Dental Hygiene Principles (elderly client LO1)
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Comfort, acceptance, responsiveness, empathy
What are the 4 principles of the CARE principle?
early adulthood, middle age, late maturity
What are the 3 developmental stages of the adult according to Havighurst?
Stage 1: early adulthood
What stage of adult development?
Establishing independence, learning to live with a marriage partner, starting a family, bringing up young children, managing a home, getting started in an occupation, taking on civic responsibilities, finding a congenial social group.
Stage 2: middle age
What stage of adult development?
Achieving adulthood and social responsibilities, establishing and maintaining an economic standard of living. Assisting one's children to become adults, developing durable leisure-time activities, relating to one's partner, accepting and adjusting to physical change. Adjusting to one's aging parent.
Stage 3: late maturity
What stage of adult development?
Adjusting to: decreasing physical strength and to death, retirement and reduced income, death of one's partner, explicit affiliation with one's age group. Meeting social and civic obligations, establishing satisfactory physical living, arrangements in light of physical infirmities.
Adult learners
The 5 assumptions related to ————— ———————: motivated to learn as they experience needs and interests that learning will satisfy, life-centered— organize adult learning in life situations not subjects. Experience is the richest source of learning, deep need to be self-directing, individual differences increase with age.
Life span
A maximal length of life potentially possible in a species (human: 110-120 years).
Life expectancy
The average number of years lived by any group of individuals born in the same period.
Geriatrics
The branch of medicine concerned with the illness of old age and their treatment.
Gerontology
The scientific study of the factors affecting the normal aging process and the effects of aging.
Chronological age
Age as measured by calendar time since birth.
Functional age
This is the term to measure a persons performance capacities.
Gait/balance
In the DH POC with older clients, assessment and observation begins in the reception area. You observe your patients ————/———————: does the client need your assistance to the treatment area? Position the dental chair at know level or higher, may be in a wheelchair and need to be transferred.
Vision and hearing impairments
Clients with ————— and ——————— impairments may need assistance to complete written forms, address using low pitch (not shouting). Address with face masks removed, miniature background noise. Ask client to reduce volume on hearing aide ONLY when rotary hand piece and ultrasonic scaler is being used. Address client directly, not the caregiver/family member.
Lubrication of the oral cavity and source of minerals for the enamel
What are the 2 roles of saliva?
Clinpro 5000, Colgate prevident
For chronic xerostomia, a 1.1% NaF gel is recommended. These are 2 examples of that:
Gel-Kam
Another recommendation for chronic Xerostomia is 0.4% stannous fluoride gel (can cause stain). An example of 0.4% stannous fluoride is:
Cholinergic agents
For xerostomia, if you were to give a medication, you would prescribe ———————— agents.
Longer
You should allow ————— time to assess results of soft tissue debridement for older clients as there is slower and decreased potential for healing.
Age-related oral changes
Alterations of the structures of the body that are not a result of the disease process (enamel, cementum, dentin, pulp).
Disease induced oral changes
These often manifest changes and pathology that is independent of the aging process.
Some evidence of thinning of the epithelium, diminished keratinization, and increased cellular density, increased alveolar bone porosity
4 age-related periodontal changes:
Age related
Are these changes age related or disease induced? Alterations in periodontal ligament cellular function, increase in fibrous intercellular substances in the gingival connective tissue, increases in calcification and arteriosclerosis of gingival vessels, reduced number of nerves in the gingiva, increase in gingival width.
Stain producing food and drink, secondary dentin
Enamel can get darker with aging due to these 2 things:
Cementum
This tooth structure increases in magnesium and fluoride content as you age:
Dentin sclerosis
Obturation of the tubules by gradual growth of the peritubular dentin. This is also known as this condition that is related to aging.
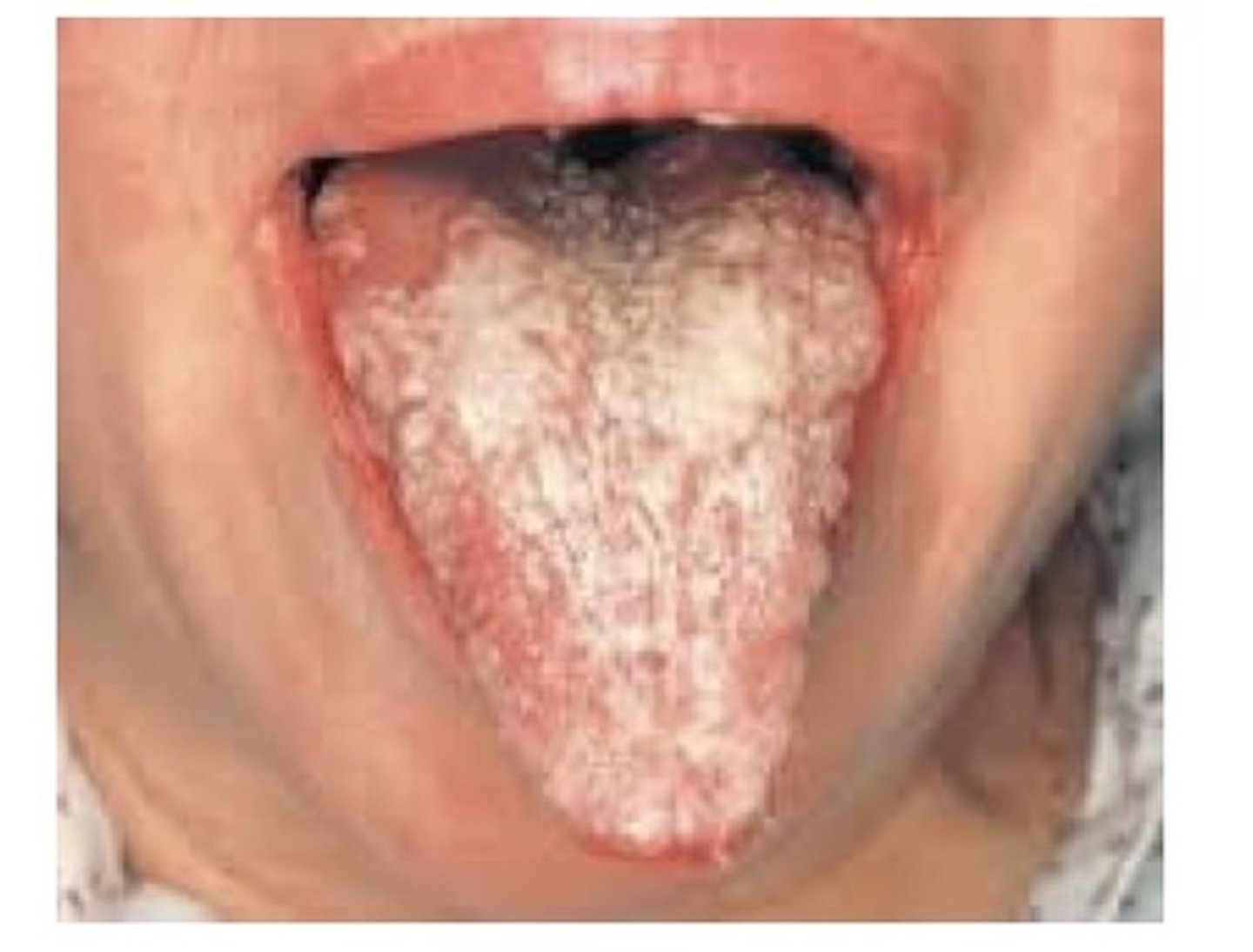
Candidiasis ("thrush")
Clinical appearance of the oral mucosa: dry, smooth, thin. This can be caused from broad-spectrum antibiotics. Resulting from Xerostomia causing medications.
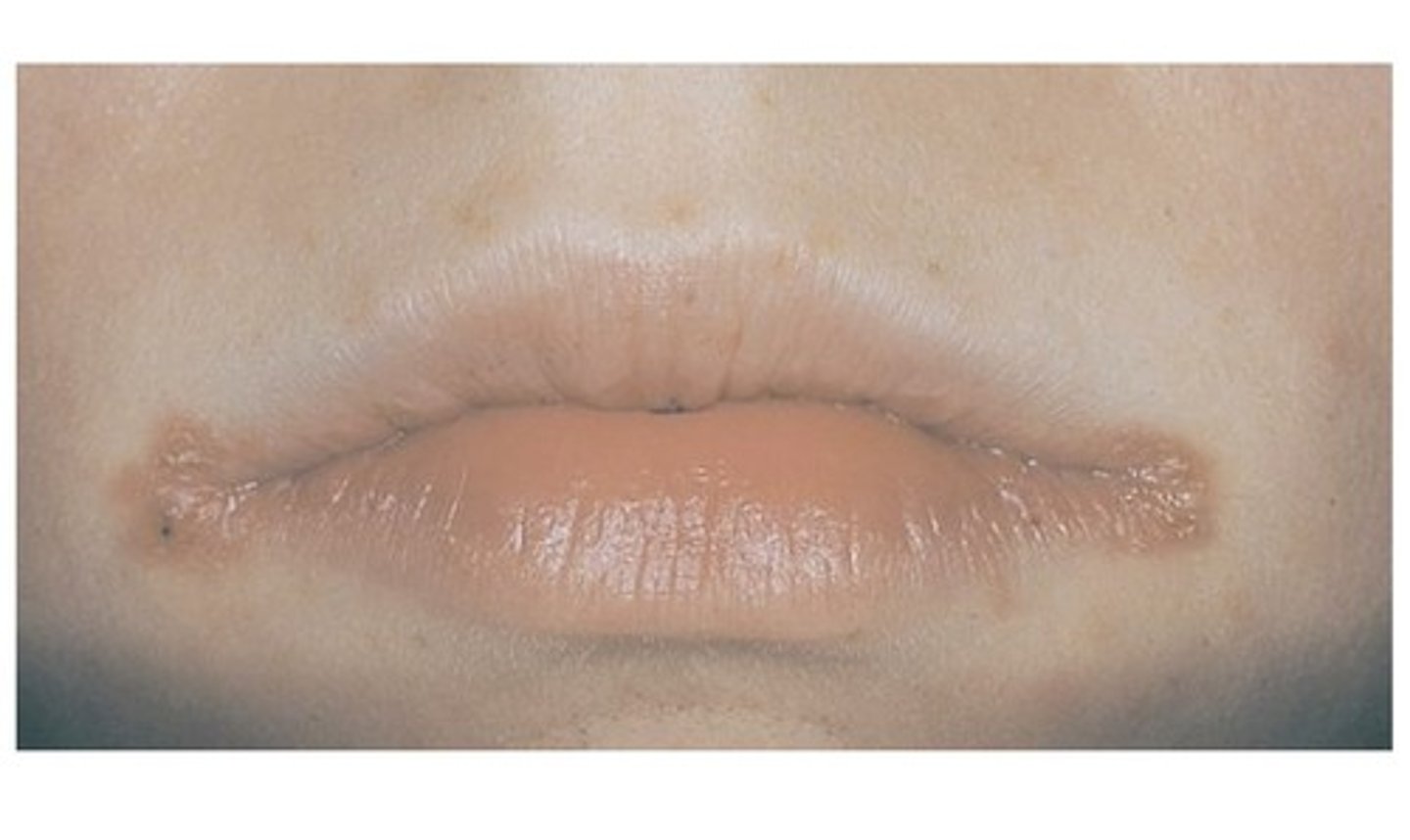
Angular cheilitis
Caused by moistness from drooling, deficiency of vitamin B2 (riboflavin), infection from Candida albicans. Common in elderly clients.
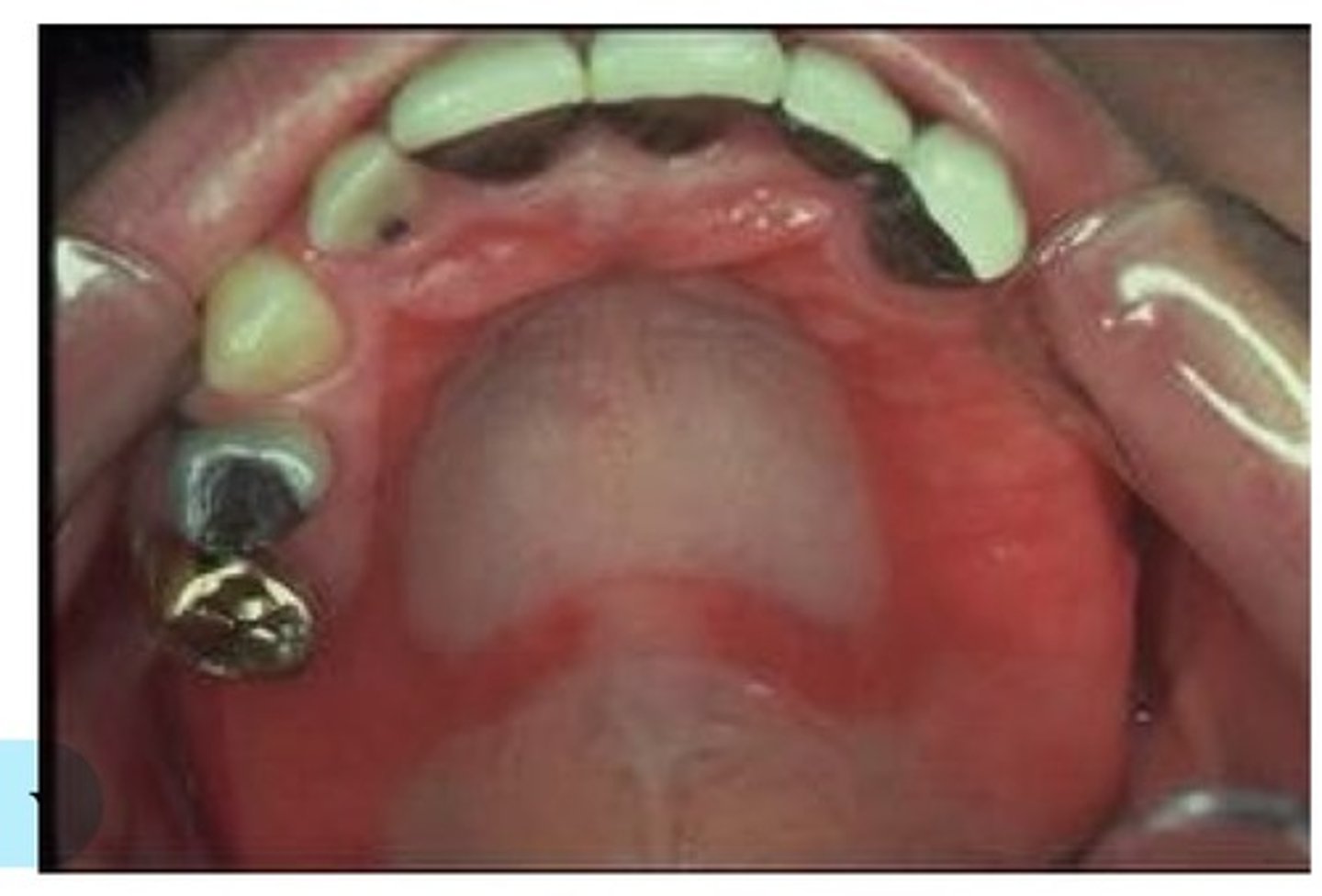
Chronic atrophic candidiasis
This is due to ill-fitting or poor denture hygiene. May result in mucosal irritation, denture stomatitis, candidiasis, denture induced fibrous hyperplasia. This is present in as many as 65% of older individuals. Associated with poor prosthesis fit, associated with retention of denture during sleeping.
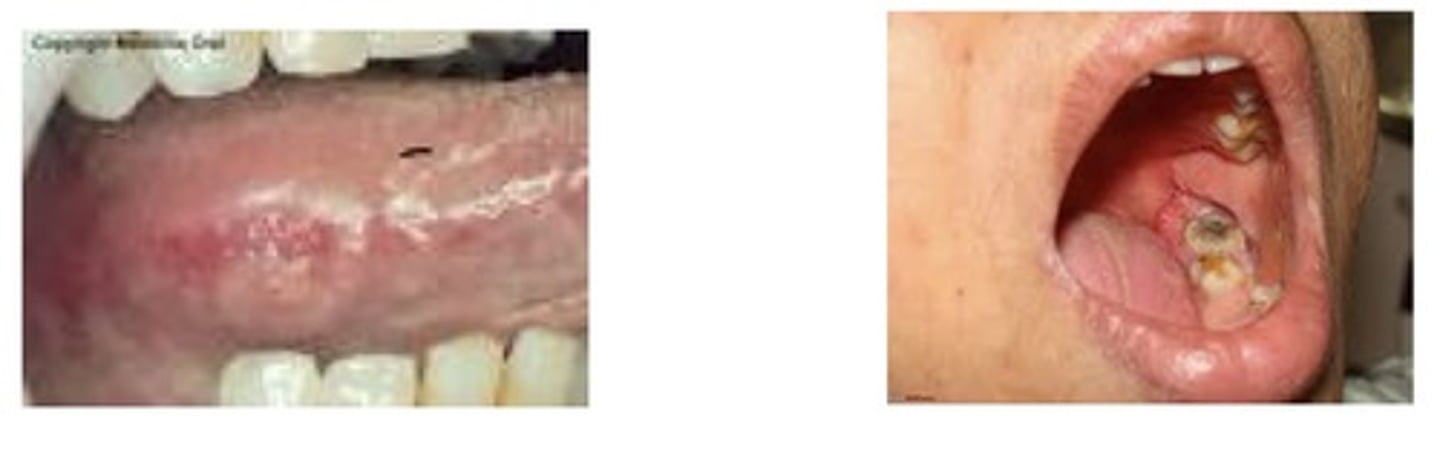
2.5%
Oral cancer represents about —.—% of total cancer diagnoses each year.
Oral cancer
Average age of diagnosis is 60 years of age. More common in men than women.
Aging
Sublingual variscolsities are changes in the tongue that are induced by:
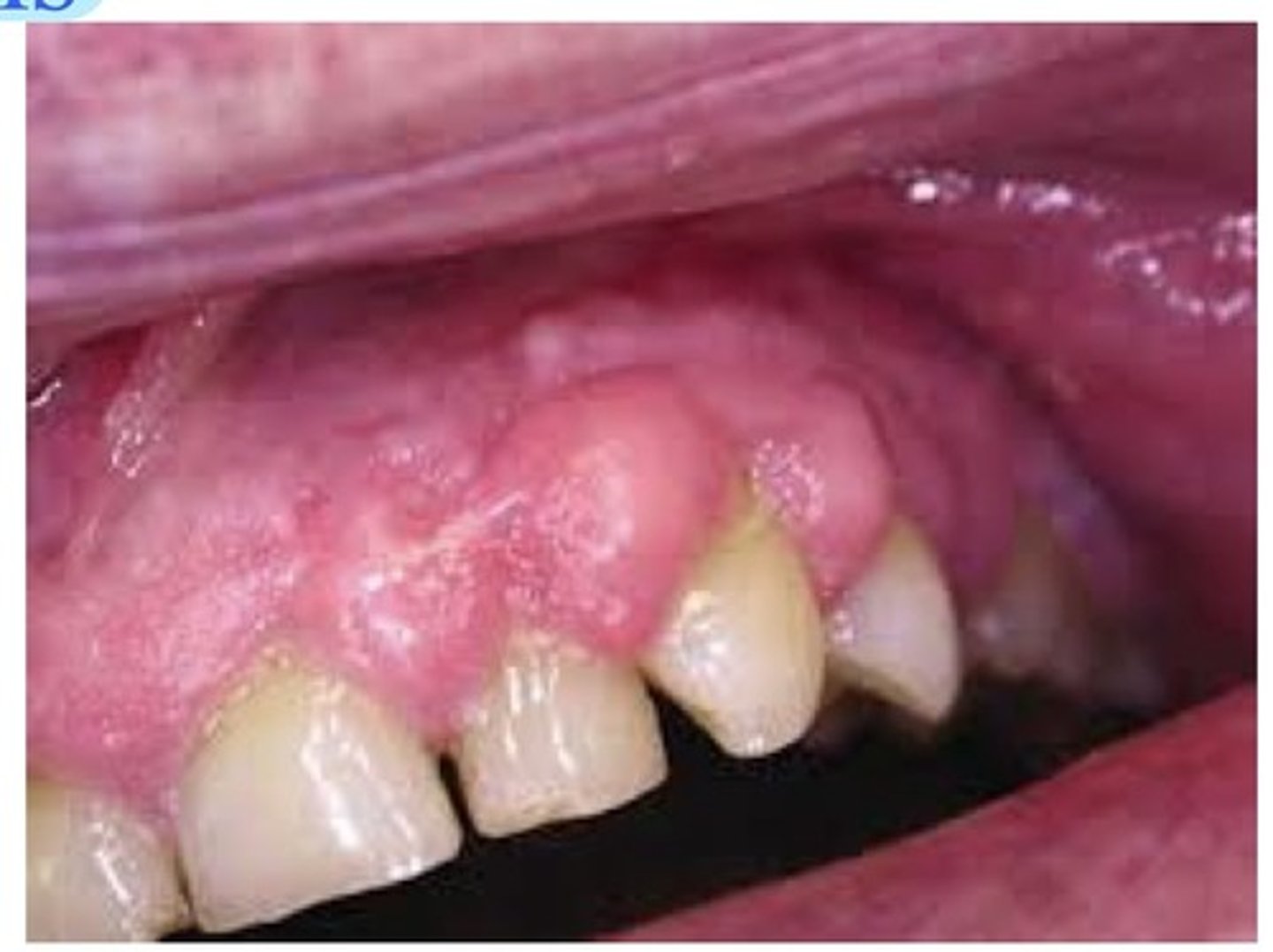
Drug induced gingival enlargement
This can be caused by anti convulsants (Phenytoin), cardiovascular drugs (Nifedipine), and immunosuppressants (Cyclospirin). Adequate plaque control, reduction of magnitude of ————— ————————, starting a regime before the meds are all important when the patient has this.
Sjögren's syndrome
This is an autoimmune disease of the salivary and lacrimal glands.
Local factors
Exposed roots and tooth longevity are ————— factors that contribute to root caries.
Aging
Changes in salivary composition and inability to complete thorough oral hygiene due to disability and/or chronic conditions. These are factors related to ————— that contribute to root caries.
7%
—% of the elderly population is institutionalized.
13%
——% of the elderly population is home bound.
11%-67%
Denture stomatitis has prevalence in ——% to ——% of denture wearers.
Drug induced Xerostomia
This condition is most common with tricyclic antidepressants, antipsychotics, atropines, beta-blockers, and antihistamines.