Ch. 12 AP Microeconomics (The Design of the Tax System)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:01 PM on 9/16/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
1
New cards
Federal Government
The U.S. __________ ___________ collects about 2/3 3 of the total taxes in our economy, around $2,568 billion in 2007, an average of about $8, 503 per person. Most of it is from the income tax, uses it to correct externalities that cannot be made efficient by private markets.

2
New cards
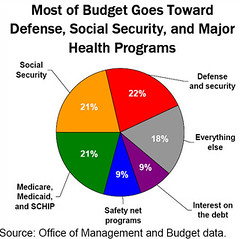
Social Security
An act passed in 1935 gave government-payed pensions to American citizens over the age 65 as well as provided help for the unemployed, the disabled, and the needy. Largest transfer payment in U.S. SPENDING.

3
New cards
16th Amendment
Amendment passed in 1913 giving the Federal Govt the power to tax. The more you make, the more you're taxed (Progressive Tax System).
4
New cards
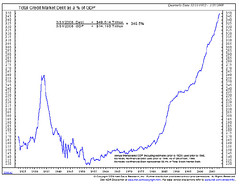
richer
The general trend when comparing GDP and taxes over time shows the ______ a country gets the more taxes that it has.
5
New cards
tax liability
The amount of total tax due the IRS after any credits and before taking into account any advance payments (withholding, estimated payments, etc.) made by the taxpayer.

6
New cards
Income Tax
Shares of individual wages and corporate revenues collected by the government. The Sixteenth Amendment explicitly authorized Congress to levy a tax on income.

7
New cards
Marginal tax rate
Tax rate that applies to the next dollar of taxable income, that increases as the amount of taxable income increases, DO NOT BE confused by this. For the first amount of money every pays the same at each level. (Just ask me if you don't get it). Is more useful than the average tax rate at showing how the current tax system distorts incentives.
8
New cards
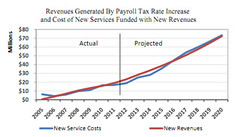
Payroll Tax
The tax on wages and salaries to finance Social Security and Medicare costs. 2nd largest source of revenue for the Federal Goverment.
9
New cards
Social insurance taxes
Taxes collected from employees and employers to pay for major social programs; also known as PAYROLL TAXES, and unemployment compensation programs; regressive taxes
10
New cards
Corporation
An organization that is authorized by law to carry on an activity but treated as though it were a single person(or single legal entity). Usually owned by stockholders who share in its profits but are not personally responsible for its debts

11
New cards
Corporate Income tax
A tax levied on a corporation's income BEFORE dividends are distributed to stockholders. 3rd largest source of income to the Federal government. Is actually a bigger burden to consumers and workers than to the owners because their elasticity is greater.
12
New cards
Transfer Payment
A public expenditure (as for unemployment compensation or veteran's benefits, or social security(the largest)) that is not for goods and services
13
New cards
National Defense
The second largest transfer payment of the federal government after social security.
14
New cards
Net Interest
The difference between interest paid and interest received by firms
15
New cards
Budget Deficit
An excess of government spending over government receipts(revenue).
16
New cards
Budget Surplus
An excess of tax revenue over government spending

17
New cards
Sales Taxes
Taxes assessed on the prices paid on most goods and services. Is a State and local government tax NOT Federal Government. Are usually 6 or 7 percent in states. Make up the vast majority of taxes in states and counties.

18
New cards
Property taxes
A tax on the value of property (capital, land, stocks and bonds, and other assets) owned by firms and households. This is a state government tax.

19
New cards
Education
The biggest expenditure for state and local governments is _________. Is followed by public welfare, then highways, and other miscellaneous stuff you could probably just guess.

20
New cards
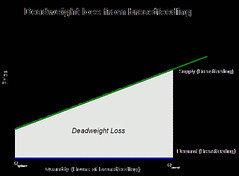
Deadweight losses
The reduction in economic surplus resulting from a market not being in competitive equilibrium, usually caused by a tax.
21
New cards
consumption tax
A tax on spending, or on the difference between what people earn and what they save, regardless of how much they earned, also called a national sales tax, is an alternate system that economists believe would work better.
22
New cards
value added tax
A tax on increased value of a product at each stage of production and distribution rather than just at the point of sale
23
New cards
tax evasion
Willful failure to pay taxes.

24
New cards
average tax rate
The total tax paid divided by total (taxable) income, as a percentage, is more useful than the marginal tax rate to determine the sacrifices made by taxpayers.
25
New cards
Lump sum taxes
Everyone owes the same amount(in dollar amount), regardless of earnings; Most efficient tax possible, but the least equitable.
26
New cards
401 k
A defined contribution plan that automatically takes out money from an employee's paycheck before income taxes and invests it in mutual funds for purposes of retirement savings.
27
New cards
Benefits principle
A principle of taxation, states that people should pay taxes based on the BENEFITS they receive from government services. Tries to make public goods more like private goods.
28
New cards
Ability to pay principle
The principle that taxes should be levied on a person according to how well that person can shoulder the burden. Sometimes is stated that "Individuals must make an equal sacrifice" Leads to two corollary notions of equity :vertical and horizontal.
29
New cards
vertical equity
The idea that taxpayers with a greater ability to pay taxes should pay larger amounts, is a corollary of the ability to pay principle. It's sister corollary is horizontal equity.
30
New cards
horizontal equity
The idea that taxpayers with similar abilities to pay taxes should pay the same amount , is a corollary of the ability to pay principle, It's sister corollary is vertical equity.
31
New cards
proportional tax
A tax for which the Percentage of income paid in taxes remains the same for all income levels
32
New cards
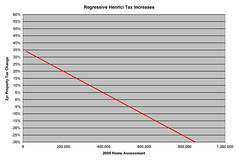
regressive tax
A tax whereby people with lower incomes pay a higher fraction(percentage) of their income than people with higher incomes. (Sales taxis an example).
33
New cards
progressive tax
a tax for which high-income taxpayers pay a larger fraction(percentage) of their income than do low-income taxpayers
34
New cards
Tax incidence
The actual division of the burden of a tax between buyers and sellers in a market
35
New cards
flypaper theory of tax incidence
A unbelievably stupid and untrue theory of tax incidence that states wherever the tax lands first pays the brunt of the tax. You would know by now that you must first analyze the elasticity.

36
New cards
Ronald Reagan
U.S. President during the conservative ascendancy of the 1980's. Argued that high tax rates distorted economic incentives to work and save. While in office he signed huge cuts in the tax rate.
