ARCH 4034 - Building Cities
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms

Washington, DC

Chandigarh, India

Canberra, Australia

Brasilia, Brazil
Who designed Brasilia
Costa and Niemeyer
Who designed DC
L’Enfant
Who designed Chandigarh
Le Corbusier
Who designed Canberra
Griffins
How do buildings generate meaning?
monumentality, denotation, metaphor

Chicago, USA

Shanghai, China

Bilbao, Spain

Maria Elena, Chile
Industrialization
process of economic and social change which shifts economic activity onto the focus of work, wages, and incomes

Shanghai, China

Shanghai, China

London, UK

Paris, France

Mumbai, India

Algiers, Algeria
Who designed Paris
Haussmann
Goals of Algiers plan
monumentality, embellishment, adjustment, hygiene

Berlin, Germany

Nairobi, Kenya (Kibera)
Beirut, Lebanon

Caracas, Venezuela
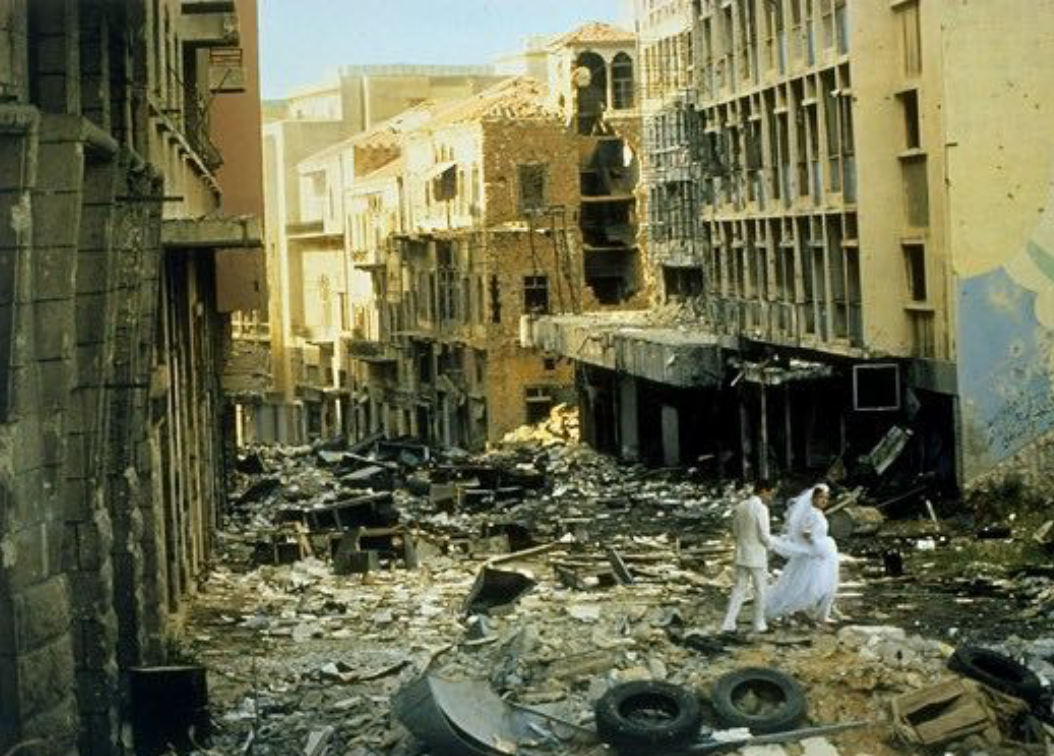

Beirut, Lebanon
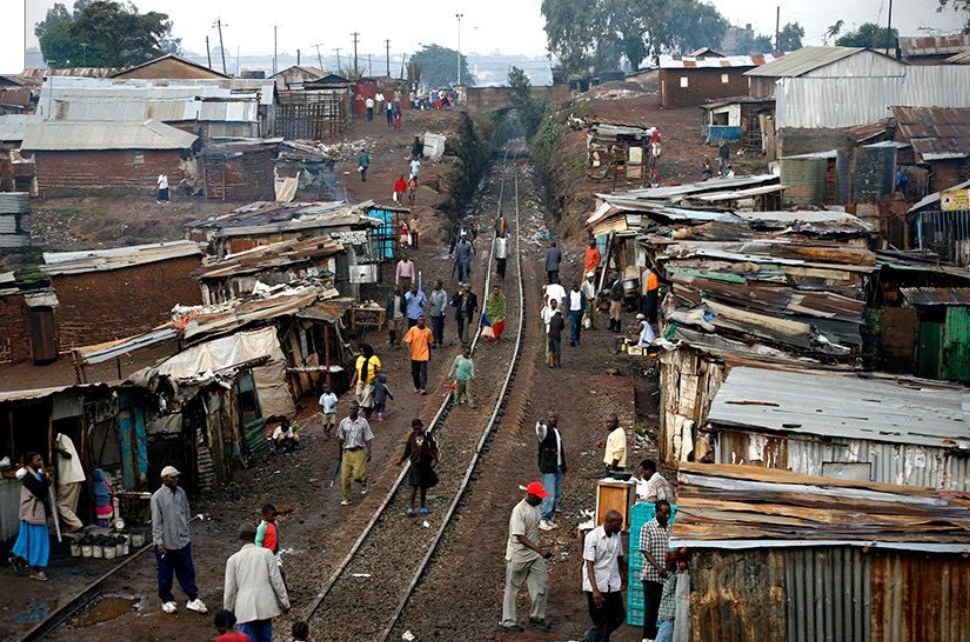

Nairobi, Kenya
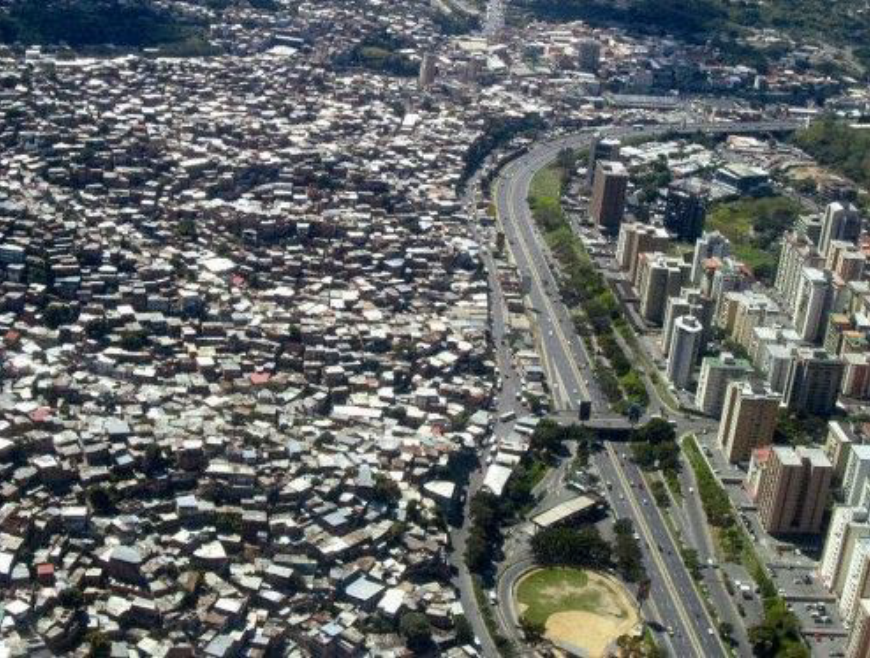

Caracas, Venezuela
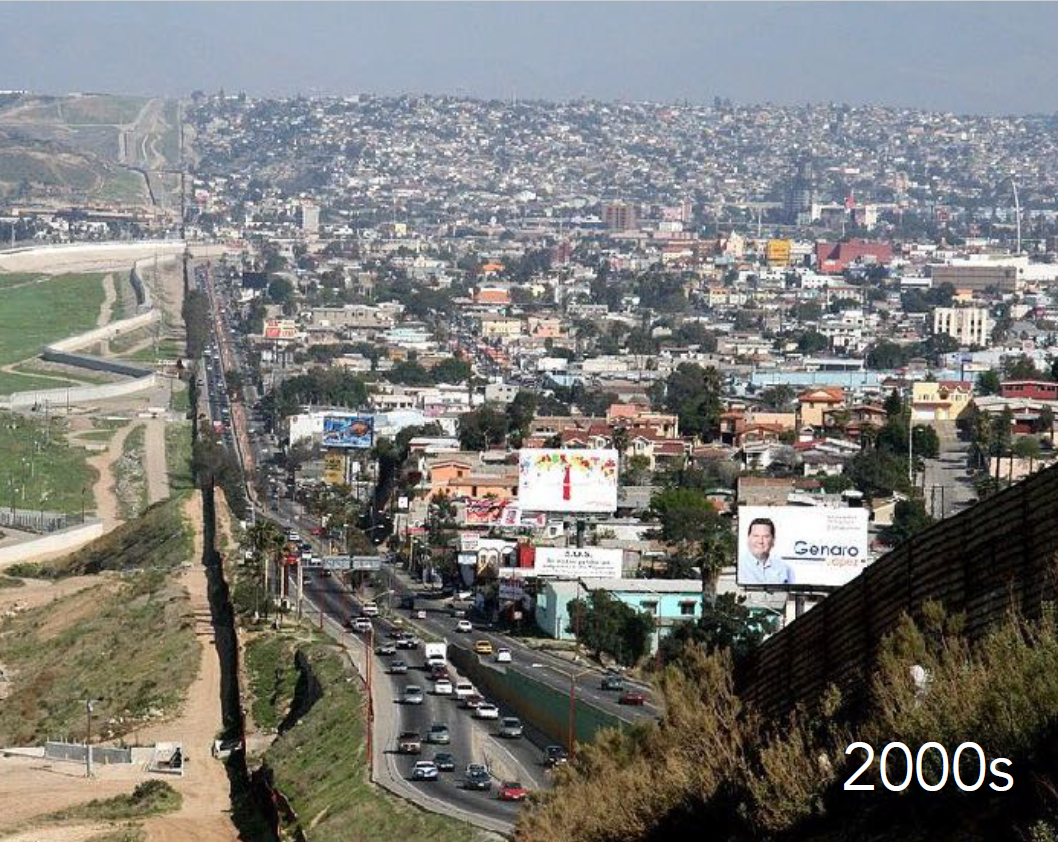

Tijuana, Mexico

Helsinki, Finland

Port au Prince, Haiti

Songdo, South Korea
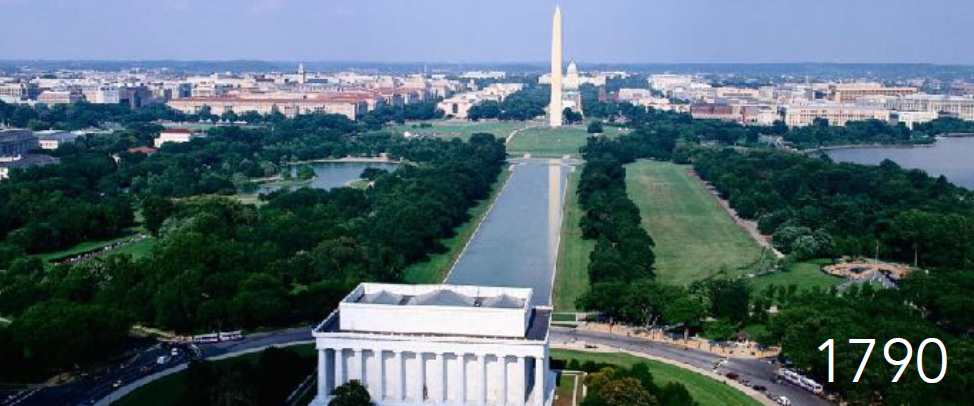
Landscape: Located on the Potomac River; flat and marshy terrain
Washington, DC
Physical Layout: Radial grid plan centered around the Capitol; grand diagonal avenues intersecting with a grid, creating public squares and vistas.
Washington, DC
History: Designed by Pierre L’Enfant in 1791 to embody Enlightenment ideals of order, symmetry, and grandeur; includes radial avenues, axial monuments, and neoclassical buildings
Washington, DC
Urban Planning Significance: Set a precedent for symbolic, non-commercial capital cities; influenced the design of Canberra and Brasília.
Washington, DC
History: Capital city - result of a design competition won by Walter and Marion Griffin in 1913; intended to balance nature and governance.
Canberra, Australia
Physical Layout: Radial geometric design with a central lake and axial alignments connecting civic zones; strong integration with landscape.
Canberra, Australia
Urban Planning Significance: Combines garden city movement principles with monumental civic design; reflects ideals of democratic governance.
Canberra, Australia
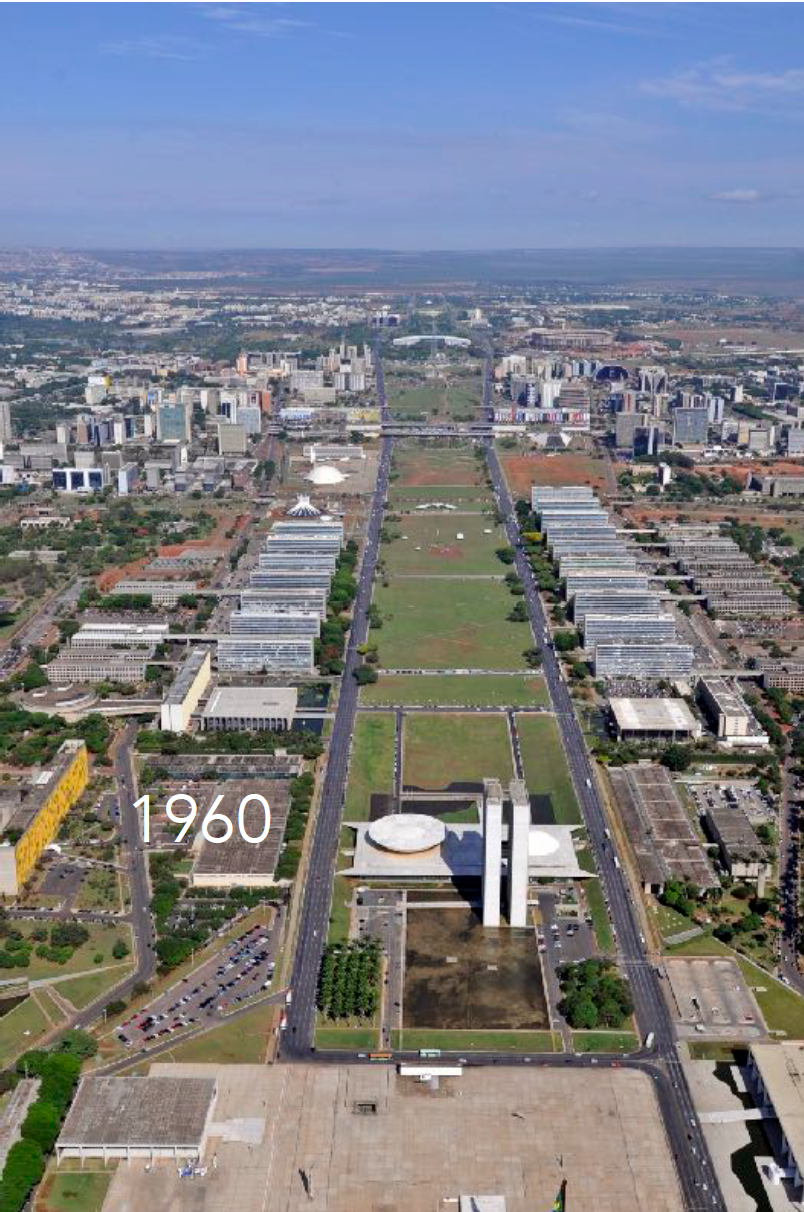
History: Created in 1960 to promote interior development; designed by Lúcio Costa and Oscar Niemeyer with clear zoning and monumental government axis.
Brasilia, Brazil
Physical Layout: Shaped like an airplane with two main axes: the Monumental Axis and the Residential Axis; strict zoning and vast open spaces.
Brasilia, Brazil
Urban Planning Significance: Landmark of modernist planning, with emphasis on form over function; criticized for inaccessibility and lack of human scale.
Brasilia, Brazil
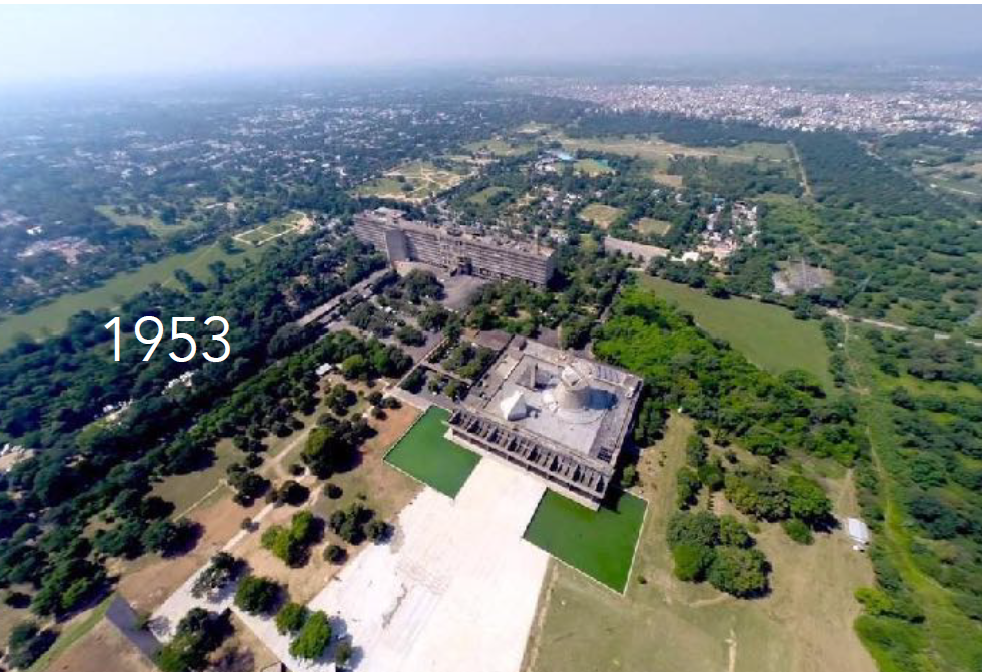
History: Commissioned after Partition; designed by Le Corbusier in the 1950s to represent a new, modern India.
Chandigarh, India
Physical Layout: Sector-based grid with defined civic, residential, and commercial zones; hierarchy of roads and green belts.
Chandigarh, India
Urban Planning Significance: Emphasizes sectoral planning and modernist zoning; model of order amid rapid urbanization.
Chandigarh, India
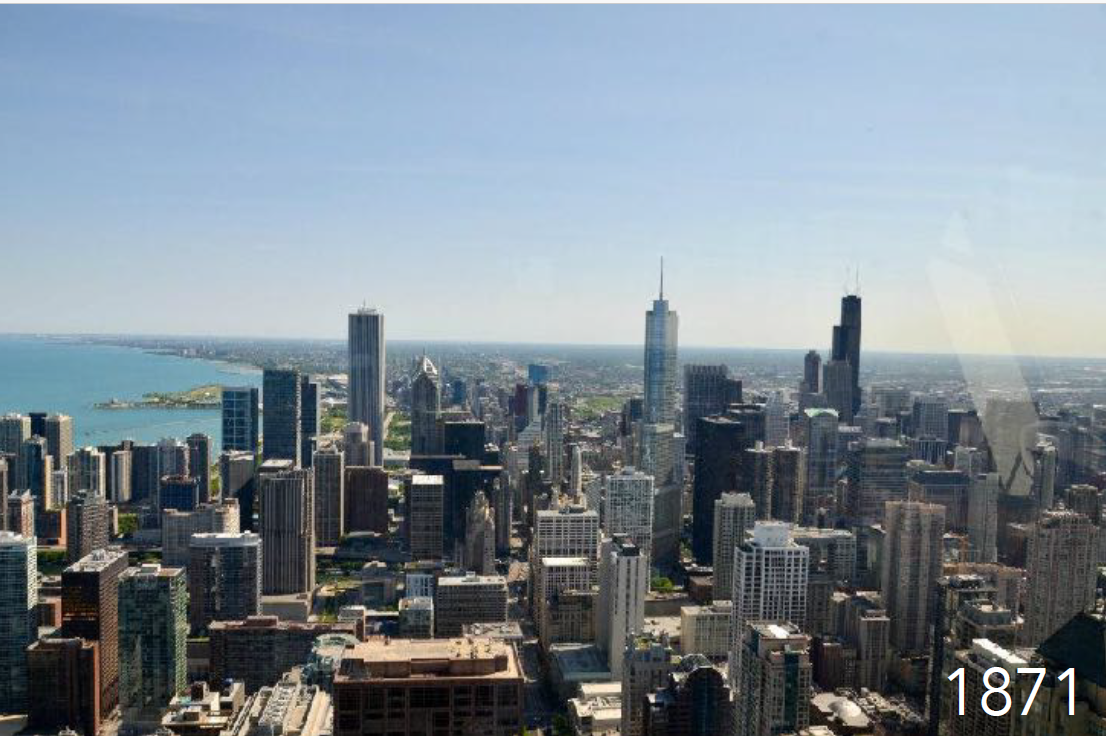
History: Rebuilt after the 1871 fire; site of the 1893 World’s Columbian Exposition; birthplace of the skyscraper and the Chicago School.
Chicago, USA
Physical Layout: Orthogonal grid layout with wide streets and alleys; lakefront development and prominent downtown skyline.
Chicago, USA
Urban Planning Significance: Influential in skyscraper development, grid planning, and early zoning laws. Marks industrialization and urbanization.
Chicago, USA
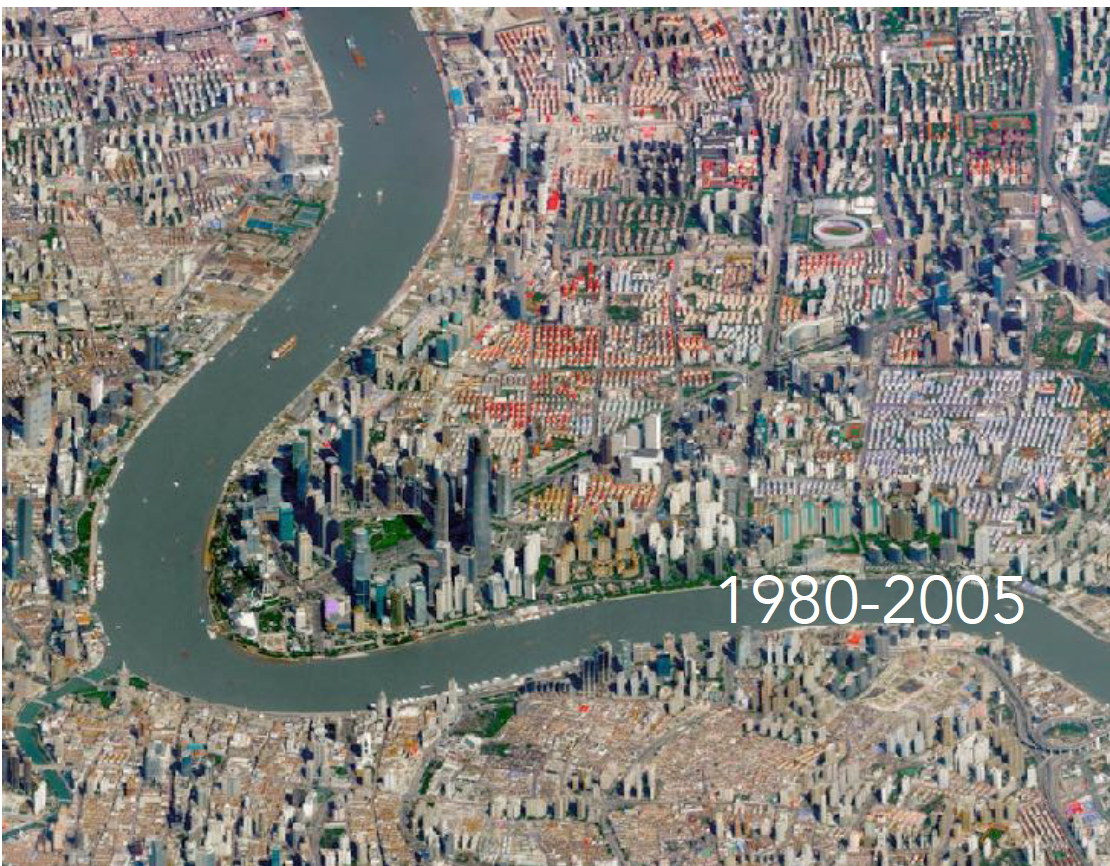
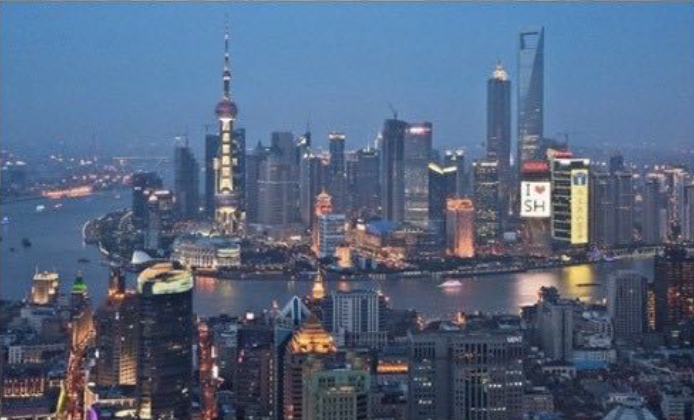
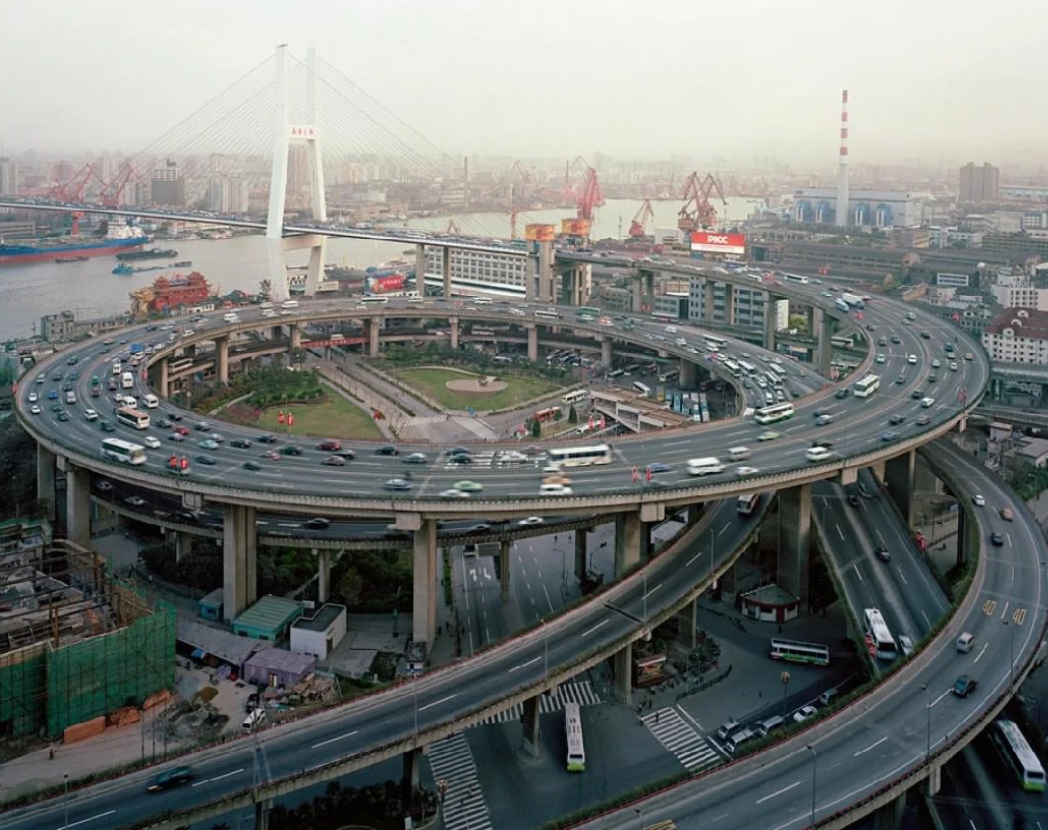
History: Developed as a colonial treaty port; transformed during socialist and post-reform periods into a financial hub.
Shanghai, China
Landscape: Coastal delta; Huangpu River divides the city
Type of City: Global megacity and economic powerhouse
Shanghai, China
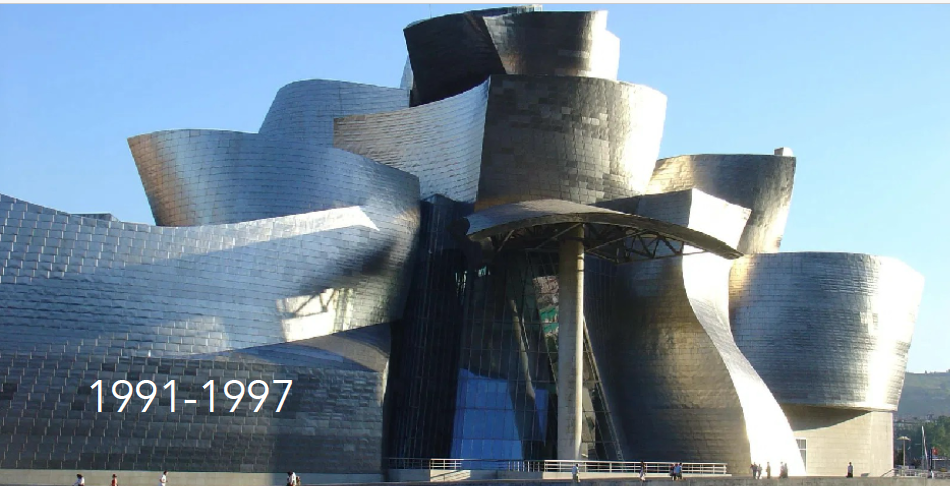
History: Former industrial center turned cultural icon with Guggenheim Museum (1997) as anchor.
Bilbao, Spain
Physical Layout: Compact riverfront city with dense historical core; urban renewal projects along the river.
Bilbao, Spain
Urban Planning Significance: "Bilbao Effect" demonstrates potential of iconic architecture in urban regeneration.
Bilbao, Spain
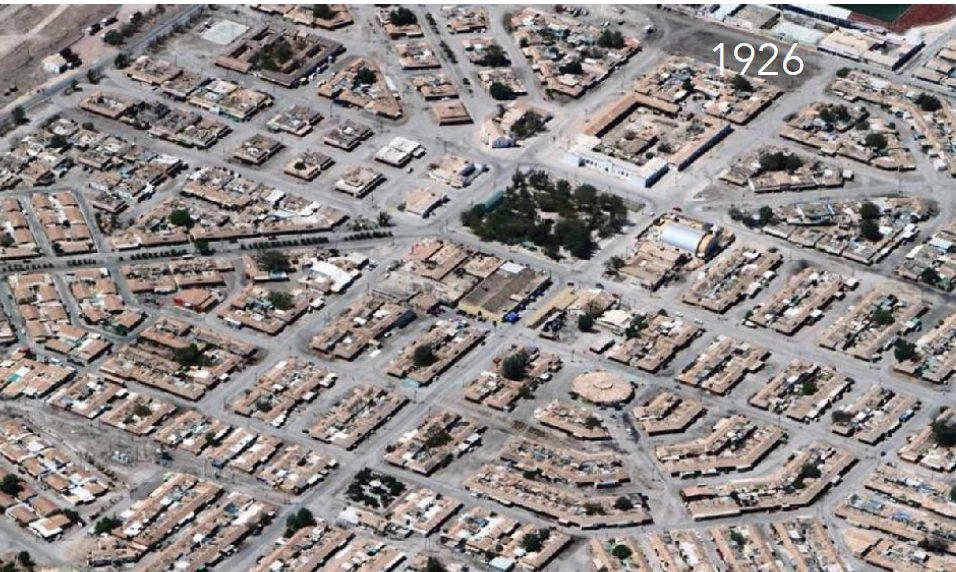
History: Built in early 20th century for saltpeter mining; one of the last nitrate towns still functioning.
Maria Elena, Chile
Physical Layout: Orthogonal grid centered around industrial facilities; minimal zoning and infrastructure.
Maria Elena, Chile
Physical Layout: Organic and radial layout from medieval core; ring roads and satellite towns reflect modern expansion.
London, UK
History: Grew from Roman Londinium; shaped by Great Fire of 1666, Industrial Revolution, and post-war reconstruction.
London, UK
Urban Planning Significance: Model of layered urban evolution; Highlights the Empire cities as power was displayed through Crystal Palace & large ports
London, UK
History: Radically transformed by Baron Haussmann in the mid-19th century; modernization of infrastructure and streetscapes.
Paris, France
Physical Layout: Radial boulevard system centered on monuments; mix of formal avenues and narrow historic streets.
Paris, France
Urban Planning Significance: Template for boulevard-centric design and urban beautification; Empire city; higher quality of life than other Empire cities
Paris, France
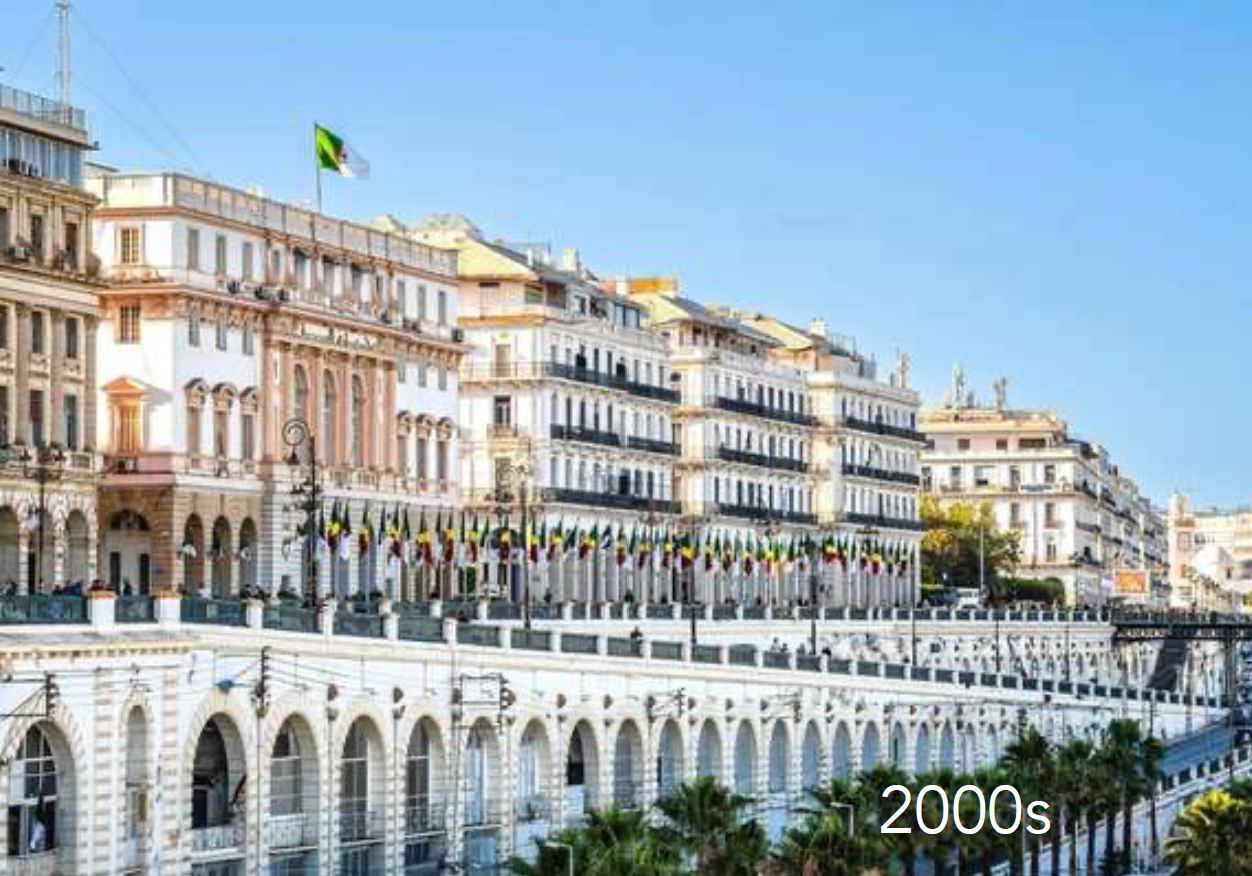
Urban Planning Significance: Represents spatial segregation of colonial urbanism; postcolonial challenges of reintegration.
Algiers, Algeria
Colonization of Algiers
Phase 1 = restructure existing urban fabric
Phase 2 = new buildings (ex: waterfront arcade)
Phase 3 = connecting paris and casbah(pre france)
Phase 4 = urban development on sea and hills
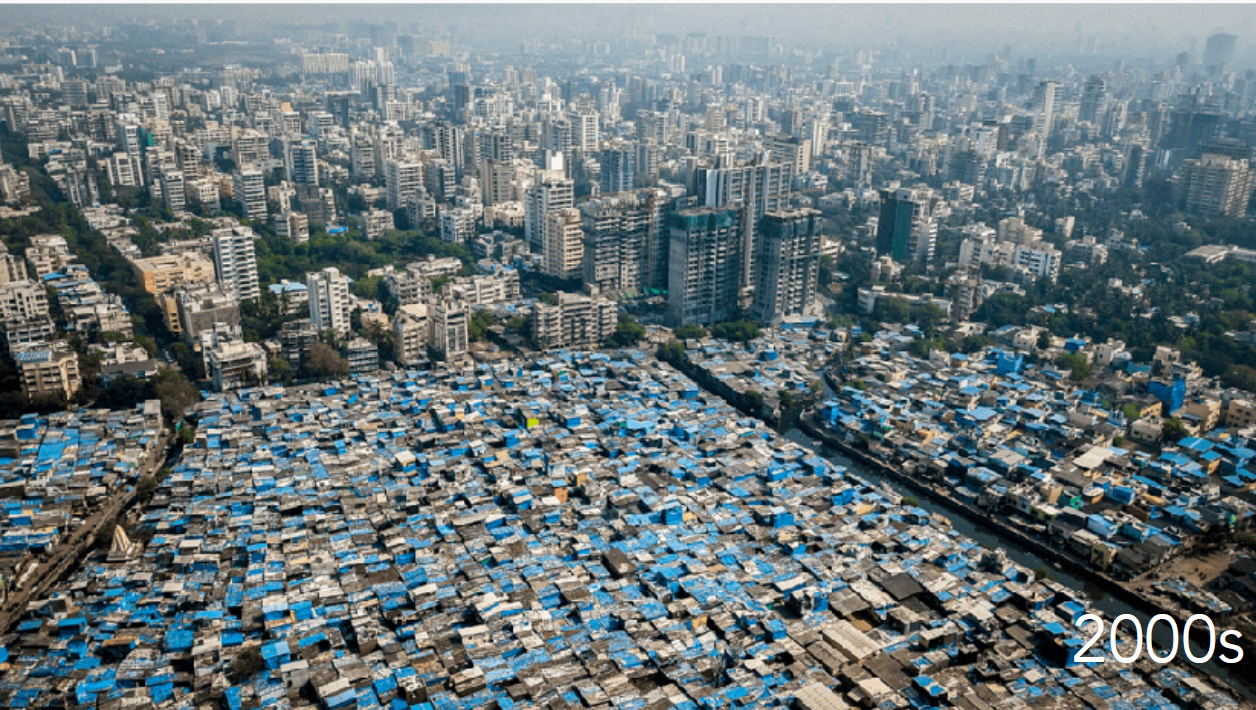
History: Colonial port city turned megacity; massive informal housing and infrastructure challenges.
Mumbai, India
Physical Layout: Mixed land uses with dense informal settlements and high-rises. Built up on port city because of British exports.
Mumbai, India
Urban Planning Significance: Contrasts planned enclaves with organic sprawl; lessons on resilience and inequality.
Mumbai, India
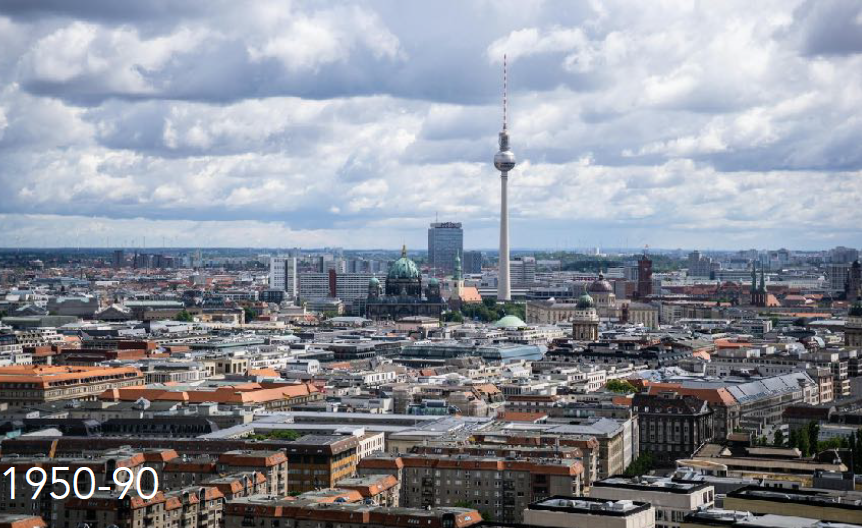
History: Shaped by WWII destruction, Cold War division, and post-1989 reintegration.
Berlin, Germany
Physical Layout: Polycentric with distinct East (brutalist)/West (modernist) forms; preservation of historical voids and green spaces.
Berlin, Germany
Urban Planning Significance: Complex palimpsest of ideologies; labs for memory, identity, and regeneration.
Berlin, Germany
Restorative nostalgia
truth of what has been lost, nationalism, oppressive (ex: East Berlin)
Reflective nostalgia
selective, personal, you can honor it but change it (ex: West Berlin)
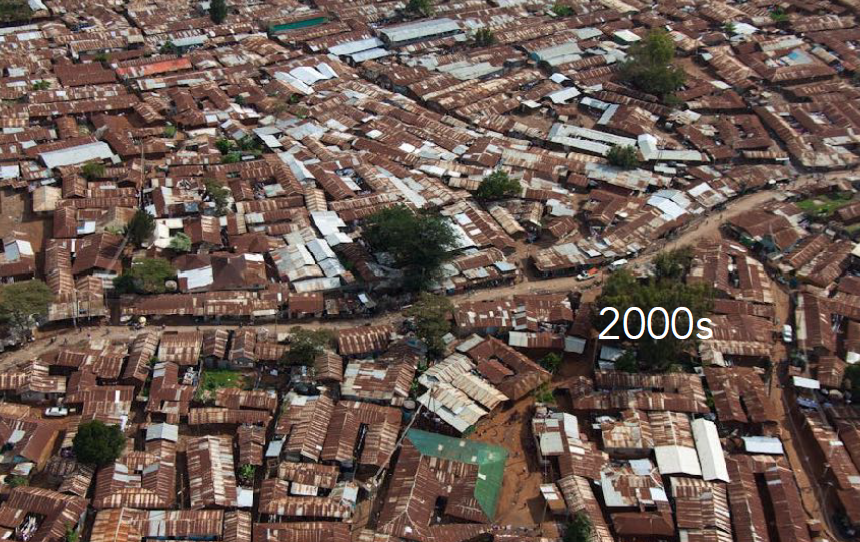
History: Originated as a British colonial rail stop; now struggles with infrastructure deficits and informal settlements.
Nairobi, Kenya
Physical Layout: Fragmented structure with elite enclaves, industrial zones, and sprawling informal settlements. (ex: Kibera (informal)/Blue Zone (fancy)
Nairobi, Kenya
Urban Planning Significance: Exemplifies urban growth pressures in Sub-Saharan Africa; need for participatory planning.
Nairobi, Kenya
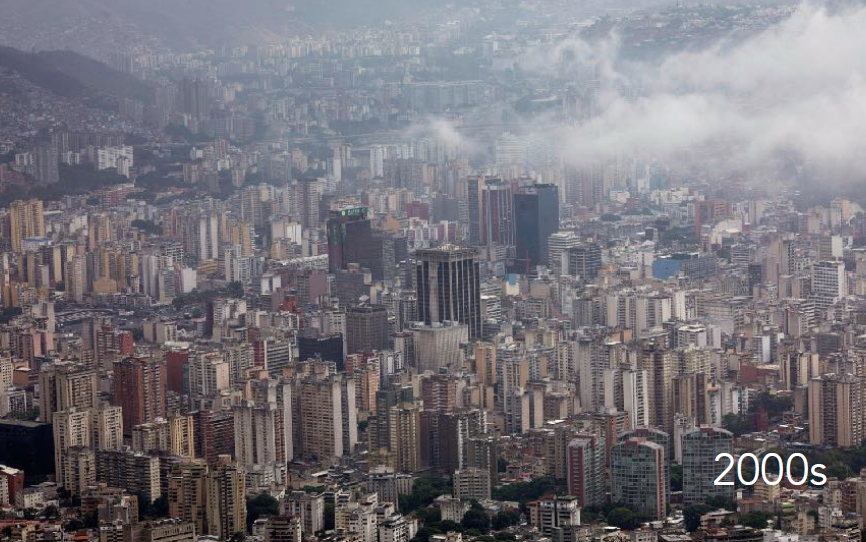
History: Located in narrow mountain valley; Modernist planning in 1950s; political and economic instability has led to urban decay. “Bleeding City”
Caracas, Venezuela
Physical Layout: Axial highways cut through dense informal and modernist sectors; Harsh divide between urban buildings and informal housing. (Barrios)
Caracas, Venezuela
Urban Planning Significance: Shows modernism’s limits amid socio-political breakdown. 50% of people live in informal settlements. Lack of urban planning.
Caracas, Venezuela
History: War-torn capital repeatedly rebuilt; mixed religious and ethnic urban fabric. Discontinuous urban patches linked by main roads.
Beirut, Lebanon
Urban Planning Significance: Reflects layered identities and reconstruction under duress; planning under crisis conditions.
Beirut, Lebanon
‘Green Line’ in Beirut
Division between Christian East and Muslim West
History: Grew with border trade and maquiladora industry; rapid migration-led expansion.
Tijuana, Mexico
Physical Layout: Irregular sprawl with mixed formal/informal zones; binational infrastructure.
Tijuana, Mexico
Urban Planning Significance: Study in binational dynamics, cross-border urbanism, and informality. Modular housing in informal areas.
Tijuana, Mexico
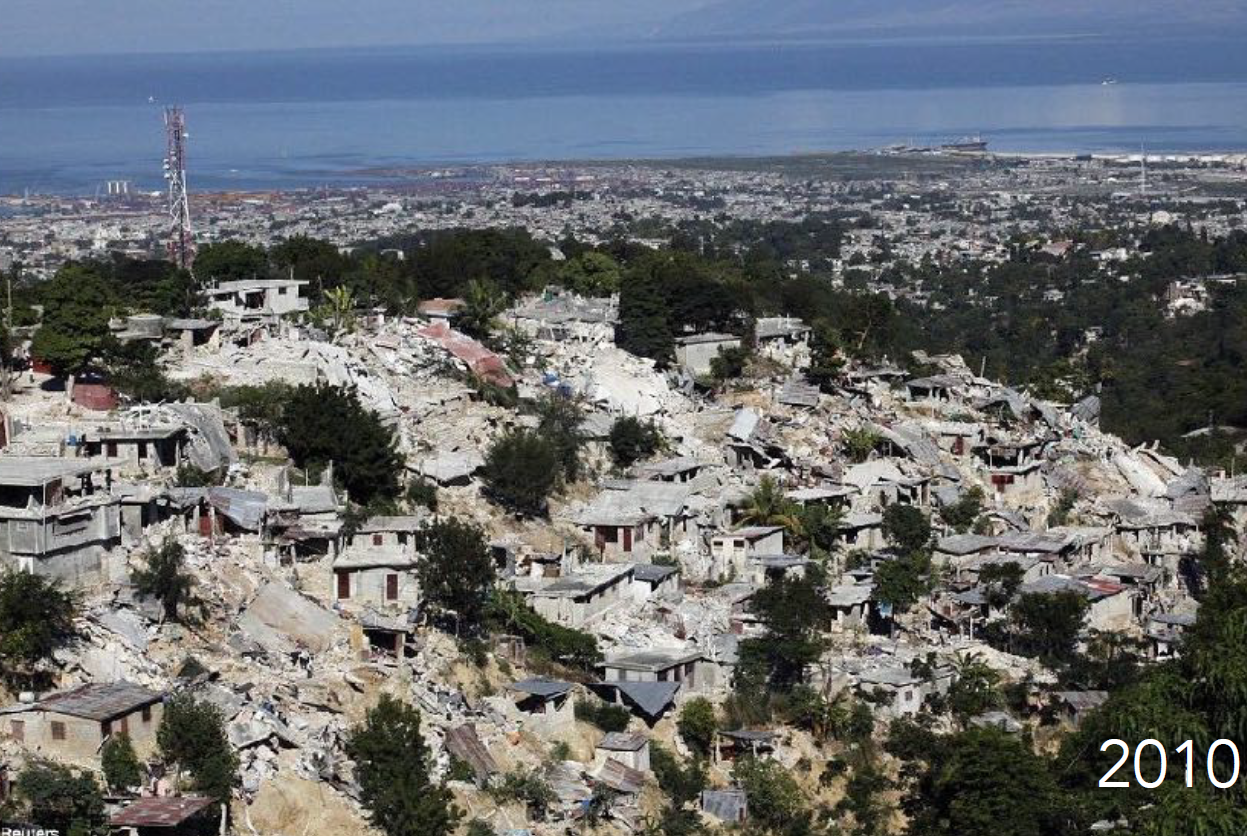
History: Capital with limited infrastructure. Devastated by 2010 earthquake; struggled with reconstruction and governance.
Port-au-Prince, Haiti
Physical Layout: Dense core with radial roads; informal hillside settlements prone to landslides.
Port-au-Prince, Haiti
Urban Planning Significance: Highlights fragility and urgency of resilient, inclusive planning in disaster-prone areas.
Port-au-Prince, Haiti
Helsinki’s 7 Vision Themes
a Urban metropolis
b Appealing living options
c Economic growth
d Sustainable mobility
e Recreation and cultural environment
f Seaside areas
g International (airports)
‘The Right to the City’ concepts by Lefebvre and Harvey
emphasizes the need for inclusivity, accessibility, and democracy in urban spaces; Urban spaces should be shaped and governed by the citizens who inhabit them, not solely controlled by market forces
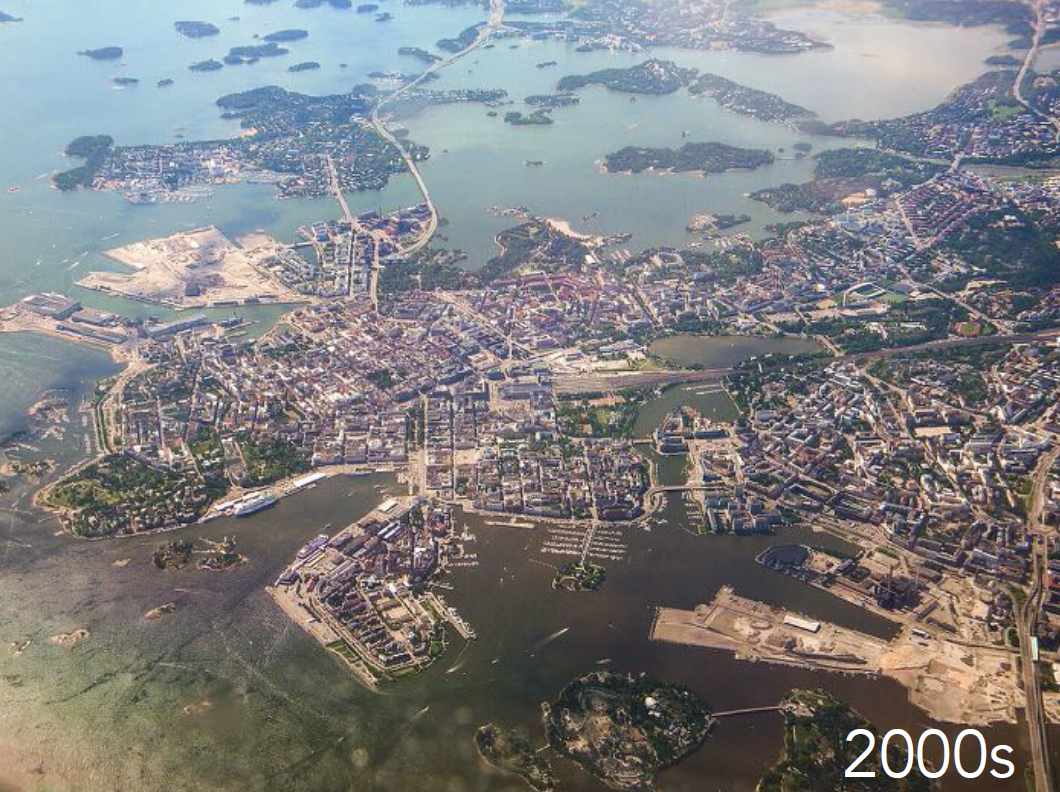
Physical Layout: Compact center with radiating neighborhoods; extensive green corridors and public transport.
Helsinki, Finland
Urban Planning Significance: Model for socially inclusive, climate-adaptive design; high urban livability.
Helsinki, Finland
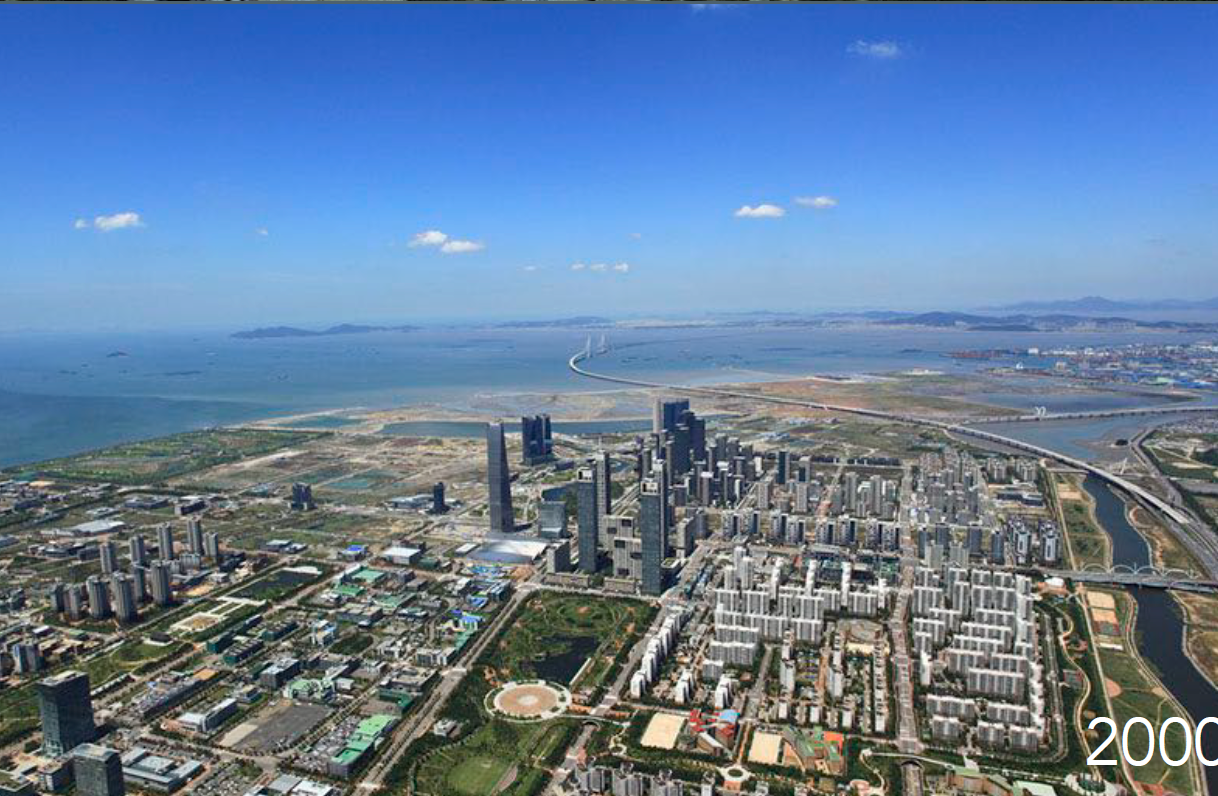
History: Planned smart city. Constructed from scratch in 2000s; intended as a green, high-tech urban prototype.
Songdo, South Korea
Physical Layout: Grid-based with modular superblocks; embedded with ICT systems and green spaces.
Songdo, South Korea
Urban Planning Significance: Test case for smart city technologies; criticized for lack of organic vibrancy. Too expensive for residents. Failed smart city
Songdo, South Korea
History: Utopian anti-urban model. Proposed in the 1930s as an alternative to industrial urbanism; emphasized individual autonomy and self-sufficiency. (Frank Lloyd Wright)
Broadacre City (Imagined)
Physical Layout: Scattered homes on large lots; each family given an acre; extensive use of highways, no traditional center. Urban Planning Significance: Critique of centralization and density; foundational to suburban ideology but criticized for unsustainable sprawl.
Broadacre City (Imagined)
History: Evolves the Broadacre City idea by embedding broadband infrastructure into decentralized living; not a real city but a concept aligned with remote work and digital nomadism. Physical Layout: Dispersed single-acre homesteads, digitally linked via high-speed internet; reduced physical density, high virtual connectivity.
Broadband Acre City
rational thought, communal property, productivity, no class distinctions or poverty, little crime or immoral behavior, religious freedom, and little violence.
More’s Utopia
equality, social harmony, and a focus on the greater good, collective ownership, harmony with nature
Campanella’s The City of the Sun
formal city, monumental, more focused on the buildings that exist (ex: buildings/roads in Mumbai)
Static City