Unit 1: Electrostatics
5.0(2)Studied by 401 people
0%Unit 1: Electrostatics Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physics
AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism
Unit 1: Electrostatics
Electric Charge
Coulomb's Law
Electric Charge
Conservation of Charge
Conductors
Insulators
Law of Electrostatics
Electric Potential
Electric Field
Electric Potential Difference
Charging and Discharging
Electrostatic Force
Rules for Drawing Electric Fields
Electric Field Strength
Point Charges
Gauss' Law
Flux
12th
Last updated 2:39 PM on 4/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
1
New cards
Charge
It is a fundamental property of matter that describes the amount of electrical energy present in an object.
2
New cards
Coulomb
SI unit of charge
3
New cards
Electric charge
It is a fundamental property of matter that arises from the presence or absence of electrons in an atom.
4
New cards
Conductors
These are materials that allow electric charge to flow freely through them.
5
New cards
Insulators
These are materials that do not allow electric charge to flow easily.
6
New cards
law of electrostatics
a set of fundamental principles that govern the behavior of electric charges at rest.
7
New cards
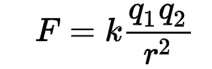
Coulomb's law
This law states that the force between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
8
New cards
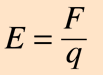
Electric field
A region in space where an electric charge experiences a force.
9
New cards
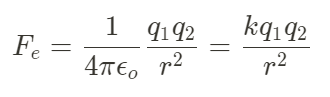
Electric potential difference
It is the difference in electric potential between two points in an electric field. It is measured in volts (V).
10
New cards
Charging
It is the process of adding electrical energy to a system.
11
New cards
Discharging
It is the process of releasing electrical energy from a system.
12
New cards
Electrostatic force
It is the force that exists between electrically charged particles.
13
New cards
Electrostatic Force Formula
14
New cards
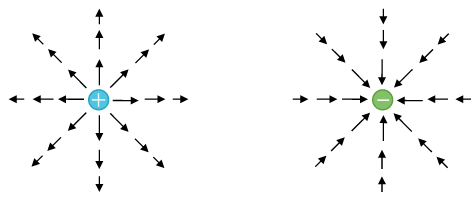
Point Charges
15
New cards
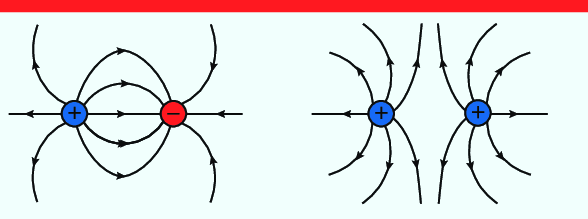
Two Point Charges
16
New cards
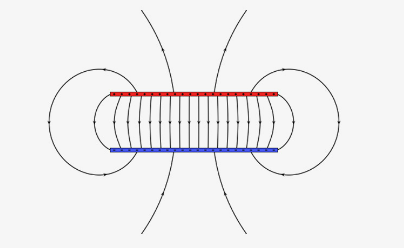
Two Parallel Plates
17
New cards
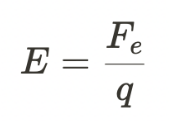
Electric field strength
It is the force per unit charge experienced by a test charge placed in an electric field. It is a vector quantity and is denoted by E.
18
New cards
Capacitors
devices that store electric charge and energy.
19
New cards
Electric motors
devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy.
20
New cards
Particle accelerators
devices that use electric fields to accelerate charged particles to high speeds.
21
New cards
Electrostatic precipitators
devices that use electric fields to remove pollutants from the air.
22
New cards
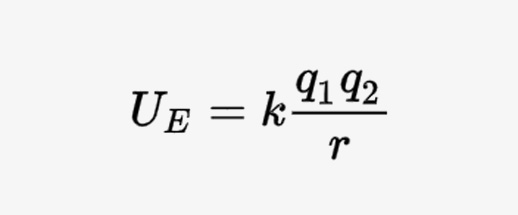
Electric potential energy
It is the energy that a charged particle possesses due to its position in an electric field. It is defined as the amount of work required to move a charged particle from infinity to a point in the electric field.
23
New cards
Joule
SI unit of electric potential energy
24
New cards
Potential difference
It is the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points in an electric circuit.
25
New cards
Gauss' Law
It is a fundamental principle in electromagnetism that relates the electric flux through a closed surface to the charge enclosed within that surface. It is named after the German mathematician and physicist Carl Friedrich Gauss.
26
New cards
Flux
It is the amount of a physical quantity passing through a given surface.
27
New cards
Extended charge distributions
This refer to the distribution of electric charge over a three-dimensional object.
28
New cards
Continuous Charge Distributions
These charge distributions are those where the charge is distributed continuously over a volume or surface.
29
New cards
Spherical Charge Distributions
These charge distributions are those where the charge is distributed uniformly over the surface of a sphere.
30
New cards
Cylindrical Charge Distributions
These charge distributions are those where the charge is distributed uniformly over the surface of a cylinder.
31
New cards
Planar Charge Distributions
These charge distributions are those where the charge is distributed uniformly over a flat surface.
32
New cards
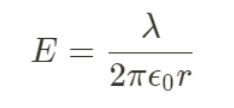
Gauss law in Line of Charge
33
New cards
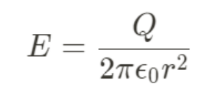
Gauss law in Point, Hoop, or Sphere (fully enclosed)
34
New cards
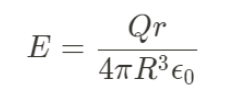
Gauss law in Sphere (not fully enclosed)
35
New cards
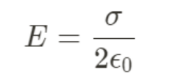
Gauss law in Insulating Sheet of Charge