MARKETING STRATEGIES
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
what are the marketing strategies from the syllabus?
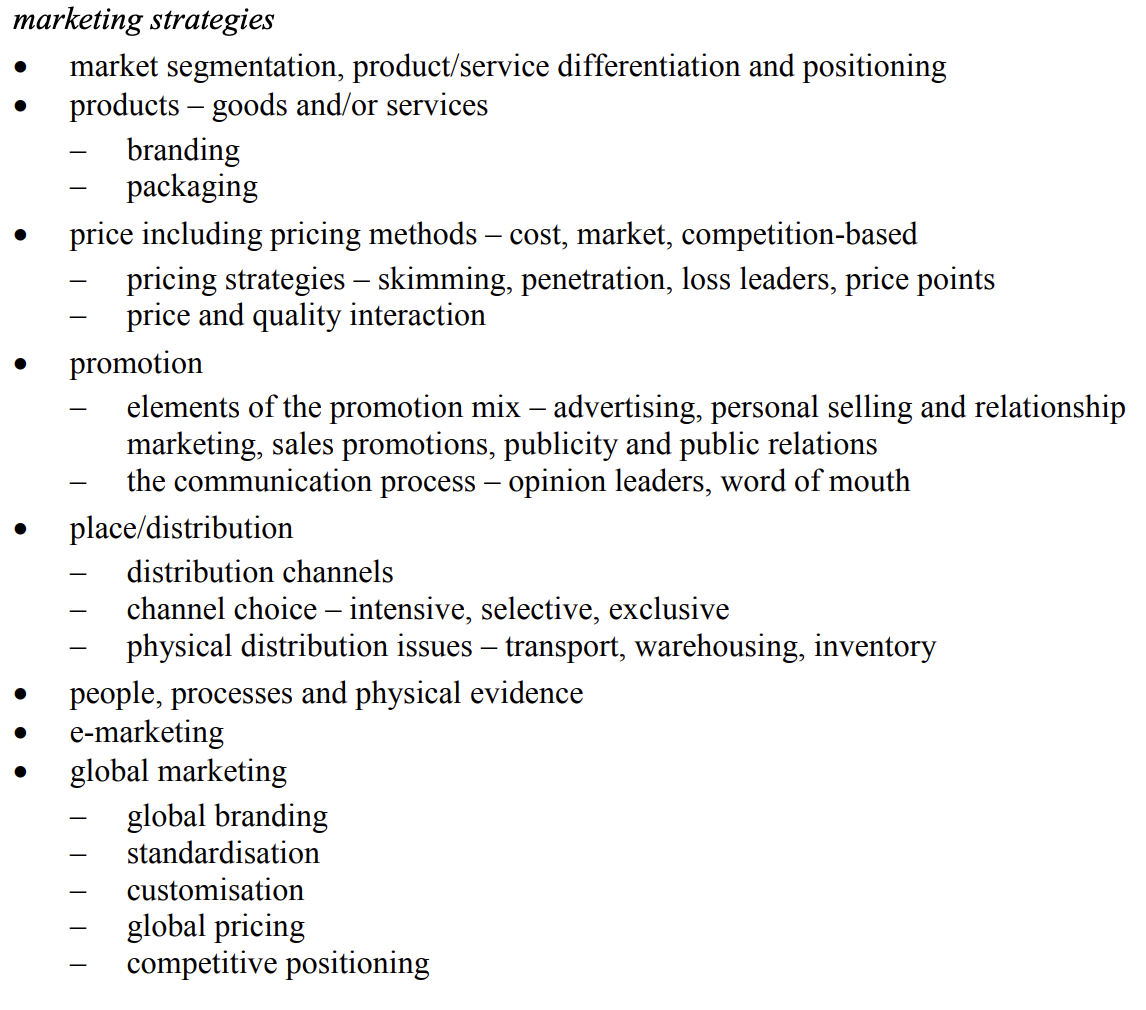
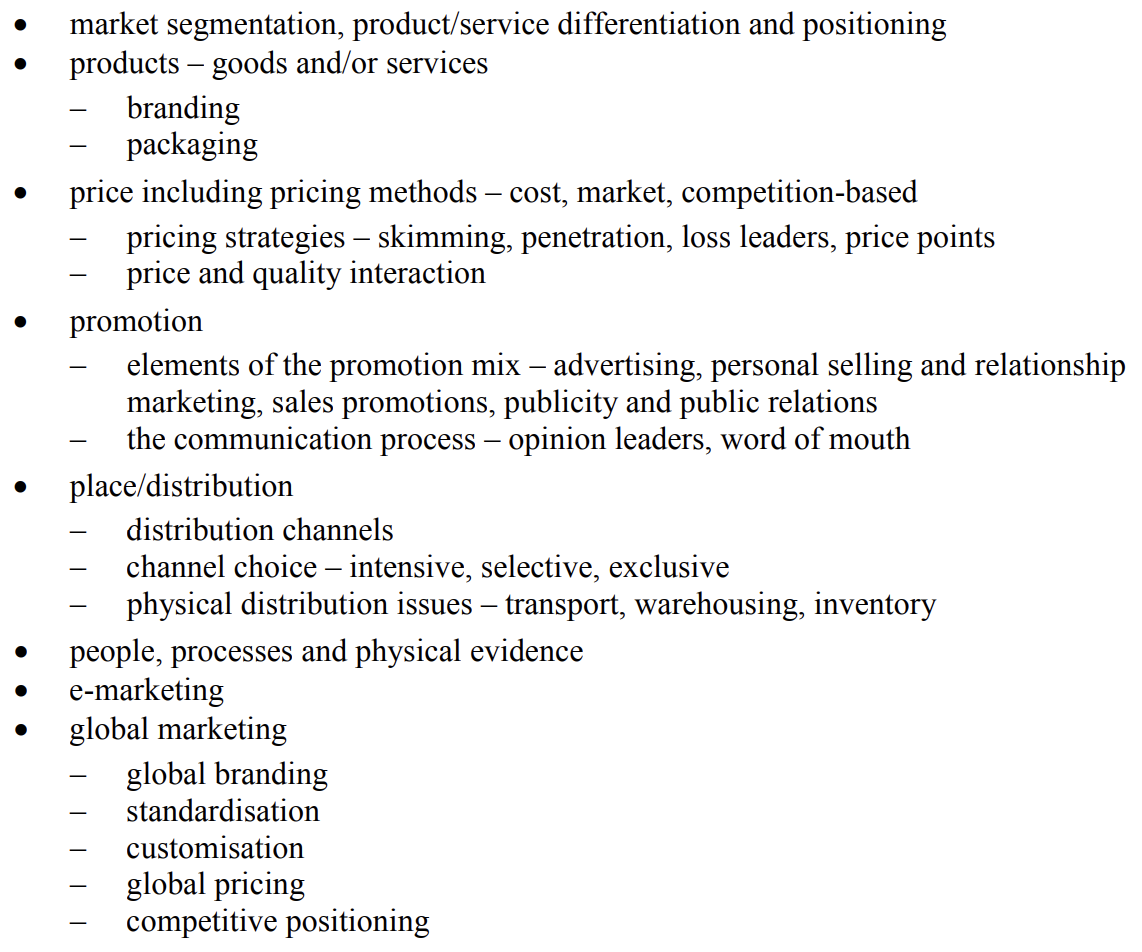
market segmentation, product/service differentiation and positioning
products – goods and/or services
– branding
– packaging
price including pricing methods – cost, market, competition-based
– pricing strategies – skimming, penetration, loss leaders, price points
– price and quality interaction
promotion
– elements of the promotion mix – advertising, personal selling and relationship marketing, sales promotions, publicity and public relations
– the communication process – opinion leaders, word of mouth
place/distribution
– distribution channels
– channel choice – intensive, selective, exclusive
– physical distribution issues – transport, warehousing, inventory
people, processes and physical evidence
e-marketing
global marketing – global branding – standardisation – customisation – global pricing – competitive positioning
What is market segmentation?
Involves dividing the total market into segments. These segments are groups of people who share one or more common characteristics
Why does a business do market segmentation?
business segments its market so it can direct its marketing strategies to specific groups of customers rather than the total market
what are the different marketing segmentation
Demographic segmentation
Geographic segmentation
Psychological segmentation
Behavioural segmentation
what is demographic segmentation?
is the process of dividing the total market according to particular features of a population, including the size, age, sex, income, cultural background and family size.
What is geographic segmentation?
is the process of dividing the total market according to geographic locations. This type of segmentation is based on the geographic units themselves (countries, states, cities, etc.), but also on various geographic factors, such as climate, cultural preferences, populations and more.
What is physiological segmentation?
is the process of dividing the total market according to personality characteristics, motives, opinions, socioeconomic groups and lifestyles.
What is behavioural segmentation?
is the process of dividing the total market according to the customers’ relationship to the product.
What is Product/service differentiation
Promoting differences between a business’s products from competitors.
This occurs when products that are the same or similar are made to appear different from and/or better than those of their competitors i.e. attempt to make their product unique.
What is Product/service positioning
- This refers to the technique in which marketers try to create an image or identity for a product/service compared with the image of competing products or services.
- Marketers try to create an image or identity for a product/service compared with the image of competing products/services. It is how customers perceive the product.
This image differentiates the product/service from competitors.
What are the marketing strategies?
What are products
Products – goods or services to satisfy a need or want in return for an exchange (usually monetary i.e. money)
A product possesses tangible and intangible benefits. This is known as the total product concept.
Tangible- refers to things that are physical, that is, items that can be touched, seen, heard or smelled
Intangible- unable to be touched; not having physical presence. Used to differentiate the product
What is branding?
A name, term, symbol, design or any combination of these that:
identifies a product
distinguishes a product from its competition
Brand names- that part of the brand that can be spoken e.g. BMW, Coca-Cola ..
how does branding help consumers?
identify the specific products that they like. Without branding, a consumer selection would be quite random because buyers could have no guarantee that they were purchasing what they preferred
evaluate the quality of products, especially when a consumer lacks the expertise to judge a product’s features
reduce their level of perceived risk of purchase. A respected and trusted brand will provide reassurance that the consumer is making the right choice
gain a psychological reward that comes from purchasing a brand that symbolises status and prestige.
How does branding help businesses
gain repeat sales because consumers recognise the business’s products
introduce new products onto the market because consumers are already familiar with the business’s existing brands
with their promotional activities because the promotion of one product indirectly promotes all other similarly branded products
encourage customer loyalty. This has the added benefit to the business of being able to charge a higher price for the product.
what does packaging involve?
Packaging involves:
the development of a container and the
graphic design for a product
why is packaging important?
Well-designed packaging will give a positive impression of the product and encourage first-time customers. For example, tasteful packaging can create an image of luxury, sensuality and exclusiveness, helping to promote the product. In addition, packaging:
preserves the product
protects the product from damage or tampering
attracts consumers’ attention
divides the product into convenient units
assists with the display of the product
makes transportation and storage easier
form of communication
What is price
Price refers to the amount of money a customer is prepared to offer in exchange for a product
why is getting the right price important?
To ensure a reasonable profit margin that will sustain the business
To stand out from competitors
price/quality relationship
Covering the costs
what factors should be considered when pricing a product?
Costs of products
Quality of the product
Competition
Economic conditions
Supply in demand
Target market
what are the different pricing METHODS
cost based
market based
competition based
what is cost-based marketing
Cost comes from cost of producing or purchasing a product and then adding a mark-up. Here the business totals up all of the costs involved in producing the product and then adds a desired margin (a percentage) on top of the costs in order to determine the price that the product will sell for.
Calculator → cost + (cost x mark-up percentage) = price
what is market-based pricing
setting prices according to the interaction between the levels of demand and supply. It is setting prices according to what the market is prepared to pay.
When demand for a product is greater than its supply, there will be a shortage in the market. This will force up the price of the good.
Conversely, when the supply of a product is greater than its demand, a surplus will exist in the market.
what is competition based pricing
where the price covers costs (cost of raw materials and the cost of operating the business) and is comparable to the competitor’s price.
Competition-based pricing is often used when there is a high degree of competition from businesses producing similar products. Once a business has established a base price, it can then decide to choose a price either:
Below that of competitors. This policy of undercutting the competition is often used as a way of breaking into an established market.
Equal to that of competitors. Following the price established by a price leader is an easy option for a business because it avoids having to undertake market research to find out what the consumer would actually pay. As well, it also avoids the risks of price competition/ war.
Above that of competitors. This is a favoured practice by businesses who wish consumers to perceive the product as superior, which appeals to the status-conscious buyer.
what are the different pricing STRATEGIES
– skimming, penetration, loss leaders, price points
what is price skimming
Business charges the highest price possible, usually during the introduction phase of the life cycle. Some consumers are willing to pay a high price for a product’s novelty features because of the prestige or status that ownership gives. Early purchasers (adopters) of innovative electronic equipment fall into this category.
Apple iphones
What is price penetration
A business charges the lowest price possible for a product
Often used to gain market share
It has a low profit margin, but selling more units so high revenue over all.
Example = kmart
what is loss leaders
A product is sold at or below cost price (what it cost to buy or make)
Why would a business use this strategy?
Attracts customers to the business
The product needs to be sold e.g use by date
Baten Switch
what is price points?
Selling products only at certain predetermined prices.
Why?
1.Psychological price points
i.e. petrol prices- $1.79 - it makes it seem less in price
2. Gaps in the pricing structure due to the difference in quality/features of the product. Enables a range of differentiated product versions to be sold to different customers
Apple selling different phones at different prices, different target markets are attracted
what is price-quality interaction and why is it important
Consumers perceive there is a price-quality relationship.--> positioning, that the customer has of the product.
i.e. Low price= perception/image of cheap
High price= aura of quality, status and distinction (prestige or premium pricing)
what is promotion?
the publicizing of a product, organization, or venture so as to increase sales or public awareness.
what does promotion attempt to do?
attract new customers by heightening awareness of a particular product
increase brand loyalty by reinforcing the image of the product
encourage existing customers to purchase more of the product
provide information so customers can make informed decisions
encourage new and existing customers to purchase new products.
what are elements of the promotional mix?
– advertising, personal selling and relationship marketing, sales promotions, publicity and public relations
what is advertising
Paid, non-personal message communicated through a mass medium e.g TV, Radio, Magazines
Communication used to reach an extremely large audience OR to focus on a small, distinct target market segment
Advertising media is a term for the many forms of electronic and print communication used to reach a large audience
what are the six main advertising medias
Mass marketing - television, radio, newspapers and magazines
Direct marketing catalogues - catalouges mailed to individual households
Telemarketing - telephone to personally contact a customer
E-marketing - internet to deliver advertising messages
Social media advertising - online advertising using platforms such as instagram
Billboards - large signs placed at strategic locations
what is personal selling and relationship marketing
Personal selling involves the activities of a sales consultant directed to a customer in an attempt to make a sale; it involves the human aspect of promotion.
It is an expensive promotional method, businesses are willing to spend the money on it because it offers three unique advantages:
The message can be modified to suit the individual customer’s circumstances.
The individualised assistance to a customer can create a long-term relationship resulting in repeat sales.
The sales consultant can provide after-sales customer service in relation to product features, installation, warranties and servicing.
Customers want more individualised treatment. businesses are looking for ways to develop long-term, cost-effective and strong relationships with individual customers, a process known as relationship marketing. The ultimate aim is to create customer loyalty by meeting the needs of customers on an individual basis, thereby creating reasons to keep customers coming back. A highly successful relationship marketing strategy is loyalty programs
what is sales promotion
A business may decide to offer a direct inducement to customers in an attempt to sell more of its product. This type of promotion is referred to as sales promotion and aims to:
entice new customers
encourage trial purchase of a new product
increase sales to existing customers and repeat purchases
what are examples of sales promotion
Limited time offers
Free gifts
Refunds
Samples
Point - of - purchase displays
Contest and giveaways
Deals
what is publicity and public relations
Publicity is any free news story about a business’s products. It differs from advertising in that it is free and its timing is not controlled by the business.
what are the main aims of publicity
enhance the image of the product
raise awareness of a product
highlight the business’s favourable features
help reduce any negative image that may have been created.
what are public relations
those activities aimed at creating and maintaining favourable relations between a business and its customers.
How does public relations assist a business in achieving its objective of increased sales.
Promoting a positive image
Effective communication of messages
Issues monitoring
Crisis management and relationship building with stakeholders.
whats the communication process
Marketing managers can use a variety of channels to communicate a message. A channel is any method used for carrying a message.
opinion leaders
word of mouth
what are opinion leaders
a person who influencers others. Their opinions are respected and they are often sought out for advice e.g Alix Earle
what is word of mouth
when people influence other during CONVERSATION, e.g trip advisor, product reviews
what are place/distribution strategies
distribution channels
channel choice – intensive, selective, exclusive
physical distribution issues – transport, warehousing, inventory
what are distribution channels
Distribution channels or marketing channels are the routes taken to get the product from the business to the customer. This process usually involves a number of intermediaries, such as the wholesaler, broker, agent or retailers.
what are the different distribution channels
Producer to customer. This is the simplest channel and involves no intermediaries. Virtually all services, from tax advice to car repairs, use this method.
Producer to retailer to customer. A retailer is an intermediary who buys from producers and resells to customers. This channel is often used for bulky or perishable products such as furniture or fruit.
Producer to wholesaler to retailer to customer. This is the most common method used for the distribution of consumer goods. A wholesaler is an intermediary who buys in bulk, from the producer, then resells in smaller quantities to retailers.
Producer to agent to wholesaler to retailer to customer. An agent distributes products to wholesalers but never owns the product. Agents are paid a commission by the producer. Usually agents are used for inexpensive, frequently used products. A business that does not have any sales representatives will often use an agent instead.
what are channel choices
How a business chooses the channel of distribution best suited to its product depends largely on the location of the business’s market or market coverage. Market coverage refers to the number of outlets a firm chooses for its product.
either
intensive
selective
exclusive
what is intensive distribution
This occurs when the business wishes to saturate the market with its product. Customers can shop at local outlets and be able to purchase the product. Many convenience goods, such as milk, lollies and newspapers, are distributed this way.
cadbury
what is selective distribution
This involves using only a moderate proportion of all possible outlets. Clothing, furniture and electrical appliances are often distributed using this method. The customer is prepared to travel and seek out a specific retail outlet that stocks a certain brand.
smeg
what is exclusive distribution
This is the use of only one retail outlet for a product in a large geographic area. This method of distribution is commonly used for exclusive, expensive products.
gucci
what are physical distribution issues
Physical distribution is all those activities concerned with the efficient movement of the products from the producer to the customer. Physical distribution is therefore the movement of the products themselves through their channels of distribution. It is a combination of several interrelated functions, including transportation, warehousing and inventory control.
what is transport physical distribution
An intricate network of transportation is required to deliver the vast array of products on supermarket shelves. Developments in packaging and transportation now permit Australian native flowers, for example, to be picked then sold in Tokyo within 24 hours.
The method of transportation a business uses will largely depend on the type of product and the degree of service the business wishes to provide. The four most common methods of transportation are rail, road, sea and air.
what is transport physical distribution issues
Cost
Time it takes
Spoil time
Damage
Environmental sustainability
Weight
what is warehousing
Warehousing is a set of activities involved in receiving, storing and dispatching goods. A warehouse acts as a central organising point for the efficient delivery of products.
what issues need to be considered
Size of the warehouse
How far away they are
How they are bringing them to the stores in time
Location
Cost
Layout
Just - in - time
what are inventory issues
Customers find it frustrating when a product they wish to purchase is ‘out of stock’, and a business that repeatedly allows this to happen will lose sales and market share.
businesses may implement an inventory control system. If a business carries too much stock on its inventory, it will experience high storage costs. However, too little stock results in lost sales or ‘stock-out costs’. The goal of inventory is to find the correct balance between these two situations.
What issues need to be considered?
JIT
Forecast the stock you are going to hold
Quantity levels
what are services marketing mix (3Ps)
people, processes and physical evidence
what does people refer to
People refers to the quality of interaction between the customer and those within the business who will deliver the service.
The business is to recruit and select the right workers and then train them appropriately on how to perform the service and leave a good impression.
How a business treats their employees as well
what do processes refer to
Processes refers to the flow of activities that a business will follow in its delivery of a service. Businesses need to ensure that their processes and procedures are customer friendly and that they satisfy customer needs.
When you order a meal from McDonald, it will be delivered in a few minutes = efficient
Any business that has an inefficient process will lose customers and damage its reputation. E.g a pizza delivered cold
what is physical evidence
Physical Evidence refers to the environment in which the service will be delivered.
The cutlery, chairs, menu of a restaurant
The location of the service being provided and the materials needed to carry out the service such as signage, brochures, business cards, business logo and website.
What is E-marketing?
E-marketing = Electronic marketing, It is the practice of using the internet to perform marketing activities, E-marketing can be used within the Marketing Mix.
E,g webpages, podcasts, blogs, SMS, Apps, Emails
how does Social media influence E-Marketing
businesses are becoming increasingly aware that social media advertising (SMA) can have positive results, especially when used in combination with traditional advertising methods. The main advantages of SMA are that it is:
inexpensive in comparison to traditional advertising methods
easy to use and monitor
an effective method to gain exposure
possible for marketers to accurately measure the reach (the number of people exposed to the message) and frequency (the average number of times someone is exposed) of SMA.
What is global marketing
A business’s marketing plan may need to be modified and adapted to suit overseas markets
Why? Each environment is unique and different e.g. laws, tastes, cultures, language, economy, competition etc.
Therefore, a business entering a new global market should implement market research. This involves finding out the needs and wants of customers. The marketing mix may need to be adapted to satisfy these needs and wants.
What are the global marketing strategies
- global branding
– standardisation
– customisation
– global pricing
– competitive positioning
What is global branding
Global branding is the worldwide use of a name, term, symbol or logo to identify the seller’s products.
what are the benefits of global branding?
It can be cost effective because one advertisement can be used in a number of locations.
It provides a uniform worldwide image.
The successful brand name can be linked to new products being introduced into the market
E>G Maccas golden arches
What is standardisation
Is a global marketing strategy that assumes the way the product is used and the needs it satisfies are the same the world over. Therefore, the marketing mix will be the same in all markets.
what are the advantages of standardisation
This strategy has obvious cost savings for businesses. Production runs can be longer, thereby achieving economies of scale; research and development costs are reduced; spare parts and after-sales service are simplified; promotion strategies can be standardised; and any evaluation and modification of the plan is a much simpler task.
Core menu items that are standardised globally are: Big Mac, Cheeseburger, Hamburger, Chicken McNuggets and Fries, and in Europe, the Filet-O-Fish
What is customisation?
A global marketing approach that assumes the way the product is used and the needs it satisfies are different between countries. Therefore, the marketing mix is customized (or altered) to suit the new market.
what are examples of global marketing
Everywhere Around the World Where McDonald’s Serves Beer
E.g. McDonalds in India
What is global pricing
Market customised pricing: sets prices according to local market conditions.
What if there was high/low levels of competition?
What if there was high/low levels of demand?
Standardised pricing- the practice of charging customers the same price for a product anywhere in the world
What is competitive positioning
Relates to how a business will differentiate its products in the minds of the consumer e.g. the perception or image the customer has of the product
How does the business “stand out” in the competitive business environment?
What is your perception or image of this brand?
what are the marketing strategies?