Topic 1: Electric Fields
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Which particles are negatively charged?
electrons
Which particles are positively charged?
protons and positrons
The atomic nucleus comprises which particles?
protons and neutrons
What type of particle/s “flow” in solid wires to create electric current?
the negatively charged electrons move while the positively charged protons don’t move
The atom is held together by the attractive electric force between the ______ ______ in the nucleus and the _____ _____.
positive protons, negative electrons
_____ and ____ have charges of opposite sign but exactly equal magnitude.
Electrons, protons
What happens when John Travolta rubs his foot on the carpet and then touches the door knob? Why?
He gets shocked because the electrons jump from him to the doorknob. When he rubs his foot, the electrons jump from the carpet to his foot. The electron affinity of John’s rubber sole is greater than the carpet, so the electrons are jumping from the carpet to John The more he rubs his foot, the more electrons jump onto his body. As the extra charge builds up, it isn’t happy because the negative charges of teh electrons all repel each other and push against each other and this results in voltage bias.
What happens when you rub a balloon against something and then touch it to a wall? Is the balloon and/or wall charged?
The electrons jump from the sweater to the balloon, the balloon becomes negatively charged as it’s gained electrons and the sweater is positively charged because it has lost electrons, so then if we release them they are attracted to each other, opposites attract each other. The wall is neutral. The negative charge of the balloon induces a dipole and so that causes the balloon to stick to the wall due to the charge separation caused by all of these negative charges.
Attraction between _____ balloon and _____ hair. _____ move from hair to balloon.
negative, positive, electrons
When two ______ materials touch each other, then _____ can ______ from one object to the other, (Do NOT have to rub!)
different, electrons, move
The objects then have _______ charges that are opposite. One object become negative and the other positive.
unbalanced
Opposite charges _____.
attract
Like charges ____.
repel
Electrons are free to move in ______ but not in ______.
conductors, insulators
In solids, _____ don’t move.
protons
Negative electrons can travel through a metal ______, but not through an ______. Protons do ____ move in solids!
conductor, insulator, NOT
If charged objects are connected with a ____, then electrons can move and _____ _____ between the objects,
conductor, evenly distribute
If charged objects are connected with an insulator, then the charge _____ ____.
cannot move
Electrons move from rabbit fur to amber. What is charge on fur? On Amber?
fur is positive and amber is negative
What is Greek word for Amber?
Electra
Electric current is in direction of _____ flow.
positive
Electric current is due to the flow of ______.
electrons
The ______ of the electrostatic force between point charges is determined using Coulomb’s Law.
magnitude
The ______ of the force is determined: opposites attract/likes repel.
direction
An _______ is said to exist in a region of space around a charged object (source). The field exerts a force on the other charged objects in the region.
electric field
The _______ of the field is defined to be the direction of the electric force that would be exerted on a small positive test charge placed at that point.
direction
______ and ______ forces are both field forces.
electric, gravitational
The Electric Field is directed ______ a positive charge.
away from
Positive charges go the ___ direction as the electric field.
same
The Electric Field is directed ______ a negative charge.
towards
Negative charges go the ___ direction as the electric field.
opposite
Is electric field a vector?
Yes
The electric field due to a point charge points ___ from positive charges and ______ negative charges.
away, towards
The electric field acts on the ______ due to other charges, not the charge itself.
charge
How would you answer this question? : Which vector describes the electric field that acts on the -3C charge?
electric field points away from positive and towards negative
For vectors regarding forces, what rules do we follow?
opposite charges attract and like charges repel
How would you answer this question? : Which vector describes the resultant force?
opposite charges attract and like charges repel
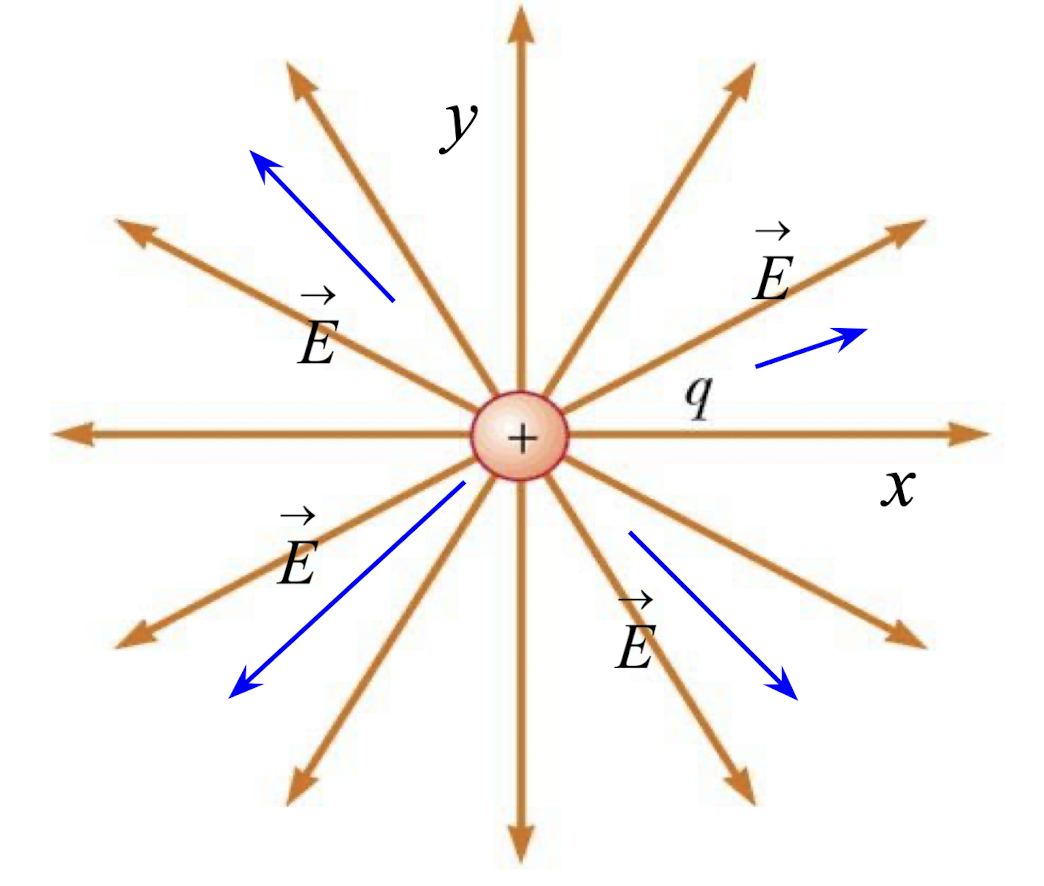
For electric field lines, we start at _____ charges or infinity.
positive
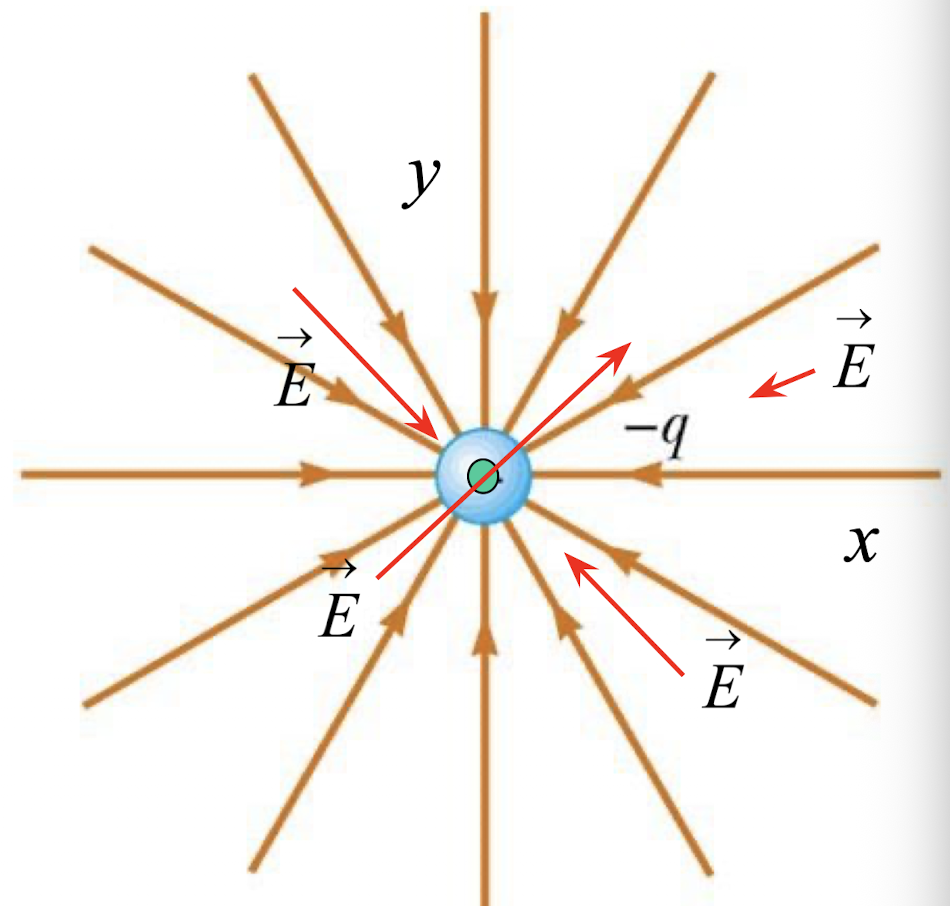
For electric field lines, we end at _____ charges or infinity.
negative
Density of lines (more lines in small area) indicate a _____ electric field.
larger
Separated electric field lines show a ____ electric field.
weaker
The greater density of the electric field lines, the ____ the electric field.
stronger
Electric field tells you direction of field if charge is _____, if ______ then force will point in opposite direction of electric field.
positive, negative
The Electric Field is ___ everywhere inside a conducting material.
zero
If there were an electric field ____ the conductor, the free charge there would move.
inside
Any excess charge on an isolated conductor resides entirely on its ____.
surface
If some excess of charge could be placed inside the conductor, the repulsive forces would push them as ______ as possible.
far apart
The electric field at the surface of a charged conductor is ______ to the surface.
perpendicular
Any non-perpendicular component of the electric field along the surface would cause the charge to _____.
move
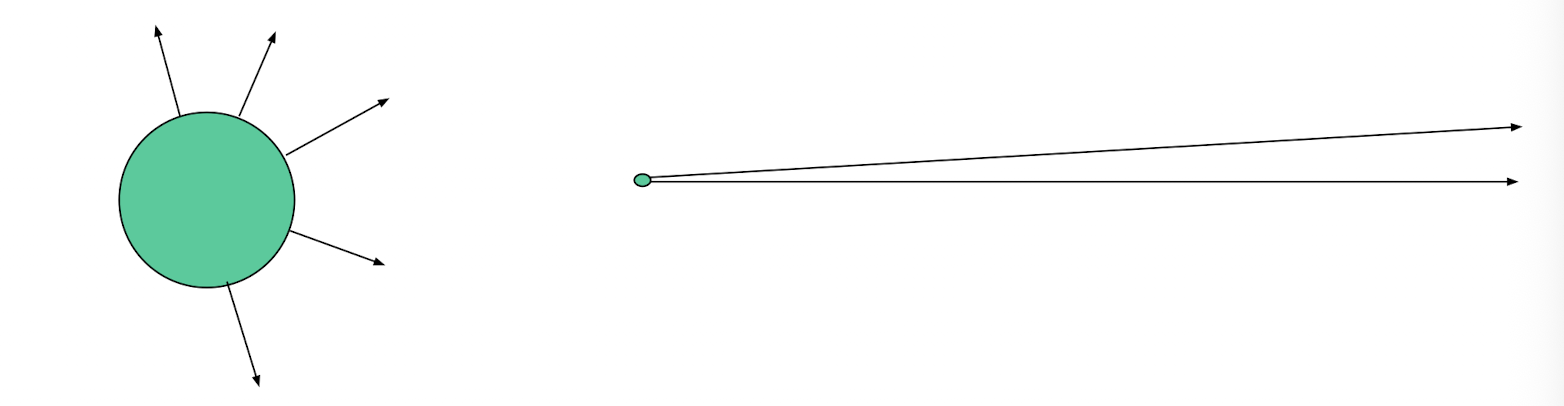
At an ___________ from a charged object the electric field is uniform in direction and magnitude.
infinite distance
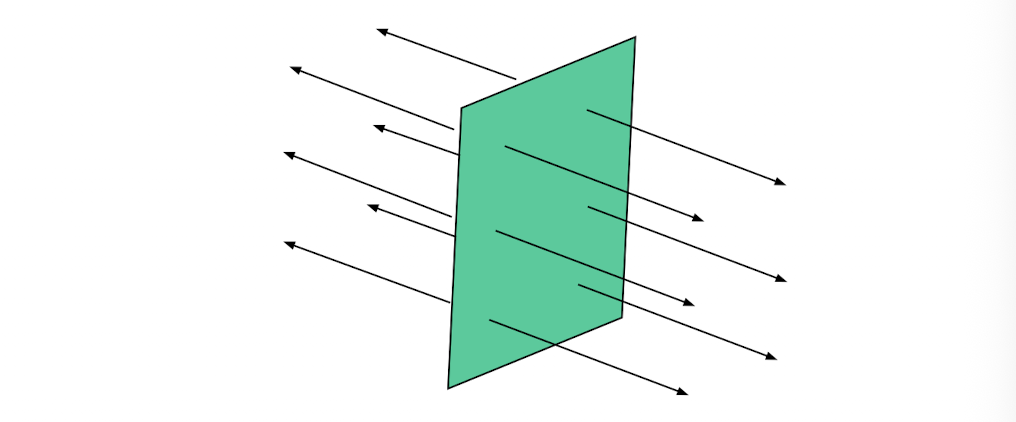
The electric field of an infinitely large charged ____ is uniform in direction and magnitude.
plate
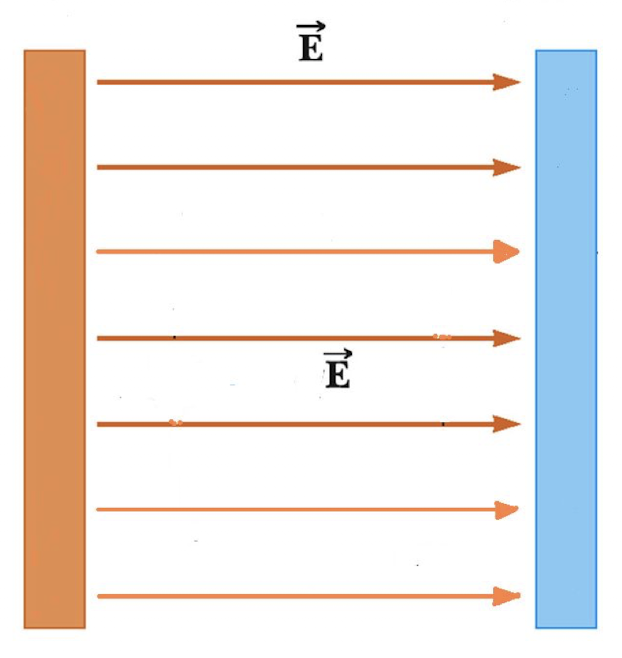
A _______ has the same magnitude and direction at all points in space.
uniform field
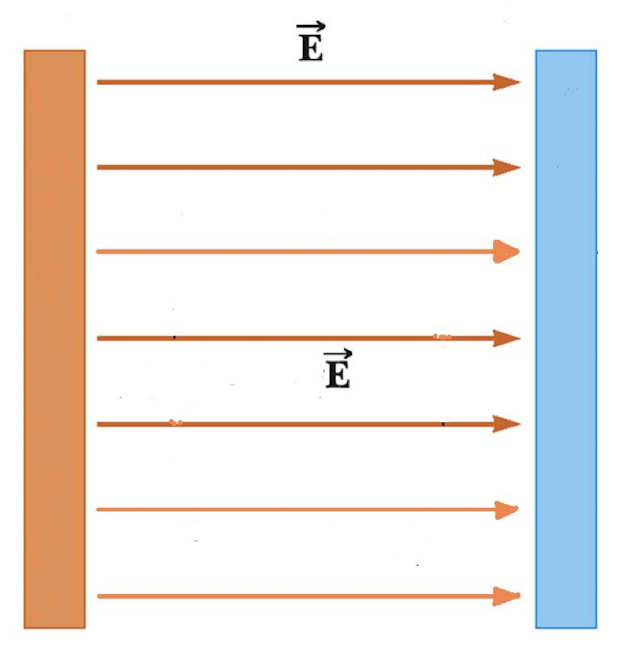
Field lines will point from _______ charged to ______ charged plates.
positively, negatively
Gauss’s Law relates the charge enclosed by an arbitrary surface and the total electric ____ through the surface.
flux
If net charges inside the surface are ______, then the flux is positive and the field lines _____.
positive, leave
If net charges inside the surface are ______, then the flux is negative and the field lines _____.
negative, enter
No charge inside of object means flux has to be ____.
zero
A closed surface through which an electric field passes is called a ______ _____.
Gaussian surface
The field of a plane depends only on its ______ density.
charge
No matter how close or far you are from the plane, the field will be the ____.
same
If the electric field near a point charge points toward that charge, then the charge is negative. True or false?
True
Near a positive charge, the electric field points away from that charge. True or false?
True
If the magnitude of charge 1 is smaller than charge 2, then the density of the electric field lines near charge 1 is smaller than near charge 2. True or false?
True
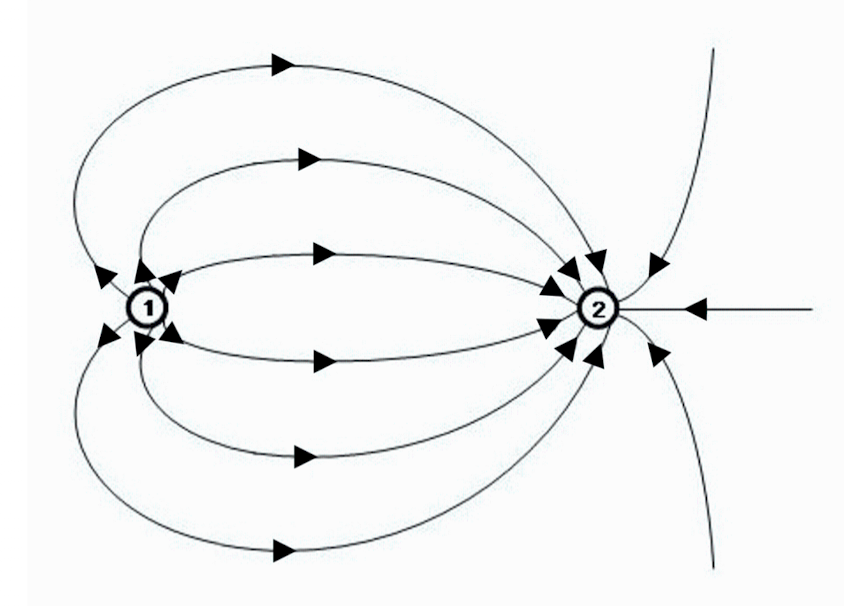
The charge on the left is negative. True or false?
False
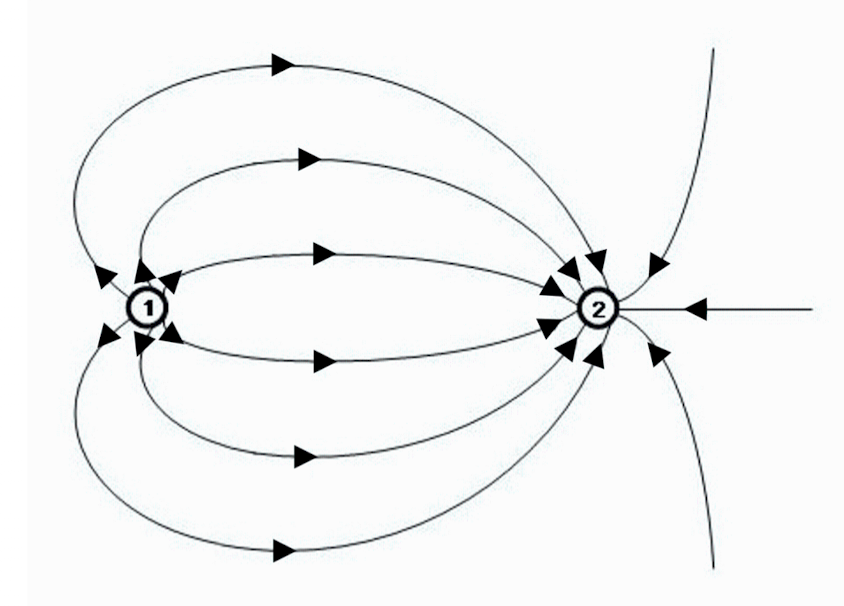
The charge on the left is smaller in magnitude than the charge on the right. True or false?
True
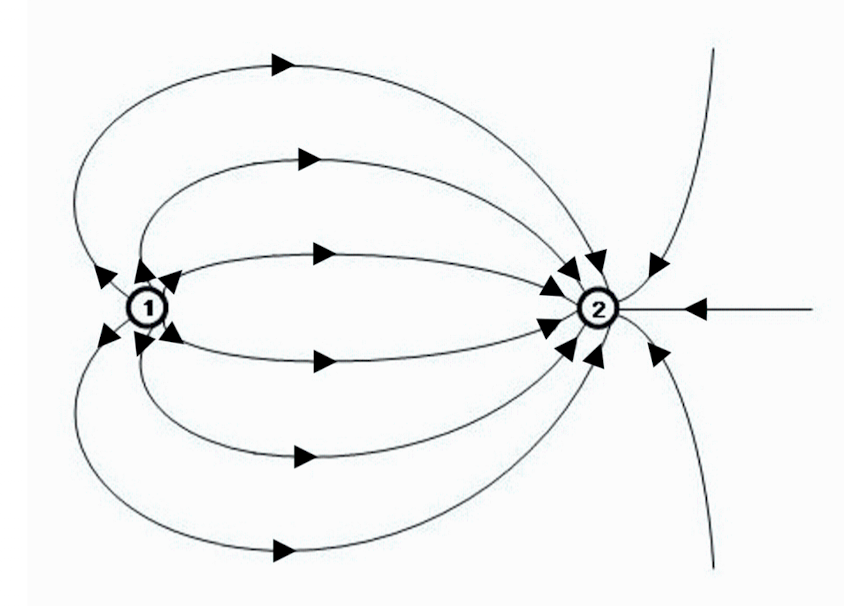
A negative test charge placed between the left and right charges will move to the left. True or false?
True
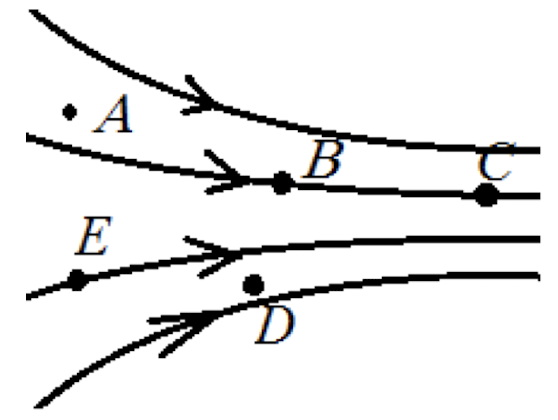
Electric field strength is greater where field lines are _____ together.
closer
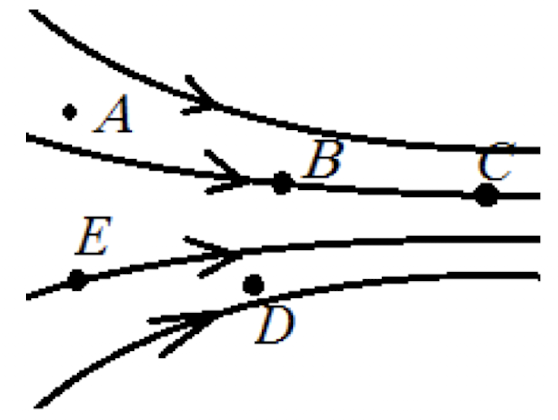
The electric field is not _____ just because no line passes exactly through a point.
zero
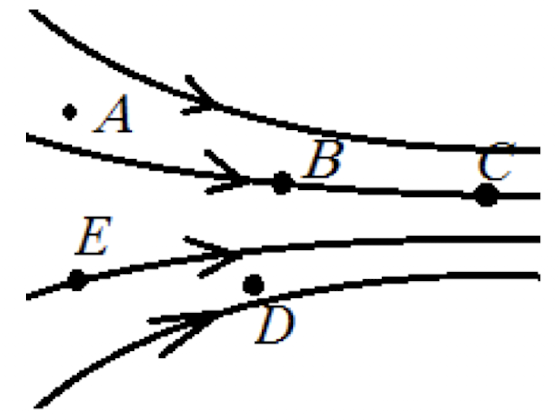
A _____ charge feels a force in the direction of the electric field.
positive
The electric flux inside a charged conductor is zero. True or false?
True
The total electric flux through a closed surface depends on all charges within and outside the surface. True or false?
False