Applications of price elasticity
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
If a business raises the price of an elastic product
total revenue will decrease as consumers respond by buying less.
However, businesses may still be forced to raise prices if production costs increase, even if it leads to lower revenue.
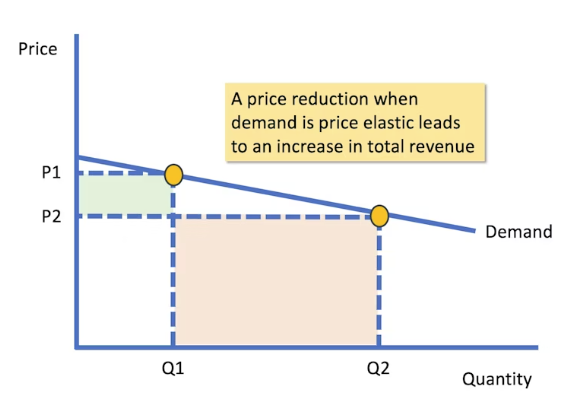
If a business lowers the price of an elastic product
total revenue will increase since demand responds strongly/ is very elastic.
this isn’t always possible: if the cost of production becomes higher than the sales price, the business would make a loss on each unit sold, reducing profit margins.
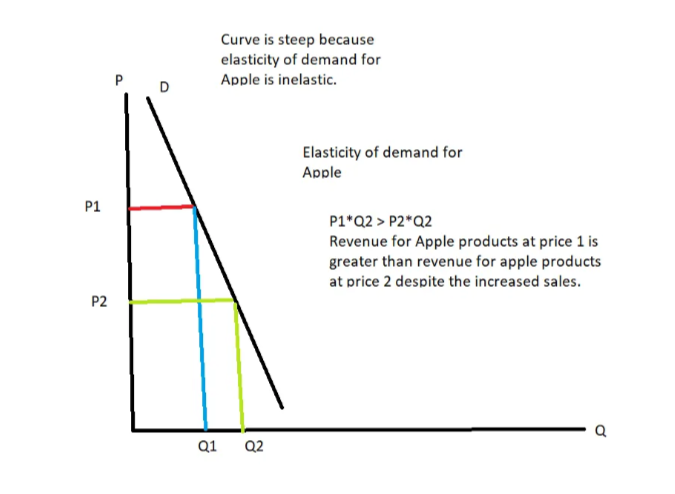
if businesses raise the price of an inelastic product
there are limits:
government regulations: e.g. energy companies (monopolies) cannot keep raising prices because of government regulations
consumer limits: e.g. apple can’t raise their prices forever because it will reach a point where no one can actually afford the product anymore
if businesses lower the price of inelastic product
If they dropped their prices, there would be more sales since the price is lower, but their overall revenue would go down, causing their profit margins to go down.
elasticity of supply for businesses in supply chains
Businesses in a supply chain depend on how quickly suppliers can adjust production when demand changes. They need to be aware of the elasticity of supply of the materials they need and plan accordingly.
If supply is inelastic, businesses may struggle to get materials in time, leading to shortages and lost sales.
Example: McCain, which makes chips, relies on potato suppliers. If demand for chips rises suddenly, they must ensure they can secure enough potatoes.
Example: A uniform shop sells cadet shirts but depends on a manufacturer to produce them. If demand rises quickly, the manufacturer may take time to respond, making supply inelastic.
price discrimination
Businesses charge different prices based on customer’s price elasticity of demand. not all firms can do it, that would be illegal.
To price discriminate, a firm must:
Segment the market (e.g., by age, gender, or location).
Ensure different price elasticities for each group (some customers are willing to pay more than others).
Prevent arbitrage, meaning consumers cannot buy at a lower price and resell or access the cheaper option easily.
Example: Hairdressers charging women more than men.
market is segmented between women and men. In a big city, this is harder because customers can find cheaper alternatives. small towns have fewer options/ no arbitrage, so this is easy to do