Money and Banking Chapters 5,7,11 and 12
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
1
New cards
Risk
A measure of uncertainty about the future payoff to an investment, assessed over some time horizon and relative to a benchmark.
2
New cards
How do we use risk to measure
We can compare two investments, see which one is riskier and by how much
3
New cards
How does risk arise?
Uncertainty about the future
4
New cards
real interest rate
nominal interest rate minus expected inflation
5
New cards
Probability theory
considering any uncertainty, we must list all the possible outcomes and then figure out the chance of each one occurring
6
New cards
How do we express a probability?
A number between 0-1. 1 being certain and 0 being definitely will not happen. All probable outcomes must add up to 1.
7
New cards
Expected Value
Expected Value = Sum of (Probability x Payoff)
8
New cards
You purchase a stock for $1000. It is equally likely to fall to $700 as it is to increase to $1400, so what is the expected value?
700 x 0.5 = 350
1400 x 0.5 = 700
Expected value = $1050
1400 x 0.5 = 700
Expected value = $1050
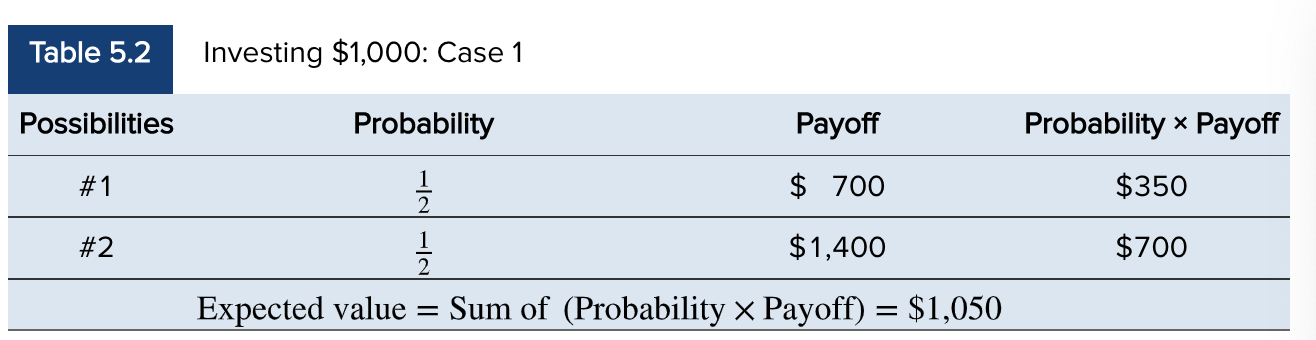
9
New cards
What is the flaw in that case?
The payoff will not be 1050. Since it is only being done once, it will be wither 700 or 1400.
10
New cards
What is average payoff?
When an investment is made multiple times so the expected value payoff is actualized.
11
New cards
What is the expected return?
The expected value - investment value.
$1050-$1000 = $50
Written as a percent, so 5%
$1050-$1000 = $50
Written as a percent, so 5%
12
New cards
Risk-free asset
An investment whose future value is known with certainty and whose return is the risk free rate of return.
13
New cards
Examples of measuring risk by quantifying the spread among an investment's possible outcomes.
Standard deviation- Measure of spread
Value at risk - a measure of the riskiness of the worst case
Value at risk - a measure of the riskiness of the worst case
14
New cards
risk premium
the expected return minus the risk-free rate of return; the payment to the buyer of an asset for taking on risk
15
New cards
idiosyncratic risks
risks unique to a select few
16
New cards
systematic risks
economywide risks that affect everyone
17
New cards
Two kinds of idiosyncratic risk
Ones that only affect certain people,
One that affect certain industries, like oil on cars
One that affect certain industries, like oil on cars
18
New cards
Two methods of diversification
Spread assets along many investments
Hedging
Hedging
19
New cards
Hedging
Reducing idiosyncratic risk by making two investments with opposing risks.
20
New cards
Interest rate spreads
The simultaneous increase in some interest rates and decline in others.
The difference between the interest rate a bank receives on its assets and the interest rate it pays to obtain liabilities.
The difference between the interest rate a bank receives on its assets and the interest rate it pays to obtain liabilities.
21
New cards
Two bond rating firms
Moodys
Standard and Poors
Standard and Poors
22
New cards
What are the label of bonds with an investment grade rating?
AAA, AA, A, BBB (BAA for Moodys) Examples are J&J, JPM Chase, Google
23
New cards
What are the label of noninvestment, speculative grade bonds?
BB, B
Ex. Brazil, Greece, Kenya
Many firms may not be allowed to invest in these
Ex. Brazil, Greece, Kenya
Many firms may not be allowed to invest in these
24
New cards
What are the label of highly speculative grade bonds?
CCC, CC, C, D
Ex. Venezuela
Ex. Venezuela
25
New cards
What percent of bonds have a ratings upgrade or downgrade yearly?
2-3% upgrade
2-3% downgrade
2-3% downgrade
26
New cards
Commercial paper
Short-term, privately issued zero-coupon debt that is low risk and very liquid and usually has a maturity of less than 270 days.
27
New cards
Who holds one third of all commerical paper?
Money-market mutual funds.
28
New cards
prime grade commercial paper
commercial paper with a low risk of default
29
New cards
benchmark bond
A low-risk bond, usually a U.S. Treasury bond, to which the yield on a risky bond is compared to assess its risk.
30
New cards
Spread over treasuries (risk spread)
The difference between the yield on a bond and that on a U.S. Treasury with the same time to maturity; a measure of the riskiness of the bond.
31
New cards
risk spread
The yield over and above that on a low-risk bond such as a U.S. Treasury with the same time to maturity, it is a measure of the compensation investors require for the risk they are bearing. Also called a default risk premium
32
New cards
Bond yield =
Bond yield = U.S Treasury yield +default-risk premium
33
New cards
When treasury yields move...
All yields move with them
34
New cards
The yield on a U.S treasury bond will be lower or higher than that of a Moodys AAA yield?
Lower, Treasury bonds are consistently the lowest
35
New cards
Are the yields higher on a Moodys AAA bond or a BAA bond?
BAA, risk requires compensation
36
New cards
Default risk is one factor that affects the return on a bond, what is another imporant one?
Taxes. Bondholders must pay income tax on the interest income they receive.
37
New cards
Taxable bond
A bond whose coupon payments are not exempt from income tax.
38
New cards
Municipal bonds
Also called tax-exempt bonds.
Bonds issued by state and local governments to finance public projects; the coupon payments are exempt from federal and state income taxes.
Bonds issued by state and local governments to finance public projects; the coupon payments are exempt from federal and state income taxes.
39
New cards
How do you calculate after tax yield?
Add the coupon yield, to face value, and subtract taxes.
The yield will reflect the difference in the final payment and how much you were taxed.
(100 face value, plus 6 dollar coupon)
30% taxation
6/.3 =1.8
106-1.8=4.2
4.2% yield
6% coupon rate
The yield will reflect the difference in the final payment and how much you were taxed.
(100 face value, plus 6 dollar coupon)
30% taxation
6/.3 =1.8
106-1.8=4.2
4.2% yield
6% coupon rate
40
New cards
Tax-exempt bond yield =
Tax-exempt bond yield = (taxable bond yield) x 1(-tax rate)
41
New cards
term structure of interest rates
The relationship among bonds with the same risk characteristics but different maturities.
(Same tax status and default risk)
(Same tax status and default risk)
42
New cards
Yields on short term bonds are more or less volatile than yields on long term bonds?
More
43
New cards
Long term yields in comparison to short term yields are higher or lower
long term yields are higher than short term yields
44
New cards
expectations hypothesis of term structure
The proposition that long-term interest rates are the average of expected future short-term interest rates. (short+short+short=long)
45
New cards
what is the logic behind the expectations hypothesis?
when interest rates are expected to rise in the future, long-term interest rates will be high than short-term interest rates.
46
New cards
yield curve
A plot showing the yields to maturity of different bonds of the same riskiness against the time to maturity.
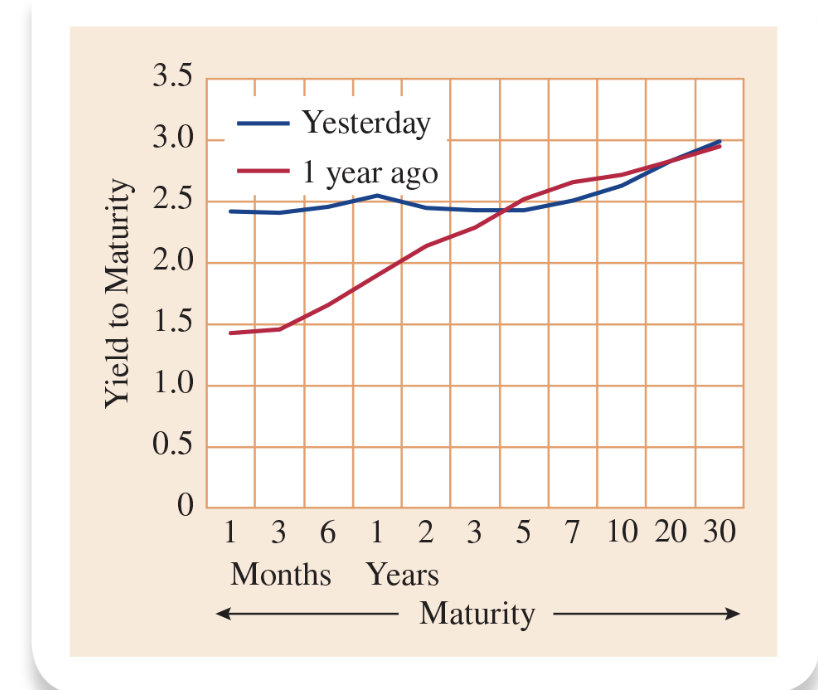
47
New cards
If interest rates are expected to rise in the future yield to maturity is expected to...
Is expected to slope up and rise
48
New cards
If interest rates are expected to remain unchanged in the future yield to maturity is expected to...
stay flat
49
New cards
If interest rates are expected to fall in the future yield to maturity is expected to...
slope down, ytm falls
50
New cards
How do you calculate the yield of a one year interest bond today
i(1t)
i=interest
t=time (today)
i=interest
t=time (today)
51
New cards
How do you calculate the yield of a one year interest bond one year from now?
ie (1t+1)
ie=EXPECTED interest
1t+1 is one year from now
ie=EXPECTED interest
1t+1 is one year from now
52
New cards
How do you calculate the yield of a one year interest bond two years from now?
ie (1t+2)
ie=EXPECTED interest
1t+2 is two years from now
ie=EXPECTED interest
1t+2 is two years from now
53
New cards
How can we calculate the value of three one year bonds in consecutive years? (expectations hypothesis)
i3t = i(1t) + ie(1t+1) + i (1t+2)/3
This essentially finds the average interest rate between the three,
This essentially finds the average interest rate between the three,
54
New cards
Expectations hypothesis format
the interest rate on a bond with n years to maturity is the average of n expected future one year interest rates.
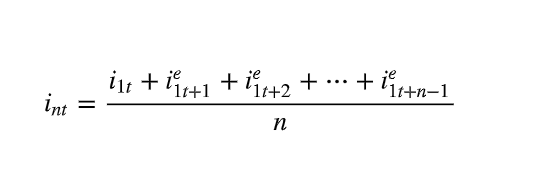
55
New cards
What can the expectations hypotheis explain and what can it not explain?
It can explain that interest rates of different maturities will move together
It can explain that yields on short term bonds are more volatile than yields on long term bonds
It cannot explain why long-term yields are higher than short term yields.
It can explain that yields on short term bonds are more volatile than yields on long term bonds
It cannot explain why long-term yields are higher than short term yields.
56
New cards
How does expectations hypothesis show that interest rates of different maturities will move together
If a current one year interest rate changes, both short term and long term bonds will move.
57
New cards
How does expectations theory explain that yields on short term bonds are more volatile than yields on long term bonds
Because long-term bonds are averages of a sequence of expected short-term rates.
58
New cards
Why cant expectations theory explain why long-term yields are higher than short-term yields.
Because the yield curve slopes up only when interest rates are expected to rise
59
New cards
Why are default free bonds risky
inflation and future interest rates
60
New cards
Why are long term bond interest rates higher than short term interest rates?
Because the risk is higher with inflation rates and future interest rates.
61
New cards
Liquidity premium theory of the term structure
The proposition that long-term interest rates equal the average of expected short-term interest rates plus a risk premium that rises with the time to maturity.
62
New cards
Liquidity premium theory long term bond yield equation
i(nt) = rp(n) + expectation hypothesis
rp=risk premium
n=amount of years
rp=risk premium
n=amount of years
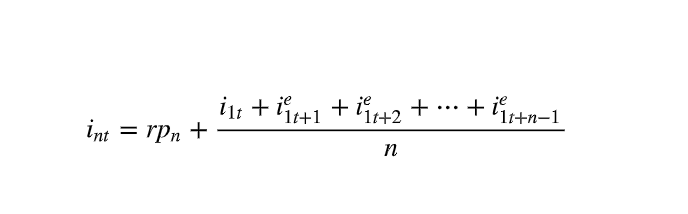
63
New cards
inverted yield curve
The rare occasion when short-term interest rates exceed long-term yields.
In this case the yield curve slopes downward as opposed to upwards.
In this case the yield curve slopes downward as opposed to upwards.
64
New cards
What does an inverted yield curve predict
a rise in interest rates and an economic downturn
65
New cards
term spread
The gap between yields to maturity on a long- and a short-term bond (usually free of default risk);
66
New cards
What is the relationship between term spread and GDP growth
When the term spread falls, GDP growth tends to fall somewhat later
67
New cards
When they do their job well, financial intermediaries
increase investment and economic growth at the same time that they reduce investment risk and economic volatility
68
New cards
two costs of lending and borrowing
transaction costs and information costs
financial institutions exist to reduce these costs
financial institutions exist to reduce these costs
69
New cards
Five functions of financial institutions as financial intermediaries
1- Pooling savings
2- Safekeeping and accounting
3-Providing liquidity
4- Diversifying risk
5- Collecting and processing information services
2- Safekeeping and accounting
3-Providing liquidity
4- Diversifying risk
5- Collecting and processing information services
70
New cards
comparative advantage leads to
specialization so that each of us ends up doing one job and being paid in some form of money
71
New cards
What do financial intermediaries take advantage of to reduce costs
economies of scale, where the price of a good or service falls as the quantity produced increases
(writing individual legal contracts would be costly)
(writing individual legal contracts would be costly)
72
New cards
information asymmetry
borrowers have information that lenders dont
73
New cards
Adverse Selection
The problem of distinguishing a good risk from a bad one before making a loan or providing insurance; it is caused by asymmetric information. (Seeing if they have good credit)
74
New cards
Moral hazard
The risk that a borrower or someone who is insured will behave in a way that is not in the interest of the lender or insurer; also caused by information asymmetry.
\
(Taking greater risk for greater reward)
\
(Taking greater risk for greater reward)
75
New cards
What is Akerlofs "Lemon" Theory
Two 2017 Honda Accords
One in bad shape for 8k, one in good shape for 20k
buyer doesnt know which is which
buyer will only pay average of 15k
This causes the expensive car to be taken off the market
Only the 8k "lemon" remains
outdated in the present
One in bad shape for 8k, one in good shape for 20k
buyer doesnt know which is which
buyer will only pay average of 15k
This causes the expensive car to be taken off the market
Only the 8k "lemon" remains
outdated in the present
76
New cards
How do you solve the hidden attributes problem
disclosure of information
77
New cards
Depository institution
A financial institution that accepts deposits and makes loans.
78
New cards
nondepository institution
A financial intermediary that does not issue deposit liabilities. (insurance is the biggest one)
79
New cards
what differentiates depository and nondepository institutions?
their primary source of funds, liability side of the balance sheet
80
New cards
A banks balance sheet says
Total bank assets = Total bank liabilities + Bank capital
81
New cards
3 types of cash assets
Reserves (Vault cas)
Cash items in process of collection
Cash items in process of collection
82
New cards
They hold it, they want liquidity
83
New cards
Four broad categories of assets
Cash, securities, loans, and all other assets
84
New cards
What percent of a banks holdings are securities
around 20%
85
New cards
What is the primary asset of banks?
Loans
86
New cards
Why did banks invest more in real estate before 2007-2009?
Mortgage Backed securities
87
New cards
Commercial banks make loans to
buisnesses
88
New cards
credit unions specialize in
consumer loans
89
New cards
Two types of deposit accounts
Transaction, and nontransaction
90
New cards
Nontransaction deposits
savings and time deposits.
Also knows as passbook savings accoiunts and Certificates of deposit.
Also knows as passbook savings accoiunts and Certificates of deposit.
91
New cards
liquidity risk
The risk that a financial institution’s liability holders will suddenly seek to cash in their claims; for a bank this is the risk that depositors will unexpectedly withdraw deposit balances.
92
New cards
interest rate risk
1. The risk that the interest rate will change, causing the price of a bond to change with it. (6) 2. The risk that changes in interest rates will affect a financial intermediary’s net worth. It arises from a mismatch in the maturity of assets and liabilities.