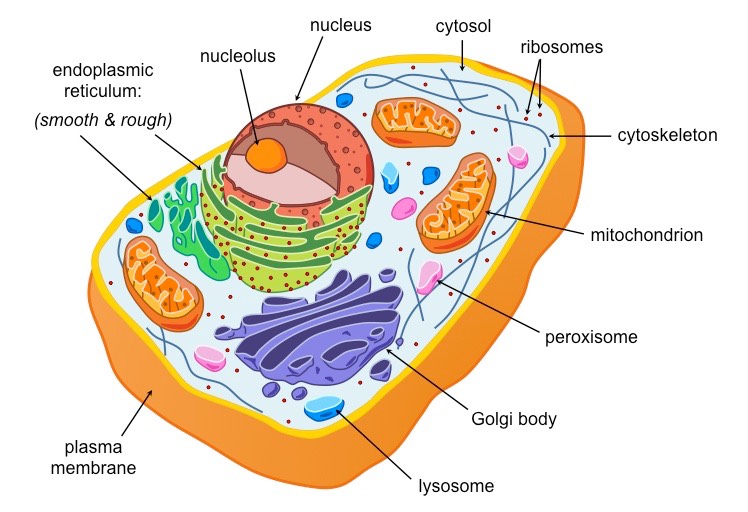
Eukaryotes
- Organisms with cells that have true nucleus
- includes Algae, Protozoa, and Fungi
Pathogens
- Microbes that cause disease
Nonpathogens
- Microbes that do not cause disease
Indigenous Microbia
-Microbes that live on and in the human body
Opportunistic Pathogens
pathogens that do not causes disease under normal conditions but have the potential to cause disease if there's opportunity.
Infectious Diseases
when a pathogen inhabits the body and cause disease
Microbial Intoxications
when a person ingest a poisonous substance that has been produced by a pathogen outside the body.
Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1632 - 1723)
invented the microscope lens that allowed visualization of organisms
Theory of Spontaneous Generation
- idea that life arises from nonliving material
- also known as "abiogenesis"
Louis Pasteur (1882 - 1895)
- introduced terms "aerobes" and "anaerobes"
- Developed Pasteurization process.
- theorized that specific microbes cause specific diseases.
- developed vaccines
Pasteurization
treating a substance with heat to kill or slow the growth of pathogens
Robert Koch (1843 - 1910)
- Established Koch's postulates - a sequence of experimental steps that verified the germ theory
- Identified cause of anthrax, TB, and cholera
- Developed pure culture methods
Koch's Postulate 1
the microorganism must be found in similarly diseased animals but not in healthy ones
Koch's Postulate 2
The microorganism must be isolated from a diseased organism and grown in pure culture.
Koch's Postulate 3
The cultured microorganism should cause disease when introduced into a healthy organism.
Koch's Postulate 4
The organism should be re-isolated and shown to be the same as the original
Germ Theory of Disease
idea that infectious diseases are caused by microorganisms and not by "unbiblical theories"
Exception to Koch's Postulates
Some pathogens cannot be grown in pure culture. Ex: Mycobacterium leprae
- human volunteers are difficult to obtain and ethical considerations limit their use
Robert Hooke (1635-1703)
- Invented the compound microscope.
- First to observe cells in 1665.
- Coined the term "Cells" from cork.
Rudolf Virchow (1821-1902)
Proposed the "The Theory of Biogenesis"
Theory of Biogenesis
life can arise only from preexisting life, and, therefore, cells can only arise from preexisting cells.
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
- have true nucleus
- cells are enclosed and by cell membranes
- 80s ribosome density
Svedberg Unit
unit for sedimentation rate, how fast particle settles (sediments)
Histones
protein molecules around which DNA is tightly coiled in chromatin
Mycoplasma
genus of bacteria that does not have a cell wall.
Prokaryotic Cell Structure
- 10 times smaller than eukaryotes
- Cell membranes enclose cytoplasm
- 70s ribosomes density
Spheroplast
A gram-negative bacterium treated to damage the cell wall, resulting in a spherical cell.
L-Forms
- gram-positive or gram-negative bacteria that naturally have a cell wall but lose it during part of their life cycle
- pleomorphic
General Shapes of Bacteria
cocci (round)
bacilli (rod-shaped)
spiral-shaped
Cocci Arrangements
-diplococci = two cocci
-streptococci = chains of four or more
-staphylococci = grape clusters
-tetrads = packs of four cocci
-octads - packs of eight
Pleomorphic
many shapes
pleomorphism
ability to exist in a variety of shape
Heat Fixation
a technique that uses the heat from a flame to attach a smear to a slide
-the sample is passed about 5 times into the flames
Methanol Fixation
flood the smear with absolute (95%) methanol for 130 seconds and remove by tilting the slide
preserves bacterial morphology
Simple Staining (Structural Staining Procedure)
- Use 1 basic stain (ex: Methylene blue) to color cells.
- Allows for visualization of the cells size, shape, arrangement, and number.
Negative Staining
- staining the background instead of the cell
- requires Indian ink or nigrosine
Endospore Staining
uses heat in order for malachite green stain to penetrate the endospore
Flagella Staining
mordant applied to increase thickness of flagella
Dr. Hans Christian Gram (1884)
developed the "Gram Staining Procedure"
Steps in Gram Staining
1. push crystal violet(1 minute)
2. rinse, put iodine (1 minute),
3. rinse, decolorize, ethanol (15seconds),
4. wash
5. safranin (30 seconds)
6. wash in water, blot, air dry.
Gram-positive bacteria
- Bacteria that have a thick peptidoglycan cell wall, and no outer membrane.
- They stain very darkly (purple) in Gram stain.
Gram-negative bacteria
- Bacteria that have a thin peptidoglycan cell wall
- They stain very lightly (pink) in Gram stain.
Acid-fast staining
developed by Paul Elrich in 1882
used to identify Mycobacterium species
Steps in Acid-fast Staining
1. primary dye: carbol fushin: colors acid-fast bacteria red
2. decolorizer: generally acid alcohol: removes stain from non-acid fast bacteria
3. counter stain: methylene blue: colors non acid fast bacteria blue
Acid-fast bacteria
Retain the primary stain even when treated with acid alcohol.
Mycobacterium
- the only acid-fast bacteria in our sputum or saliva
Motility
- ability to move
- presence of axial filaments or flagella
Flagella
A long, whip-like filament that helps in cell motility.
Axial Filaments
- Found in spirochetes
Anchored at one end of a cell
- Rotation causes cell to move like a corkscrew
Flagella Arrangement
Monotrichous = single flagellum.
Lophotrichous = tufts of flagella at one end.
Amphitrichous = single flagella at both ends.
Peritrichous = flagella over entire cell.
Amphilophotrichous = tufts of flagella at both ends.
Colony
a mound or pile of bacteria on the surface of a solid culture medium
Atmospheric Requirements
Bacteria can be classified on the basis of their atmospheric requirements, including their relationship to O2 and CO2
Capnophiles
Microbes that require high CO2 conditions
Obligate aerobes
require O2 to survive
Microaerophiles
require oxygen concentration lower than air
Aerotolerant anaerobes
do not utilize oxygen but can survive and grow in its presence
facultative anaerobes
can live with or without oxygen
Obligate anaerobes
can only grow in an environment without oxygen
Thioglycollate broth
the region of medium in which the organism grows depending on the oxygen it needs
Methods for Cultivation of Anaerobes
Candle Jar Method and gas Generator or Gas-Pak Jar Method
Temperature Requirements
some bacteria can grow at near freezing or hot temperatures
fastidous organism
any organism that has a complex nutritional requirement
Pathogenecity
ability of a microorganism to produce disease
Pili
Appendages that allow bacteria to attach to each other
Fimbriae
similar to pili but shorter, used for attachment to surfaces
Microbial Infection
microorganism itselt is the causative agent
microbial intoxication
a disease that results from ingestion of a toxin that was produced by a pathogen in vitro (outside the body)
Exoenzymes
enzymes secreted outside the cell wall
Genetic Composition
Bacteria are identified using some type of procedure that analyzes their DNA or RNA
Halophiles
salt - loving
thermophiles
heat - loving
hyphae
The branching, threadlike tubes that make up the bodies of multicellular fungi
superbugs
antibiotic resistant bacteria
mycelium
mass of hyphae
sporangium
sacs that contains spore