BIOL 302 Genetics Lecture 15: Chromosome Abnormalities and DNA Mutation
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Epigenic Modification
Altering of Histones in Nucleosomes (Etc, addition of methyl groups for tightening, acetyl groups for loosening)
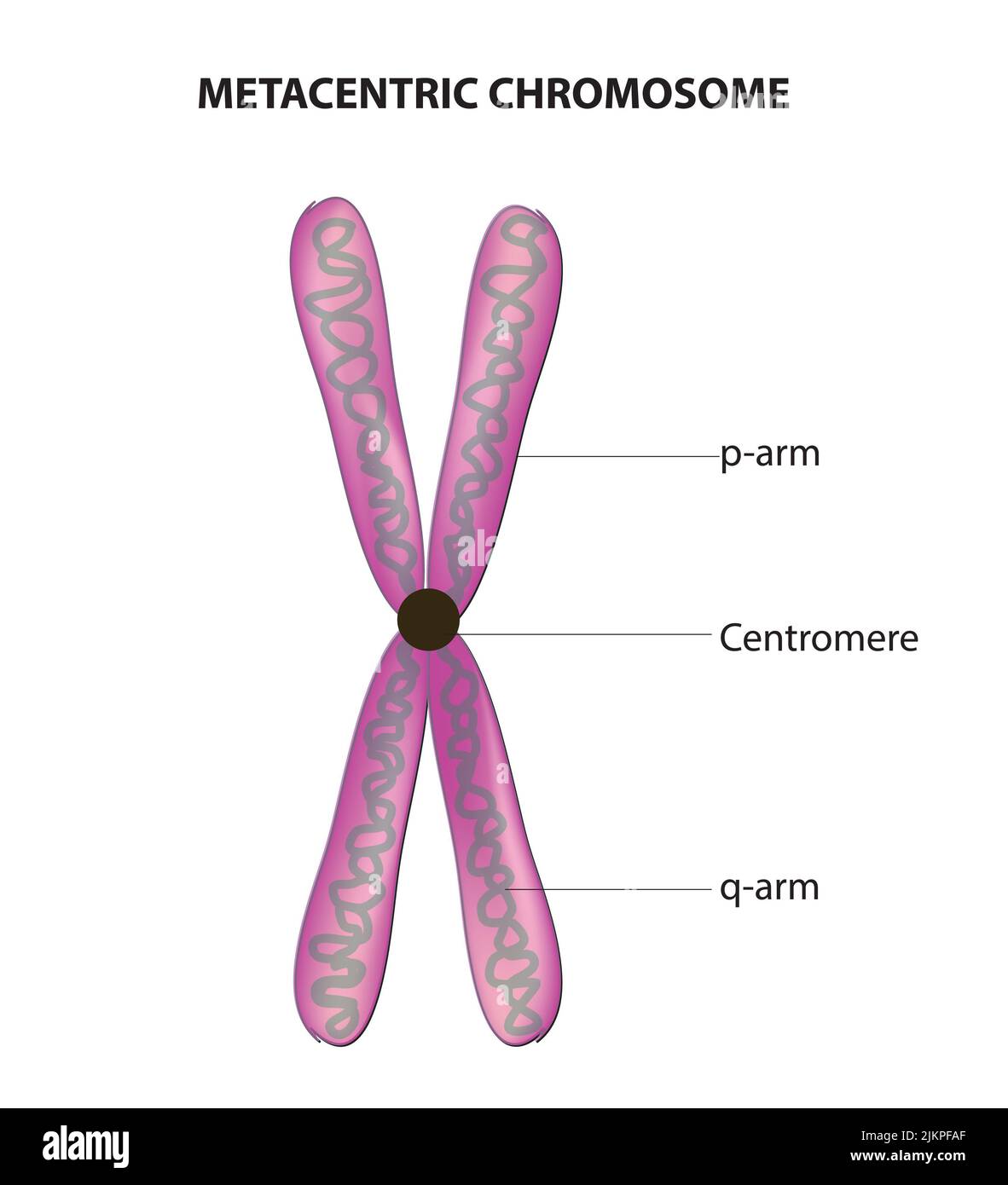
Metacentric Centromere
Centromere is close to center of chromosome
Submetacentric Centromere
Centromere is between terminal end and center of chromosome
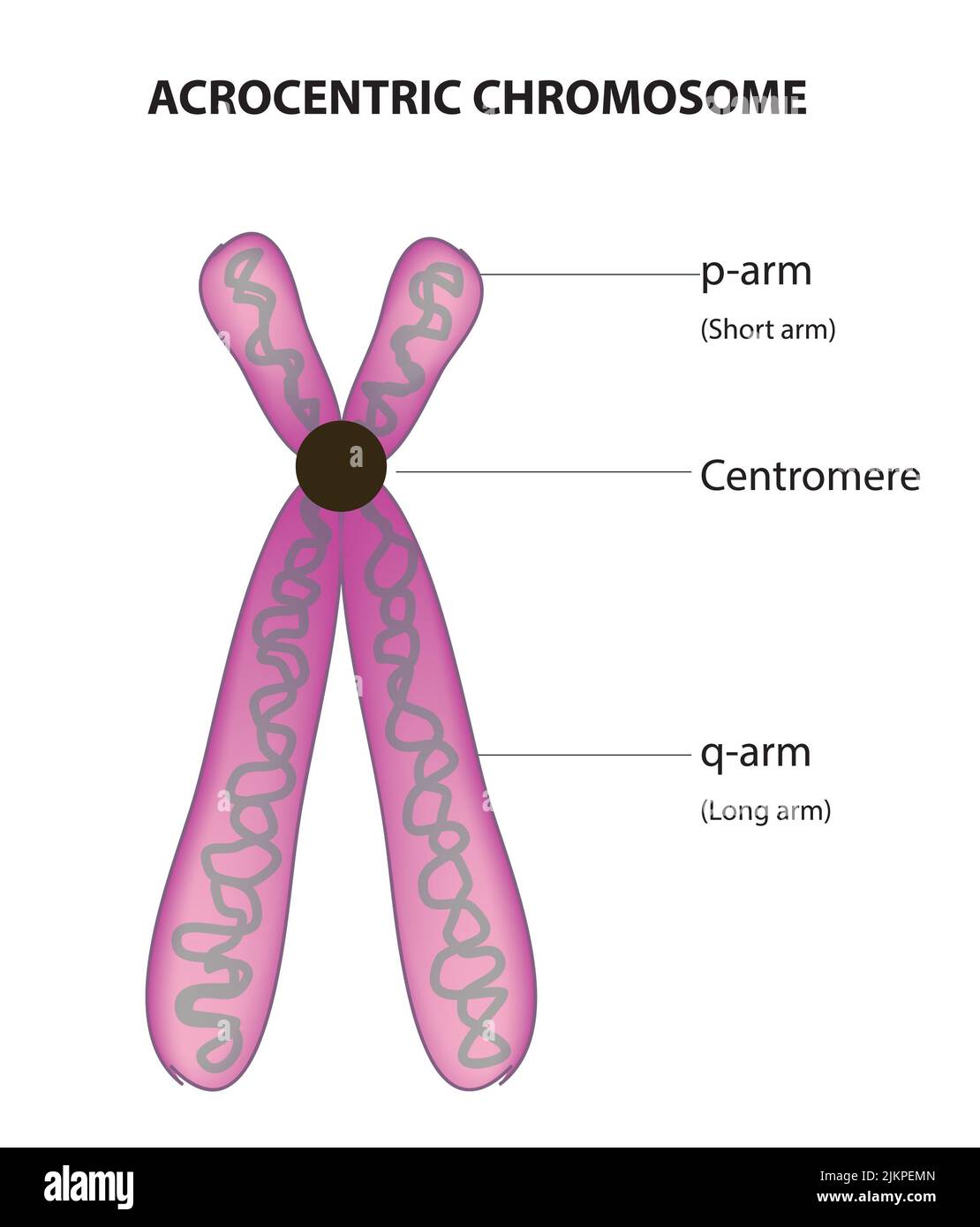
Arocentric
Centromere is close to terminal end of chromosome
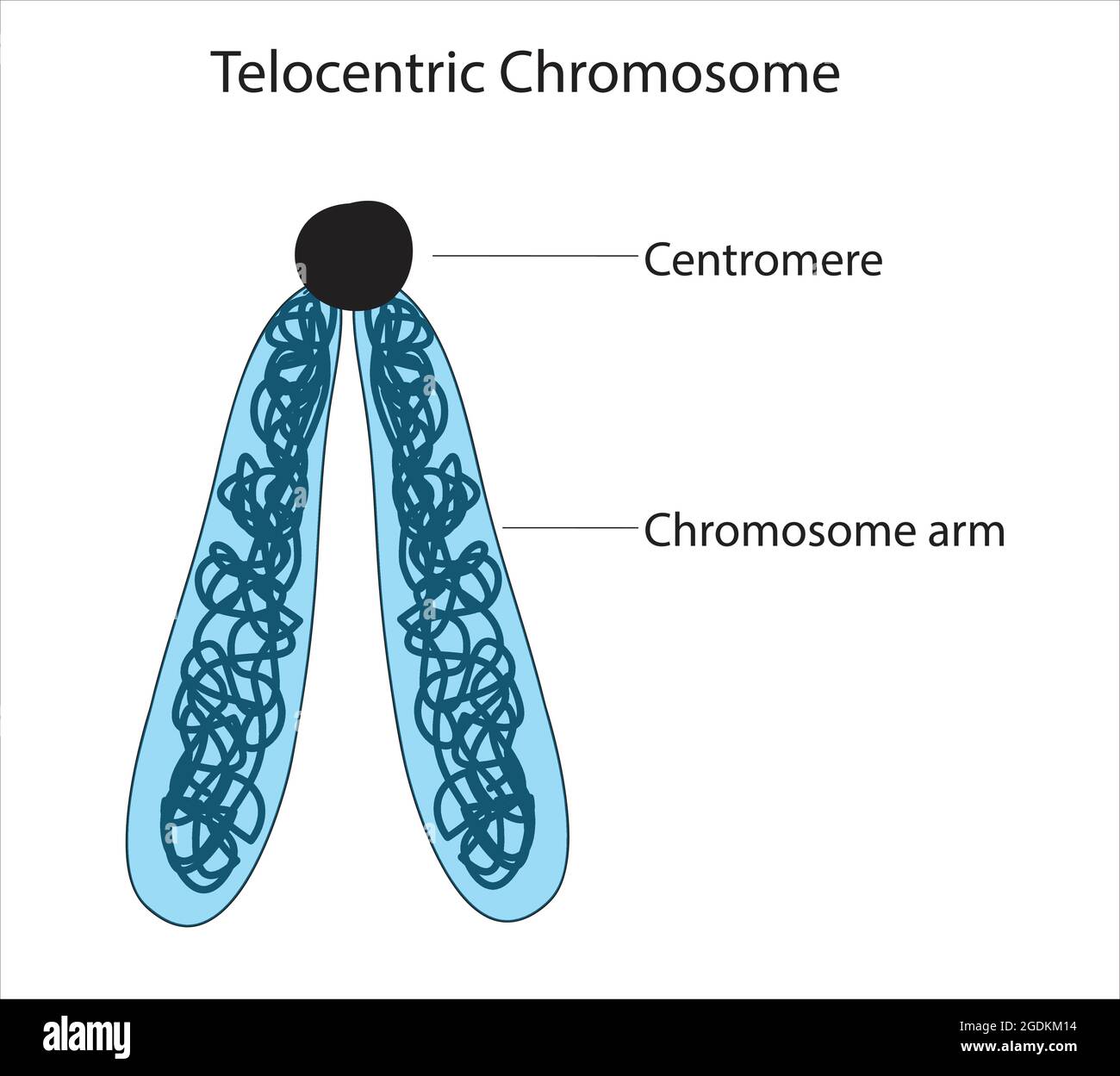
Telometric Centromere
Centromere is at the end of chromosome, no p or q arm
P arm of Chromosome
Short end of chromosome
Q arm of chromosome
Long end of chromosome
Giesma Banding
Type of chromosome banding used to identify human karyotypes
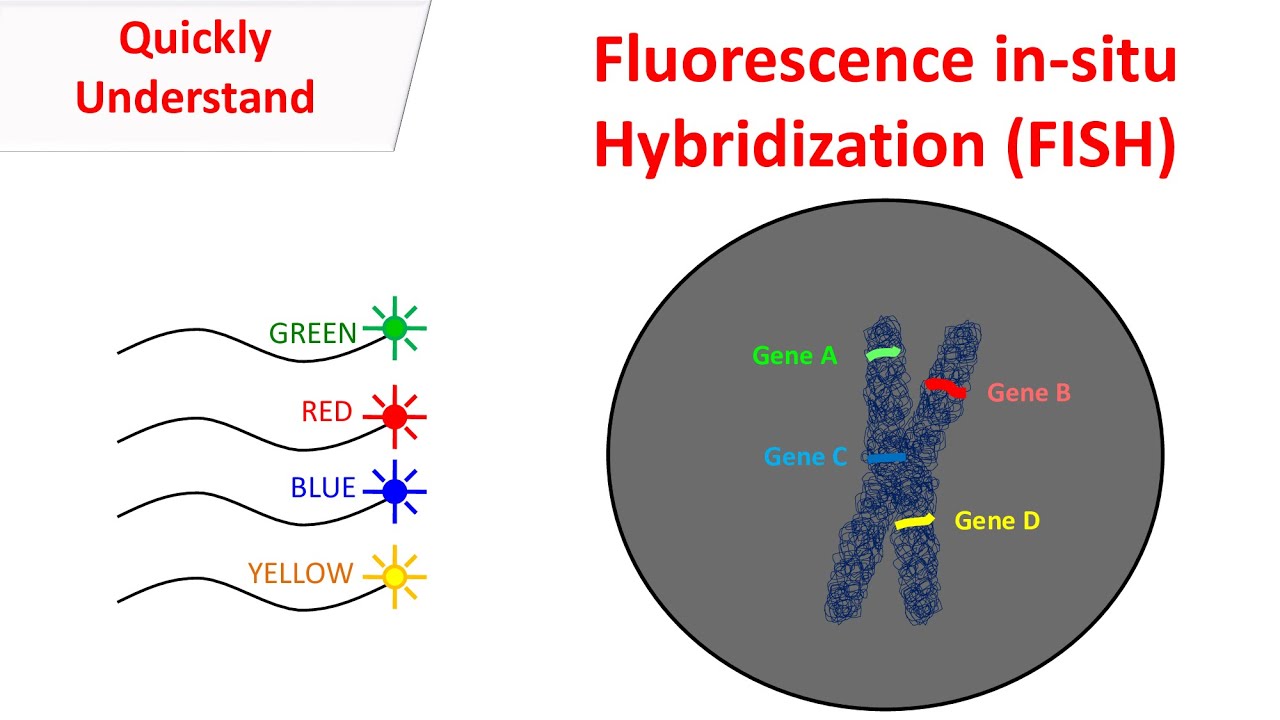
FISH (Florescent in situ hybridization)
Provides different colors for chromosome pairs, can be used to detect microdeletions
Euchromatin
Regions of chromosome less condensed during interphase, contains less actively expressed genes
Heterochromatin
Condensed regions of chromosome
Facultative: sometimes condensed, sometimes non condensed
Constitutive: Always condensed, usually near centromere or telomeres
Interchromosomal Domain
Region in nucleus where transcriptionally active parts are found
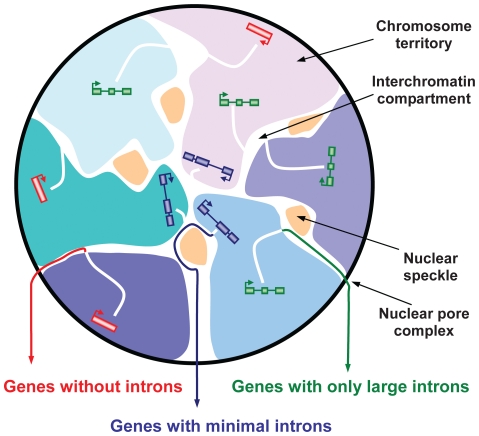
Chromosome Territory
Early replicating parts found near center, later ones found near peripheral
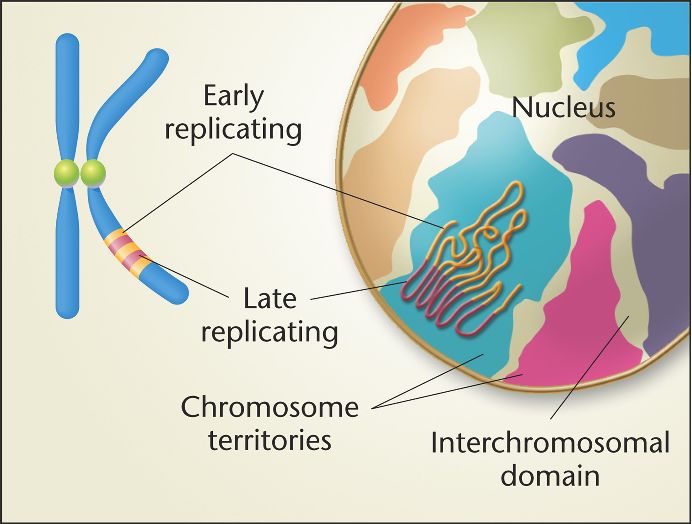
Centromere Structure
Composed of kinetochore proteins and spindle microtubles, constitutively heterochromatic
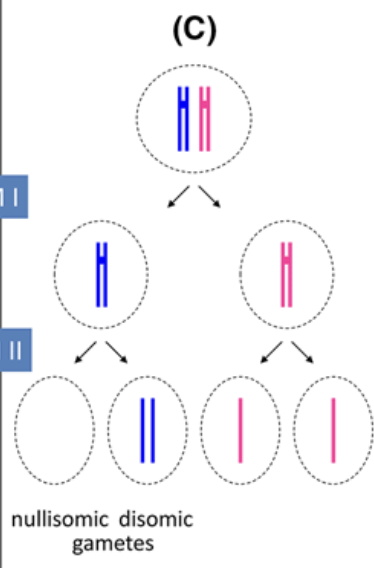
Nondisjunction: Meiosis I
Failure of chromosomes to seperate in anaphase of meiosis I, leads to all offspring to be aneuploid, with either (2n+1) or (2n-1) after gamete addition
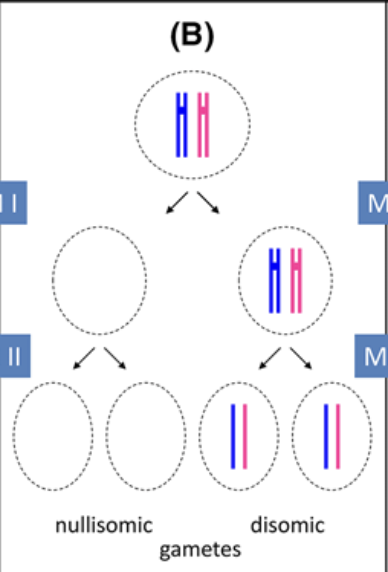
Nondisjunction in Meiosis II
Failure of chromosomes to seperate during anaphase of meiosis 2, leading to half of the offspring to be aneuploid (one 2n+1, the other 2n-1 after gamete addition)
Klinefelter syndrome
Chromosome 47, XXY Trisomy
Jacob Syndrome
Chromosome 47, XYY Trisomy
Triple X syndrome
Chromosome 47, XXX Trisomy
Turner Syndrome
Chromosome 45, XO
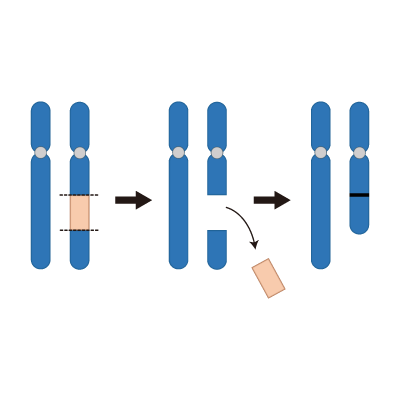
Intersitial Deletioin
Partial chromosome deletion caused by a chromosome breakage at 2 points
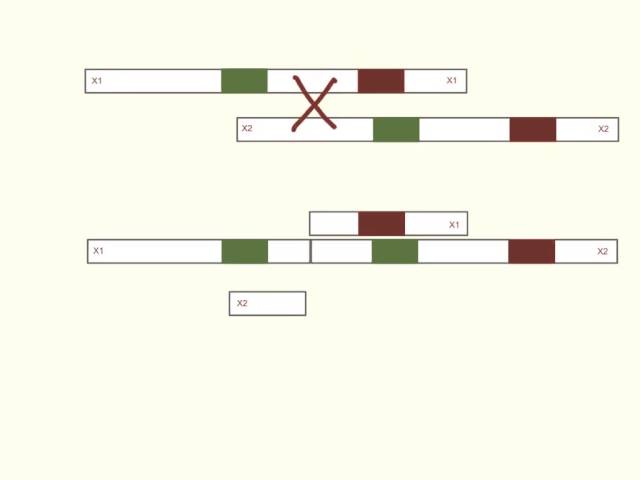
Unequal Crossover
Misalignment of chromosomes during cross over, results in the partial deletion of one chromosome and the partial duplication of another
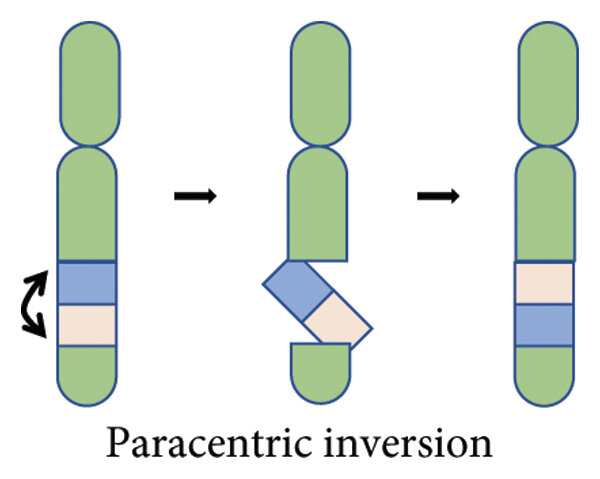
Paracentric Inversion
Centromere is outside the inverted region that is reattached
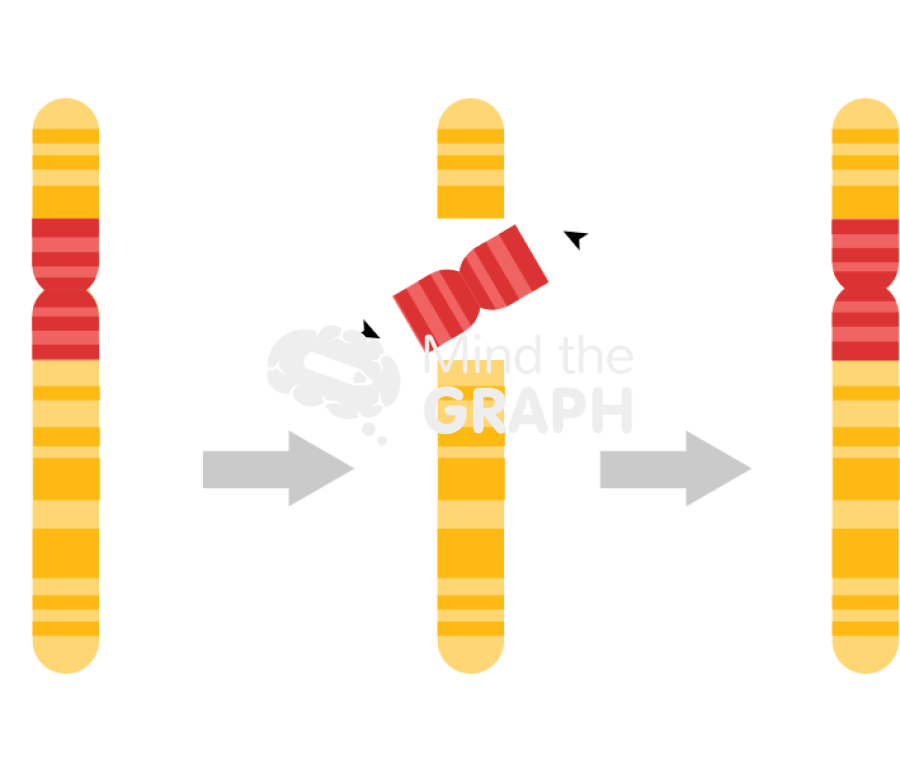
Pericentric Inversion
Centromere included in the inverted region that is reattached
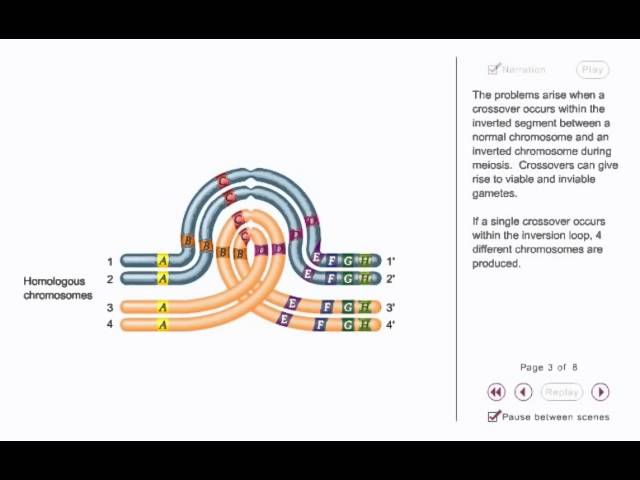
Inversion Loop
Caused by alignment of normal and inverted homolog, crates a dicentric chromosome leading to a loss of the acentric fragment
Unbalanced Translocation
Translocation of fragment to another non-homolog, with no swap
Balanced Translocation
Swap of fragments of non homologs
Mutation Hotspot
Gene where mutations occur at an elevated frequency, usually cause by a larger gene size
Base pair mutation
A base pair of a codon-anticodon is swapped
Transition Mutation
A pyramidine/purine nucleotide is swapped with another (C→U, G→ A)
Transversion Mutation
A purine is swapped with a pyramidine, or vice versa (C/U/T→G/A)