Drugs targeting the HPG Axis - lecture 29
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
drugs we need to know
drugs we need to know

endocrine physiology
endocrine physiology

Hormone Transport
Circulate Freely or Bound
Sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG)- regulates availability and activity in body
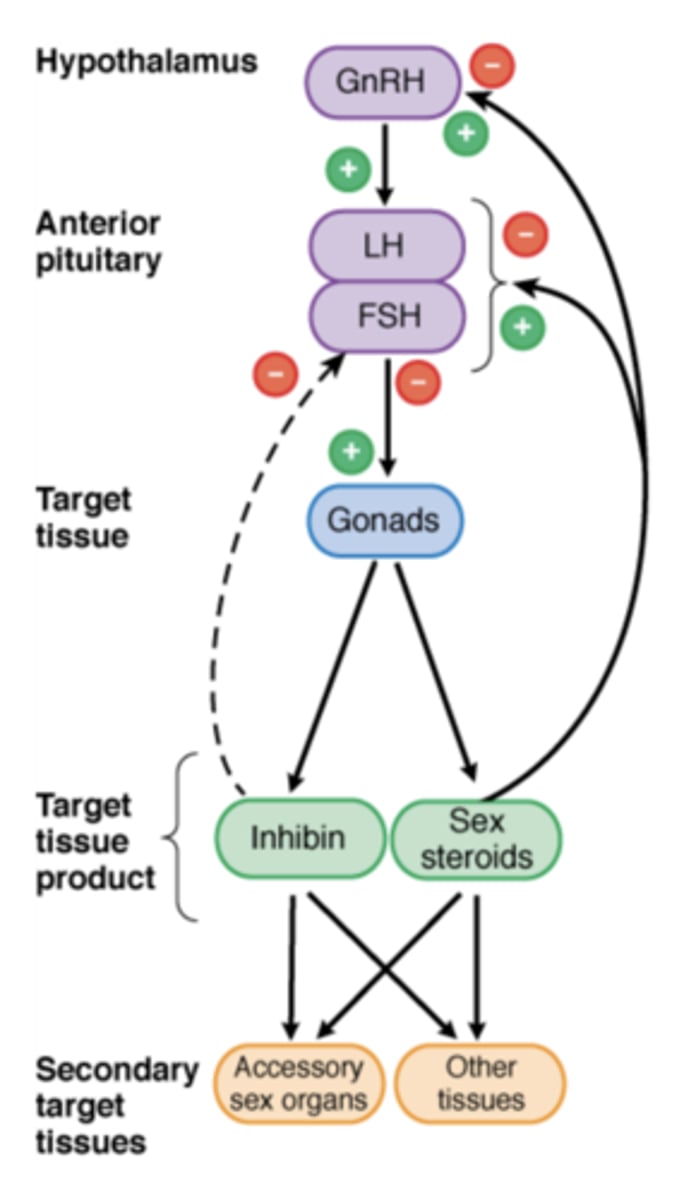
Feedback Mechanism
regulates sex hormones availability and activity in body
Removal of Hormone from Circulation
Metabolic Transformation
- liver(main site), periphery
Metabolic Clearance
- undergo urinary secretion, liver, saliva, sweat, brain
Gonadotropic Hormones GnRH, LH, FSH
Gonadotropic Hormones GnRH, LH, FSH
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
pulsatile secretion
Cyclical secretion luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
females
ovary
LH: ovulation, corpus luteum
FSH: dvpt follicle, estradiol and progesterone
males
testes
LH: Leydig cells: testosterone
FSH: Sertoli cells: spermatogenesis
positive
Preovulatory surge of estrogen: ___________ feedback.
negative
Androgens and estrogens: ___________ feedback
Inhibin
negative feedback on FSH secretion by the pituitary
Hormone Receptor GnRH, LH, FSH - MOA
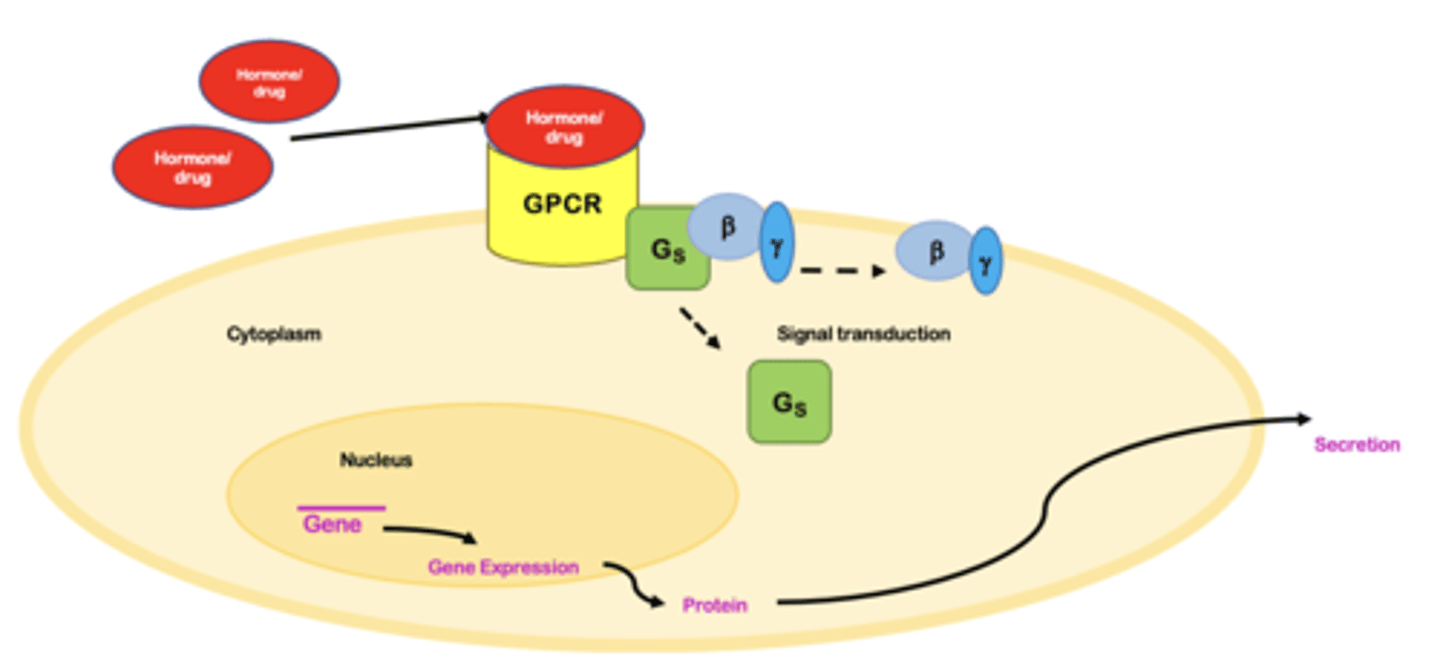
G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) - cell surface membrane receptor
Hormone released from the hypothalamus or pituitary binds to its receptor expressed on the cell membrane of targeted organ
Signal transduction
Can activate or repress gene transcription
Binding of hormone to its receptor leads to synthesis and secretion of hormones
GnRH Agonists
GnRH is normally secreted in pulsatile manner.
Stimulating FSH and LH release in a non pulsatile manner causes continuous stimulation of the gonadtrophs receptors and causes down-regulates GnRH receptors on gonadotrophs (clinical use).
GnRH agonists uses
Palliative therapy and treatment of advanced prostate cancer and premenopausal hormone receptor-positive (HR+) advanced breast. Avoid premature LH surge (ovulation) in in-vitro fertilization (IVF protocols)
Suppress/delay puberty in gender-questioning and transgender youth (off-label)
Suppress steroid-responsive condition: endometriosis, uterine fibroids, acute intermittent porphyria, priapism
Pharmacological castration (e.g., precocious puberty)
Test hypothalamic vs. pituitary defects in diagnoses of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (HH) : measurement of LH and FSH secretion before/after GnRH drug administration
goserelin (Zoladex)
MOA - agonists at the GnRH receptor (GPCR receptor) continued receptor occupancy by goserelin, however, ultimately causes a down-regulation of production of LH and FSH and a resultant decrease in testosterone and estrogen levels (desensitization of GnRH receptor)
Initial stimulates production of LSH and FSH which in turn stimulates synthesis and secretions of sex hormones, testosterone and estrogen in a non-pulsatile manner. The non-pulsatile release of sex hormones causes disruption of the endogenous hormonal feedback systems, causing downregulations of GnRH receptor resulting in the down-regulation of testosterone and estrogen production.
Other GnRH agonist: leuprolide (Lupron) and triptorelin (Decapeptyl)
GnRH Agonists - goserelin (Zoladex)
Adverse Effects: bone pain, hot flashes, sweating, decreased bone density, decreased libido, dizziness, vertigo, insomnia, headaches
-- Females: Typical symptoms of menopause: depression, generalized pain, vaginal dryness might occur
-- Males: erectile dysfunction
Therapy in non-life-threatening diseases (e.g. endometriosis, uterine fibroids) typically limited to six months.
Drug Interactions: decreases efficacy of androgen therapy
Contraindications: pregnancy, breast-feeding, osteoporosis, undiagnosed abnormal vaginal bleeding
ganirelix (Antagon, Cetrorelix, Cetrotide) - GnRH Antagonists
Uses: Inhibit premature (LH) surges in women undergoing ovarian hyperstimulation with FSH and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), followed by subsequent Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) procedures.
Mechanism of Action: antagonists at the GnRH receptor (GPCR)
Administer subcutaneously during certain phases of fertility (mid to late follicular phase of menstrual cycle. Inhibits the secretion of LH>>FSH in a dose dependent manner.
Adverse effects: nausea and headaches, anaphylaxis.
Contraindications: primary ovarian failure, pregnancy, breast feeding
Androgen
Estrogen
Progesterone
Androgen
Estrogen
Progesterone
synthesis
synthesis
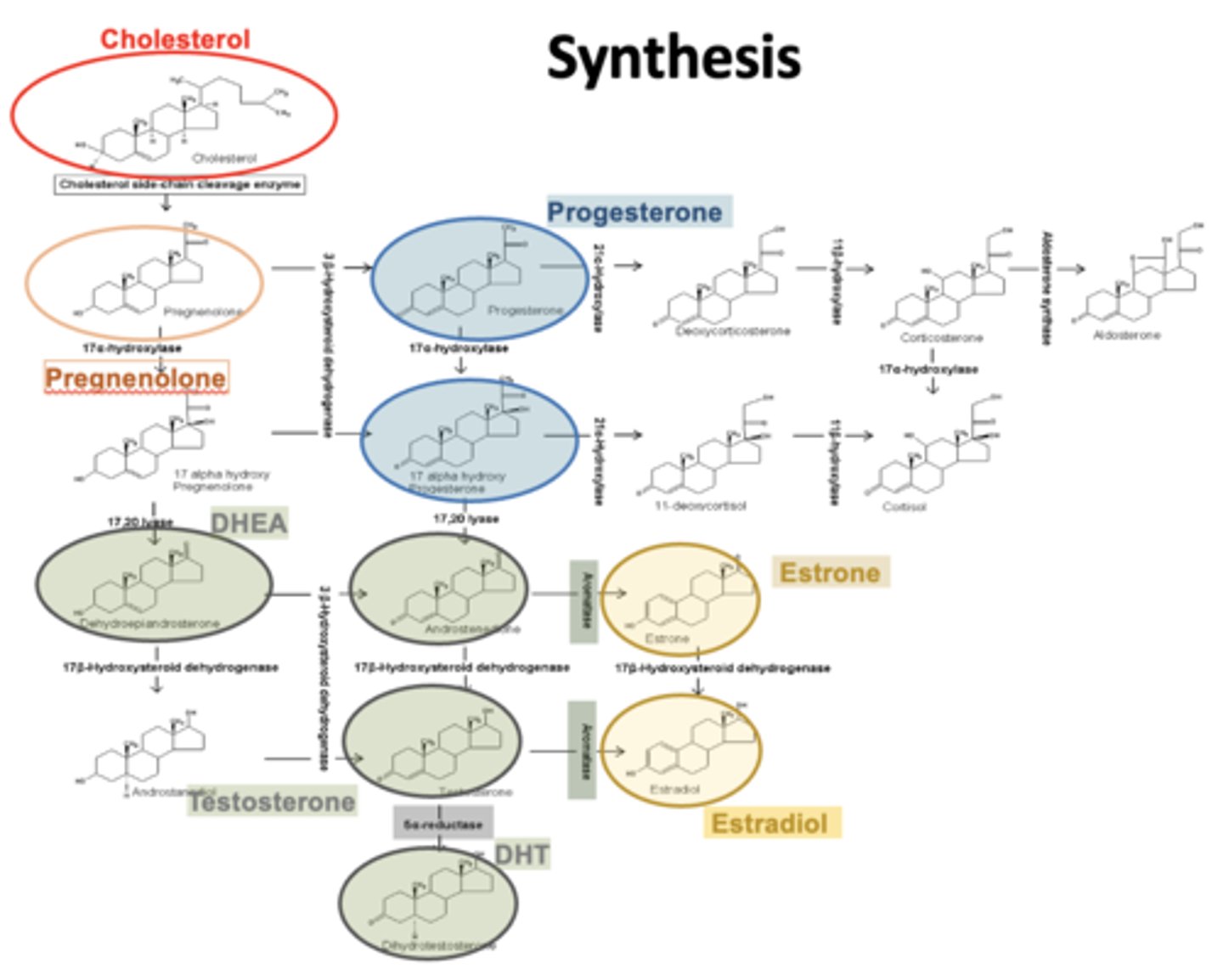
Nuclear Receptor Androgens, Estrogen - MOA
Function as molecular switches in response to hormone binding
Hormone diffuses through the cell membrane binds to receptor in the cytoplasm
The hormone bound receptor can now travel to the nucleus through a nuclear pore
The hormone bound receptor binds to its hormone receptor element (HRE) located on DNA
Binding of the hormone bound receptor to HRE leads to modulation of gene transcription
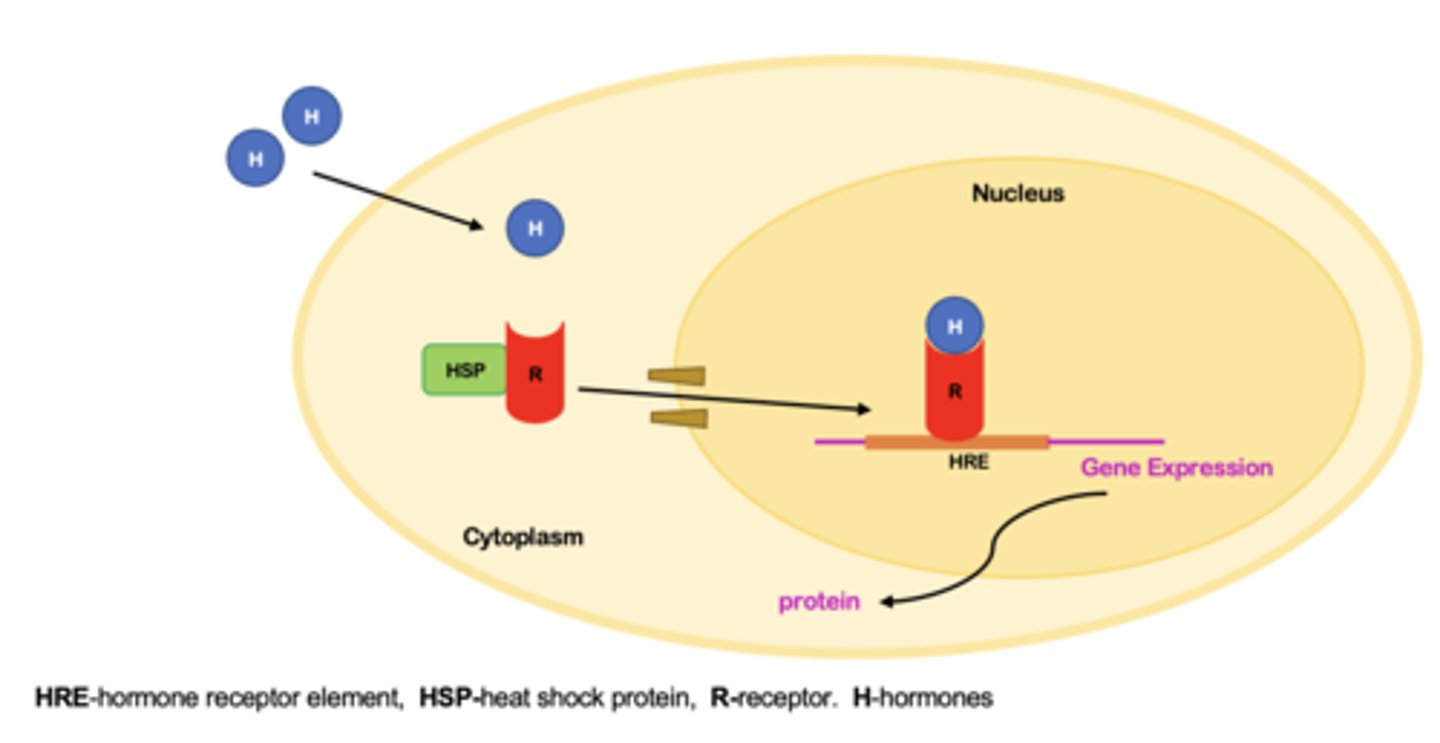
Mechanism of Action (MOA): Enzyme Inhibitor
Mechanism of Action (MOA): Enzyme Inhibitor
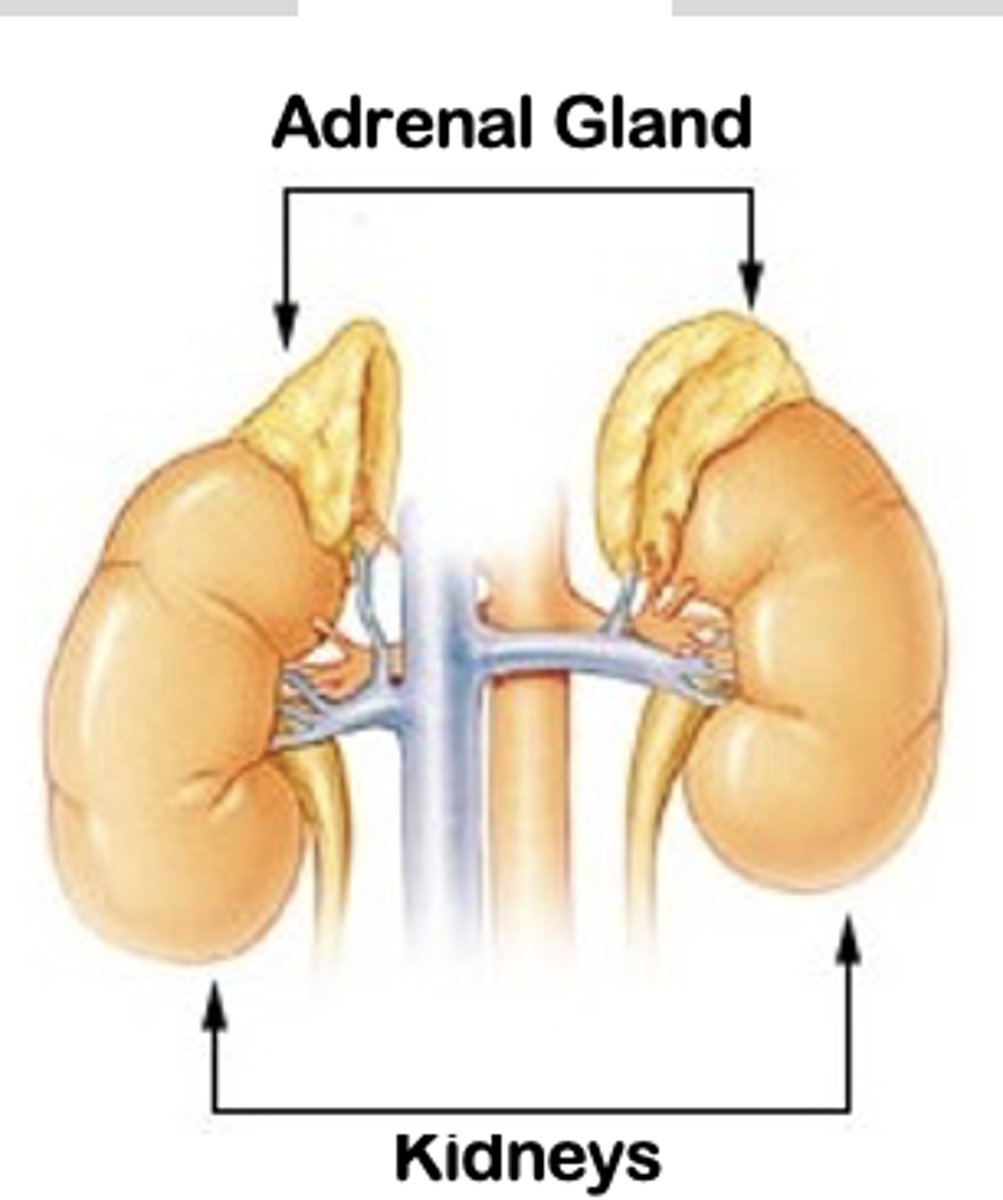
male androgens
Leydig cells of the testes
Adrenal gland
female androgens
Theca cells of the ovarian follicle
Adrenal gland
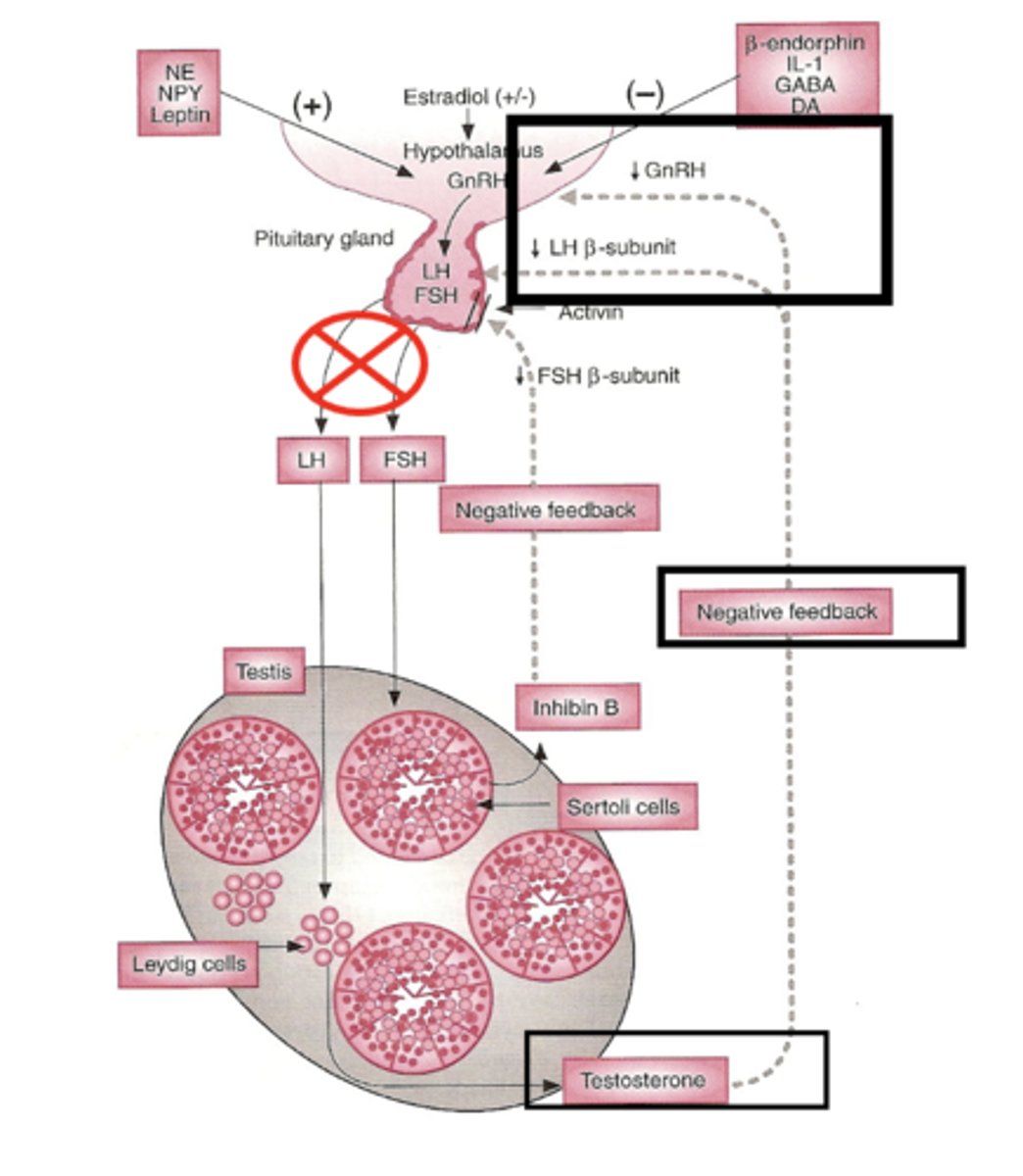
Androgens Regulation – Feedback Loop
Androgens Regulation – Feedback Loop
Treatable Conditions
Male hypogonadism: develop or maintain secondary sex characteristics
Prostate Cancer
Male Pattern Baldness
Gender Transition
Adult Male Hypogonadism S/S
Infertility
Small prostate and testes
Gynecomastia
Adolescent Male Hypogonadism S/S
Delayed onset of puberty
Lack of facial or body hair development
Shortness of stature
Underdeveloped testicles and penis
Methyltestosterone (Covaryx) - testosterone analog
Testosterone Replacement Therapy Delivery Methods
Transdermal patch containing testosterone esters is applied each night to your back, abdomen, upper arm or thigh
Injections are given in a muscle
Gel rubbed into skin on upper arm or shoulder, or apply with an applicator under each armpit, or pump on your inner thigh - potential side effect: the possibility of transferring the medication to another person avoid skin to skin contact until gel is dried
Gum and cheek (buccal cavity) small putty-like substance delivers testosterone through the natural depression above your top teeth where your gum meets your upper lip (buccal cavity)
Implantable pellets testosterone containing pellets surgically implanted under the skin and need to be placed every three to six months
Orally – not recommended for long-term hormone replacement because it might cause
liver problems (1st pass). Monitoring for both beneficial and deleterious effects are required for all therapeutics
flutamide (EVLEXIN) - Androgen Receptor Antagonist
Uses:
in conjunction with GnRH analogs to treat metastatic prostate cancer
Treatment for Hirsutism in women (due to hepatoxicity should not be used for cosmetic purposes)

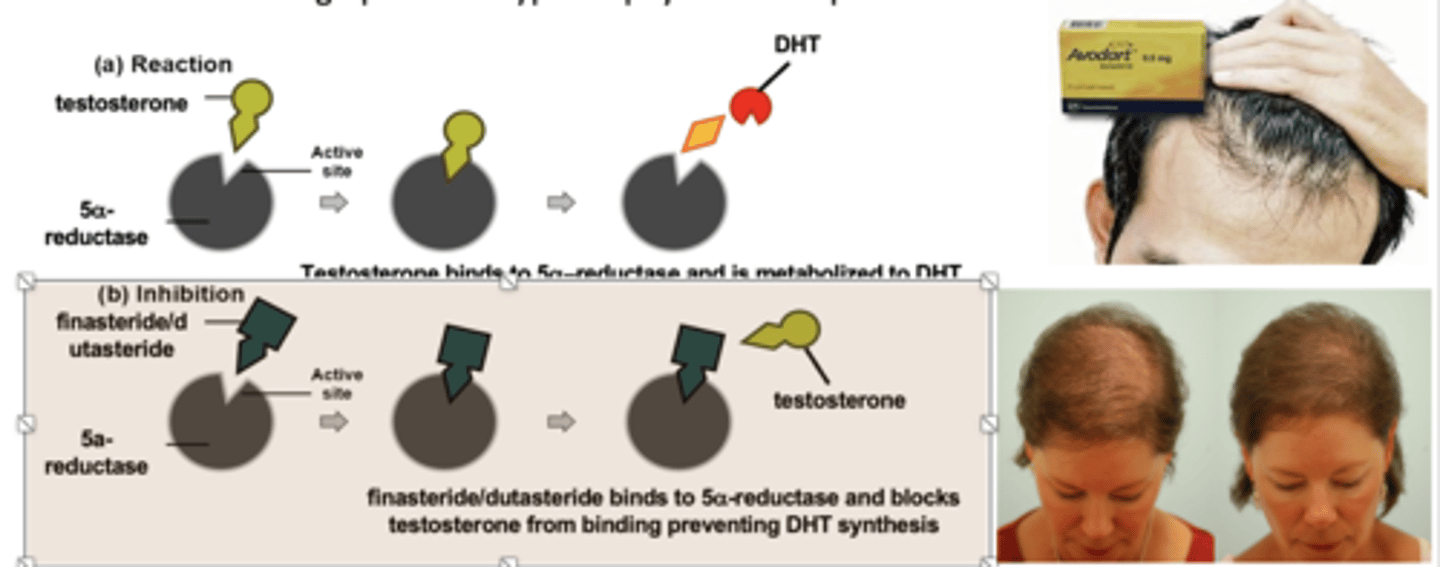
finasteride (Proscar, Propecia) - 5a-dihydrotestosterone (DHT) Synthesis Inhibitor
5a-reductase inhibitor
Used to treat benign prostatic hypertrophy and male patterned baldness
Use in women: Treatment for polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Contraindicated for women of childbearing age: Can cause birth defects in male children
dutasteride (Avodart)
Used to treat benign prostatic hypertrophy and male patterned baldness
Androgens: Side Effects
Potential Side Effects of Excessive Androgen Treatment
Reduced spermatogenesis and fertility due to feedback inhibition of LH and FSH secretion from anterior pituitary
Acne, particularly in women due to androgen stimulation of sebaceous glands beneath skin
Virilization (including facial hair and hirsutism) in women and children
In older men, increased risk of benign prostate hyperplasia and prostate cancer
Hepatotoxicity ( for testosterone derivatives )
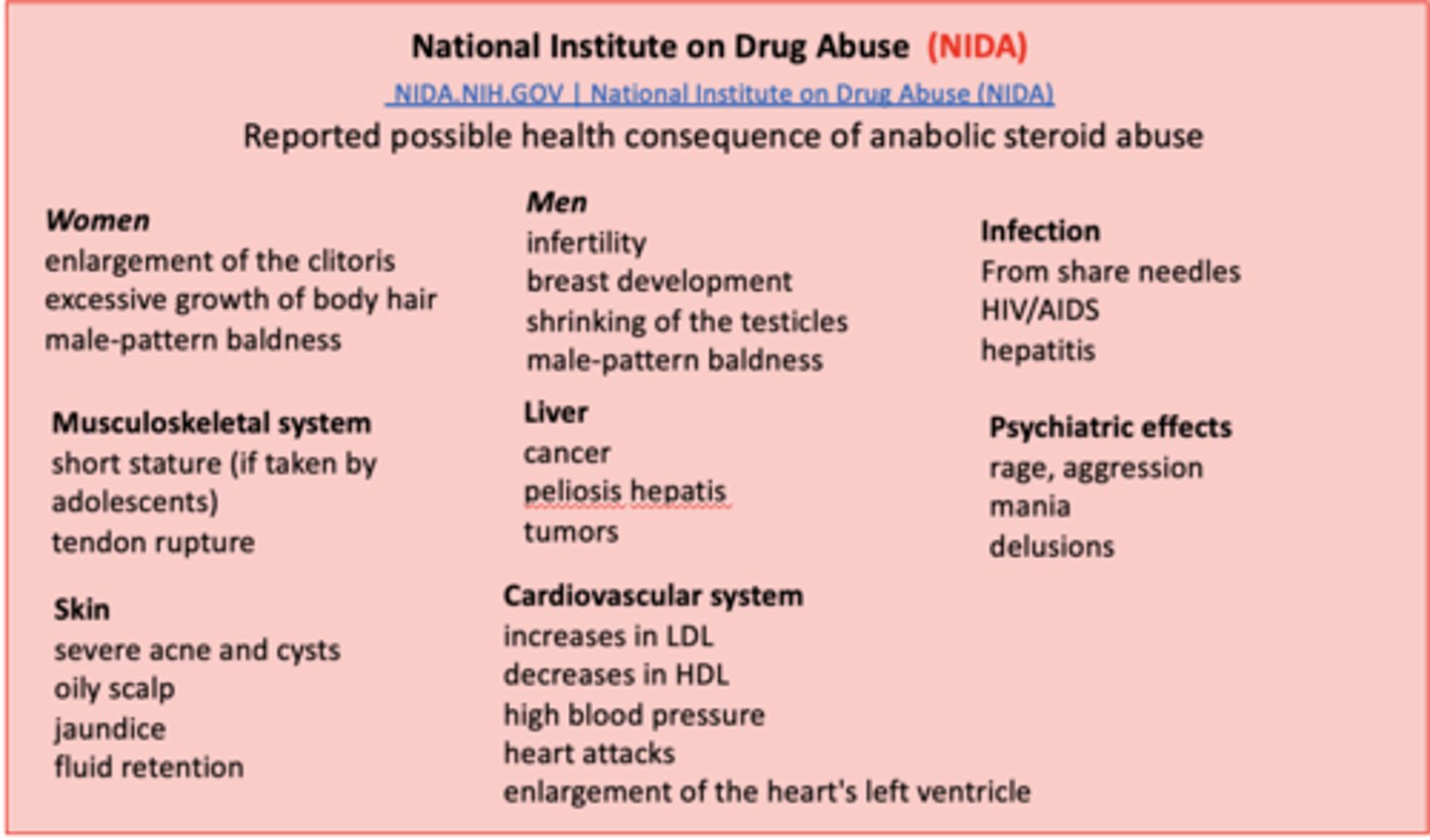
National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)
Steroid abuse disrupts the normal production of hormones in the body, causing both reversible and irreversible changes.
Anabolic steroid abuse has been associated with a wide range of adverse side effect
male estrogens
17 b-estradiol (estradiol)
Produced by the Leydig cells and in adipose tissues
Growth spurt, skeletal maturation, epiphyseal plate closure, maturation of sperm
female estrogens
17 b-estradiol (estradiol)
principal estrogen premenopausal
Estrone
primary circulating estrogen post menopause
Estriol
Principal estrogen produced by the placenta
Development of female sex organs and secondary sex characteristics, regulate menstrual cycle, skeletal maturation, mood, neuroprotection
Therapeutic Uses of Estrogens
Postmenopausal Hormonal Therapy
Oral Contraceptives
Primary Hypogonadism
Suppress ovulation in patients with intractable dysmenorrhea or hirsutism
Fertility Treatments
Gender Transition
review
review
ethinyl estradiol, agonist at the estrogen receptor
(Progestin – medroxyprogestrone) - Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
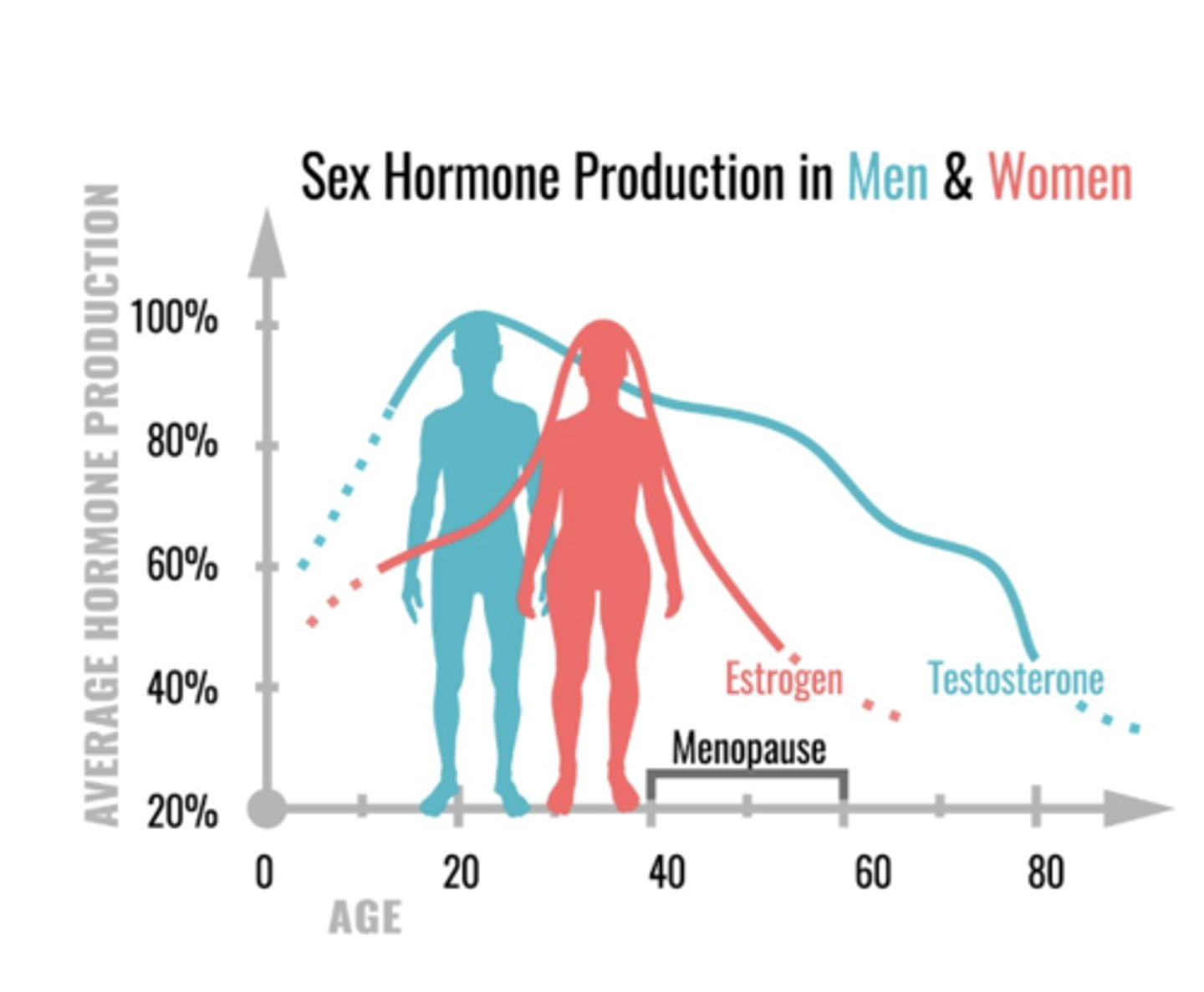
Usually occurs in late 40s, early 50s
Estrogen and progesterone levels decline
Since estrogen plays other roles within the body, other systems are affected
symptoms of menopause:
-Hot flashes
-Changing sleep patterns
-Emotional changes (mood swings)
-Headaches
-Heart Palpitations
-Generalized Itching
Therapeutic Estrogens
Side effects :
Nausea, fluid retention, breakthrough bleeding, change in menstrual flow, breast tenderness.
Adverse Effects:
Thrombolytic complications; endometrial carcinoma; breast carcinoma; and hypertension.
In men feminization of genitalia & impotence.
contraindications:
Pregnancy, incomplete bone growth, undiagnosed genital bleeding; stroke, thrombophlebitis, or thromboembolic disease, heart disease.
Women with family history of breast or uterine cancer (BRCA gene)
Drug Interactions:
decrease efficacy of hypoglycemic agents
increase adverse effects of tricyclic antidepressants
herbal supplement - St. John's wort may cause loss of contraceptive or hormonal-replacement efficacy of estrogens
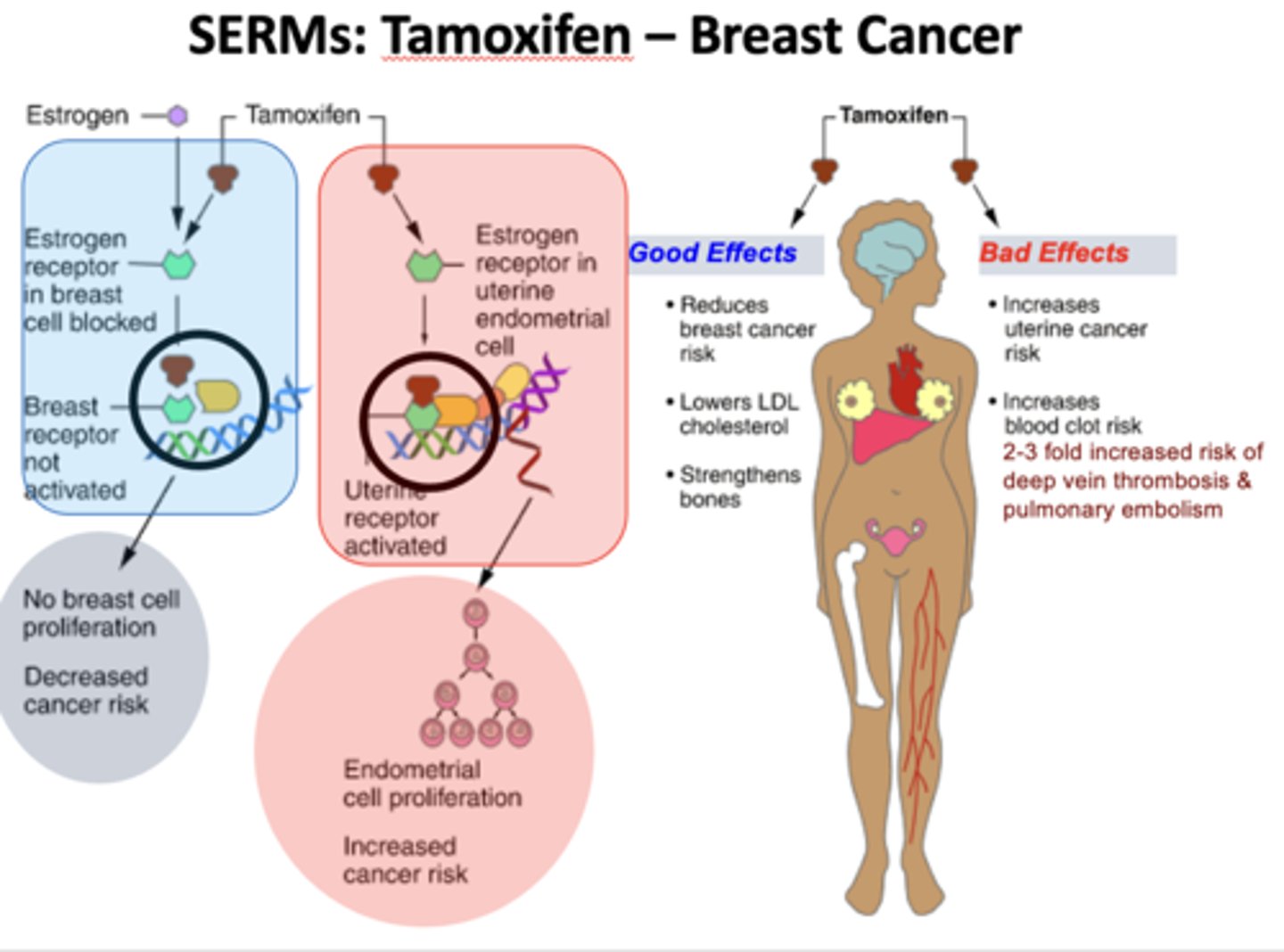
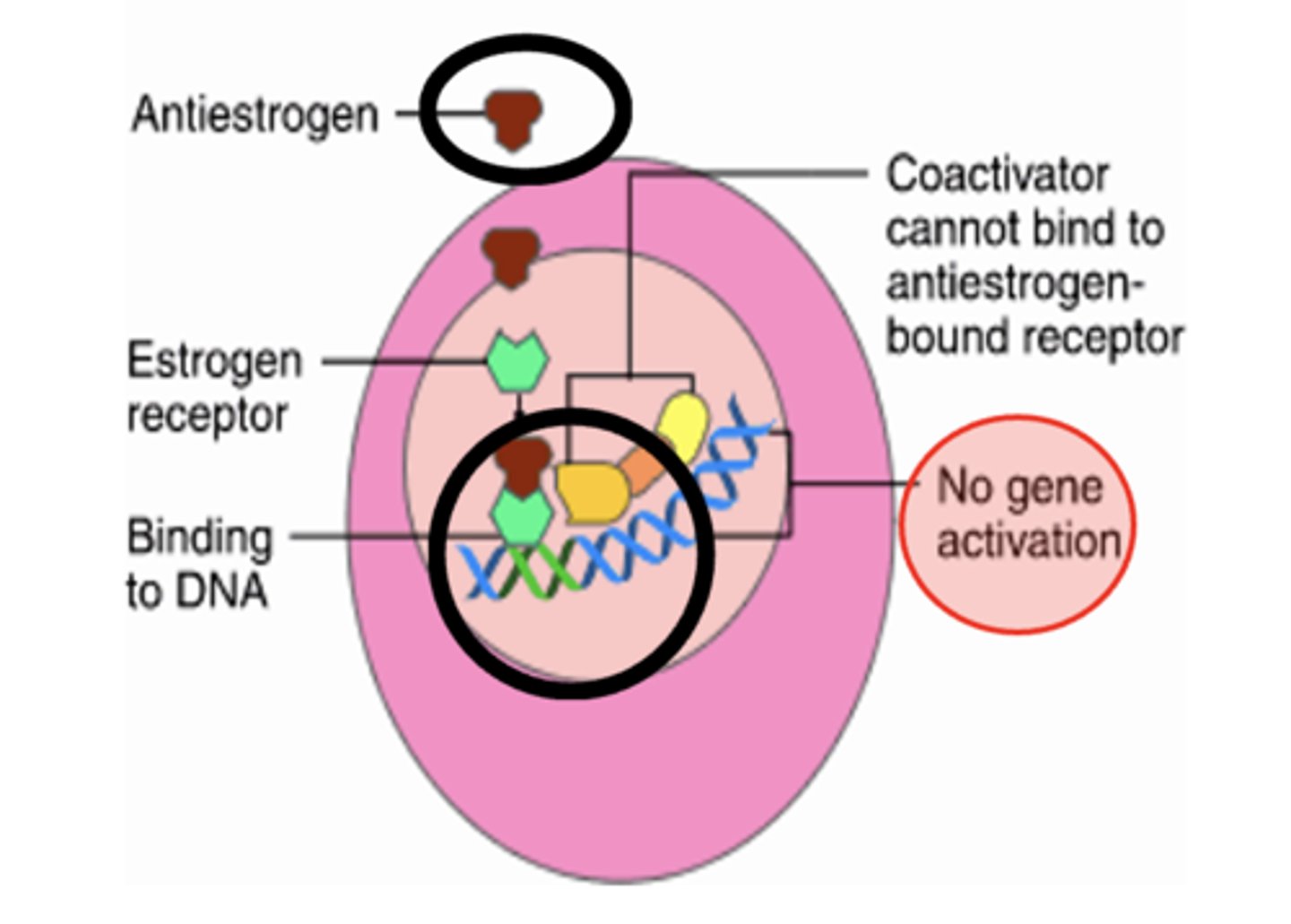
SERMs - Selective Estrogen-Receptor Modulators
display selective agonism or antagonism according to different tissues
Selectivity is possible because:
-- Estrogen receptors (ER), ER-a and ER-b show differential tissue expression
-- Tissue dependent responses ranging between pro-estrogenic, partially estrogenic and anti-estrogenic effects
Therapeutic Uses:
- Cancer Chemotherapy
- Prevent and treat osteoporosis
- Fertility
Selectivity is possible because:
- Estrogen receptors (ER), ER-a and ER-b show differential tissue expression
- Tissue dependent responses ranging between pro-estrogenic, partially estrogenic and anti-estrogenic effects
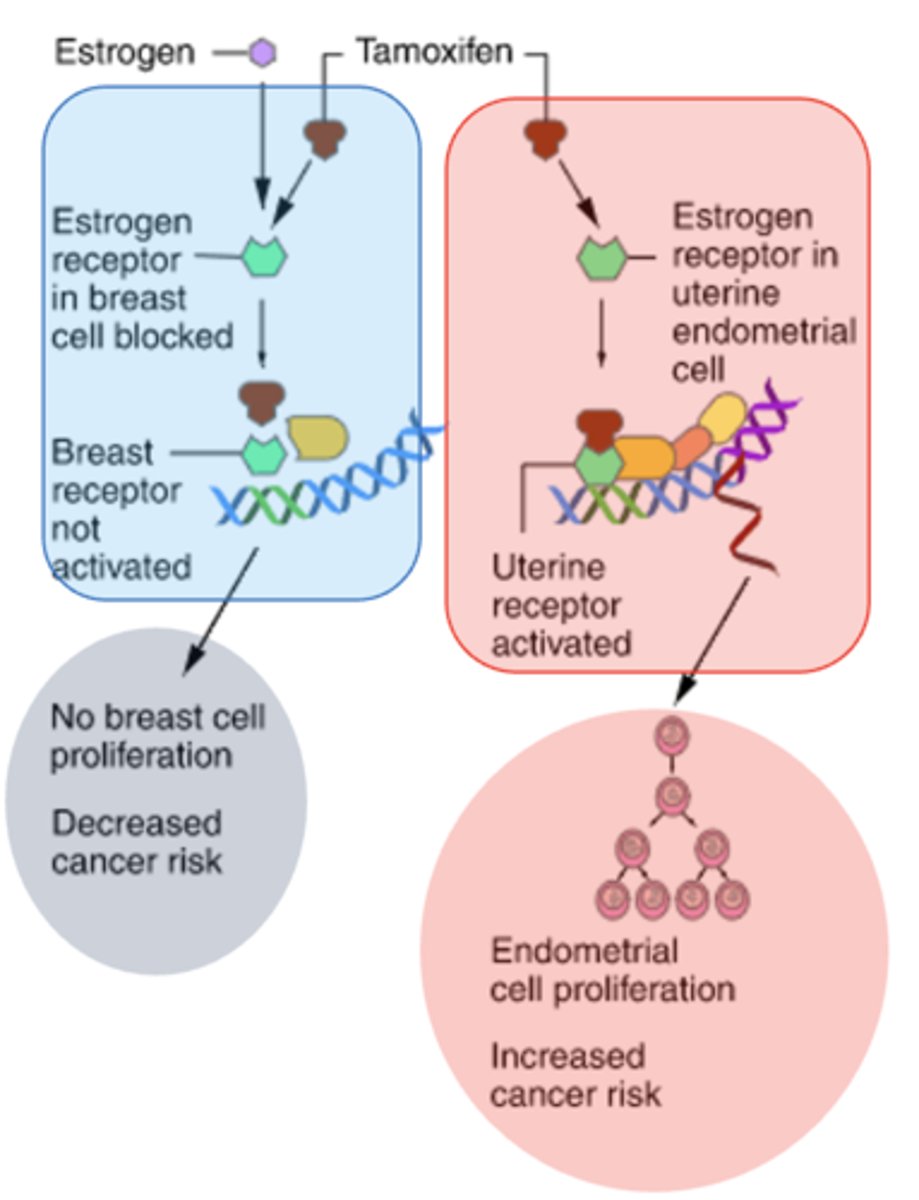
tamoxifen - SERMs Selective Estrogen-Receptor Modulators
display selective agonism or antagonism according to different tissues
Cancer Chemotherapy
clomiphene also clomifene – SERMs Selective Estrogen-Receptor Modulators
Fertility induction of ovulation in women with an intact hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis
-- Oppose the negative feedback effects of endogenous estrogen. Increases GnRH and therefore increases the amplitude of the LH and FSH pulses.
Adverse effects: multiple births, ovarian cysts
Used off-label by men to treat both male infertility and secondary hypogonadism because it increases serum testosterone levels.
Abused by health athletes for performance enhancement
second gen - not in red
second gen - not in red

bazedoxifene (Duavee): - third generation
Approved in 2013, marketed in 2014 as a combination therapy with estradiol for the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis.
First modern HRT therapy without a progestin for postmenopausal women with an intact uterus – reduced risk of breast tenderness compared to traditional HRT.
fulvestrant - Anti-Estrogens
ICI 182,870 (FASLODEX)
- pure estrogen antagonist
- effective in treating tamoxifen-resistant tumors
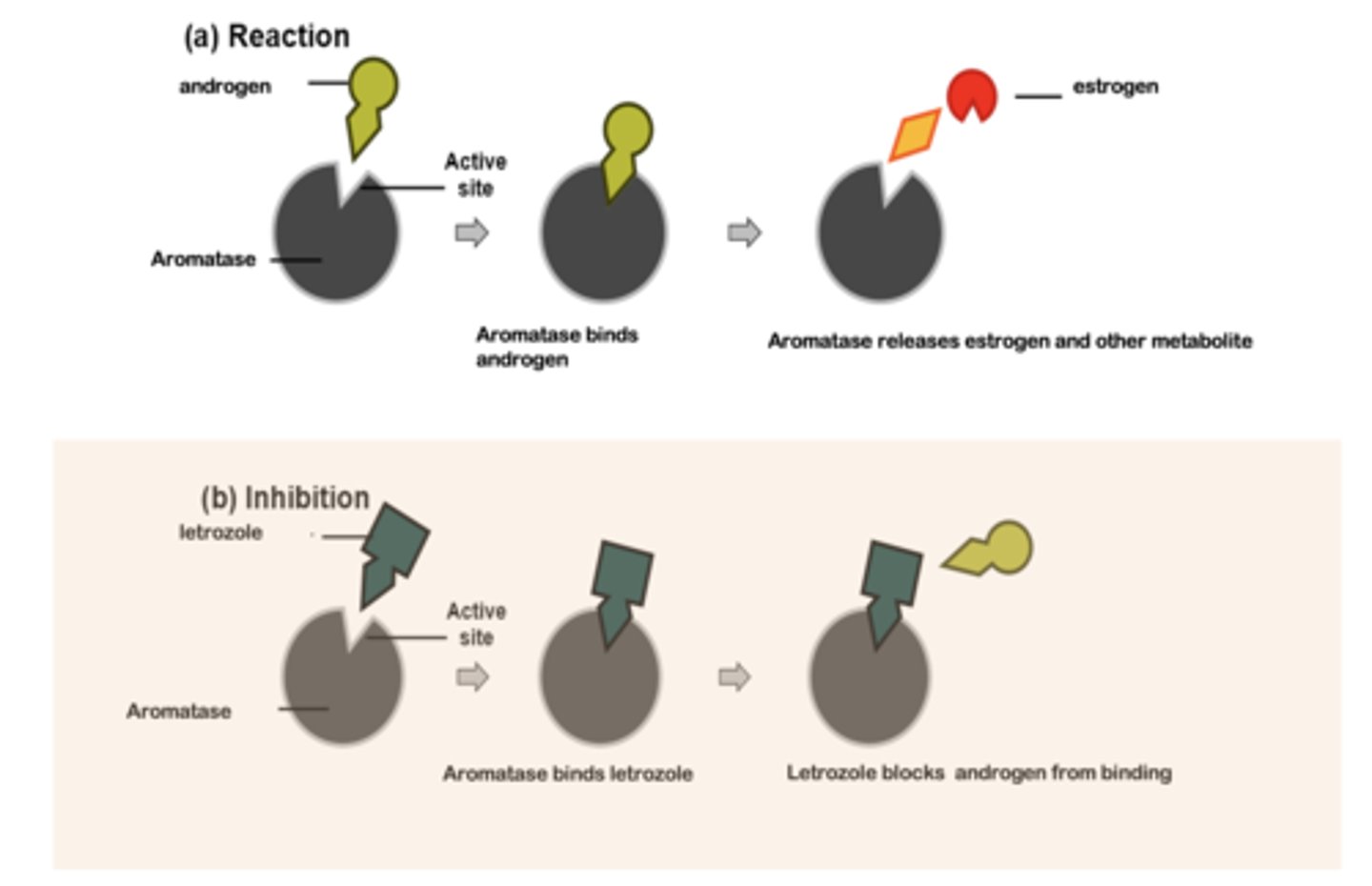
letrozole (Femara) - Estrogen Synthesis Inhibitors
aromatase inhibitor
anastrozole (Arimidex)
Specifically block the local production of estrogens in hormonally-responsive tissues.
Uses:
- Second-line treatment for breast cancer in patients whom tamoxifen therapy is unsuccessful, but new studies rapidly proving its efficacy and promoting earlier use
- Aromatase inhibitors do not have the bone protecting activity of tamoxifen, and adjuvant therapies to prevent bone loss are in trials
letrozole
moa of ...
male progesterone
Produced in response to LH
Secreted by the testes and adrenal gland
female progesterone
Produced in response to LH
Secreted by the corpus luteum, placenta and adrenal gland
birth control - progestins
Make it difficult for sperm to reach egg by thicken cervical mucus and thin the uterine lining
Prevent ovulation, but not consistently
Prevent the egg from fully developing
Make it harder for a fertilized egg to attach to the uterine lining
Menstrual Cycles - progestins
Regulate menstrual cycles (start and stop menstrual cycle, amenorrhea)
other conditions - progestins
Help maintain pregnancies (during low progesterone production)
Counteracts estrogen effect on thickening of the uterine lining during HRT
Treat pain related to endometriosis
Stimulate appetite in AIDS or cancer patients DS or cancer
Progestins – Therapeutic Progesterone
Naturally occurring progesterone (low oral bioavailability
Synthetic progestins
19-nor testosterone derivatives display primarily progestational rather than androgenic activity
Estrane family – first generation
norethindrone; norethindrone acetate
Gonane family - second and third generation
replacement of the 13-methyl group of norethindrone with a 13-ethyl substituent are more potent progestins and less androgenic: norgestrel, levonorgestrel, drospirenone (antiandrogenic, anti-mineralocorticoid)
Uses: HRT - Formulations
Early HRT used estrogen alone: increased risk of uterine (endometrial) cancer. As a result, addition of progestin is now used to limit endometrial hyperplasia, medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) is most used.
Various regimens are used: estrogen for 25 days with inclusion of MPA during last 10-13 days of estrogen, 5-6 days with no hormones
-- Combos of estrogens with progestins:
FEM HRT (estradiol plus norethindrone acetate)
ORTH PREFEST (estradiol plus norgestimate)
Route of administration
Vaginal creams (PREMARIN) or a ring device (ESTRING) can be used instead of oral doses . Reduces vaginal dryness, yeast infections and urinary tract infections.
CombiPatch (estradiol/norethindrone acetate) twice weekly transdermal patch Alcohol free, lasts 3.5 days
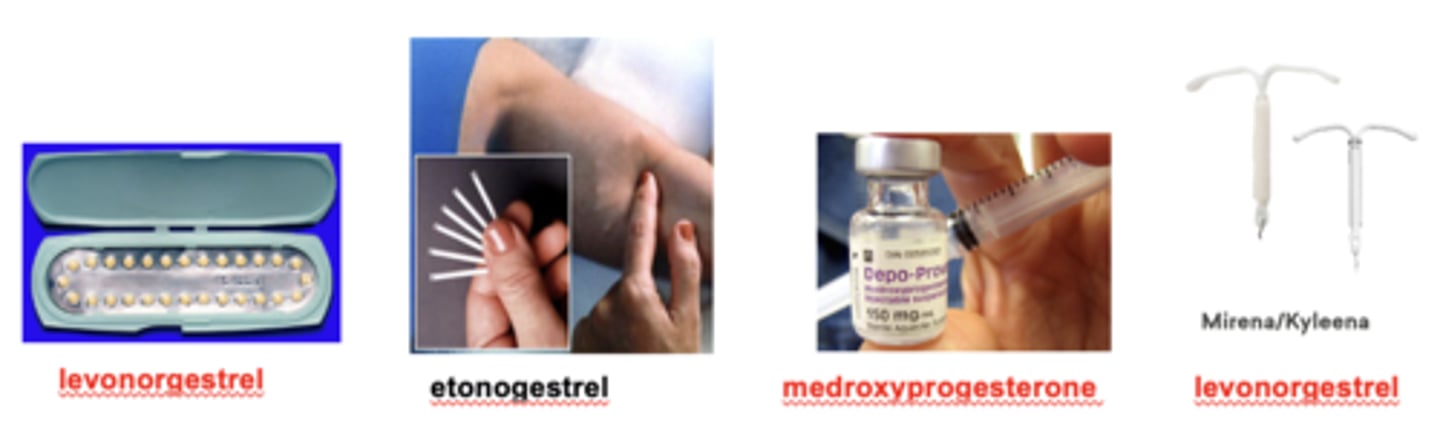
Progestin Only Contraceptive - Contraception Administration
Oral formulations of norethindrone (Micronor) or levonorgestrel (Ovrette) taken daily
Subdermal implants of etonogestrel (Nexplanon) for slow-release and long-term contraceptive actions (up to four years)
IM injections of medroxyprogesterone (Depo-provera) that provides effective contraception for 3 months
Intrauterine device (IUD) that releases low amounts of progesterone locally (Mirena lasts up to 8 years).
Other Beneficial Effects of
Oral Contraceptives
1. Decreases Dysmenorrhea
2. Decreases benign breast and ovarian cysts
3. Regulates cycle in anovulatory women
4. Decreased blood loss during menstruation
5. Reduction in ovarian and endometrial cancer
Estrogens: ethinyl estradiol
Absorbed efficiently in GI tract. Mestranol is biologically inactive and must be metabolized to ethinyl estradiol. Peak plasma levels within 1 hr after oral administration
Progestins: 19-NOR Steroids
Removal of 19-carbon changed major hormonal effect from an androgen to progestin while maintaining oral activity.
Estranes
have some androgenic activity as well as estrogenic/anti-estrogenic actions. Rapidly absorbed (norethindrone)
Gonanes
More potent than estranes and less androgenic activity and are now used in the 3rd generation combination oral contraceptives (norgestrel, norgestimate, levonorgestrel, drospirenone)
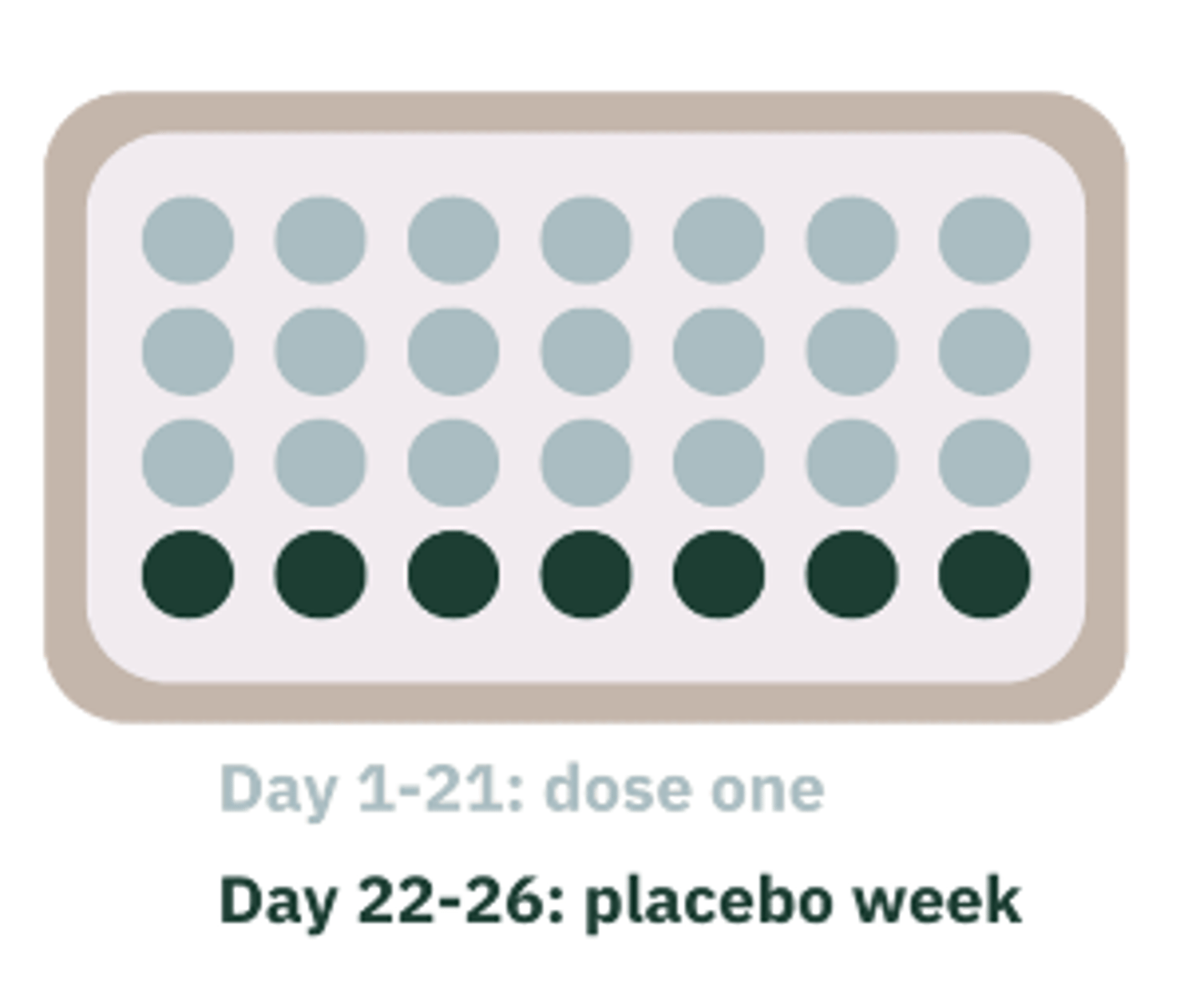
Monophasic
Fixed concentrations of estrogen and progestin, which is taken for 21 days followed by 7 days of "hormone-free" pills.
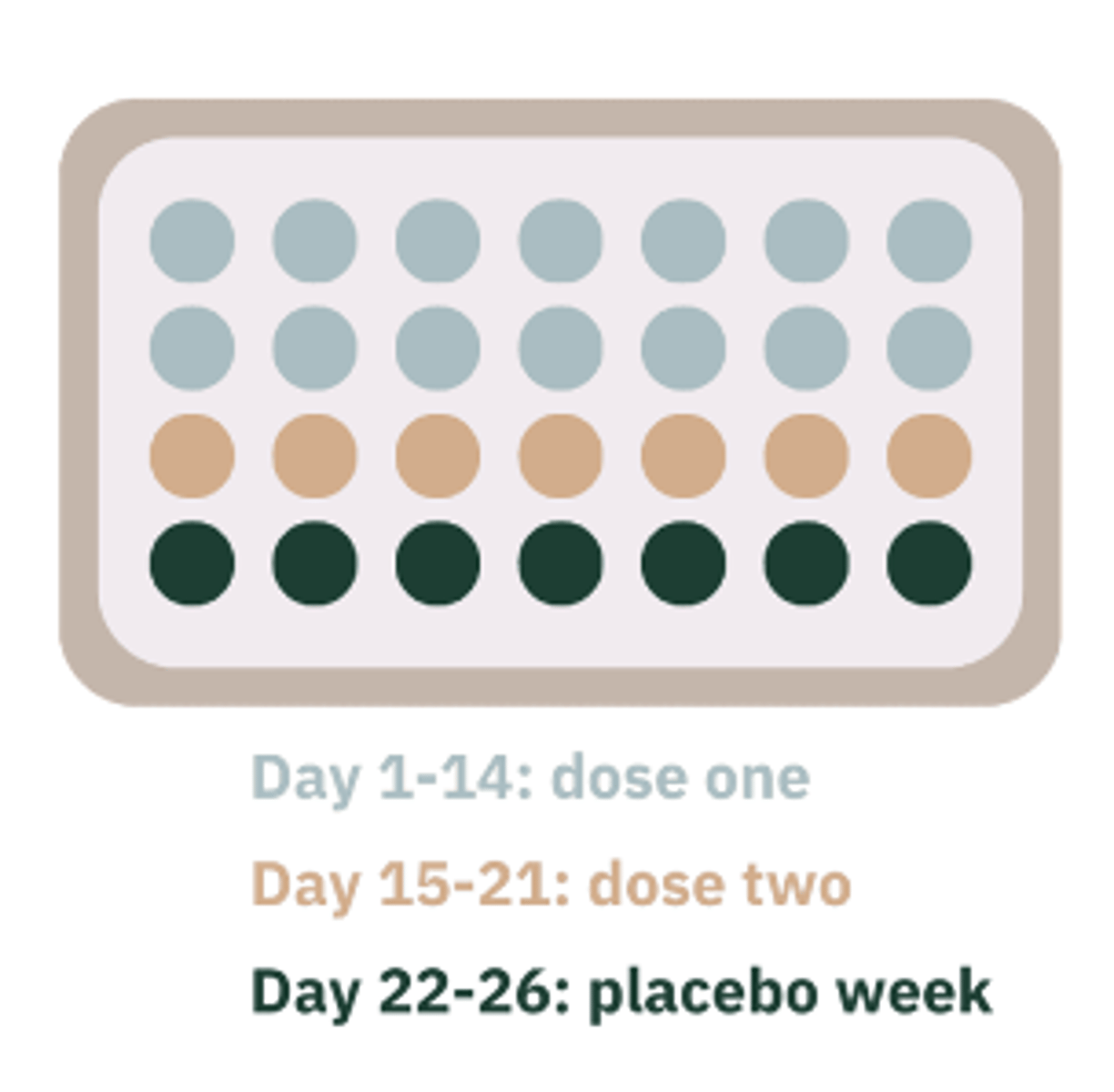
Biphasic
Fixed concentration of estrogen with 2 different concentration of progestin. Lower concentration in the first 1-14 days and then higher concentration for the next 15 – 21 days. followed by 7 days of “hormone-free” pills.
Triphasic
Fixed concentration of estrogen with 3 different concentrations of progestin. Lower concentration in the first 1-6 days and then higher concentration for the next 7-11 days. Then highest dose 12-21 days followed by 7 days of "hormone-free" pills.
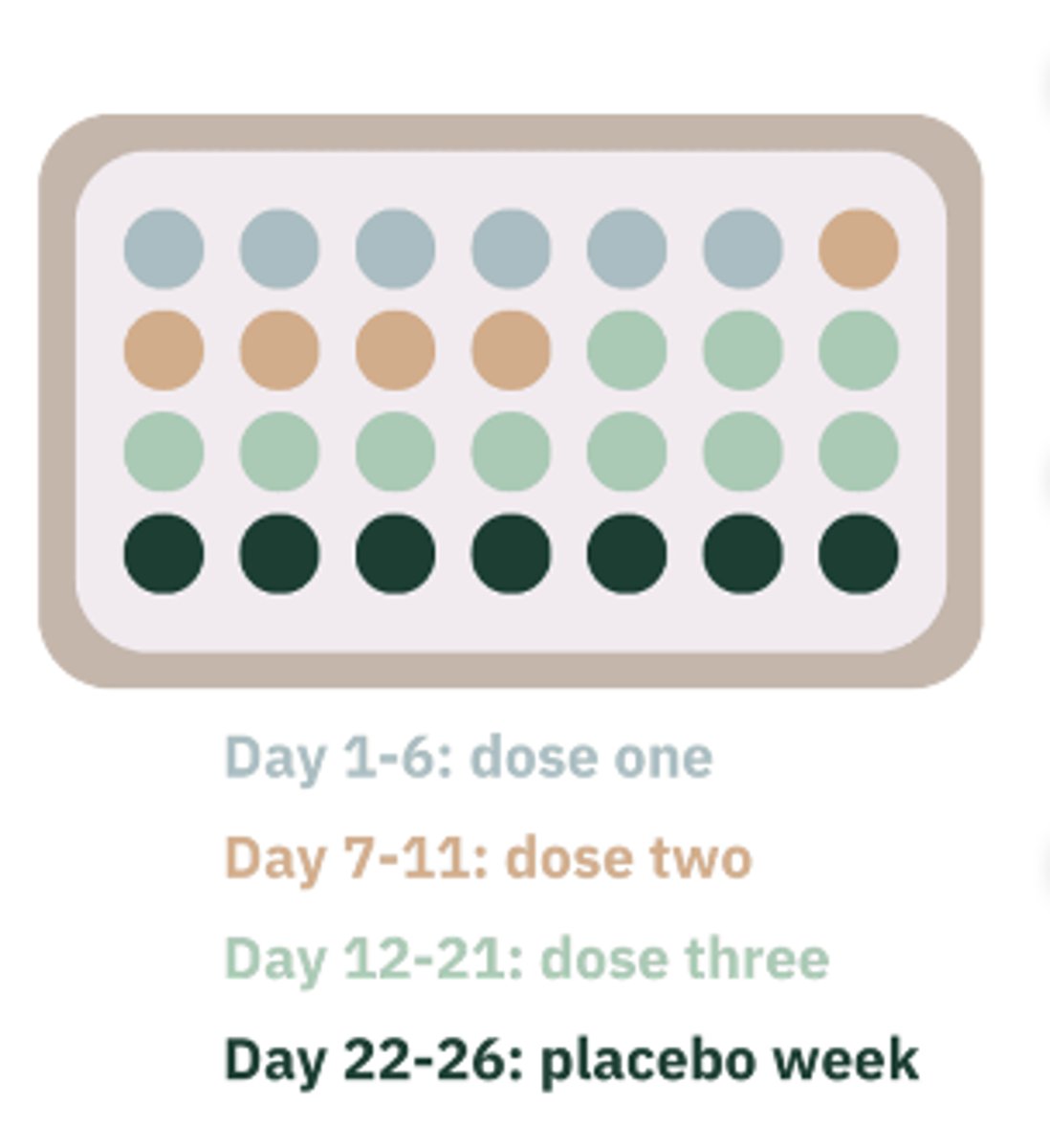
levonorgestrel / ethinyl estradiol - Extended-cycle Birth Control Pill 84/7 formulation
0.15 mg / 0.03 mg
And either placebo or ethinyl estradiol tablets 0.01 mg tablets)
Brand Names: Jolessa, Quasense, Seasonale, Seasonique
Advantages
-- Period once every 3 months
-- Period last about 3 days with decreased bleeding
Side Effects:
-- Breakthrough bleeding and spotting
Emergency Contraceptives
Drugs used for the prevention of pregnancy following unprotected intercourse or a known or suspected contraceptive failure. Emergency contraception prevents pregnancy by delaying or inhibiting ovulation, or release of an egg:
Louisiana HOUSE BILL NO. 1061 - HEALTH/WOMEN'S: Provides for procedures for victims of sexually-oriented criminal offenses. Every state has its own regulations
Emergency hormone contraceptive regimens are highly effective and decrease the risk of pregnancy by 75 percent
To be effective these must be taken within 72 hours of intercourse no more than 120 hours (5 days)
May also inhibit ovulation or fertilization depending on timing of administration Alteration of the endometrium, sperm penetration, and tubal motility are also affected. ESTABLISHED PREGNANCIES ARE NOT HARMED
Two products are available:
Plan B: 0.75 mg levonorgestrel
Preven: 0.25 mg
levonorgestrel and 0.05 mg ethinyl estradiol (this product includes a pregnancy test kit)
Anti-seizure medications
St. John’s wort
Anti-tuberculosis drugs such as rifampin
HIV protease inhibitors
Drugs that disrupt liver metabolism and increase estrogen metabolism in oral contraceptives:
Oral contraceptives effect the activity of other drugs
anticoagulants - increases effectiveness
benzodiazepines - inhibit metabolism in some benzodiazepines
beta-blockers - inhibit metabolism in some benzodiazepines
corticosteroids
tricyclic antidepressants - increase levels in the blood; therefore, higher risk of toxicity and side effects
ABSOLUTE Effects: Contraindications for contraceptives with estrogen
History of thromboembolism, stroke
Impaired liver function
Known or suspected breast cancer
Undiagnosed abnormal vaginal bleeding
Known or suspected pregnancy
Smokers over age 35 (may use progestin-only)
RELATIVE Effects: Contraindications for contraceptives with estrogen
Migraine headaches
Hypertension - ok if <35, or healthy, or BP controlled
Elective surgery: Discontinue 4wks. prior to major surgery
Gallstones/ Cholecystitis
Epilepsy: anti-seizure meds may decrease effectiveness of OCP's
Diabetes: small risk or worsening vascular disease
The Menstrual Cycle | 3D Animation (2/2)
The Menstrual Cycle | 3D Animation (2/2)
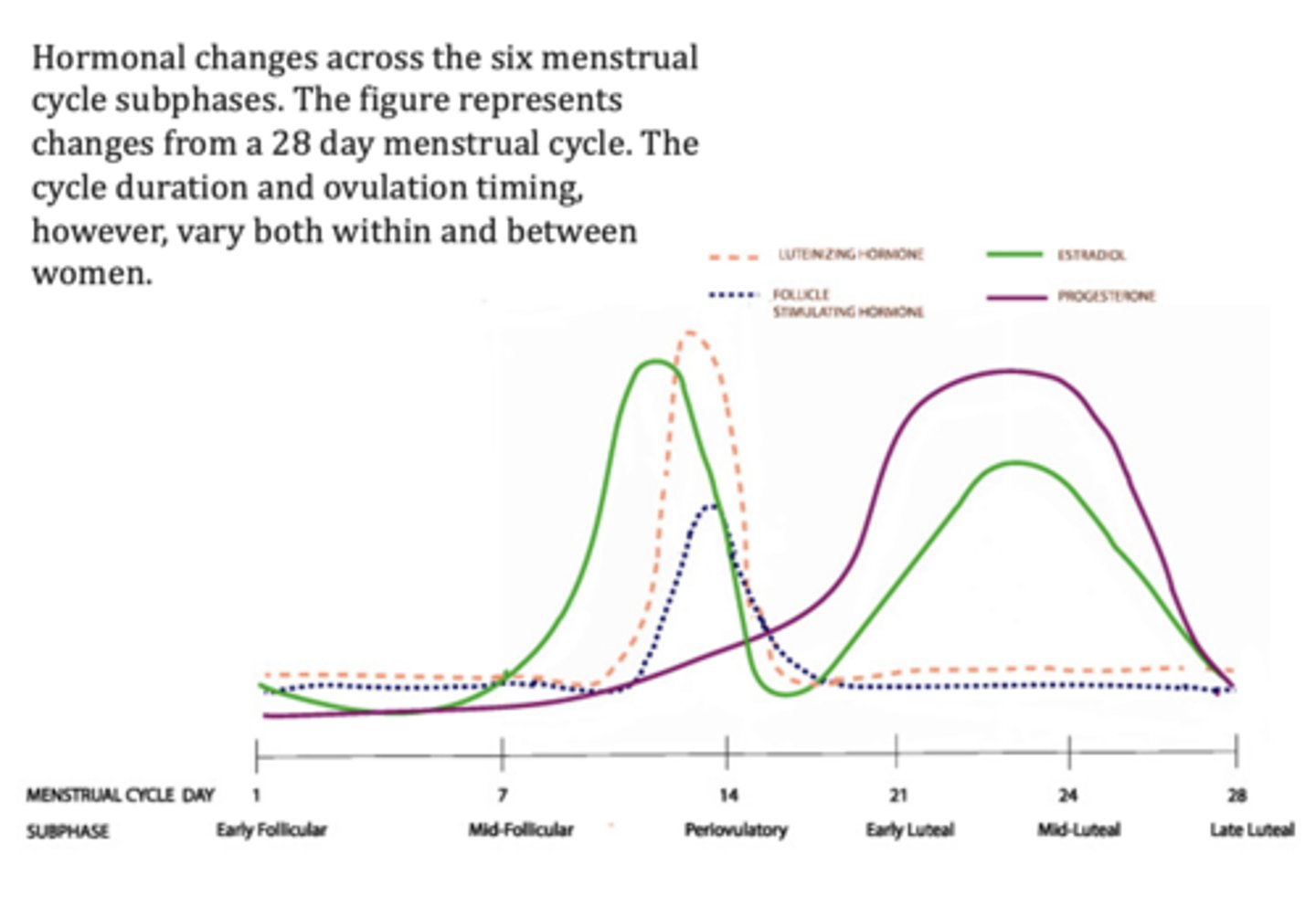
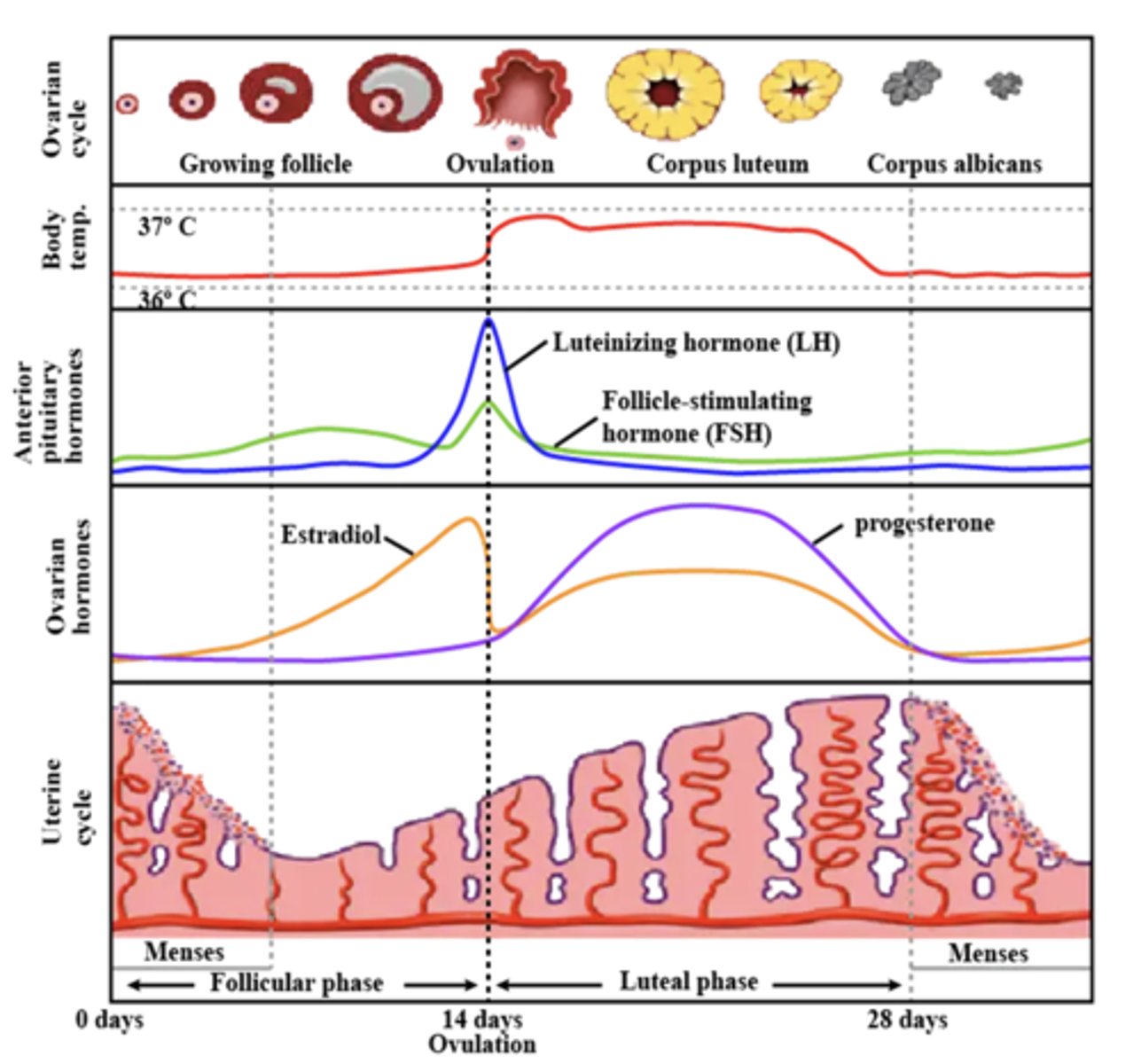
Hormonal changes
across the six menstrual cycle subphases. The figure represents changes from a 28 day menstrual cycle. The cycle duration and ovulation timing, however, vary both within and between women.