experimental chemistry (chap1) -olevel pure chem
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
what is the SI unit for time
second (s)
SI unit for temperature
Kelvin (K)
SI unit for length
metre (m)
SI unit of mass
kilogram (kg)
SI unit for volume
cubic metre (m3)
what are some examples of insoluble gases
hydrogen (insoluble)
oxygen (insoluble)
carbon dioxide (slightly soluble)
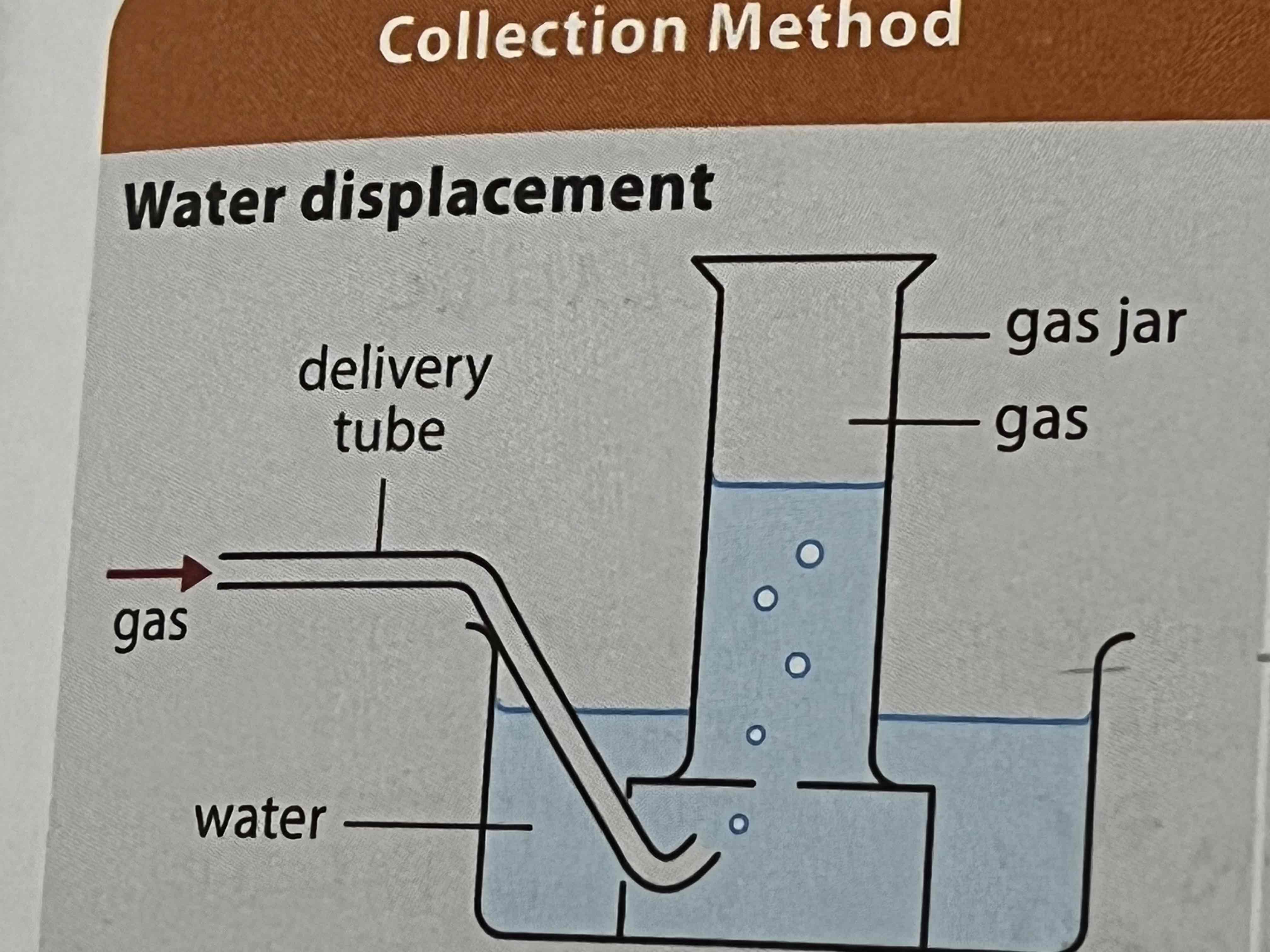
what method of collecting gases can be used for insoluble gases
water displacement
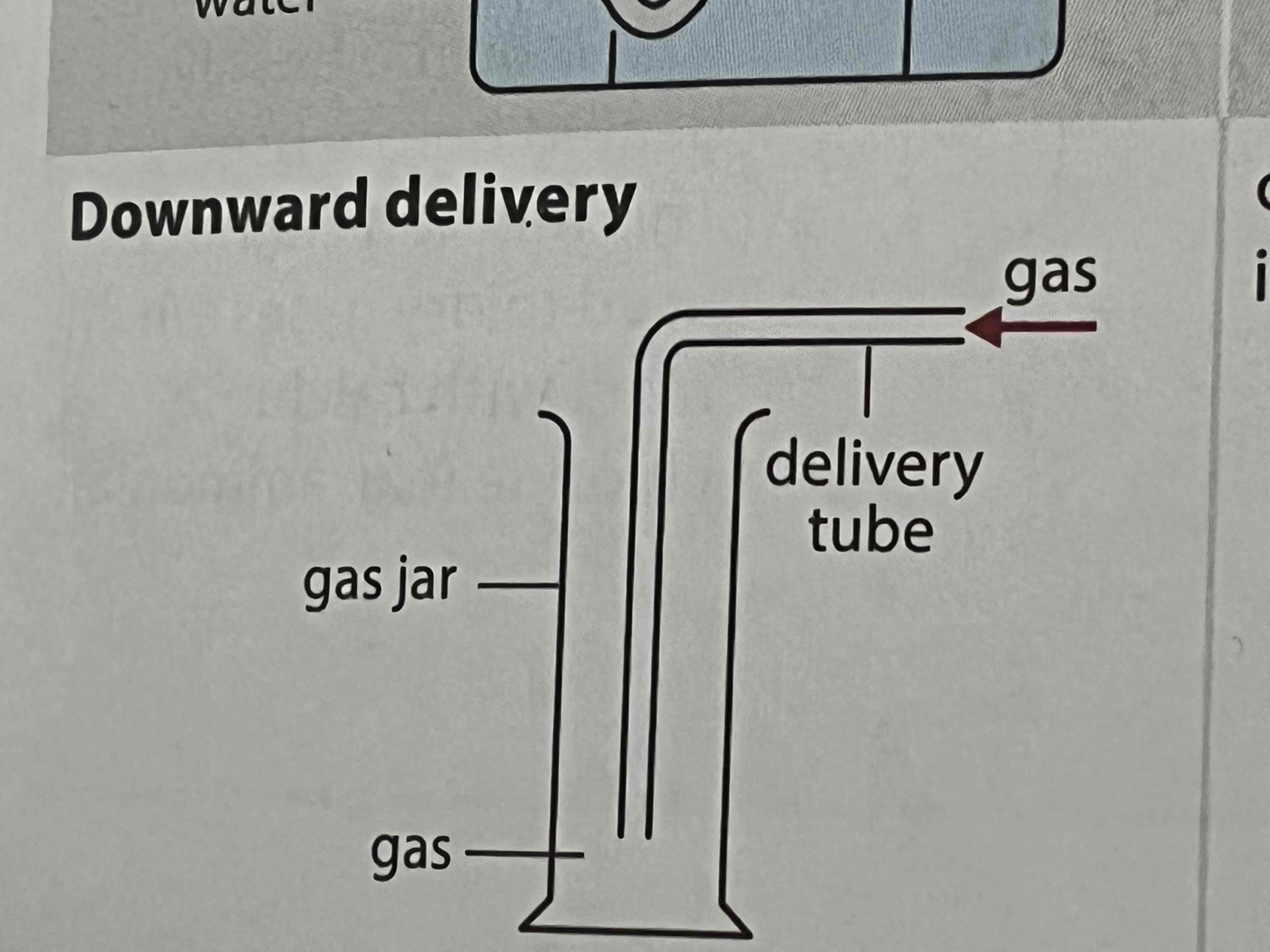
what method of collecting gases can be used for gases denser than air
downward delivery
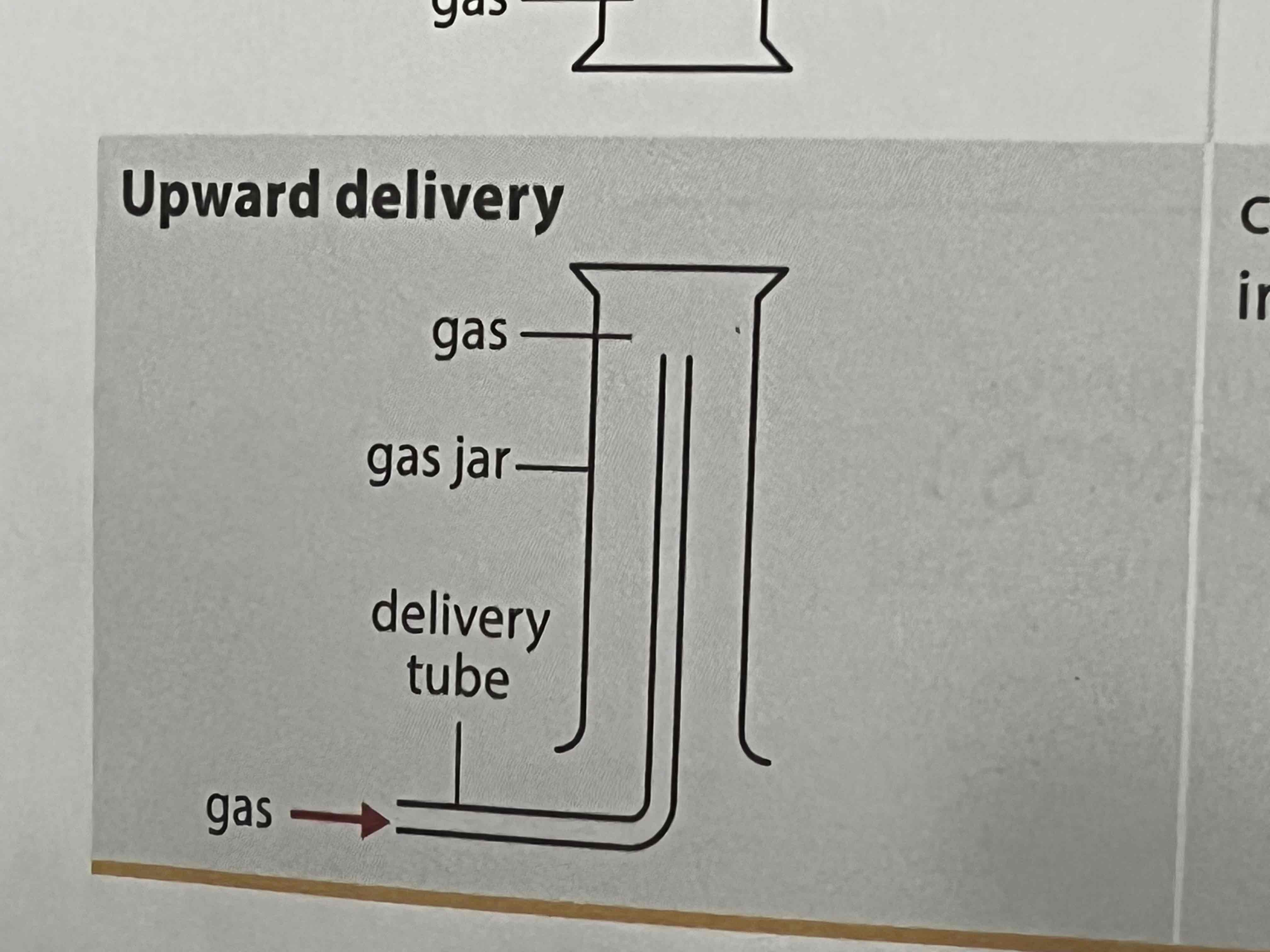
what method of collecting gases can be used for gases less dense than air
upward delivery
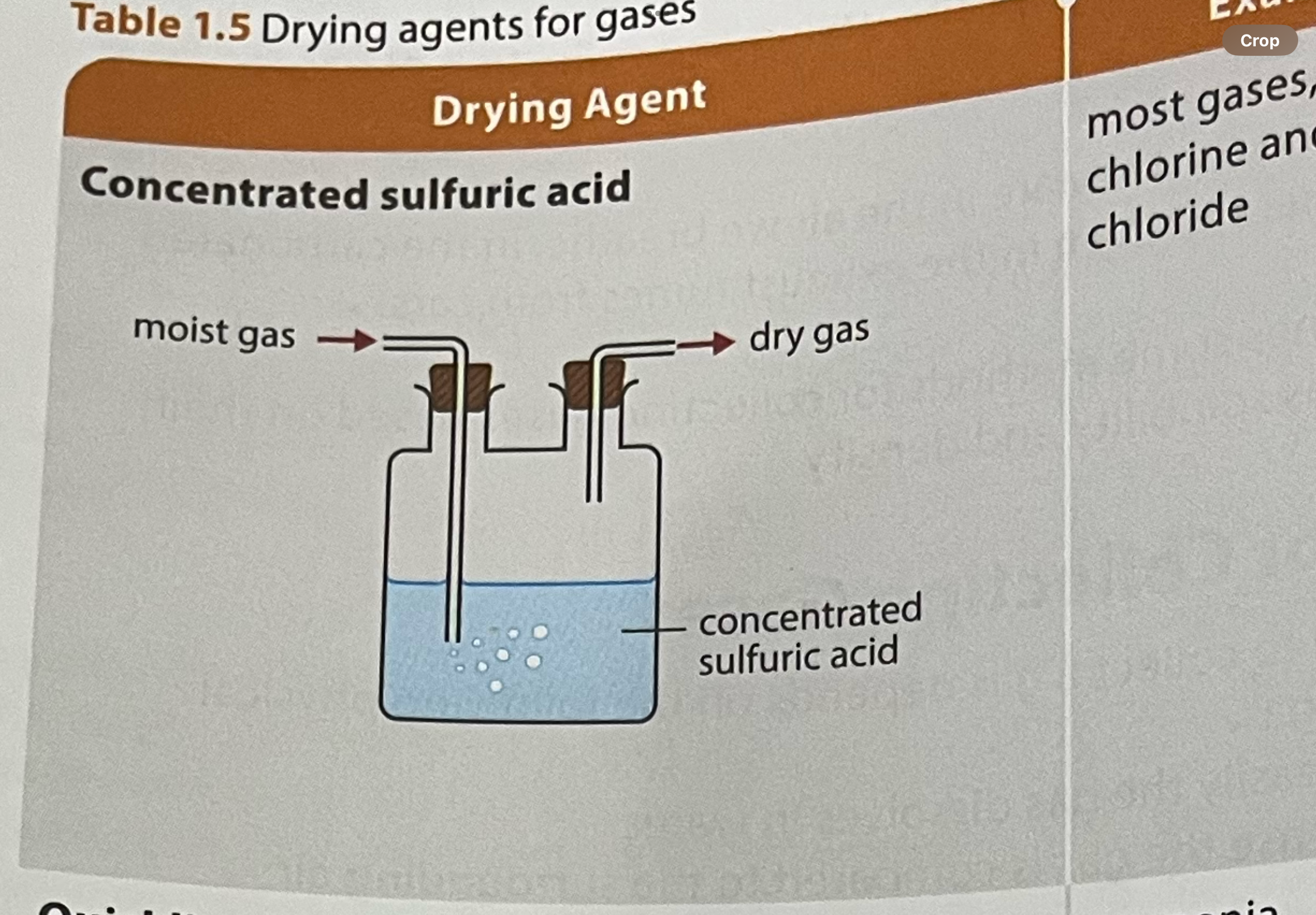
what are some drying agents for drying of gases
concentrated sulfuric acid
quicklime (calcium oxide)
fused calcium chloride
what gases can and cannot be dried with concentrated sulfuric acid
not suitable for gases which react with sulfuric acid (alkaline/ basic gases)
most gases including chlorine and hydrogen chloride
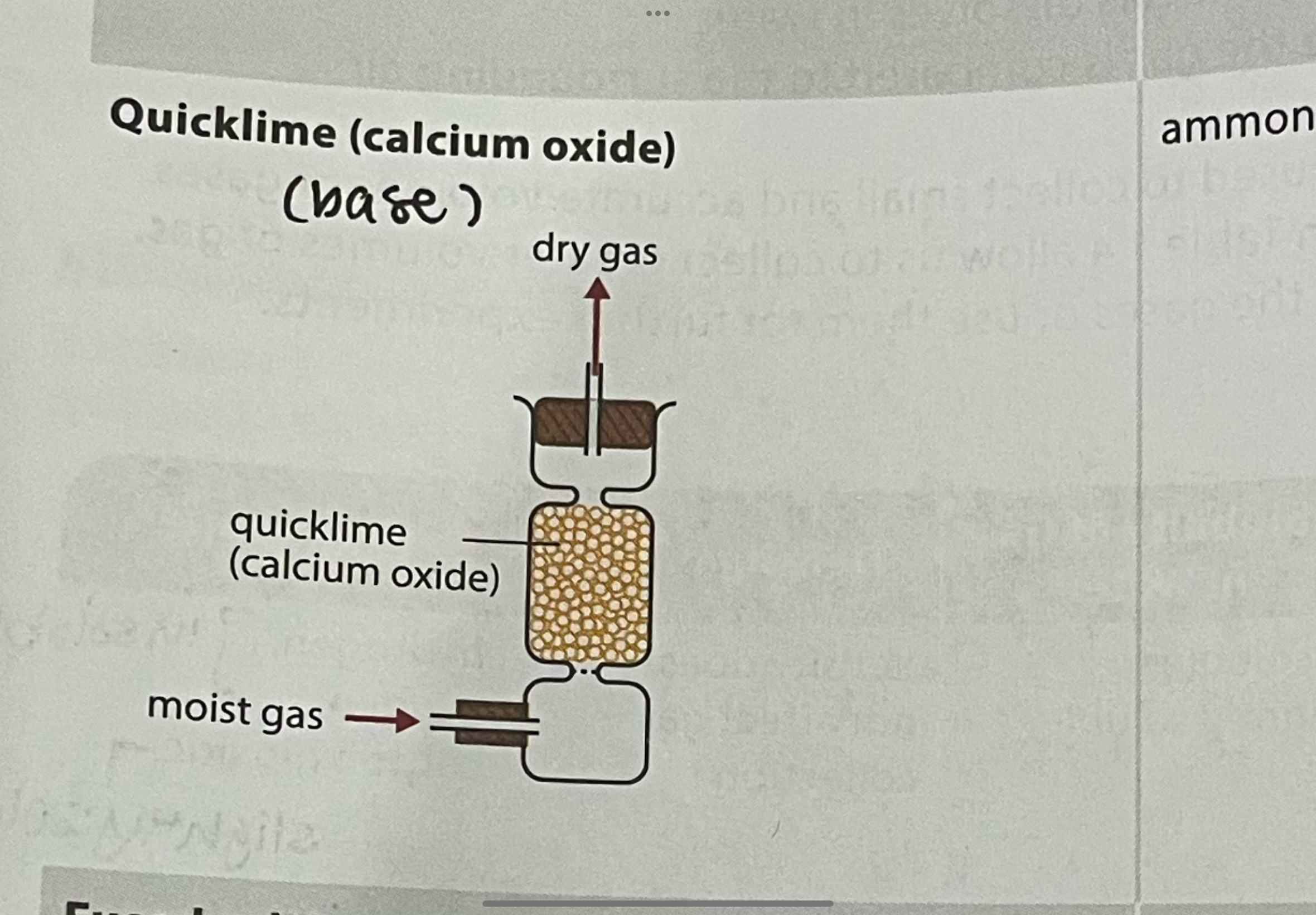
what gases can and cannot be dried with quicklime
quicklime must be freshly heated before use
cannot be used to dry gases that react with calcium oxide (acidic gases)
can be used for ammonia
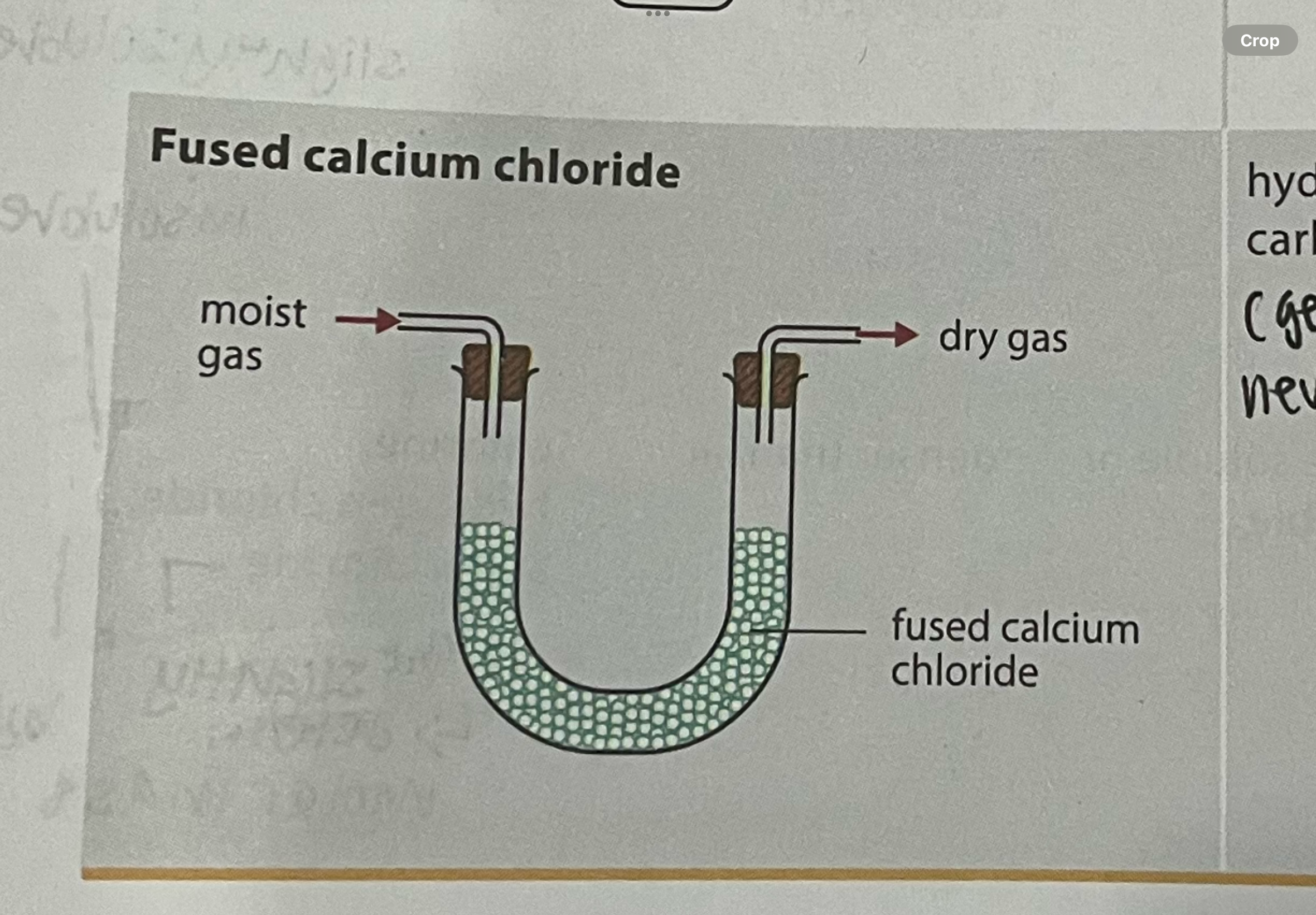
what gases can and cannot be dried with fused calcium chloride
must be freshly heated before use
cannot be used to dry gases that react with calcium chloride (eg ammonia)
hydrogen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide (generally for neutral gases)
what are some common substances that undergo sublimation
iodine, ammonium chloride
describe the process of simple distillation of saltwater
the salt water is heated. boiling chips are added to ensure the liquid boils smoothly and evenly. at 100 degrees, the water boils. the vapour rises and enters the condenser.
the condenser provides a cool environment for the vapour to condense into liquid
the water vapour loses heat and cools in the condenser and condenses back to liquid water. pure water is collected in the conical flask as distiliate
what is chromatography used for
is used to separate a mixture of substances which have different solubilities in a given solvent
What are some examples of locating agents in paper chromatography
UV lights
ninhydrin
describe the process of fractional distillation of ethanol-water mixture
as the solution is heated, both ethanol and water vapour rise up the column
as water has a higher boiling point than ethanol, the water vapour condenses on the cool surfaces in the fractionating column and the liquid water returns to the flask
ethanol vapour continues to rise. it exits the column, loses heat to the cooler surface of the condenser and condenses in the condenser as a liquid and ethanol is collected first as the distilate.