Antineoplastics: antimetabolites, dna elongation inhibitors, antifolates
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
nucleotides, chain elongation
MOA of antimetabolites:
- inhibit enzymes that synthesize ________
- some arrest _____ _______ by incorporation into DNA
purine and pyrimidine antagonists
what are the 2 subclasses of antimetabolites?
thymidylate synthase
pyrimidine antagonists inhibit _____ _____, the enzyme that carries out the rate limiting step in dTMP synthesis, which eventually leads to cell death
AMP, GMP
purine antagonists inhibit the biosynthesis of ____ and ____
5FU, floxuridine, capecitabine
what are the 3 examples of pyrimidine antagonists?
5FU
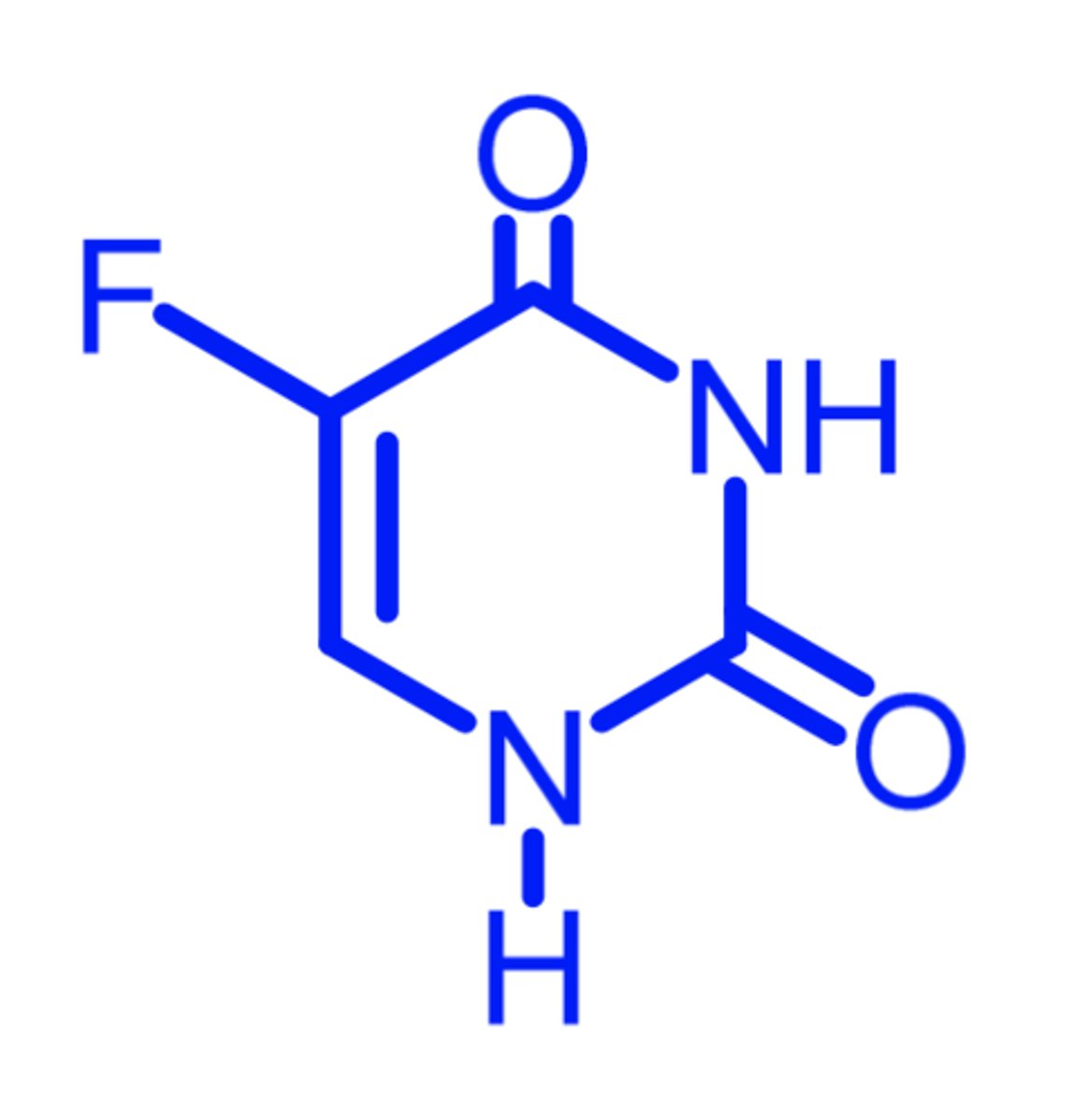
5FU
(pyrimidine antagonist -- antimetabolite)
ROA: IV, topical
SAR: needs to be activated for 5-F-dUMP (which can be recognized by TS)
MOA: thymidylate synthase inhibitor
- gives false substrate that binds + enters reaction, then stops it
- 5-F-dUMP, 5-10THF, and TS form a ternary complex that cannot eliminate a proton + causes irreversible inhibition of TS
indication: palliative treatment of colorectal, breast, stomach, and pancreatic cancers
- topical: actinic or solar keratosis
ADME: rapidly cleared, 20% excreted unchanged in urine, most metabolized in liver by dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase
- pts w genetic deficiency of DPD = inc risk of life threatening consequences
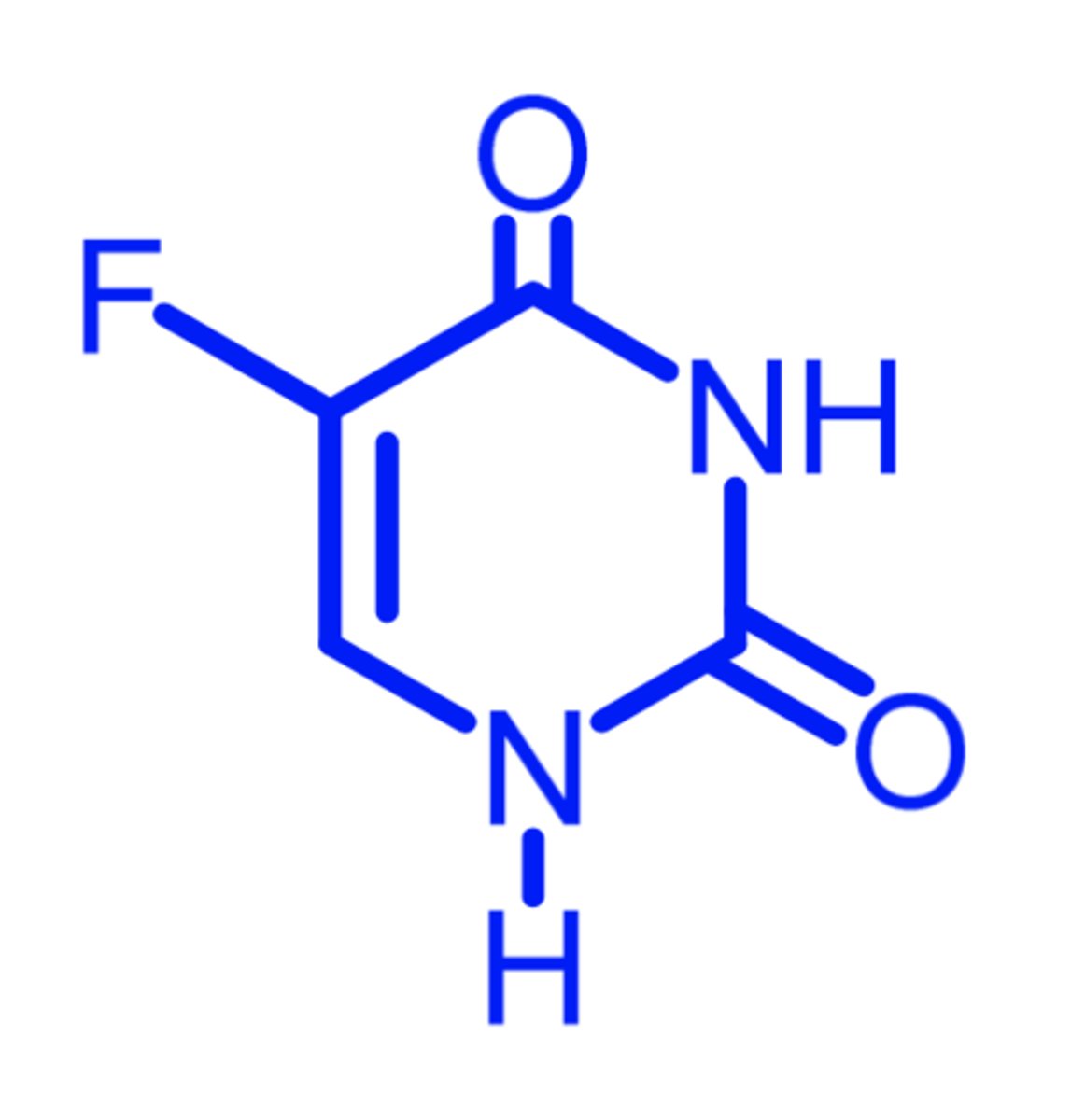
floxuridine
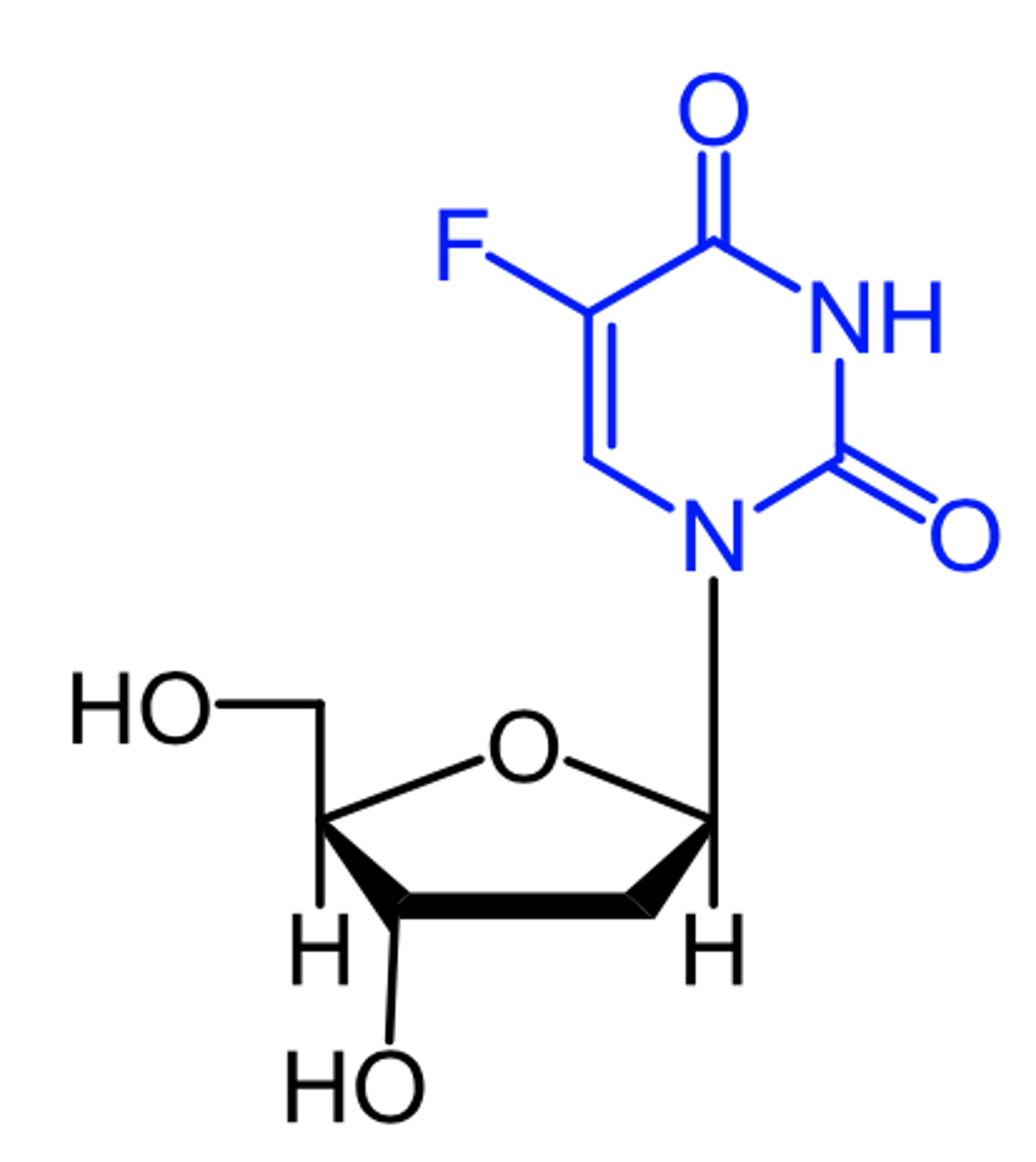
floxuridine
(pyrimidine antagonist -- antimetabolite)
ROA: IV, regional arterial infusion
MOA: converted to 5-F-dUMP in vivo (active form) which then causes irreversible inhibition of TS
indication: GI adenocarcinoma metastatic to liver
AE: use w extreme caution in impaired renal or hepatic function
- can be removed by dialysis
- lower risk of N/V
- PK not impacted by DPD
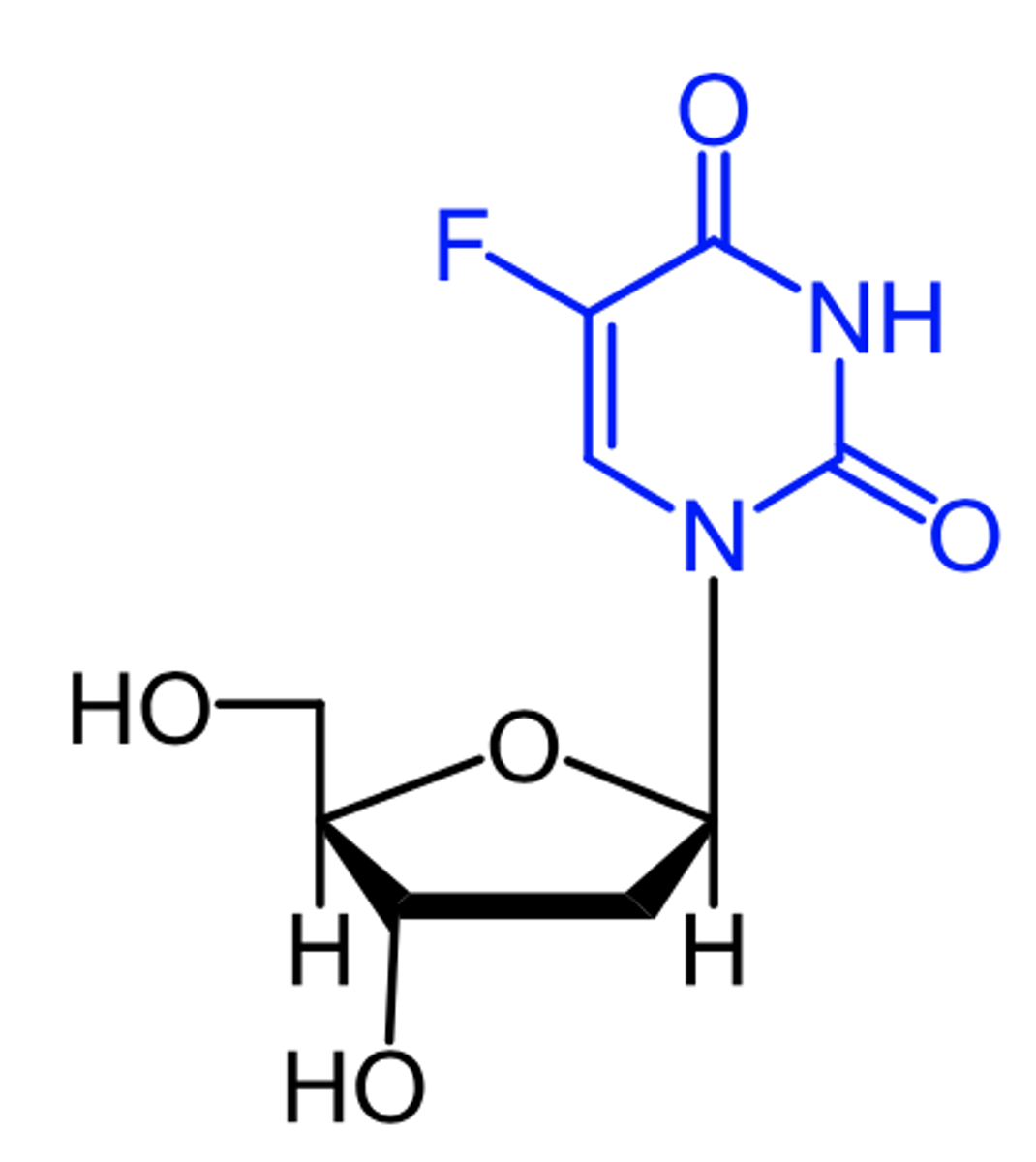
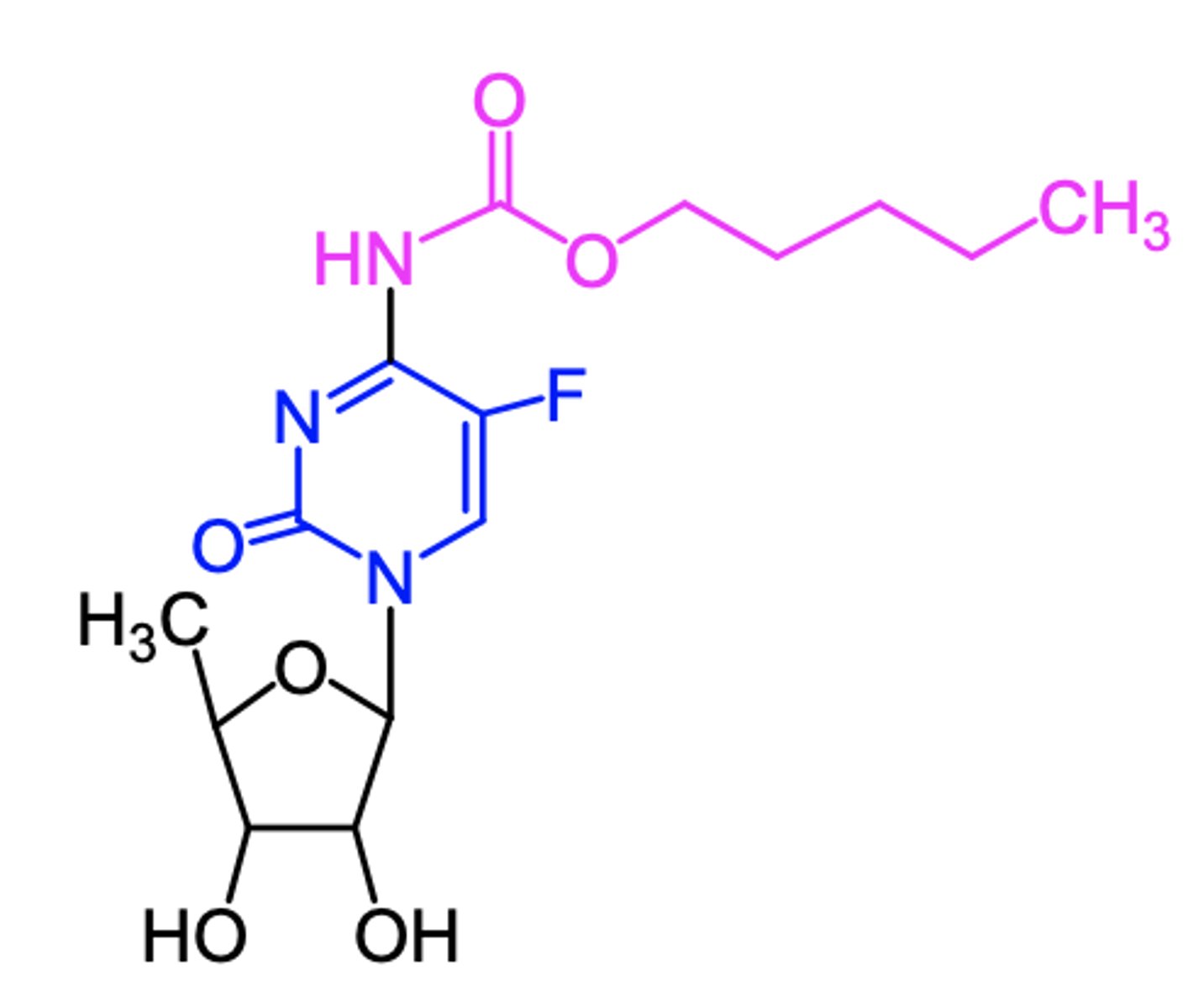
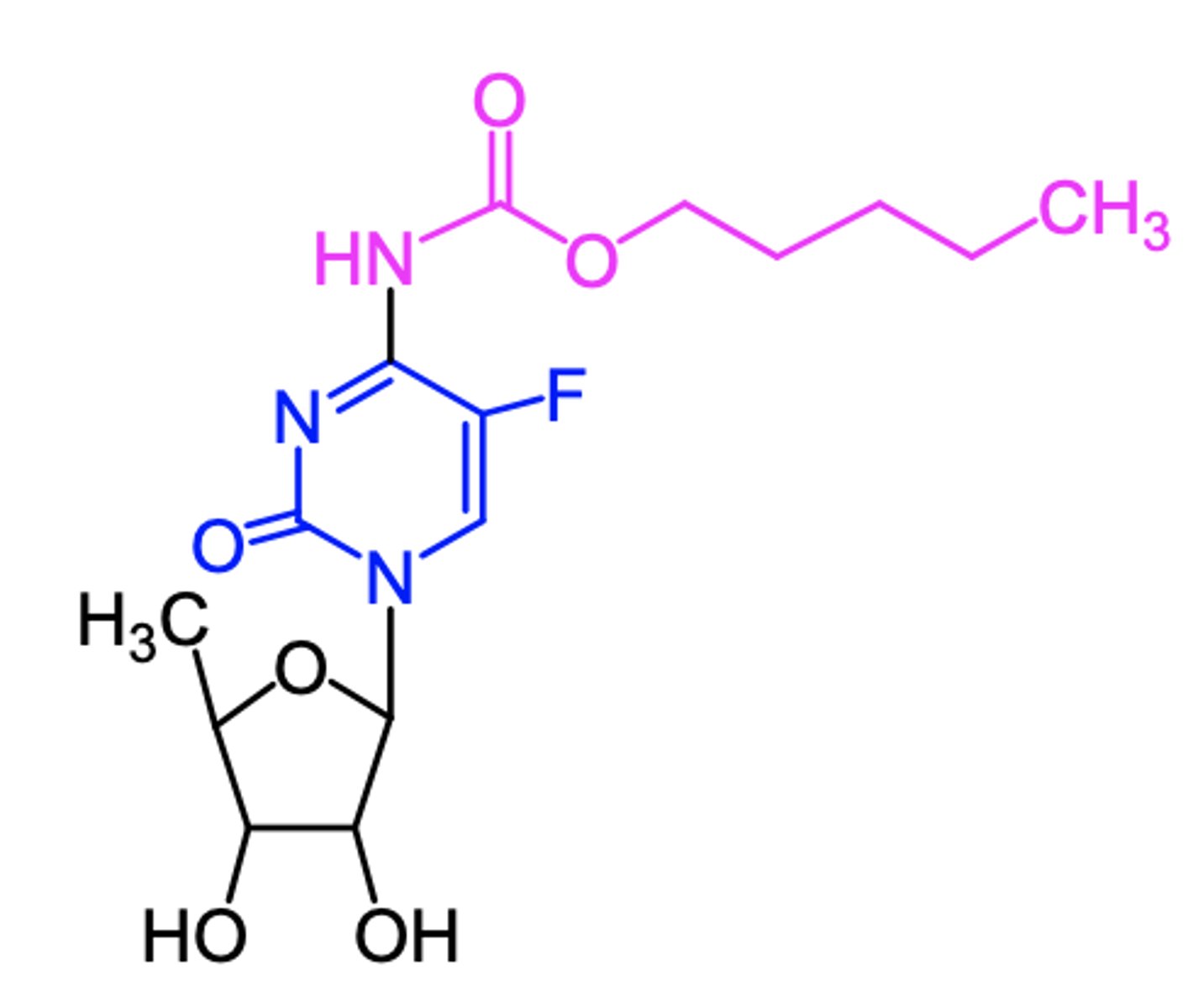
capecitabine
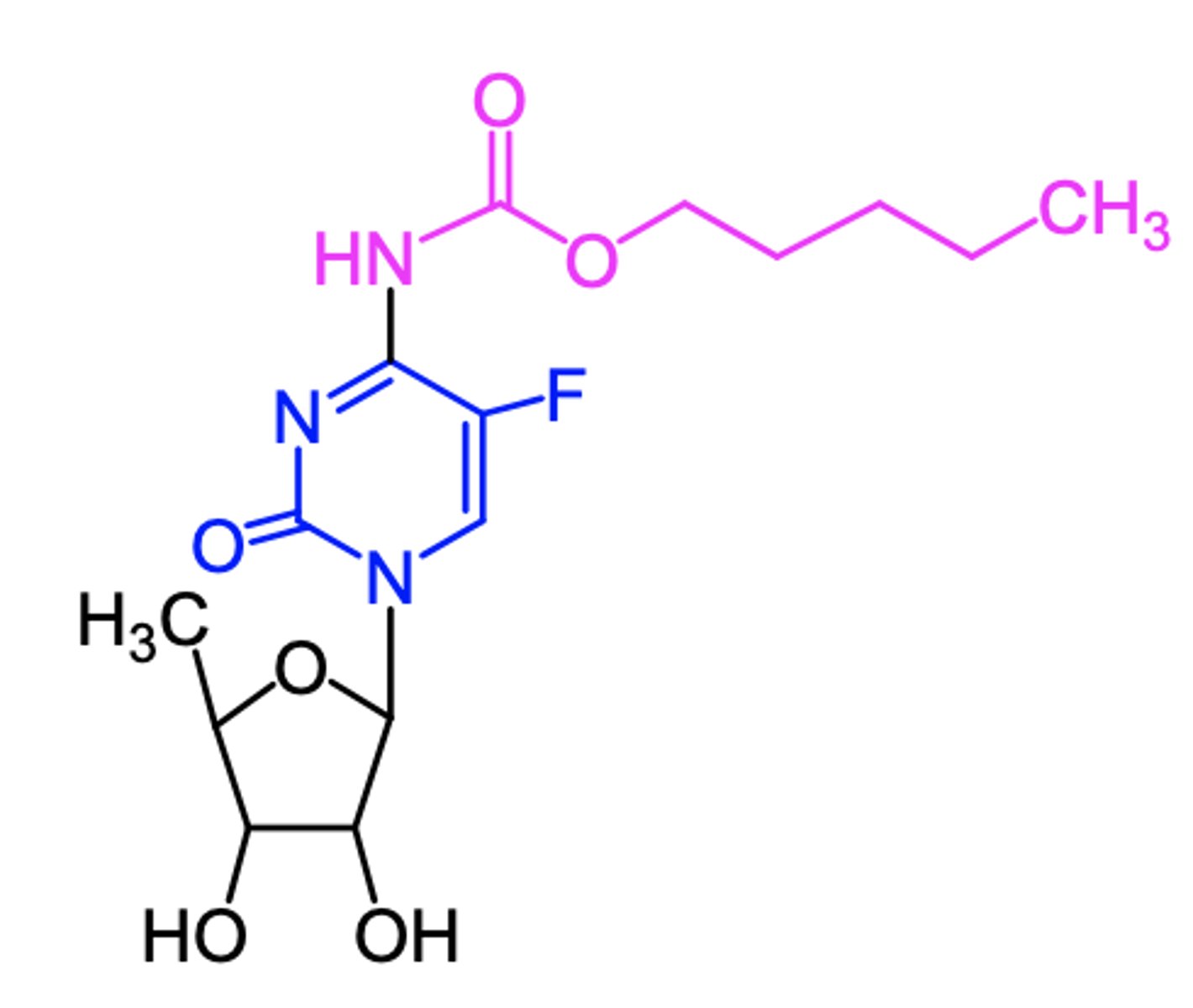
capecitabine
(pyrimidine antagonist -- antimetabolite)
ROA: oral
MOA: prodrug converted to 5-F-dUMP in vivo which then irreversibly inhibits TS
indication: first-line for colorectal cancer
- alone/combo w docetaxel for metastatic breast cancer
AE: myelosuppression, N/V, severe diarrhea , potentially disabling disorder of "hand and foot syndrome"
DDI: warfarin (lethal)
ADME: rapid absorption, negative food effect, variable Cmax and AUC
5FU
which is associated with genetic polymorphisms of DPD?
a. 5FU
b. floxuridine
c. capecitabine
floxuridine
which can be removed by dialysis?
a. 5FU
b. floxuridine
c. capecitabine
capecitabine
which pyrimidine antagonist is first line therapy for colorectal cancer?
hand and foot syndrome
what is a potentially fatal side effect associated with capecitabine?
warfarin
what drug does capecitabine have a lethal DDI warning with?
capecitabine
which can be given orally?
a. 5FU
b. floxuridine
c. capecitabine
5-F-dUMP
all pyrimidine antagonists need to be activated in vivo to what?
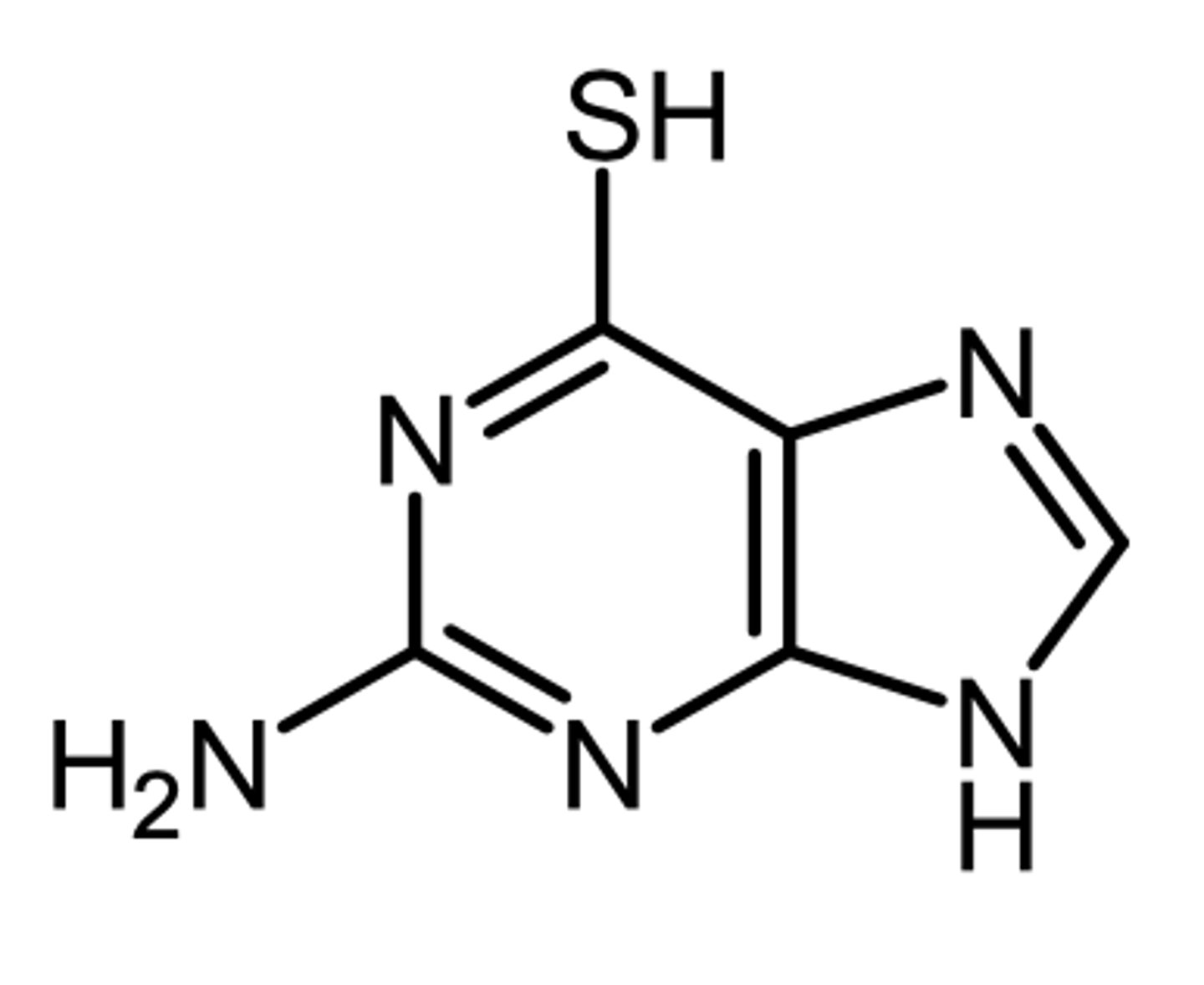
6MP, 6TG
what are the 2 examples of purine antagonists?
6MP
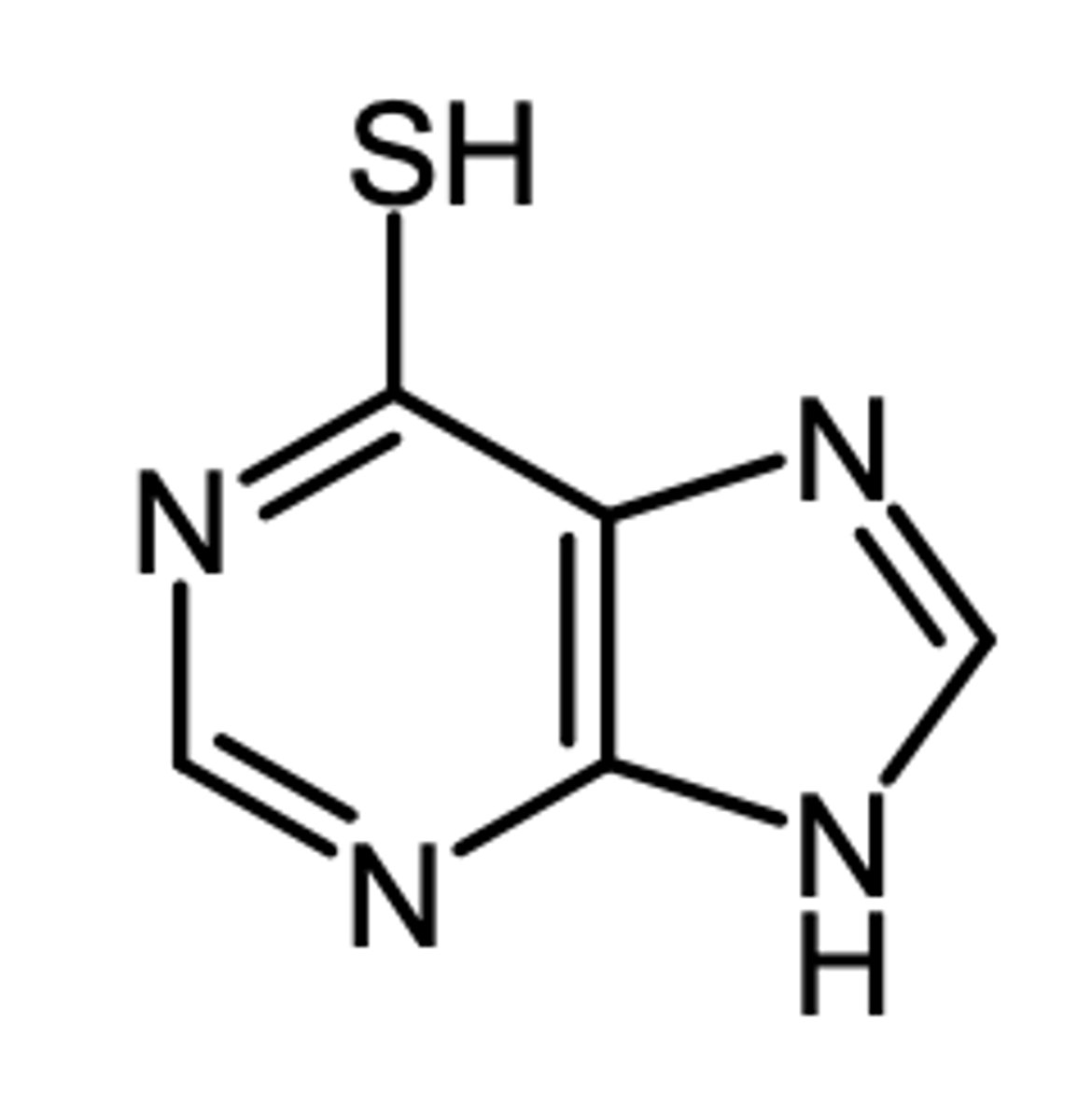
6MP (6-mercaptopurine)
(purine antagonist - antimetabolite)
ROA: oral
MOA: inhibits de novo synthesis of AMP and GMP by inhibiting glutamine amino phosphoribosyl (rate limiting enzyme) and is then incorporated into RNA and DNA
- lower risk of mutagenesis and 2º malignancy
indication: acute lymphatic and myelogenous leukemia
resistance:
- active uptake via nucleoside transporters
- deficiency in activating HGPRT enzyme
AE: myelosuppression, hepatotoxic at high doses
- genetic deficiency of TPMT = inc risk of purinethol toxicity
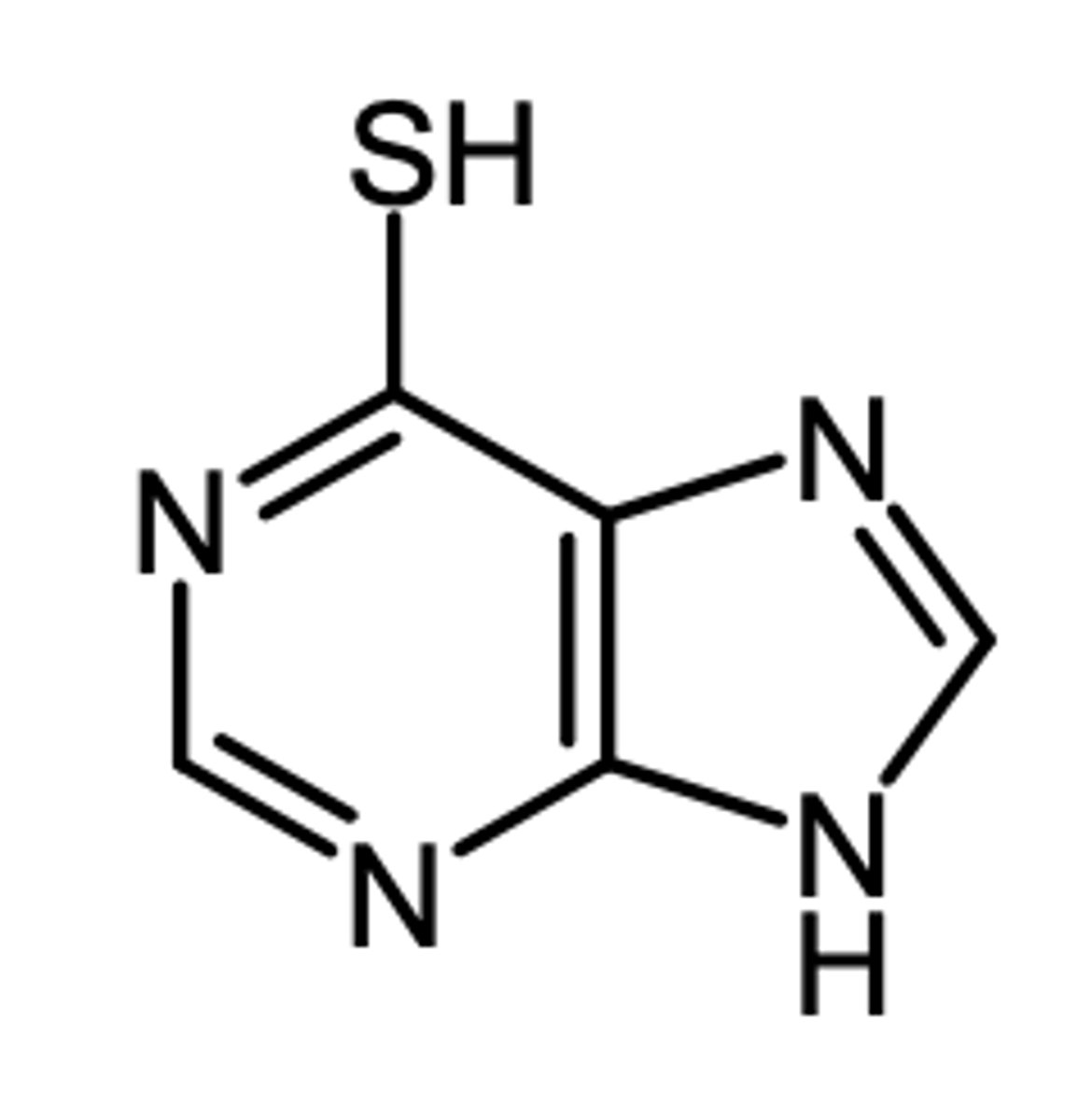
6TG
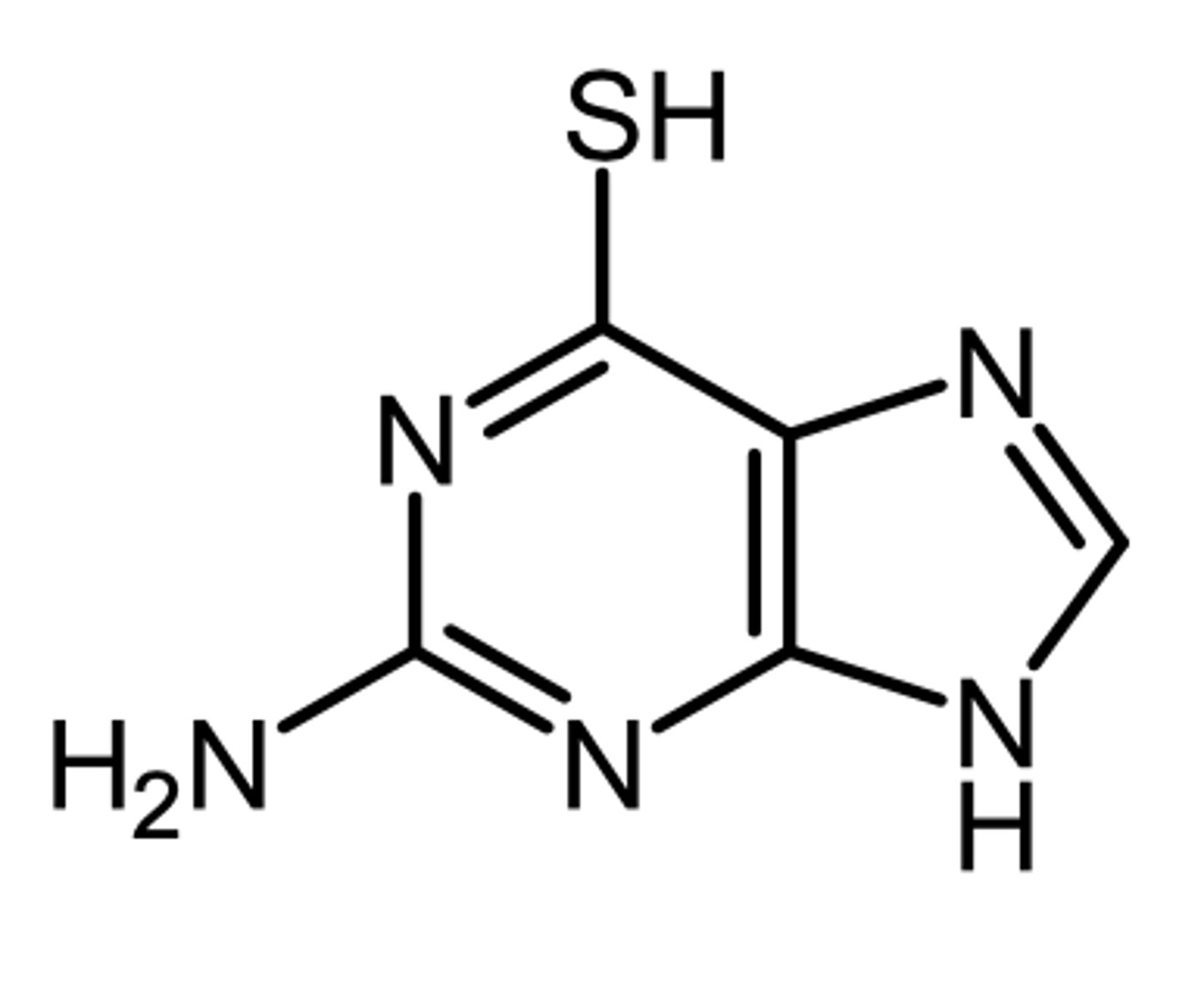
6TG (6-thioguanine)
(purine antagonist - antimetabolite)
ROA: oral
MOA: inhibits de novo synthesis of AMP and GMP by inhibiting glutamine amino phosphoribosyl (rate limiting enzyme) and is then incorporated into RNA (active form) and DNA
indication: nonlymphatic leukemias
AE: TPMP deficiency = serious myelosuppression
oral
what is the ROA for 6-MP and 6-TG?
cytarabine, gemcitabine, fludarabine
what are the 3 examples of dna polymerase + chain elongation inhibitors?
cytarabine
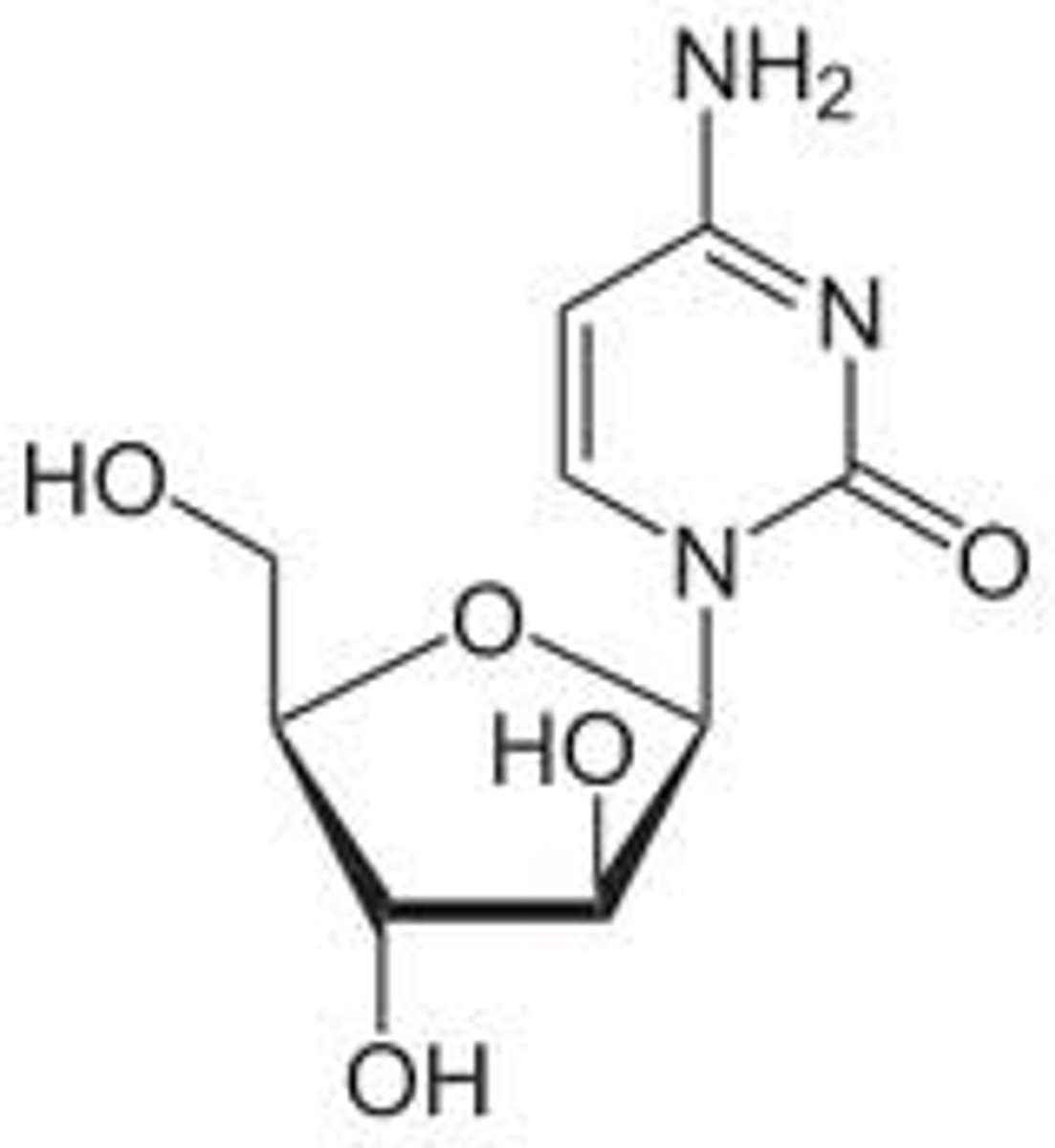
cytarabine
(dna polymerase + chain elongation inhibitor)
ROA: IV, in combo
MOA: prodrug that needs to have triphosphate attached for activation, which is then incorporated into growing DNA + preventing chain elongation
- also inhibits DNA/RNA polymerases + nucleotide reductase
- active in S phase
indication: acute nonlymphatic leukemia
- intrathecal admin: meningeal leukemia
SAR: differs from cytidine bc there is an arabinose instead of ribose
gemcitabine
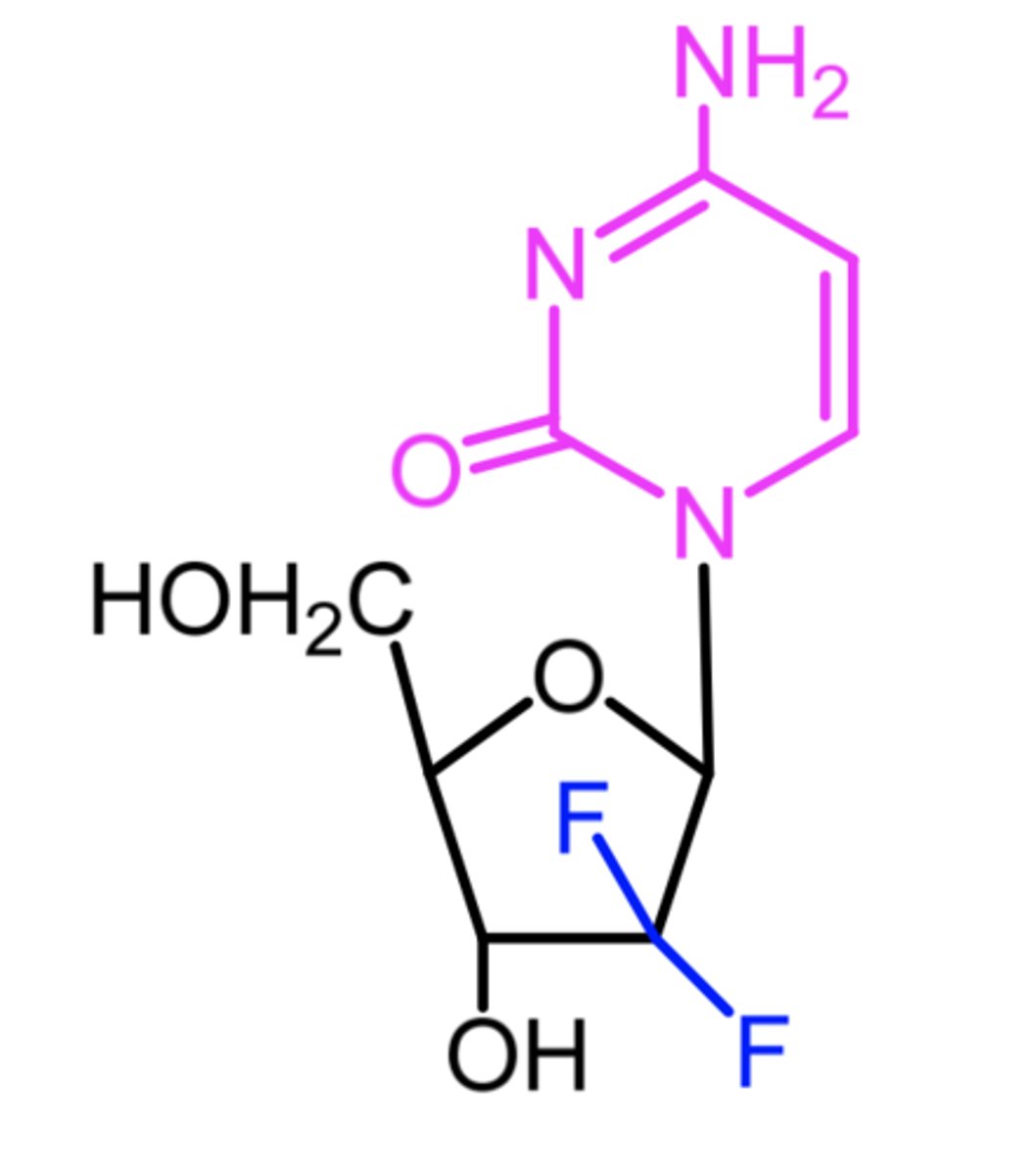
gemcitabine
(dna polymerase + chain elongation inhibitor)
ROA: IV
SAR: active = triphosphate form
MOA: DNA polymerase inhibitor
- incorporated into elongating DNA , then only 1 NT can be added eventually leading to cell death
- diphosphate form inhibits ribonucleotide reductase
indication: 1st line for adenocarcinoma of the pancreas
- (+) carboplatin = advanced ovarian cancer
- (+) paclitaxel = 1st line for metastatic breast cancer
- (+) cisplatin = 1st line for NSCLC
ADME: longer t1/2 than cytarabine due to gem-difluoromethylene group
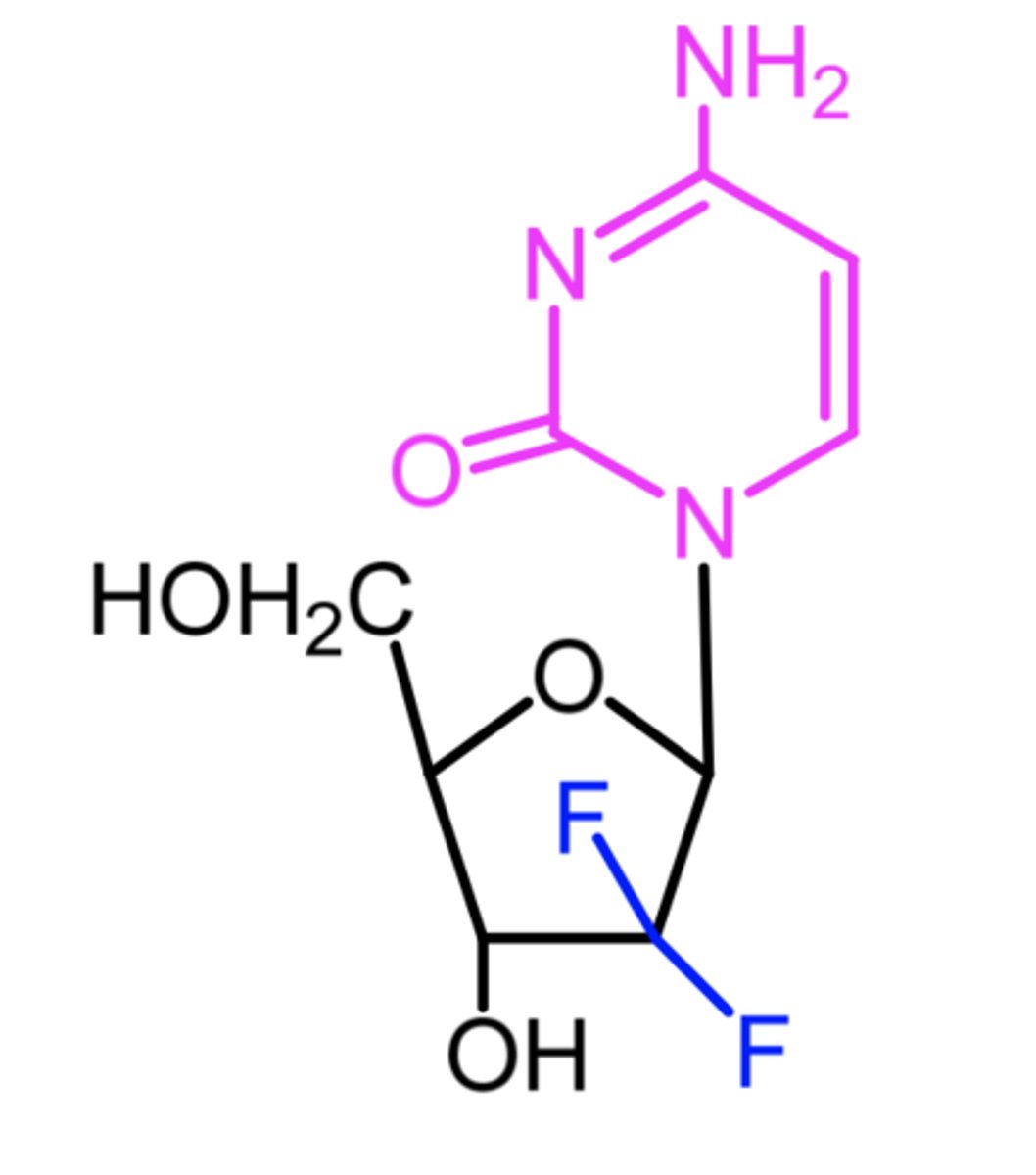
fludarabine
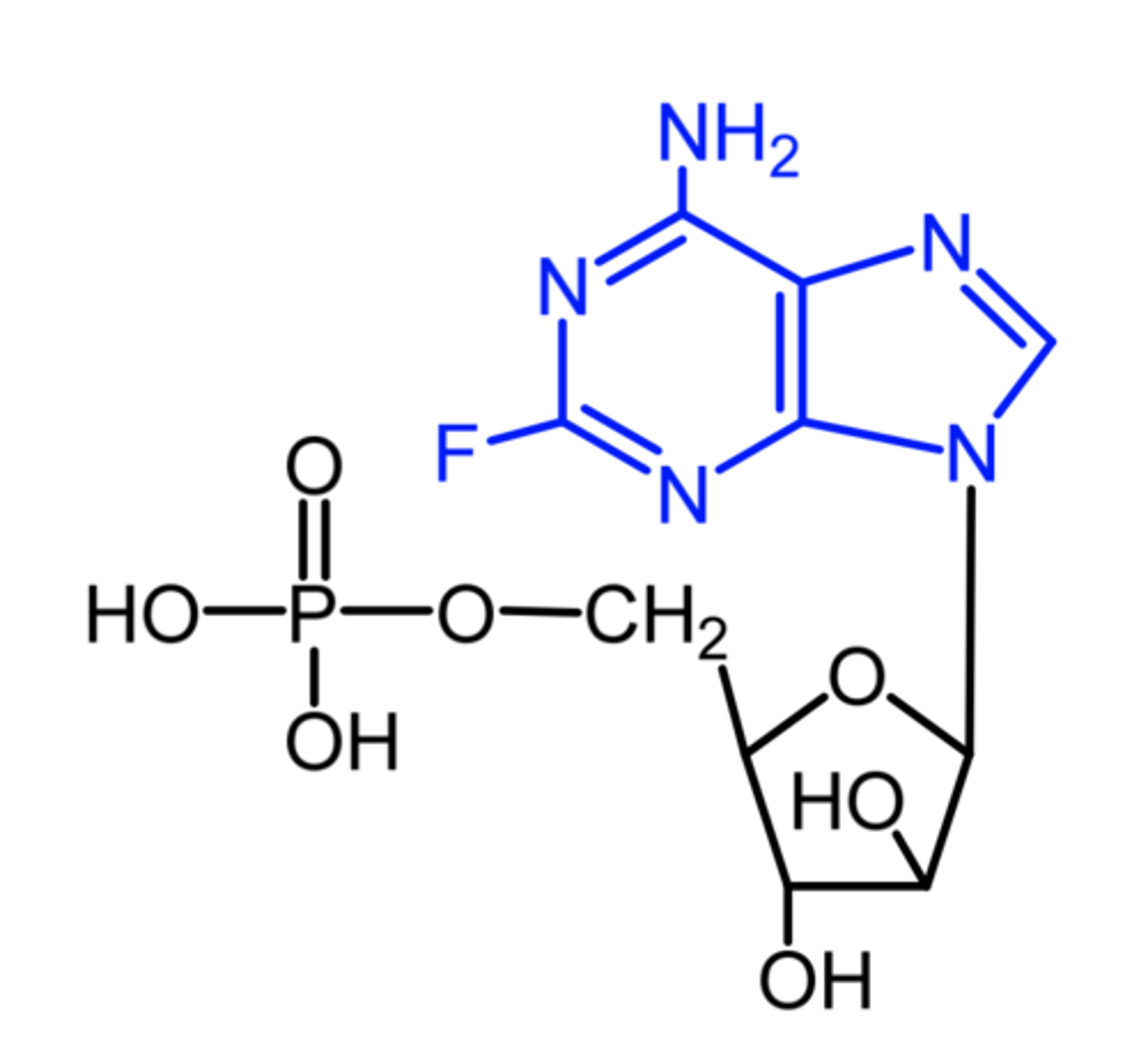
fludarabine
(dna polymerase + chain elongation inhibitor)
ROA: IV
SAR: marketed as phosphate to inc aqueous solubility for IV admin
- triphosphorylated to active triphosphate (2-fluoro-ara-ATP) in vivo
MOA: DNA polymerase inhibitor
- ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor
indication: b-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- cells w high levels of deoxycytidine kinase will respond well this agent
AE: "aids in a bottle" due to significant immunosuppressant activity
ADME: relatively resistant to degradative action of adenosine deaminase
triphosphate
in what form are all dna polymerase + chain elongation inhibitors active?
gemcitabine
which has a longer t1/2:
a. cytarabine
b. gemcitabine
gemcitabine
what is the 1st line treatment for adenocarcinoma of the pancreas?
fludarabine
which agent is associated with the AE "aids in a bottle"?
a. cytarabine
b. gemcitabine
c. fludarabine
both
antifolates inhibit the synthesis of:
a. purines
b. pyrimidines
c. both
methotrexate
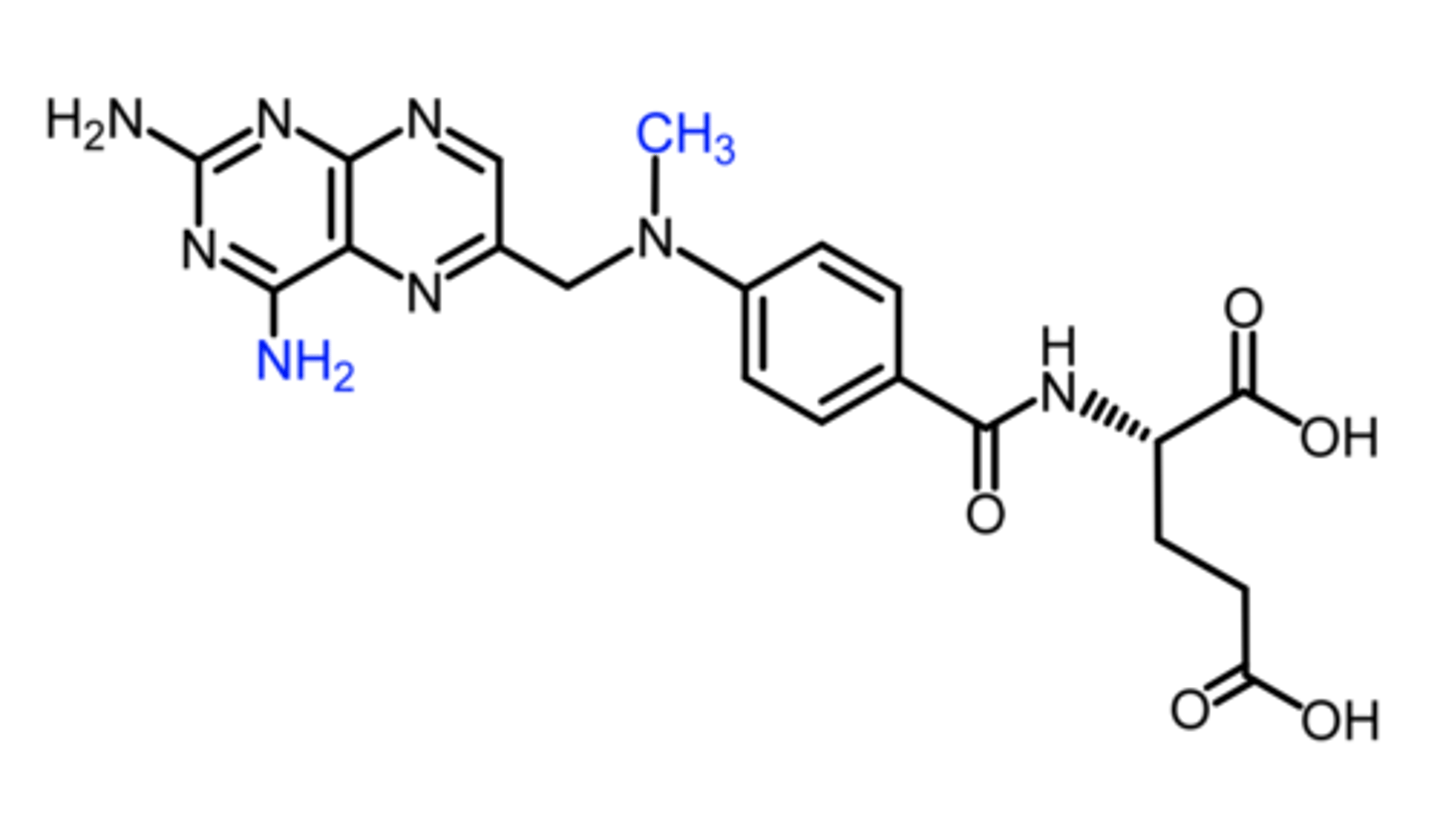
methotrexate
(antifolate)
ROA: PO, IV
MOA:
- DHFR inhibitor = blocks dTMP synthesis
- inhibits GAR transformylase, a key enzyme in synthesis of purine nucleotides
- works in S phase
SAR: undergoes intracellular FPGS-catalyzed polyglutamation, which adds several anionic carboxylate groups
indication: breast, lung, head, and neck cancers
- non-hodgkin's lymphoma
- psoriasis, RA
- off label: MS
AE: toxicity occurs at high doses
- use leucovorin as rescue therapy
note: cancer cells become resistant over time
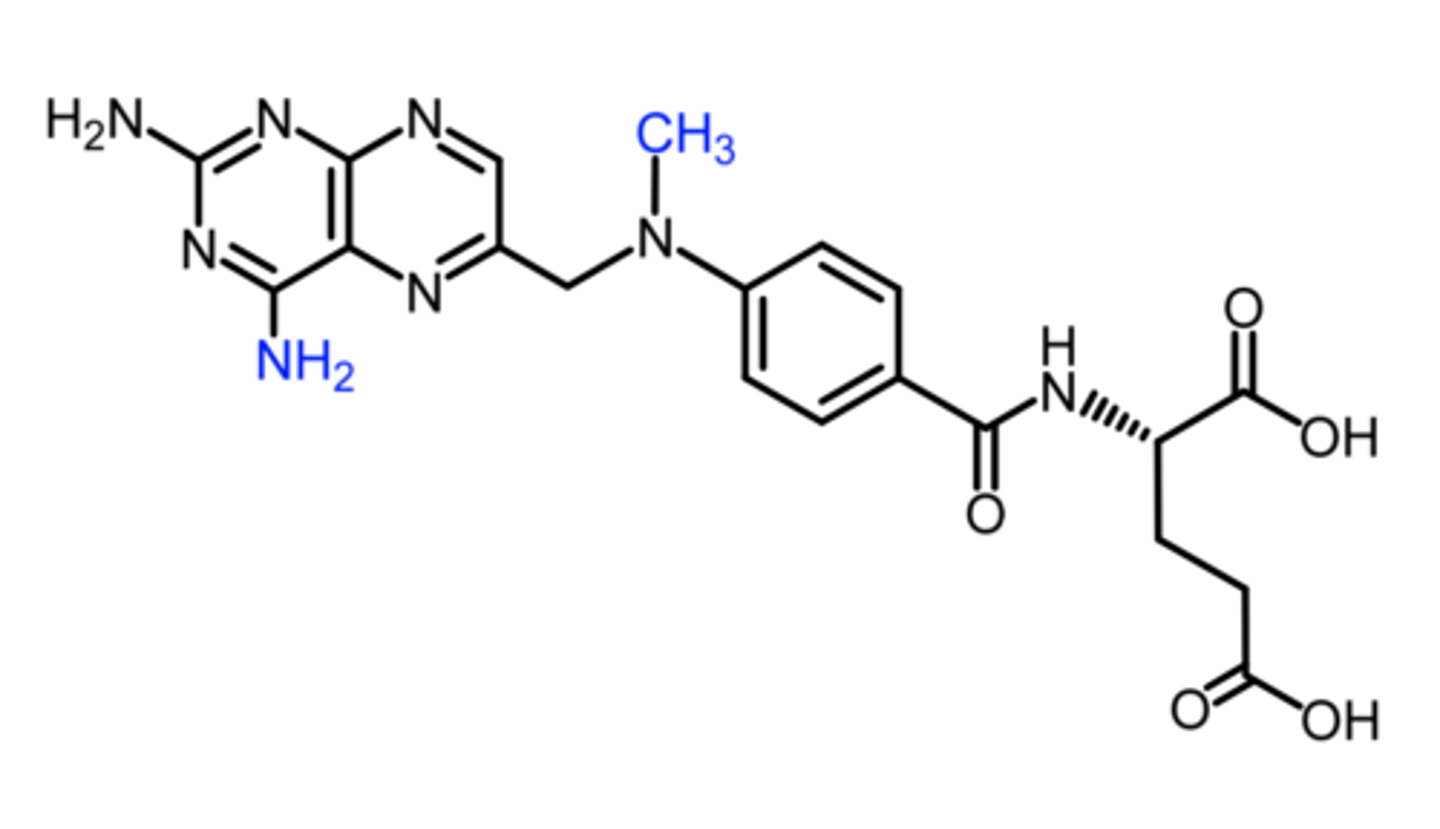
leucovorin
what should be used for methotrexate toxicity?
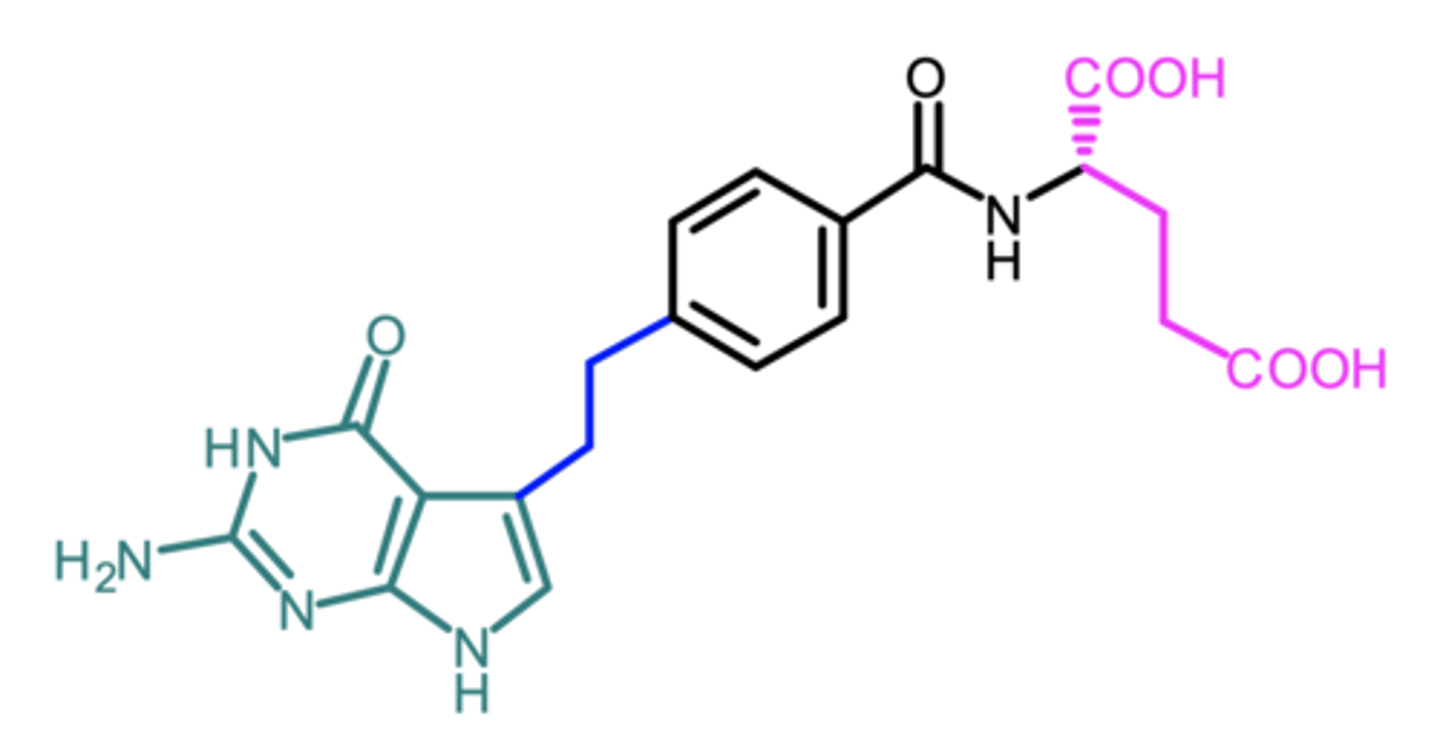
methotrexate, pemetrexed
what are the 2 examples of antifolates?
pemetrexed
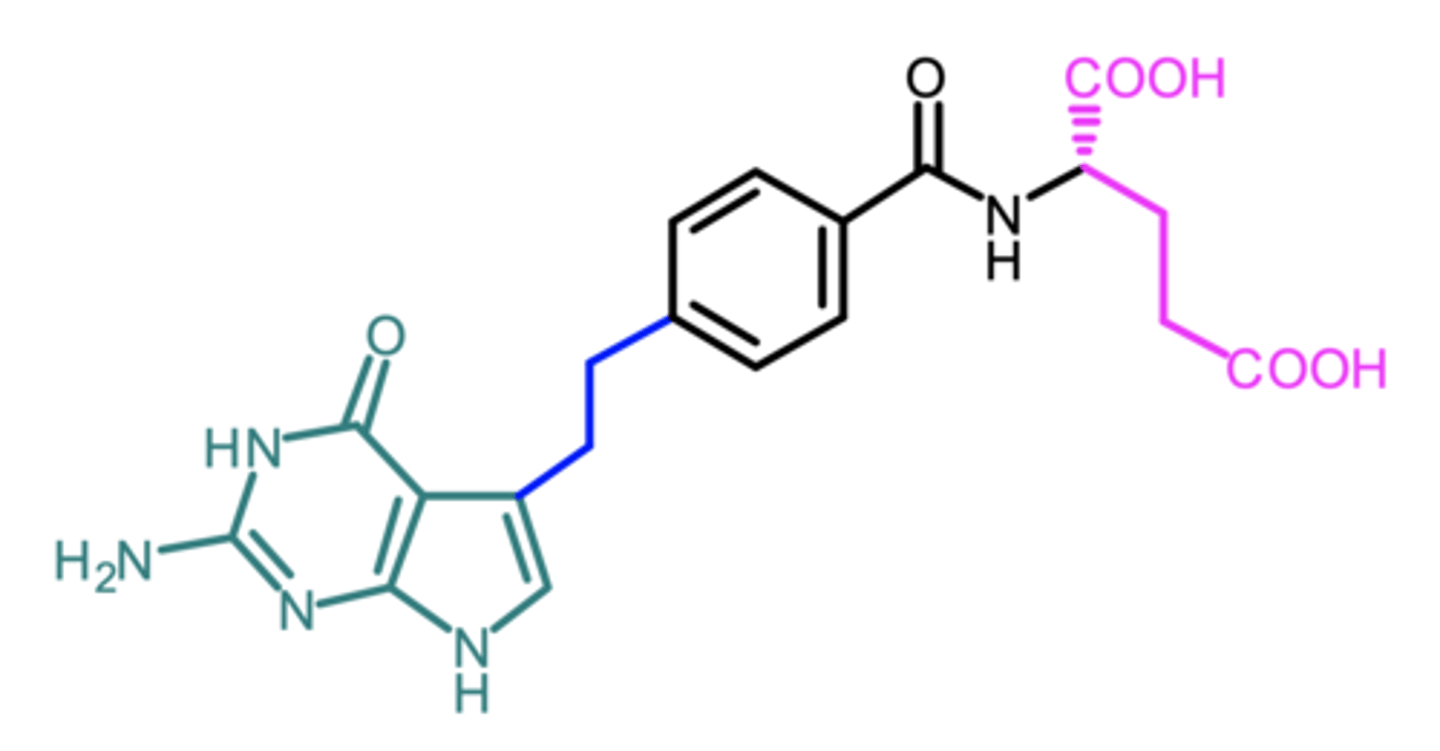
pemetrexed
(antifolate)
ROA: IV
MOA: inhibits synthesis of pyrimidine and purine nucleotides via inhibition of DHFR and GAR transformylase
indication: NSCLC, malignant pleural mesothelioma (combo w cisplatin)
ADME: dose-proportional Cmax and AUC, 81% ppb
AE: myelosuppression, neutropenia, nausea, mucositis