A&P Nervous System Practice Test
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
The basic functions of the nervous system include
Integration, Sensation, Response
____________________ are involved in insulin and myelination in the Central Nervous System.
Oligodendrocyte
_______ enter the spinal cord through the dorsal nerve root
Sensory axons
Which neurotransmitter is released at neuromuscular junctions?
Acetylcholine
What are the four major regions of the brain?
Cerebrum, Diencephalon, Brainstem and Cerebellum
Identify the statement that best differentiates gray matter and white matter.
Gray matter consists of cell bodies and dendrites, white matter consists mostly of myelinated axons.
In the Spinal Cord, the _________________ matter contains dendrites and cell bodies and the _________ matter contains myelinated axons.
Grey; white
What is the name for the topographical representation of the sensory input to the somatosensory cortex?
homunculus
A __________________________ is a specific segment of skin supplied by a single spinal nerve.
Dermatome
Which of the following is NOT a glial cell of the Central Nervous System?
Satellite cells
Voltage-gated Na+ channels open upon reaching what state?
threshold
___________ is the area which controls voluntary skeletal muscle activity.
Primary Motor Cortex
Which of the following events is NOT a characteristic of an action potential?
As Na+ enter, the inside of the plasma membrane becomes more negative
The ______________________________ area processes motor information and is located in the _____________ lobe.
Premotor cortex; frontal
Which of the following is NOT a lobe of the cerebrum?
Hypothalamic lobe
A group of Neuron Cell bodies in the Central Nervous System is called
Nucleus
The junction of a neuron with another cell is a/an __________.
synapse
Receptors can be classified into types on the basis of which of the following criteria:
Cell type
Which of the following is TRUE regarding the spinal cord?
Ascending tracts carry information to the brain
Where in the brain is the location of conscious thought processes and the origin of intellectual function?
Cerebrum
_______ is the connective tissue which covers individual axons.
Endoneurium
The ____________________ is an ascending tract associated with fine touch and proprioceptive sensations.
Dorsal column system
_____ are involved in immune surveillance and phagocytosis in the Central Nervous System
Microglia
Which of the following is NOT a TASTE?
Spicey
__________ interpret the chemical stimuli within the body.
Chemoreceptors
The _____________________ area processes visual information and is located in the ___________ lobe.
Visual association area; occipital
Which term describes a bundle of axons in the peripheral nervous system?
nerve
There are _____ spinal nerves
31
Which part of a neuron transmits an electrical signal to a target cell?
Axon
____________ are collections of neuron cell bodies located outside of the central nervous system.
Ganglia
The ___________________ controls smooth muscle and glandular tissue in the digestive system.
Enteric nervous system
In the Spinal Cord, the _____matter contains dendrites and cell bodies and the _____ matter contains myelinated axons.
Grey, White
What is the function of the Astrocyte cells?
Support and maintenance of neurons in the CNS
An action potential occurs when____________________
The membrane potential reaches threshold level
Which neurotransmitter is released at neuromuscular junctions?
Acetylcholine
The spinal nerves consist of ____ covered with endoneurium, ____ covered with perineurium.
Axons, fasicles
________________ receive sensory information from the periphery
Dorsal Root Ganglion
A nerve plexus is ________________________
a network of nerve fibers
Draw and label the main parts of a multipolar neuron (CNS). Which glial cell is involved with myelination?
Oligodendrocytes
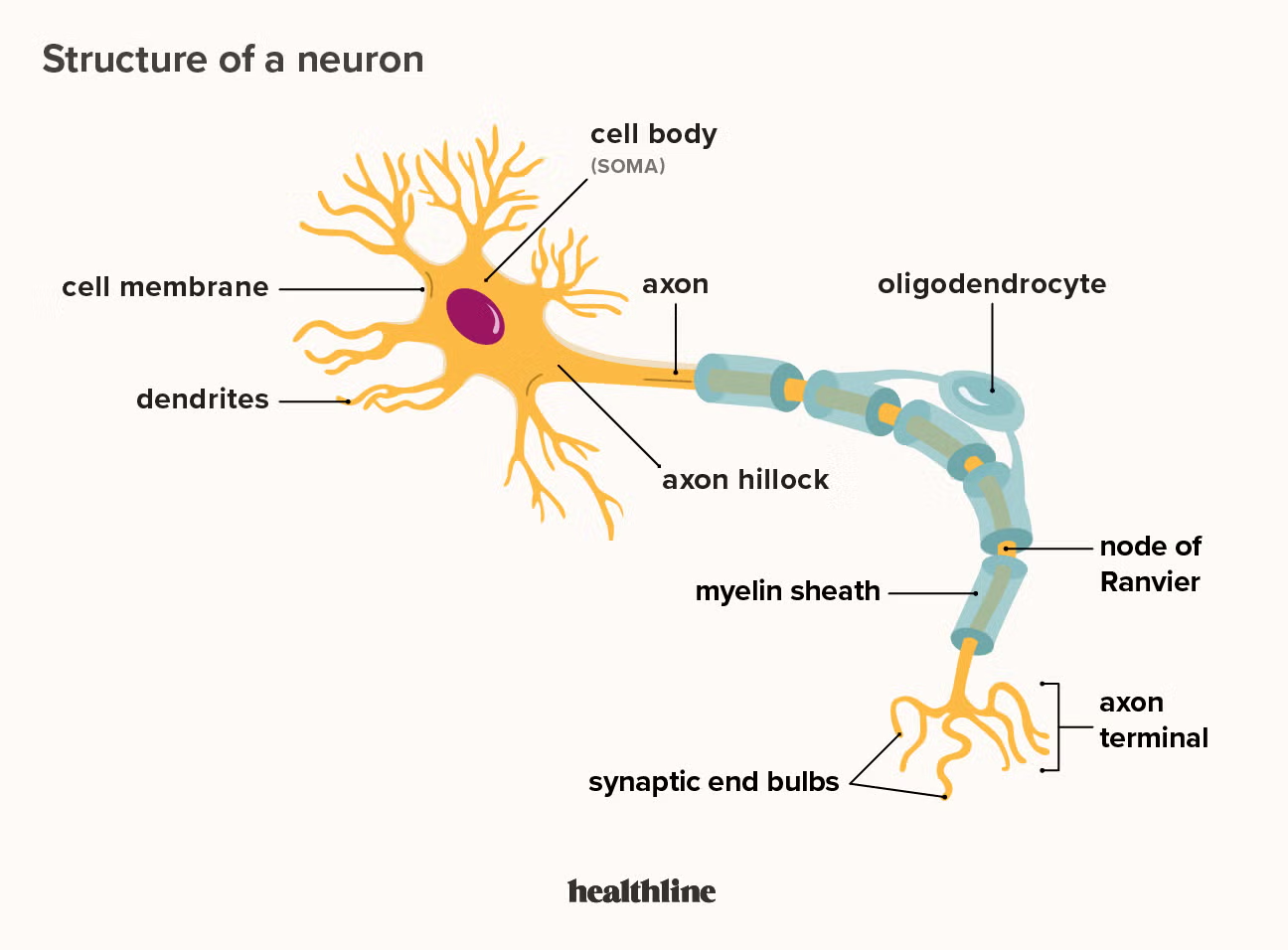
An _______________ is a receptor that interprets stimuli from organs and tissues within the body.
Interoceptor
______ is the connective tissue layer of the outer covering of the nerve
Epineurium
The parasympathetic fibers originate from ___________
brainstem and sacral spine
The ____________________ is an ascending tract associated with fine touch and proprioceptive sensations.
Dorsal column system
Which type of fiber could be considered the longest?
Preganglionic parasympathetic
Which term describes a bundle of axons in the peripheral nervous system?
Nerve
Which location on the body has the largest region of somatosensory cortex representing it, according to the sensory homunculus?
lips
What are the names of the specialized cells found in the retina which initiate the process of visual stimuli?
Rod & Cone Photoreceptors
The ______________________________ area processes motor information and is located in the _____________ lobe.
Premotor cortex; frontal
What are the four major regions of the brain?
Cerebrum, Diencephalon, Brainstem and Cerebellum
The sympathetic nervous system contains _______ ganglion.
23
Which of the following is FALSE regarding the Brainstem?
The medulla oblongata is involved in respiratory and cardiac functioning
The pons is involved in breathing
The brainstem integrates information about visual, auditory and somatosensory space
The brainstem is made up of hypothalamus and thalamus
The brainstem is made up of hypothalamus and thalamus
________ enter the spinal cord through the dorsal nerve root
Sensory axons
During depolarization of the plasma membrane __________
Na+ moves rapidly into the cell
Which of the following is FALSE regarding Autonomic tone?
More sympathetic signal includes release of acetylcholine (Ach)
The balance of autonomic tone is achieved by neurotransmitter release
All of the answers are FALSE
Organs receive inputs from both sympathetic and parasympathetic input
More sympathetic signal includes release of acetylcholine (Ach)
Where are taste buds located?
Papillae of the tongue
The nervous system _____
maintains homeostasis
monitors internal and external stimuli
All of the choices are correct
transmits information in the form of action potentials
All of the choices are correct
_______ is the area in the brain which receives general somatic sensory information
Primary Somatosensory Cortex
_______ is involved in integrating information, maintaining homeostasis and has an autonomic response and endocrine system components.
Hypothalamus
_____ are processes that conduct electric signals toward the cell body.
Dendrites
______ respond to physical stimuli such as pressure and vibration
Mechanoreceptors
A bundle of Axons in the Central Nervous System is called
Njucleus
___ are involved in insulin and myelination in the Central Nervous System.
Oligodendrocytes
Which of the following is TRUE regarding the spinal cord?
Peripheral information travels into the anterior horn via the anterior root
Ascending tracts carry information to the brain
Motor information travels out through the dorsal horn via the dorsal root
Ascending tracts carry information to the brain
Ascending tracts carry information from the brain
_____ and _____________ are glial cells found in the central nervous system
Satellite and Schwann cells
Astrocytes and Oligodendrocytes
Astrocytes and Schwann cells
Ependymal cells and Satellite cells
Astrocytes and Oligodendrocytes
Choose ONE of the senses and describe how the sensation is perceived and how the information is sent to the brain. Provide detail on this.
How Hearing Works:
Sound waves enter the ear
Sound starts as vibrations in the air. These vibrations travel into the outer ear (the part you can see, called the pinna) and move through the ear canal until they reach the eardrum (tympanic membrane).The middle ear amplifies the sound
When the eardrum vibrates, it moves three tiny bones in the middle ear — the malleus (hammer), incus (anvil), and stapes (stirrup). These bones amplify the vibrations and send them to the inner ear.The inner ear turns vibrations into electrical signals
The vibrations reach the cochlea, a spiral-shaped, fluid-filled structure in the inner ear. Inside the cochlea are hair cells that bend in response to the movement of the fluid.The auditory nerve sends information to the brain
These electrical signals travel along the auditory nerve to the brainstem and then to the auditory cortex in the temporal lobe of the brain.The brain interprets the sound
The brain processes these signals to recognize the sound’s pitch, loudness, and location. This allows you to understand what you’re hearing — for example, identifying it as music, speech, or a dog barking.
Draw the spinal cord and label the key components of the spinal cord. Add detail about where ascending / descending tracts travel.
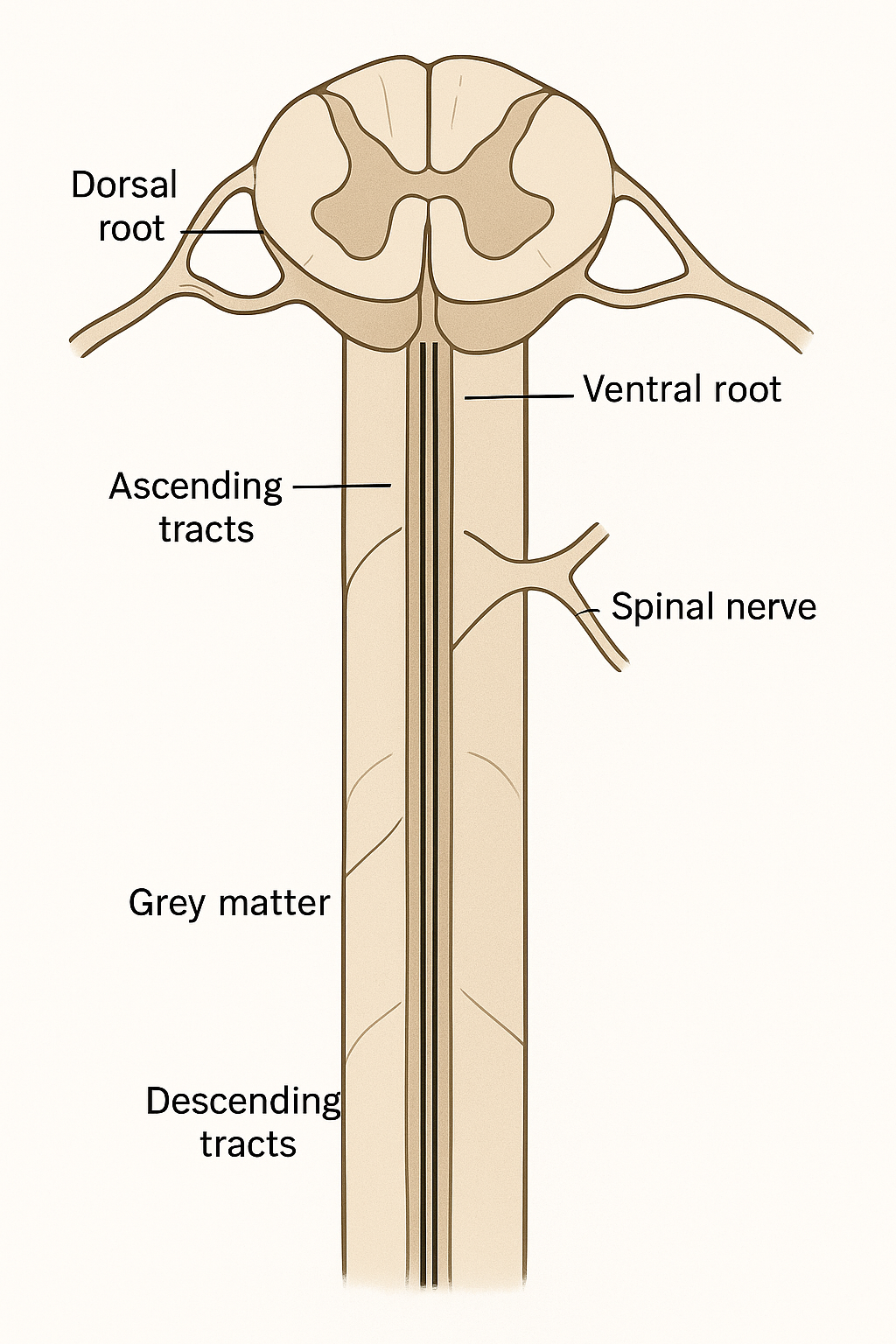
Describe the Spinothalamic Tract in the Spinal Cord. Is the tract / column sensory or motor? Ascending or descending? Where in the spinal cord does it run? Where does the information come from and go to?
The spinothalamic tract is a sensory pathway in the spinal cord. It is ascending. It is located in the white matter of the spinal cord. Information comes and goes from the sensory receptors in the skin to the thalamus.
Name the four spinal nerve plexuses. For each one, add detail of which level of the spinal cord does it come from. Further, provide details of where in the body the plexus is involved.
Cervical plexus
spinal level C1-C4
supplies muscles and skin of the neck, shoulders, and upper chest.Brachial plexus
C5-T1
muslces of the upper limbsLumbar plexus
L1-L4
lower abdomen muslces and hip flexorsSacral plexus
L4-S4
buttocks, high, lower leg, and foot
supplies nerves to the thighs and most of the legs and foot
How many Spinal Nerves are there? Do spinal nerves contain sensory fibers, motor fibers or both? Where does the sensory axon enter the spinal cord? Where does the motor fiber exit the spinal cord?
There are 31 spinal nerves. Spinal nerves contain both sensory and motor fibers. The sensory axons enter through the dorsal root. While the motor fiber exits the spinal cord through the ventral root.
Draw and label the following lobes of the Cerebrum: Frontal Lobe, Parietal Lobe, Temporal Lobe, Occipital Lobe.
—