Neurons
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is neuroscience?
The study of the nervous system including the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system
What are the statistic regarding neurological diseases in the UK
Neurological diseases affect approximately 1 in 6 people in the UK, with conditions like stroke, epilepsy, and multiple sclerosis being among the most common. 1 in 5 deaths occur due to neurological conditions.
What are the factors that cause neurological disease?
Aging population
Complexity of the neural system
Environmental & lifestyle risks
Limited treatment options (few preventative)
What is the basic unit of the nervous system?
The neuron or ‘nerve cell’
How many neurons are present in the CNS and PNS?
The CNS contains ~86 billion neurons
Cerebral cortex ~16 billion neurons
Cerebellum (majority) more than 16 billion
The PNS contains ~ 100-500 billion neurons
What cells make up the Nervous system and what are their main functions?
Neurons
Process information
Sense environmental changes
Communicate changes to other neurons
Command body response
Glia
Insulates, supports, nourishes
Contributes to regulation of neurons
How do neurons communicate?
Using electrical and chemical signals
What is the typical neuron composed of?
Soma (cell body)
Dendrites
Axon
How is a neurons structure beneficial for them?
The structure of neurons allows for this cell-type to possess rapid, long-distance communication of electrical and chemical signals throughout the nervous system
What does the stoma (cell body) contain?
The Nucleus
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Nissl body (granular structure consisting of ER and free ribosomes)
Smooth ER and Golgi apparatus
Mitochondrion
The Neuronal Membrane
The Cytoskeleton
What is the nucleus responsible for?
Gene expression
Transcription
RNA processing
What is the Smooth ER and Golgi Apparatus?
The sites for preparing/ sorting proteins for delivery to different cell regions (trafficking) and regulating substances
What is the mitochondrion?
The site of cellular respiration where the Krebs cycle takes place producing the cell’s energy source - ATP
What is the Neuronal Membrane?
The barrier that encloses cytoplasm
~5nm thick
Protein concentration in membrane varies
Structure of discrete membrane regions influences neuronal function
What is the Cytoskeleton?
The internal scaffolding of the neuronal membrane
Is not static (constantly changing)
Has three ‘bones’: microtubules, microfilaments, neurofilaments
What is the Axon?
Axons are long projections responsible for relaying/ sending information from one neuron to the next
What is the Axon made up of?
Axon hillock (beginning)
Axon proper (middle)
Axon terminal (end)
Myelin sheath
What is the Myelin Sheath?
A fatty insulation layer around the axon that offers protection and speeds up signal transmission
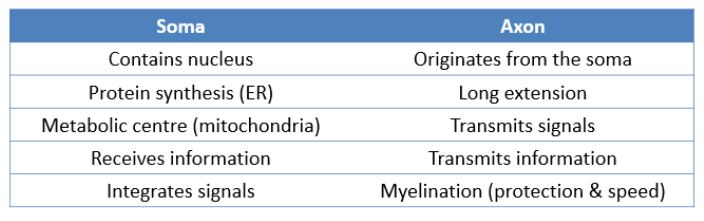
What are the differences between Axon and the Soma?
What is the Axon Terminal?
The endpoint of the axon, where signals are passed to other cells via synapses. It is crucial for communication and forms a synapse with another neuronal cell to facilitate communication. It contains synaptic vesicles filled with neurotransmitters.
What are Neurotransmitters (NTs)?
NTs are chemicals that are released in response to an electrical impulse (action potential). NTs bind to receptors on the next cell, passing information from one neuron to another or to a target cell e.g. muscle or gland.
What is the synapse?
The point of communication between neurons which occurs by synaptic transmission
The Axon is referred to as the presynaptic location of the neuron
This is where electrical-to-chemical-to-electrical transformation occurs
Synaptic transmission dysfunctions cause mental dissorders
What are the types of synapses?
Chemical
Communicate with chemicals (neurotransmitters)
Electrical
Communicate with electricity
What is the difference between Afferent and Efferent Axons?
Afferent (carry to): Carry information toward a particular point
Efferent (carry from): Carry information away from a point
What are Dendrites responsible for?
Dendrites are responsible for receiving and processing information sent from the axon of the neuron acting as the ‘antennae’ of neurons. Dendrites for dentritic trees consisting of numerous branches. They are referred to as the postsynaptic location of the neuron and can be ‘smooth’ or ‘spiny’.

What is this classified as and why?
It is unipolar - has a single neurite

What is this classified as and why?
Bipolar - has two neurites
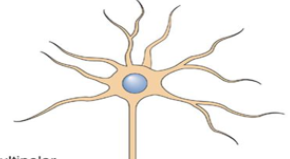
What is this classified as and why?
Multipolar - has more than two neurites
What would a star-shaped Neuron be classified as?
Stellate cells
What would a pyramid-shaped neuron be classified as?
Pyramidal cells
What do motor neurons do?
Transmit messages from the brain to the muscles to generate movement
What do sensory neurons do?
Detect light, sound, odour, taste, pressure, heat and send messages to the brain
What do non-motor or sensory neurons do?
They control involuntary processes e.g. heartbeat, release of hormones, digestion etc