Chapter 1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Marieb and Hoehn ------ Athens Tech
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Anatomy
Studies the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another.
Subdivision of Anatomy
1. Macroscopic
2. Microscopic
3. Developmental
Macroscopic (Gross) Anatomy
Study of larger structures that are easily visible
Examining the structure of body
Cadaver dissection
Comparative anatomy
Examining structure of the human body
1. Inspection
2. Palpation
3. Auscultation
4. Percussion
Regional anatomy
All the structures (muscles, bones, blood vessels, nerves, etc.) in a particular region of the body, such as the abdomen or leg, are examined at the same time.
Systemic anatomy
Body structure is studied system by system. For example, when studying the cardiovascular system, you would examine the heart and the blood vessels of the entire body.
Surface anatomy
The study of internal structures as they relate to the overlying skin surface.
Microscopic anatomy
Deals with structures too small to be seen with the naked eye.
Cytology
The study of the cells of the body
Histology
The study of tissues
Developmental anatomy
Traces structural changes that occur in the body throughout the life span.
Embryology
A subdivision of developmental anatomy, concerns developmental changes that occur before birth.
Pathological anatomy
Studies structural changes caused by disease.
Radiographic anatomy
Studies internal structures as visualized by X-ray images or specialized scanning procedures.
Physiology is the study of
the normal functions of the organ systems.
Bases on the organ system
1. focuses on cellular & molecular levels of the body
2. Electrophysiology
3. Comparative physiology
Renal physiology
Concerns kidney function and urine production
Neurophysiology
Explains the workings of the nervous system
Cardiovascular physiology
Examines the operation of the heart and blood vessels
Chemical level
The simplest level of the structural hierarchy. At this level, atoms. tiny building blocks of matter, combine to form molecules such as water and proteins.
Principle of complementarity of structure & function
Structure often dictates function
Cellular level
All cells have some common functions, but individual cells vary widely in size and shape, reflecting their unique functions in the body
Tissue level
Tissues are groups of similar cells that have a common function.
Organ level
Extremely complex functions become possible.
Organ system level
Organs that work together to accomplish a common purpose
Organismal level
Represents the sum total of all structural levels working together to keep us alive
Anatomical Variation
the normal flexibility in the topography and morphology of body structures
Necessary Life Functions
1. Maintaining boundaries
2. Movement
3. Responsiveness
4. Digestion
5. Metabolism
6. Excretion
7. Reproduction
8. Growth
Contractility
The muscle cell's ability to move by shortening
Movement
Includes the activities promoted by the muscular system,
Example: such as propelling ourselves from one place to another by running or swimming, and manipulating the external environment with our nimble fingers
Digestion
The breaking down of ingested foodstuffs to simple molecules that can be absorbed into the blood
Responsiveness, excitability, irritability
The ability to sense changes in the environment and then respond to them
metabolism = catabolism + anabolism
All chemical reactions that occur within body cells.
1. breaking down substances into their simpler
building blocks
2. synthesizing more complex cellular structures
from simpler substances
3. using nutrients and oxygen to produce ATP
4. energy-rich molecules that power cellular
activities.
Excretion
The process of removing wastes, or excreta, from the body
Reproduction
Occurs at the cellular and the organismal level.
Growth
An increase in size of a body part or the organism as a whole
Water
Accounts for 60% to 80% of our body weight and is the simple most abundant chemical substance in the body
Nutrients
Substances in food that your body needs to grow, to repair itself, and to supply you with energy
Organ systems of the body
1. integumentary
2. skeletal
3. muscular
4. nervous
5. endocrine
6. cardiovascular
7. lymphatic
8. respiratory
9. digestive
10. urinary
11. reproductive Male/Female
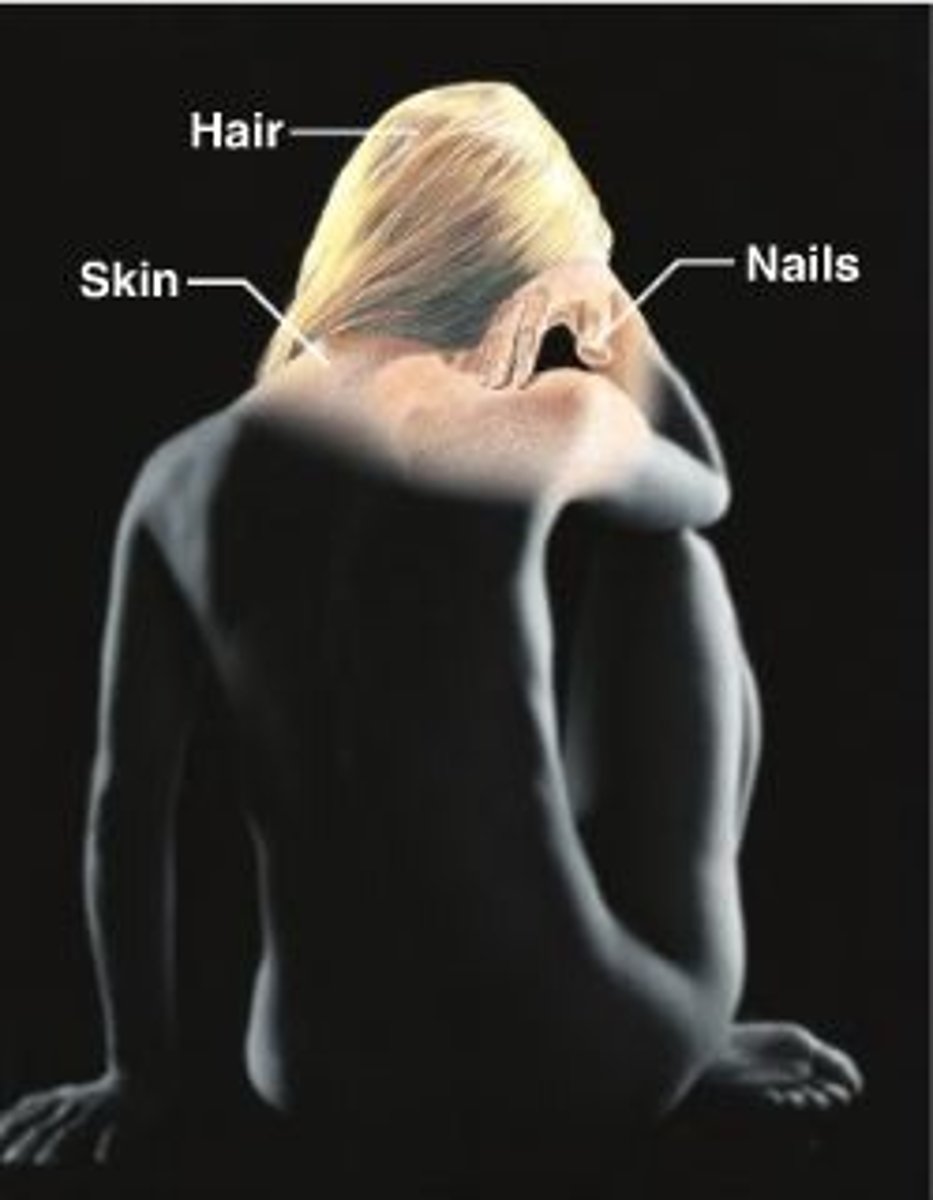
Integumentary system
Hair, skin, nails. Houses receptors and sweat/oil glands
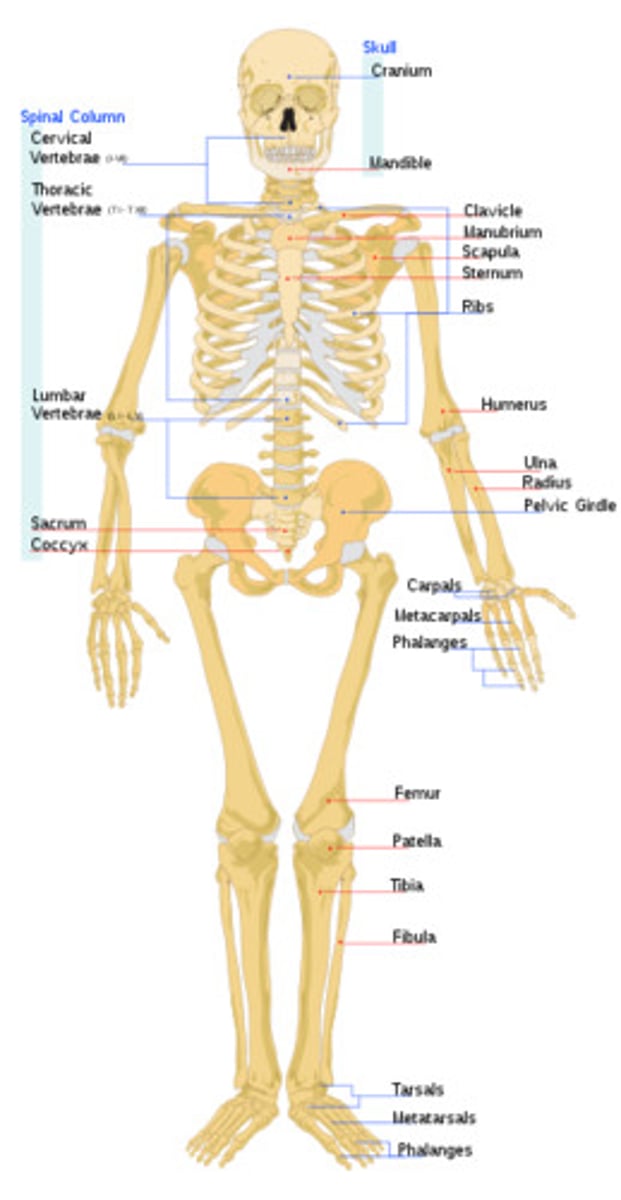
Skeletal system
Bones; provides protection and suspport
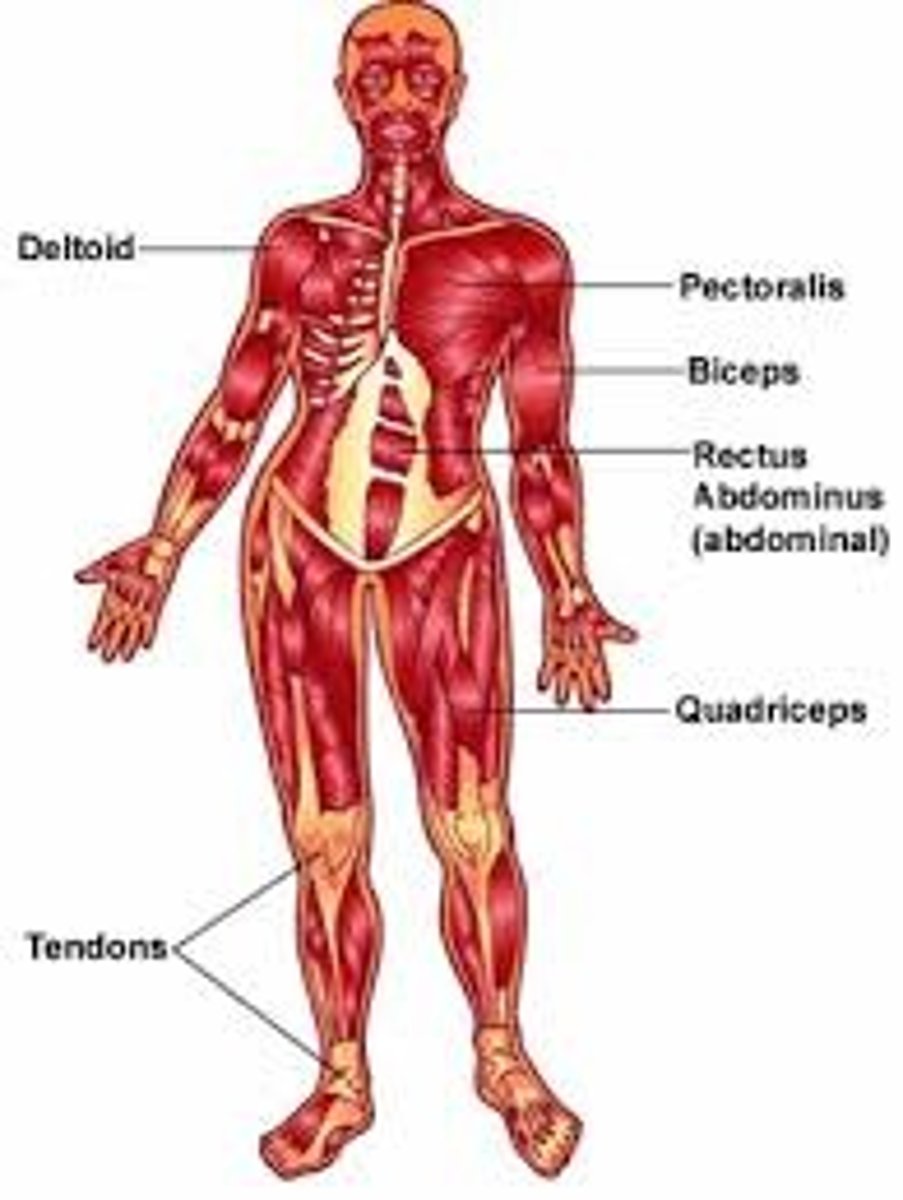
Muscular system
skeletal muscles; posture, heat, movement
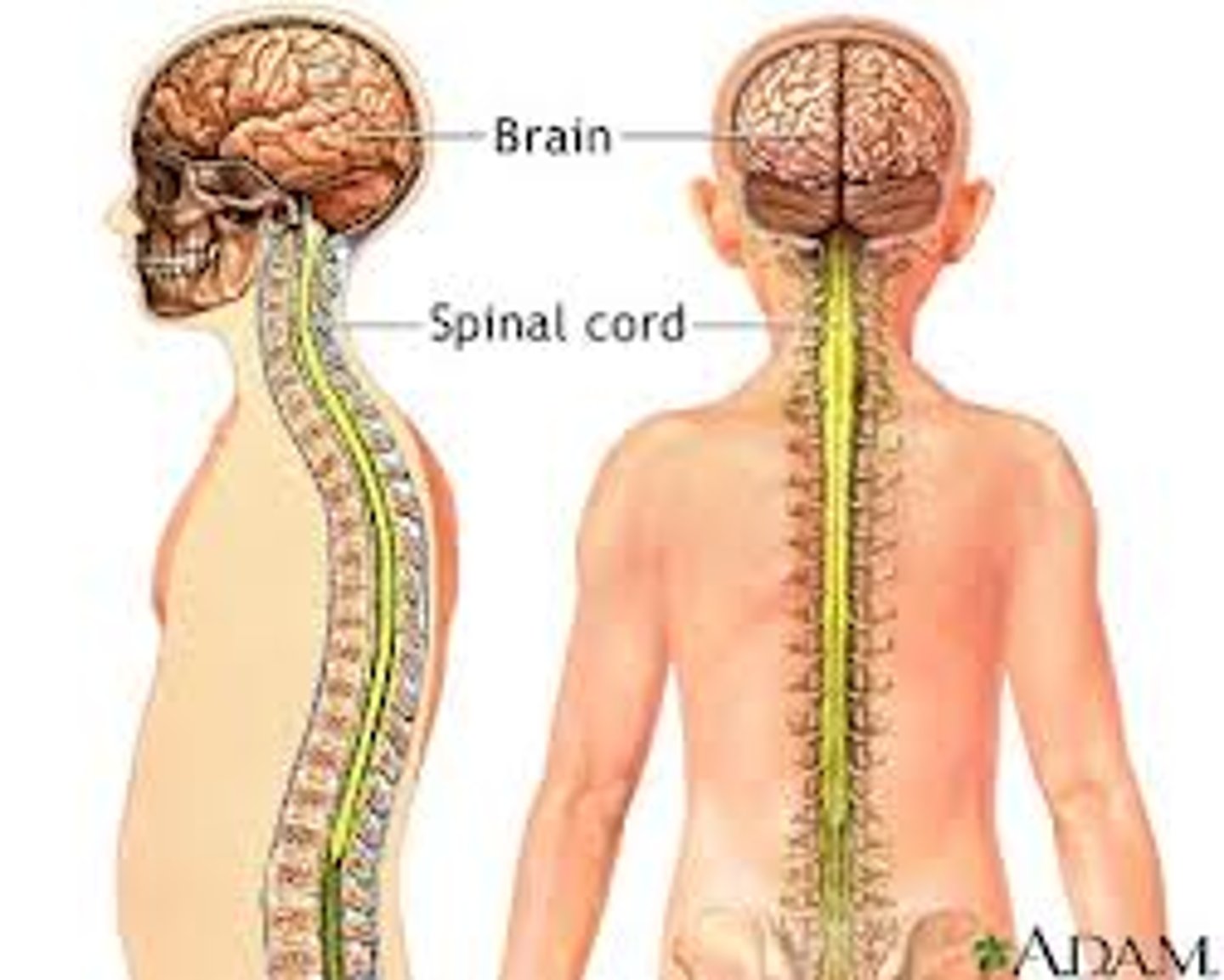
Nervous system
Body's control system, responds to internal and external changes by stimulating proper body part; brain, spinal cord, nerves
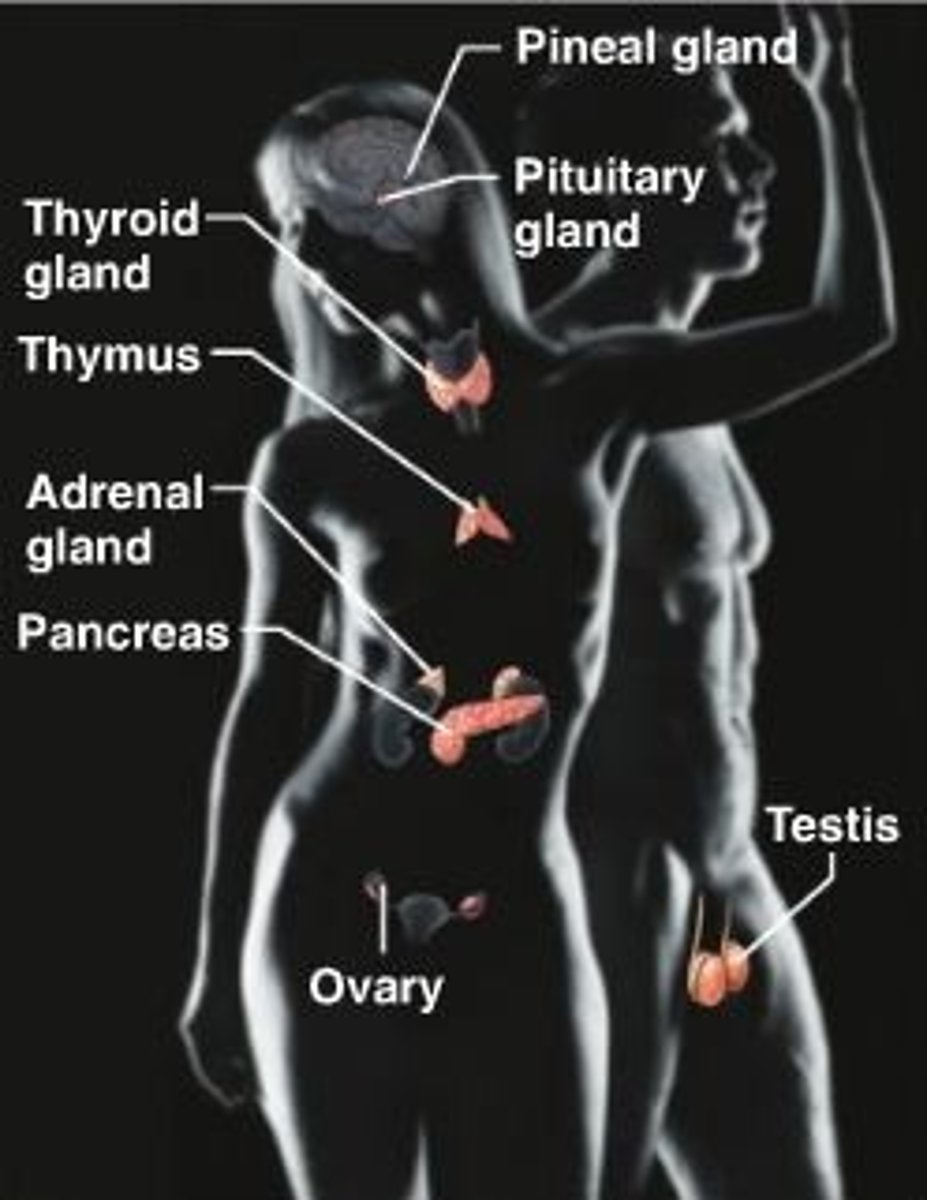
Endocrine system
thyroid, thymus, adrenal gland, pancreas, ovary, testis, pituitary gland, pineal gland. Release hormones.
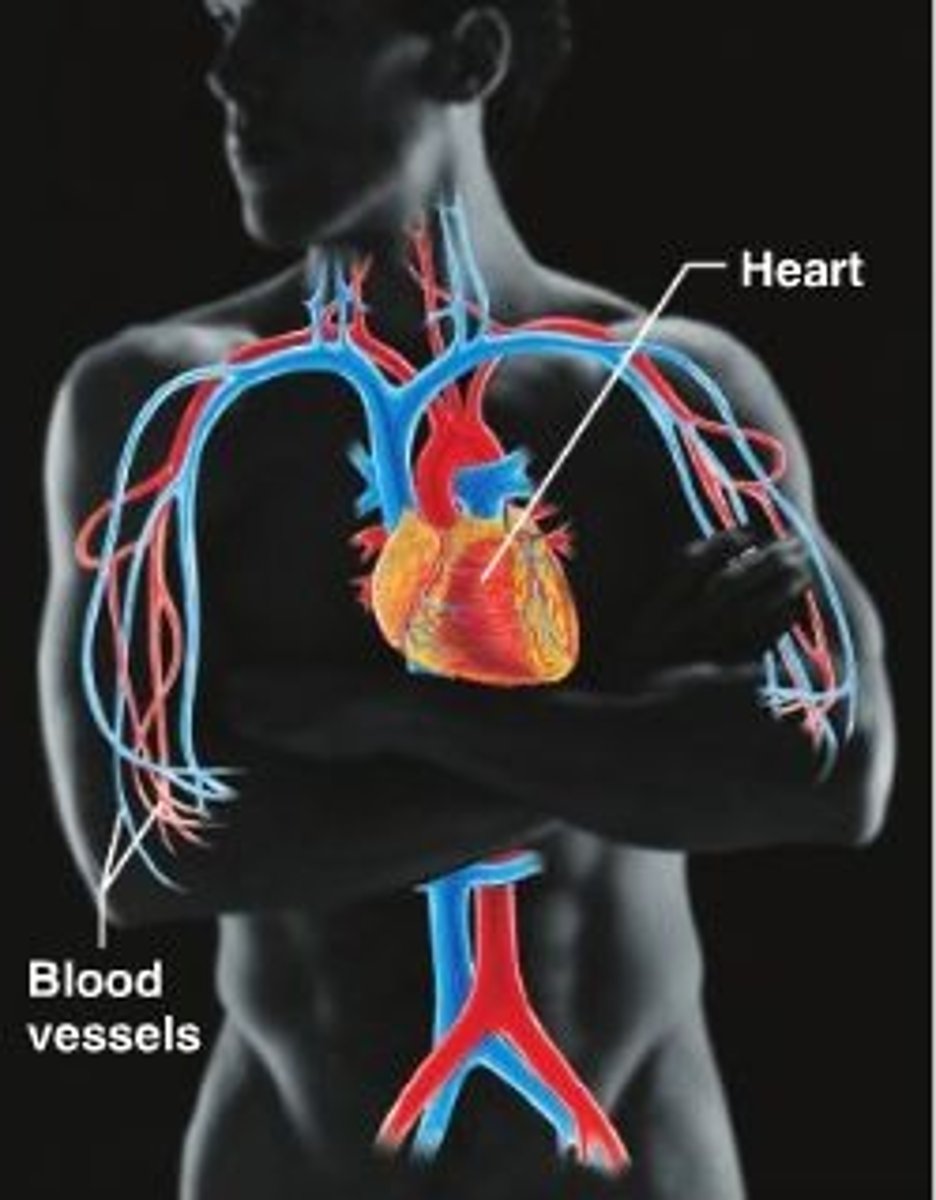
Cardiovascular
Blood vessels, veins, arteries, heart. Transport blood, oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients
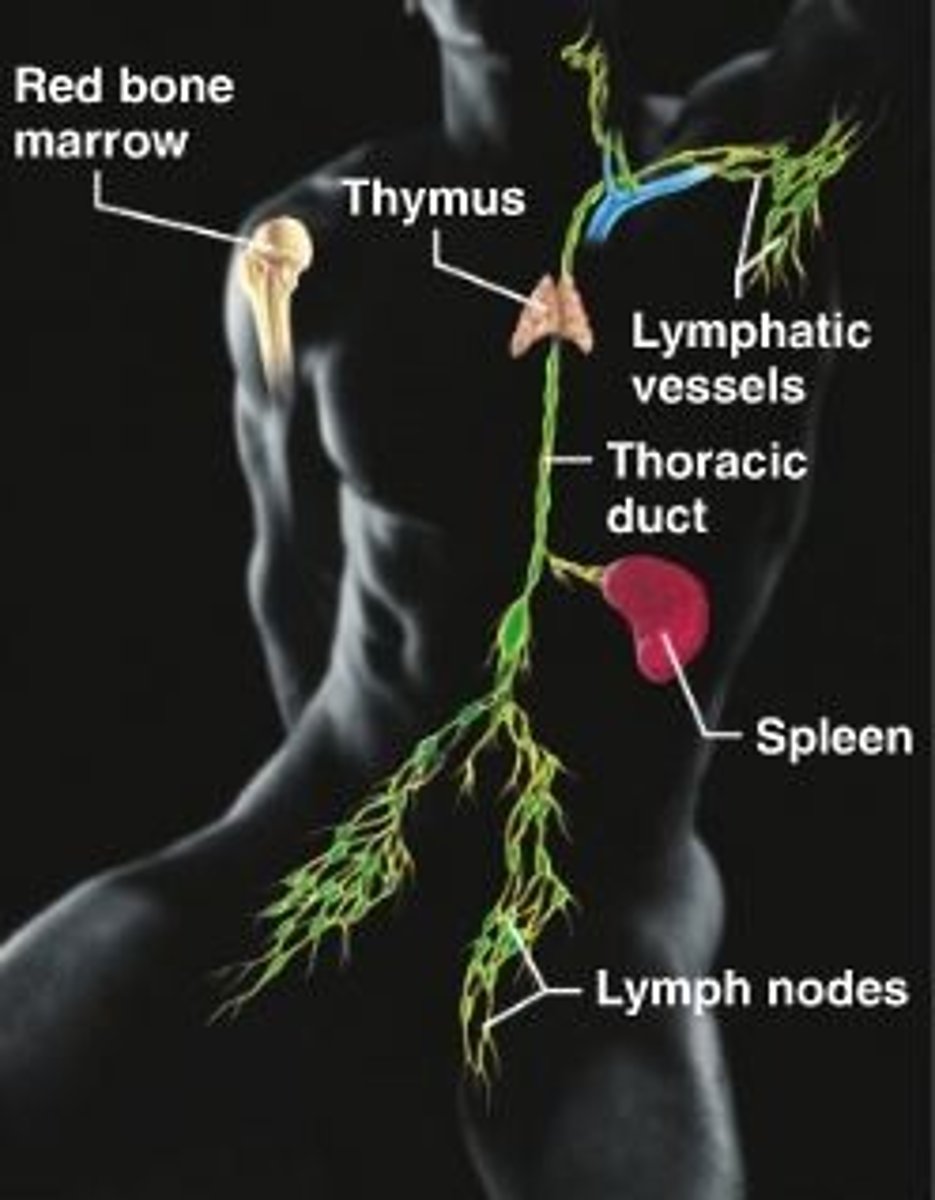
Lymphatic system/immunity
lymph nodes, spleen, thoracic duct, lymphatic vessels, thymus, red bone marrow. Transports fluid, white blood cells for immunity
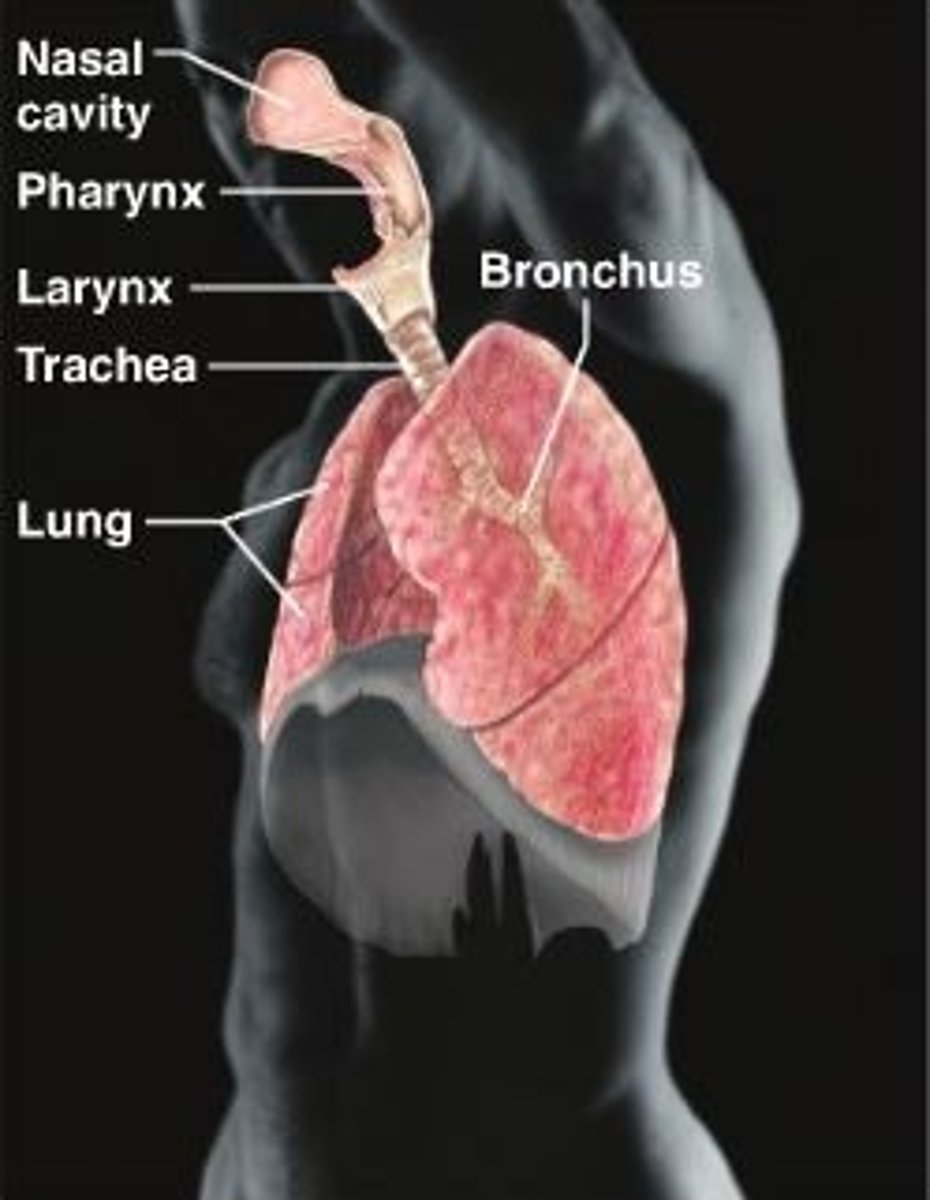
Respiratory system
Nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, lung, bronchi. Supply blood with oxygen & remove carbon dioxide.
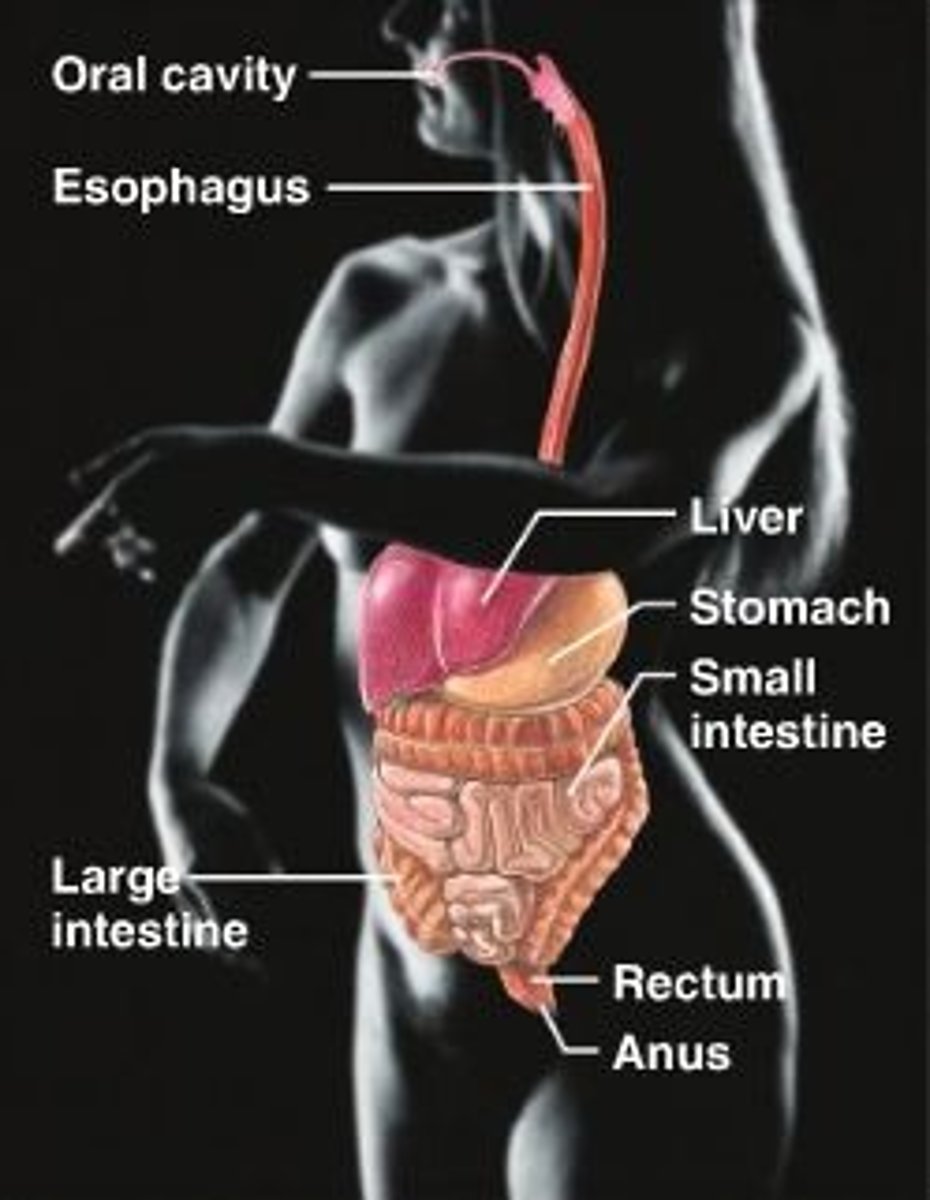
Digestive system
oral cavity, esophagus, liver, stomach, small intestine, rectum, anus, large intestine. Break down food to absorb nutrients.
reproductive system (female)
ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, mammary glands
-produces and transports eggs
-site of fetal development, fetal nourishment, childbirth, and lactation
-secretes hormones
-sexual function
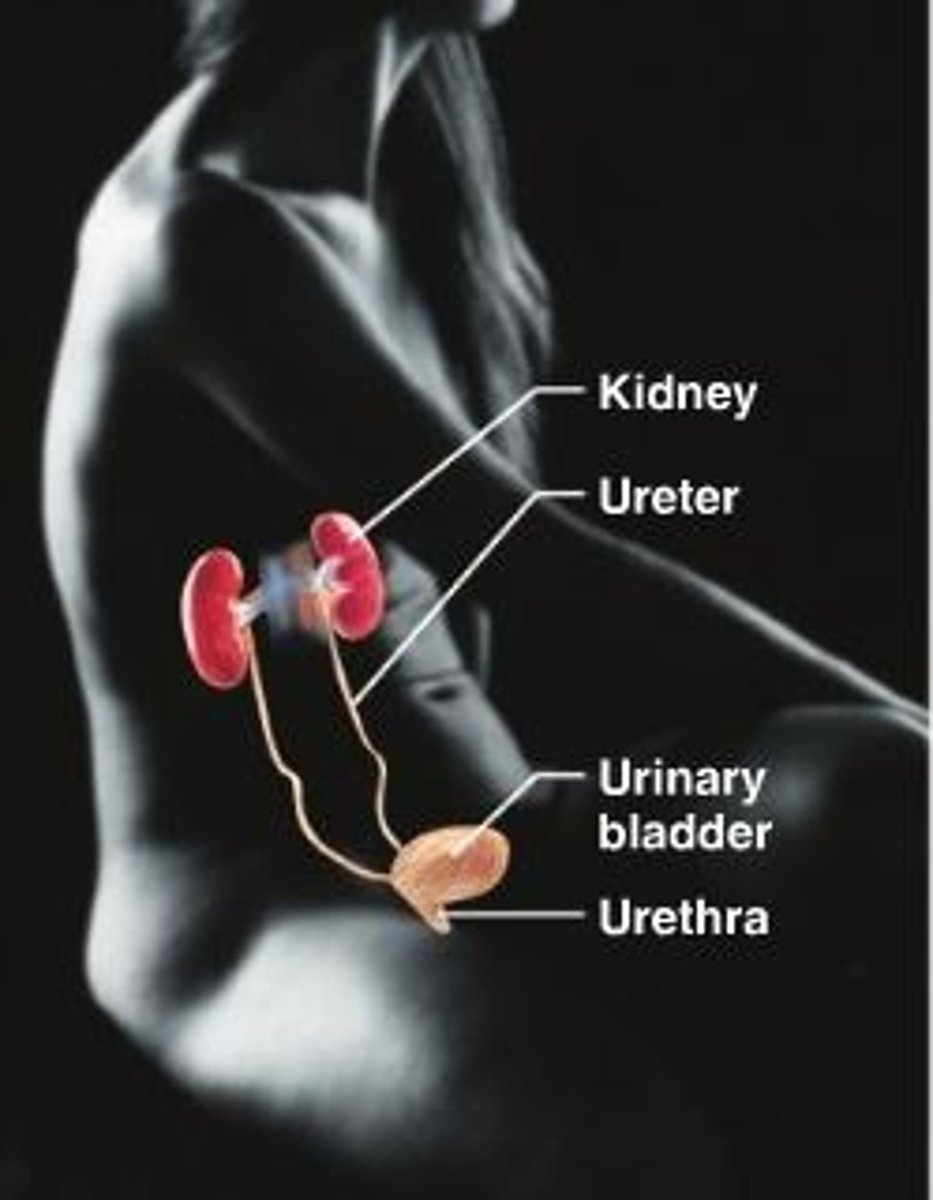
Urinary system
Kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra. Eliminates nitrogenous wastes, regulates water.
Normal body temperature
98.6 degrees
Atomospheric pressure
The force that air exerts on the surface of the body
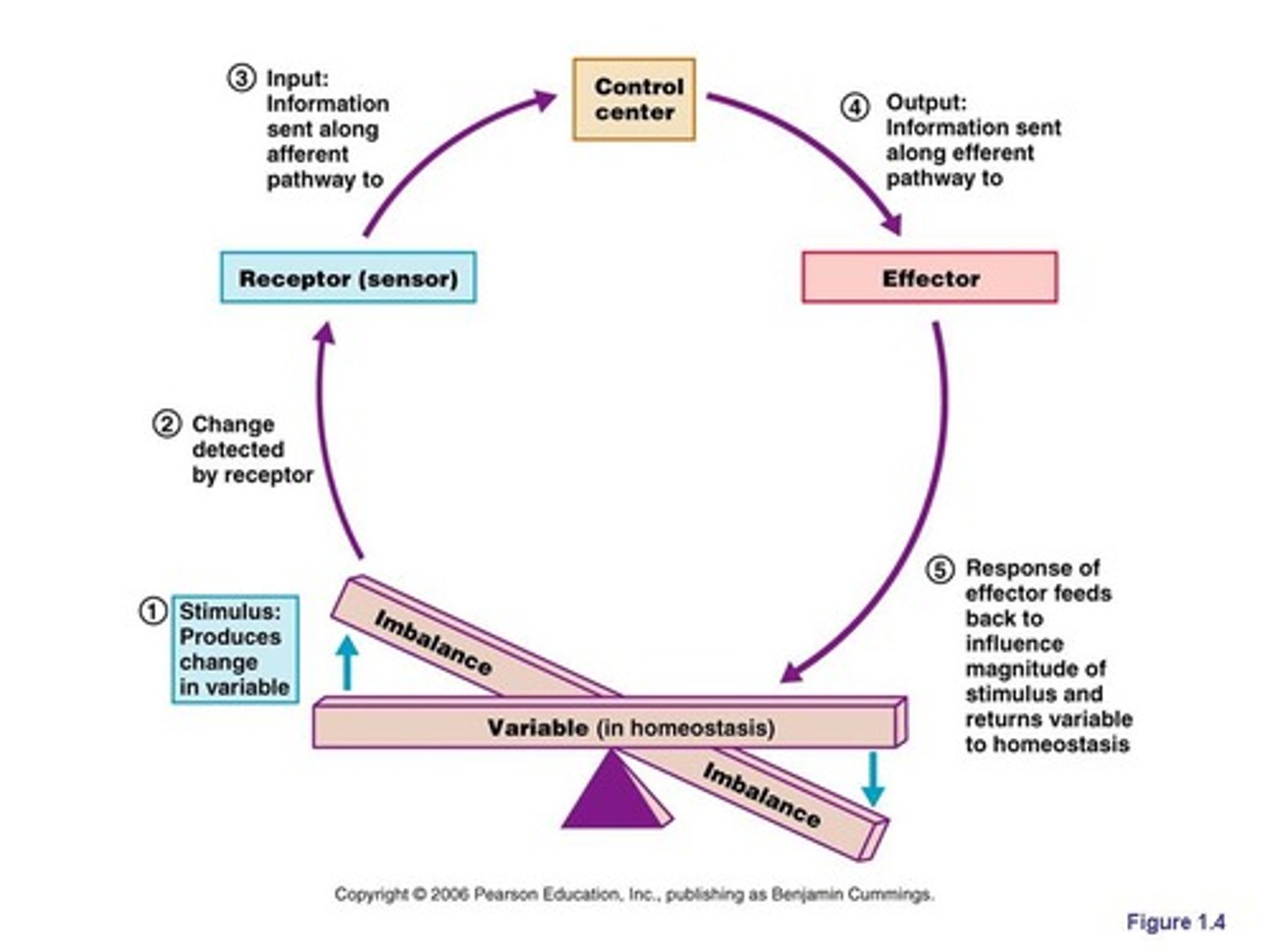
Homeostasis
Maintenance of relatively stable internal comditions despite continuous changes in the environment.
Homeos = similar/same Stasis = Involves 3 components
1. Receptor
2. Control center
3. Effector
Variable
the factor or event being regulated
Receptor
Some type of sensor that monitors the environment and responds to changes called stimuli, by sending information to the second component, the control center
Control center
Determines the set point, which is the level or range at which a variable is to be maintained
Effector
Provides the means for the control center's response to the stimulus
Negative feedback mechanisms
The output shuts off the original effect of the stimulus or reduces its intensity
Thermoreceptors
respond to changes in temperature.
Example
1.Vasodilation - enlarging the diameter of a vessel
1. vasoconstriction - narrowing of blood vessels
Neural and Endocrine Regulation
-hormones and neurotransmitters both interact with specific receptors
-binding to a receptor causes a change within the cell
-there are mechanisms to turn off target cell activity; the signal is either removed or inactivated
Baroreceptors
Cells that are sensitive to blood pressure changes.
Positive feedback mechanisms
The result or response enhances the original stimulus so that the response is accelerated
homeostatic imbalance
a disturbance in homeostasis resulting in disease
- increases risk of disease
- associated with aging
- destructive positive feedback mechanisms may take over