D&T Gaps
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
How are MDF Boards made?
Trees are cut down and then debarked.
The wood is then chipped into small pieces.
They are then cleaned and pulped turning softwood chips in to wood fibres.
Urea formaldehyde is added to the mixture and the material is pressed into sheets.
These sheets are then dried, trimmed and sanded.
Positives of Natural Fibres?
Properties of natural fibres to make them suitable for clothing include:
Thermal properties
Absorbency for dyeing
Soft handle
Good drape
Can be washed and ironed
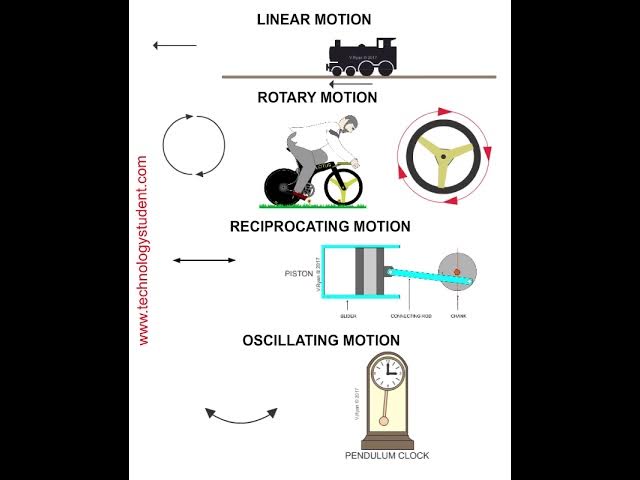
oscillating vs reciprocating motion
Thermosetting vs Thermoforming Plastics recycling
Thermosetting are much harder to recycle
Thermoforming are easier to recycle
What is plasticity?

PLA
3D printers
Biodegradable
Not from oil


What is virtual marketing?
Virtual marketing involves promoting products or services through online channels. This includes:
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Improving website visibility on search engines.
- Social Media Marketing (SMM): Engaging with customers on platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter.
- Email Marketing: Sending targeted emails to promote products or services.
- Content Marketing: Creating and distributing valuable content to attract and retain customers.
- Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising: Running online ad campaigns where you pay for each click.
Deepwater Horizon?
The Deepwater Horizon oil spill occurred in 2010 in the Gulf of Mexico, becoming one of the largest marine oil spills in history. Key facts include:
- Date: April 20, 2010
- Location: Gulf of Mexico, at the Macondo Prospect
- Cause: An explosion on the Deepwater Horizon oil rig, which was operated by BP
- Oil Spill Volume: Estimated at 4.9 million barrels (210 million gallons)
- Environmental Impact: Extensive damage to marine and wildlife habitats, including the death of thousands of birds, sea turtles, and marine mammals
- Economic Impact: Significant losses for the fishing and tourism industries
- BP's Costs: Over 65 billion in fines, settlements, and cleanup costs
What is Fairtrade?
Fairtrade is an initiative that ensures producers in developing countries receive fair prices and decent working conditions. Key aspects include:
- Fair Prices: Farmers receive a minimum price that covers their production costs and provides a living income.
- Working Conditions: Promoting safe and healthy working environments for farmers and workers.
- Community Development: Investing in community projects such as schools, healthcare, and infrastructure.
- Environmental Sustainability: Encouraging environmentally friendly farming practices.
- Empowerment: Empowering farmers to have more control over their livelihoods and futures.
What is FSC?
The Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) is an international organization that promotes responsible management of the world's forests. Key points include:
- Certification: FSC certifies forests and forest products that meet specific environmental and social standards.
- Standards: Ensuring forests are managed in an environmentally appropriate, socially beneficial, and economically viable manner.
- Logo: The FSC logo on a product indicates that it comes from responsibly managed forests.
- Benefits: Protecting biodiversity, preventing deforestation, and supporting the rights of workers and local communities.
Dyson's success?
Dyson's success is attributed to innovative design, effective marketing, and continuous improvement. Key aspects include:
- Innovative Design: Dyson focuses on creating products that solve everyday problems through unique and inventive engineering solutions. For example, the bagless vacuum cleaner uses cyclone technology to maintain suction power.
- Marketing: Dyson effectively communicates the benefits of its technology through demonstrations and advertising, emphasizing superior performance and reliability.
- Continuous Improvement: Dyson invests heavily in research and development, constantly refining its products based on user feedback and technological advancements.
- Brand Image: Building a premium brand associated with quality, innovation, and a forward-thinking approach.
- User-Centric Approach: Focusing on user needs and preferences to create products that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
Design failures?
Notable design failures include the Edsel car, New Coke, and the Apple Newton. Lessons learned include:
- Edsel Car: Introduced by Ford in 1957, it failed due to poor market research, unattractive design, and timing issues. The lesson is the importance of understanding consumer preferences and conducting thorough market research.
- New Coke: Coca-Cola reformulated its classic drink in 1985, leading to widespread consumer backlash. The lesson is to respect brand heritage and avoid unnecessary changes to successful products.
- Apple Newton: Launched in 1993, this PDA suffered from poor handwriting recognition and high cost. The lesson is the need for robust testing and usability, ensuring technology meets user expectations.
General Lessons:
- Understand Market Needs: Conduct thorough research to ensure products align with consumer demands.
- Test Thoroughly: Ensure products are fully functional and meet user expectations before release.
- Protect Brand Equity: Avoid drastic changes to successful products that could alienate customers.
- Consider Timing: Launch products when the market is ready and consumer needs align with the offering.
Primary research?
Examples of primary research include surveys, interviews, focus groups, and experiments. Details include:
- Surveys: Gathering quantitative data from a large sample through questionnaires.
- Interviews: Collecting qualitative data through one-on-one conversations to understand individual perspectives.
- Focus Groups: Facilitating group discussions to explore opinions and attitudes.
- Experiments: Conducting controlled tests to determine cause-and-effect relationships.
Secondary research?
Examples of secondary research include literature reviews, market reports, and data analysis from existing sources. Details include:
- Literature Reviews: Analyzing existing research papers and scholarly articles to gather background information.
- Market Reports: Utilizing reports from market research firms to understand market trends and consumer behavior.
- Data Analysis: Examining existing datasets to identify patterns and insights.
Tessellation?
Tessellation involves arranging shapes to cover a surface without gaps or overlaps. Reducing waste in cutting involves:
- Efficient Layout: Arranging shapes in a tessellated pattern minimizes waste by maximizing material use.
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD): Using software to optimize layouts and reduce scrap.
Other ways than Tesselation to reduce material wastage.
Techniques to minimize wastage when cutting, other than tessellation, include:
Nesting: Positioning shapes closely together to reduce gaps.
Common Line Cutting: Cutting along shared edges to reduce the number of cuts.
Blade Placement: Place blades towards the wastage, as blades do result in material being lost.
Laser cutting: lasers can be very fine, even to 0.2mm reducing wasted material when cutting.
Offcuts Reuse: Utilizing leftover pieces for smaller components or products.
Optimal Cutting Paths: Planning cutting paths to minimize material removal.
Material Selection: Choosing materials that are easier to cut and produce less waste.
Alignment: Make sure that this is on point to minimise wastage. This can be done by aligning the datum, or alignment points.

