Pharmacology II Unit 3 Review
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Cancer Treatment Modalitites…
Primary Induction Chemotherapy: used for advanced cancers
Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: used for localized cancers which surgery is incomplete effective
Adjuvant chemotherapy: complementative therapy to early surgery
Cell Cycle Specific anticancer drugs (CCS) Outline
G1 → S Phase: topo II; etoposide; topo I; irinotecan
S phase: antimetabolites; capecitabine, 5-FU, methotrexate
G2 phase: Doxorubicin
M phase: paclitaxel, vincristine
Cell Cycle Non-specific anticancer drugs (CCNS) Outline
Alkylating agents: cyclophosphamide
Platinum analogs: carboplatin, cisplatin
Cancer Chemotherapy Drug Resistance Mechanisms:
Either primary/spontaneous or acquired means of resistance
Gene mutations
Increased DNA repair capabilities
Efflux of drug
Production of “scavengers” → neutralize cancer drugs
Altered drug metabolism (decreased activation of pro-drugs, increased deactivation of active drugs)
Immortalization due to telomere lengething…
Alkylating Agents Overview
Cytotoxic chemotherapy… NON-cell cycle specific
→ MOA: covalent attachment of alkyl groups to DNA and associated protein
Interference with DNA leads + DNA lesions to programmed cell death
Mispairing
Ring opening
Cross-linking
cyclophosphamide, platinum agents
Cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide: DNA Alkylating anti-cancer agent
Pro-drug
High ORAL bioavail
ADR:
Production of Acrolein toxic byproduct → accumulates in bladder; hemorrhagic cystitis
MESNA co-treatment: complexes with acrolein and incativates it
Resistance Mechanism…
Increased inactivation of drug
Increased DNA repair mechanisms
Decreased PRO-DRUG ACTIVATION
Platinum Alkylating Agents…
Cisplatin and Carboplatin (reduced nephrotoxicity)
→ MOA: inter and intra-strand cross links attach DNA together → p53 tumor suppressor activation AND cell death
IV admin
ADR:
Ototoxicity
Nephrotoxicity → dose limiting
Nausea/vomiting induced dehydration
Resistance Mech: p53 mutation
Doxorubicin/Daunorubicin
Doxorubicin/Daunorubicin (Anthracyclines) → Targets S phase (DNA replication and division) (CCS)
→ MOA: topoisomerase II inhibition, intercalation into DNA helix, O2 radical production, DNA/RNA strand scission leads to cell death
ADR: heart failure, GI toxicity
Doxorubicin can be complexed with dexrazoxane to mitigate free radical formation
Bleomycin
Bleomycin (Glycopeptide) → Targets G2 phase (CCS)
→ MOA: intercalation of DNA, iron (Fe+) binding, free radical generation; apoptosis
used for testicular cancer curative agent in combo
ADR: pulmonary fibrosis leads to lifetime dosing consideration
inactivated by bleomycin hydrase
Methotrexate
Methotrexate → S phase specific CCS (Antimetabolite chemoTX)
→ MOA: decreases purine precursors by blocking folate conversion
Competitive inhibitor of dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR)
Inhibition of BOTH purine and pyrimidine synthesis
ADR: mucosal ulcers, teratogenic due to folic acid needed for fetus
Polyglutamation for MTX: traps MTX within cancer cell
→ via folic polyglutamate synthase (enhanced activity in cancer cells)
Decreases lipid solubility and traps MTX in cancer cells
Mechanism of Resistance:
Altered DHFR (binding site mutation)
Decreased MTX uptake
Decreased Polyglutamation
Methotrexate Rescue
“Folinic acid rescue”: MTX administered with Leucovorin (reduced folate)
→ protects non-tumor cells by providing folate
5-Fluorouracil 5-FU
Thymidylate Synthase Inhibitor (anti-metabolite chemo) ((CCS S phase))
→ Pro-drug activation into 5-dUMP → inhibition of thymidylate synthase enzyme
Decreases Base pair produciton therefore decreases DNA replication
Inhibition of RNA processing
Incorporation into DNA
Mechanism for Resistance:
Decreased pro-drug activation
Altered thymidylate synthase enzyme binding site
ADR:
Mucositis
Hand-foot syndrome
Catabolism of 5-FU:
→ Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPYD) = rate limiting step in pyrimidine catabolism
Individuals with decreased DPD are unable to metabolize 5-FU away effectively
Toxic levels of 5-FU accumulation
Pharmacogenomic testing needed
Lower 5-FU dose for those with poor DPD function
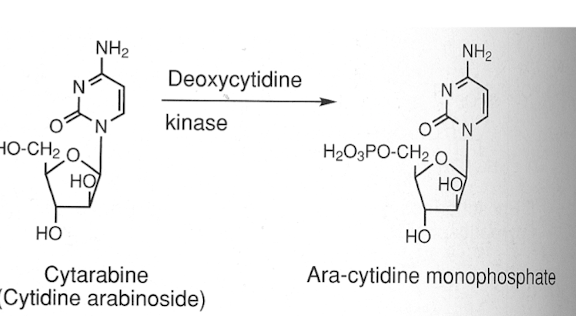
Cytarabine (Ara-C)
Cytarabine (Ara-C): purine/pyrimidine analogs
→ MOA: incorrect substrates for DNA/RNA leads to chain termination during S PHASE (CCS)
Competitive inhibitor of DNA polymerase
Activated via deoxycytidine kinase into active form of analog
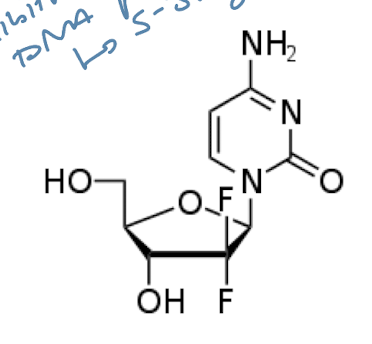
Gemcitabine
Gemcitabine: Purine/pyrimidine analogs
→ fluorinated cytidine analog for S-PHASE SPECIFIC CYTOTOXICITY
Competitive inhibitor of DNA Polymerase; inhibits DNA synthesis
Early chain termination
Azathioprine (AZA)
Purine Metabolism Inhibitors…
Azathioprine (AZA): pro-drug converted to 6-Mercaptopurine → 6-TGNs (S-PHASE CCS)
The drug used hypoxanthin-guanine phosphoribsoy HPRT enzyme for pro-drug activation
6-TGNs incorporated into DNA/RNA and arrest replication → trigger cell death
Resistance: decreased HPRT activity, increased inactivation via TPMT
Allopurinol interferes with azathioprine metabolism → leads to TOXIC accumulation of 6-MP
→ co-administration of 6-MP + allopurinol reduced 6-MP dosing
Microtubule Polymerization: M-PHASE SPECIFIC CCS
Vincristine/Vinblastine: inhibit polymerization/formation of microtubules; Mitotic Arrest (M)
Vinblastine: myelosuppression, Vincristine: peripheral neuropathy
Decreased microtubule stabilization inhibits Mitosis from occurring in dividing cells
Taxanes: Paclitaxel/Docetaxel: inhibit DE-polymerization of tubules (locks them together) (M)
Abraxane (paclitaxel liposomal re-formulation) decreases hypersensitivity
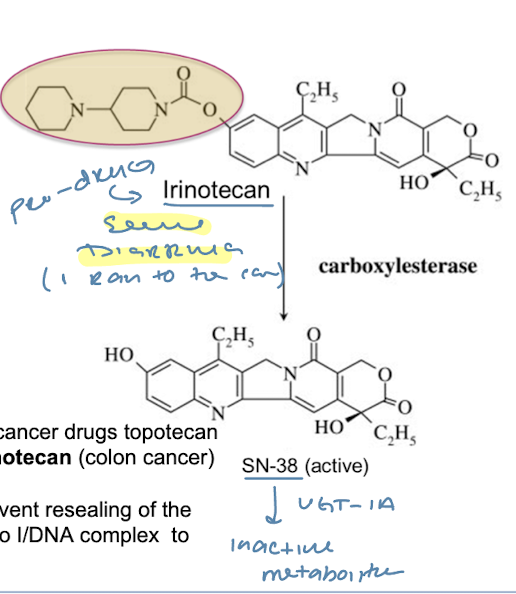
Topoisomerase I Inhibitors
M-phase specific CCS
Irinotecan: pro-drug converted into active form SN-38 via Carboxylesterase
→ MOA: inhibition of topo I leads to double strand DNA breaks
ADR: severe GI and diarrhea side effects
Topoisomerase II Inhibitors
Etoposide → accumulation of strand breaks; prevents re-ligation of broken strands
M-phase arrest
Protein-Kinase Depedent Pathways…
ErbB family → EGFR, Her2/neu
Receptor tyrosine superfamily: IGF-1R, VEGF, PDGFR
RAS-RAP-MAPK
BCR-Abl (non-RTK)
PI3K-Akt
EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor
EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor
→ increased expression in cancer cells
Activation of EGFR cascade → cell proliferation, apoptosis inhibition
Erlotinib: direct EGFR receptor antagonist binds INTRACELLULARLY to TK DOMAINS
→ oral, small molecule, tyrosine kinase inhibitor
ADR: diarrhea, skin rash, anorexia, hand-foot skin reactions
Lapatinib: EGFR/HER2 dual inhibitor (tyrosine kinase inhibitor)
Cetuximab, Trastuzumab → EGFR extracellular biologics mAb
Directed against EGFR
ADR: infusion reactions, hypomagnesemia
mAb Mechanism of Resistance: mutated KRAS
→ constitutively activated allowing for EGFR-independent growth of cancer cell
Bcr-Abl + Philadelphia Chromosome…
→ transduction of genetic material from normal chromosome 9 ←→ chromosome 22
Extended chromosome 22
Bcr-Abl fusion results in: constitutively ACTIVE Abl TK activity: cancer cell growth for Myelogenous Leukemia
Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor FOR Bcr-Abl Kinase…
Imatininb (Gleevec): direct Bcr-Abl kinase
Binds catalytic pocket and inactives kinase enzyme
Cancer treatment: kills rapid divide cells
Resistance Mech: mutation of Bcr-Abl binding domain
→ T315 mutants: steric clash PREVENTs imtainib binding
Bevacizumab
Bevacizumab: binds VEGF and prevents signal cascade for cell growth
ADRs
Severe hypertension
Risk of bleeding
Congestive heart failure
Preforation of nasal septum, bowel, stomach
Sorafenib/Sunitinb
Sorafenib/Sunitinb: VEGF Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (platelet-derived growth factor receptor)
→ MOA: inhibits ATP binding kinase domain (decreases signal cascade)
ADRs
Skin rash
Hand-foot syndrome
Cardiac dysfunction
Proteinuria
Resistance: mutated FLT3 leads to growth factor-indepdent cell signaling
Everolimus
Everolimus: Analog of rapamycin…
Antifungal/anti-neoplastic → inhibits MTOR pathway; decreased cell survival
Proteasome Pathway and Cancer…
Proteasome Pathway and Cancer…
Ubiquitin is needed for cellular degradation of proteins
→ cancer cells deplete ubiquitin levels to evade protein lysis allowing for cell survival
Proteasome inhibitors: prevent degradation of pro-cell death proteins:
E3 ligase targets, EGFR, p53, cyclin, cyclin-depedent kinases
Bortezomib
Bortezomib: Proteasome inhibitor…
→ prevents degradation of pro-apoptotic proteins
Leads to increased misfolded proteins, decreased cell function, and cell death
ADR: shingles (prophylactic acyclovir), heart failure
Non-Hodkin’s Lymphoma Neoplastic B cell Target Summation.
Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: cancer arising from overgrowth of cancerous B-cells in blood
→ CD20 protein: expressed on surface of normal and malignant B cells
mAb targeting of CD20 allows for antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity
Results in short term immune deficiency (due to wiping of both normal and cancerous B-cells)
CD20 is NOT expressed on naive, B-cell progenitors allowing for replenishment of B-cells after treatment
CD20 Receptor Antibodies…
→ Rituximab and Obinutozumab
Bind to CD20 on malignant (and normal) B-cells
Does not target healthy B-cell precursors….
Rituximab: B-cell CD20 mAb
Blocks CD20 signaling
Recruits NK cells
Recruits Macrophages
Employes complement system
Resistance: decreased complement activation, decreased CD20 expression
ADR: neutropenia, fever, and infusion reactions
Obinutuzumab: CD20 B-cell mAb targeting
Ibritumomab: CD20 B-cell mAb conjugated with radioactive yttrium-90 to enhance killing of cancer B- cells
PD-1 and PD-L1…
PD-1: programmed death receptor: expressed on activated immune cells
Inhibited when bound to PD-L1
PD-L1: expressed by tumor cell to bind PD-1 and inhibit T-cell killing it
Tumor cells overexpress
PD-L1 to evade destruction via T-cells by PD-1 binding immune suppression
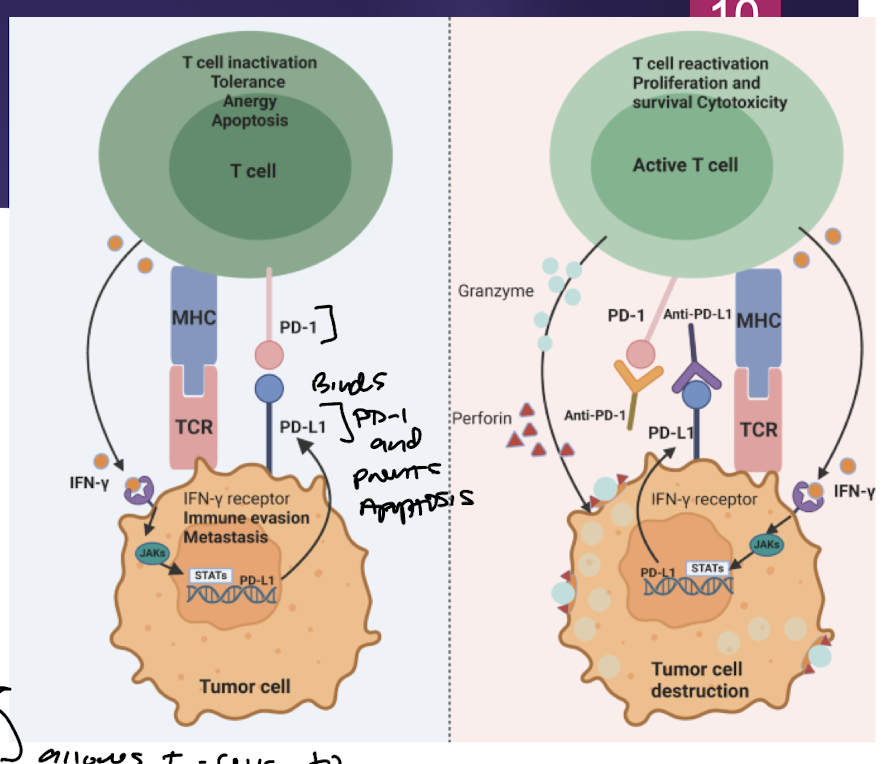
Pembrolizumab and Nivolumab
PD-1 Targeted mAb → block T-cell’s PD-1 from being bound and inactivated by PD-L1 on tumor cell
Pembrolizumab and Nivolumab
ADR: immune mediated organ inflammation, immune mediated hashimoto’s hypothyroidism
Ipilimumab
CTLA-4: immune down-regulation receptor expressed on T-cells
→ cancer cells upregulate CTLA-4 to inhibit immune response
Ipilimumab
Blocks CTLA-4 expression on tumor cells allowing for cytotoxic T-cell action
CAR-T Cell Chemo Treatment
→ collection of patient’s T cells
Modifcaiton to express CAR protein → allows targeting of cancer cells
Re-infusion into patient who has been conditioned…
Downside:
Conditioning chemotherapy
Reduces current T-cell population
Allows for repopulation of modded T-cells
ADR:
Cytokine Release Storm
→ too potent immune response after CAR-T infusion
Dangerous high fever
Drops in blood pressure
Treat with steroids to avoid
Tisagenlecelucel
Tisagenlecelucel: gene therapy
mAb that targets CD19 expressing B-cells
B-cell lymphoma
Follicular lymphoma
ADR:
cytokine release storm
Immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome