Evolution Honors Bio
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
species
A group of similar organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring.

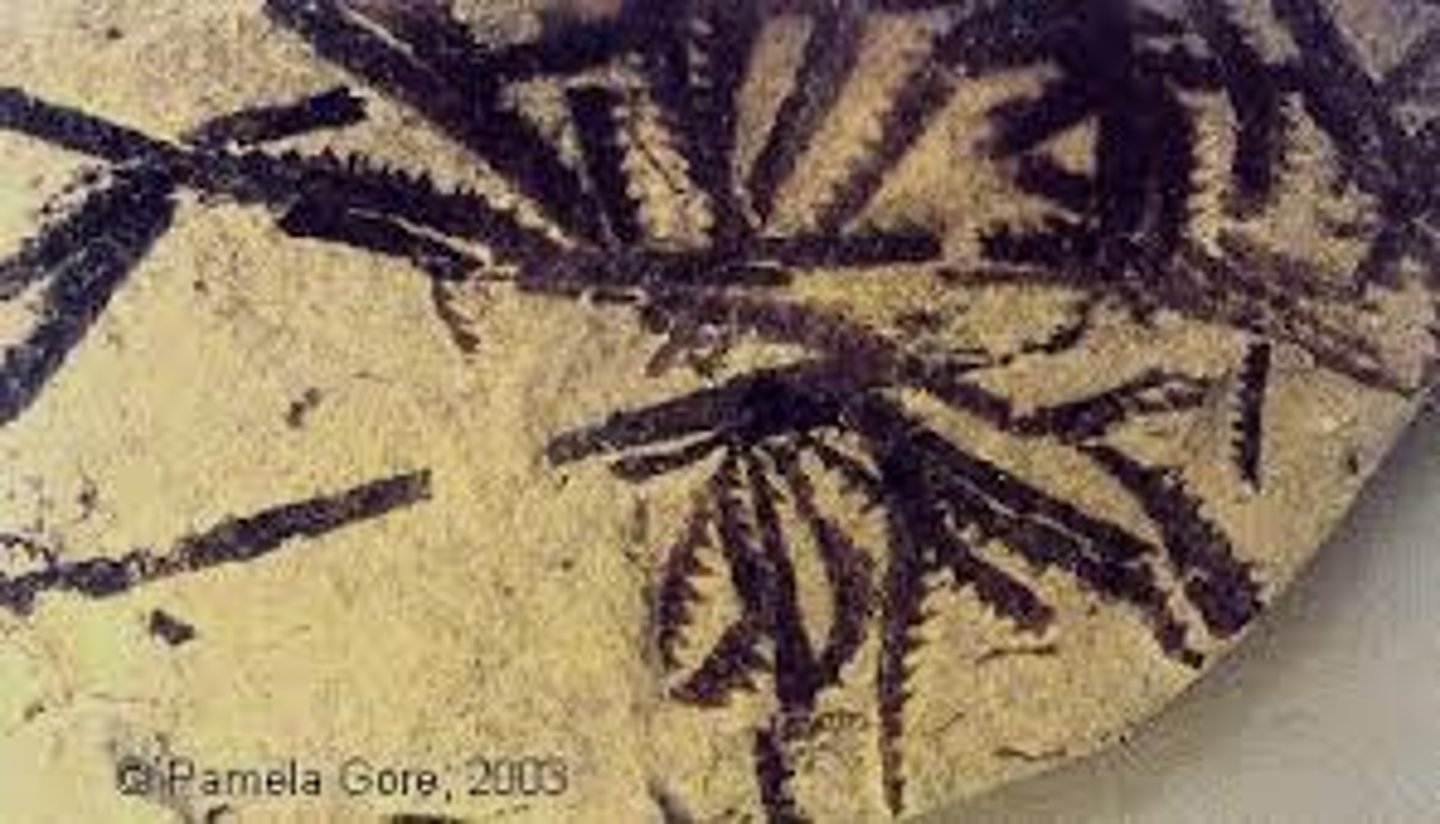
fossil
A trace of an ancient organism that has been preserved in rock

adaptation
A trait that helps an organism survive and reproduce
evolution
Change in a kind of organism over time; process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms.
scientific theory
A well tested concept that explains a wide range of observations

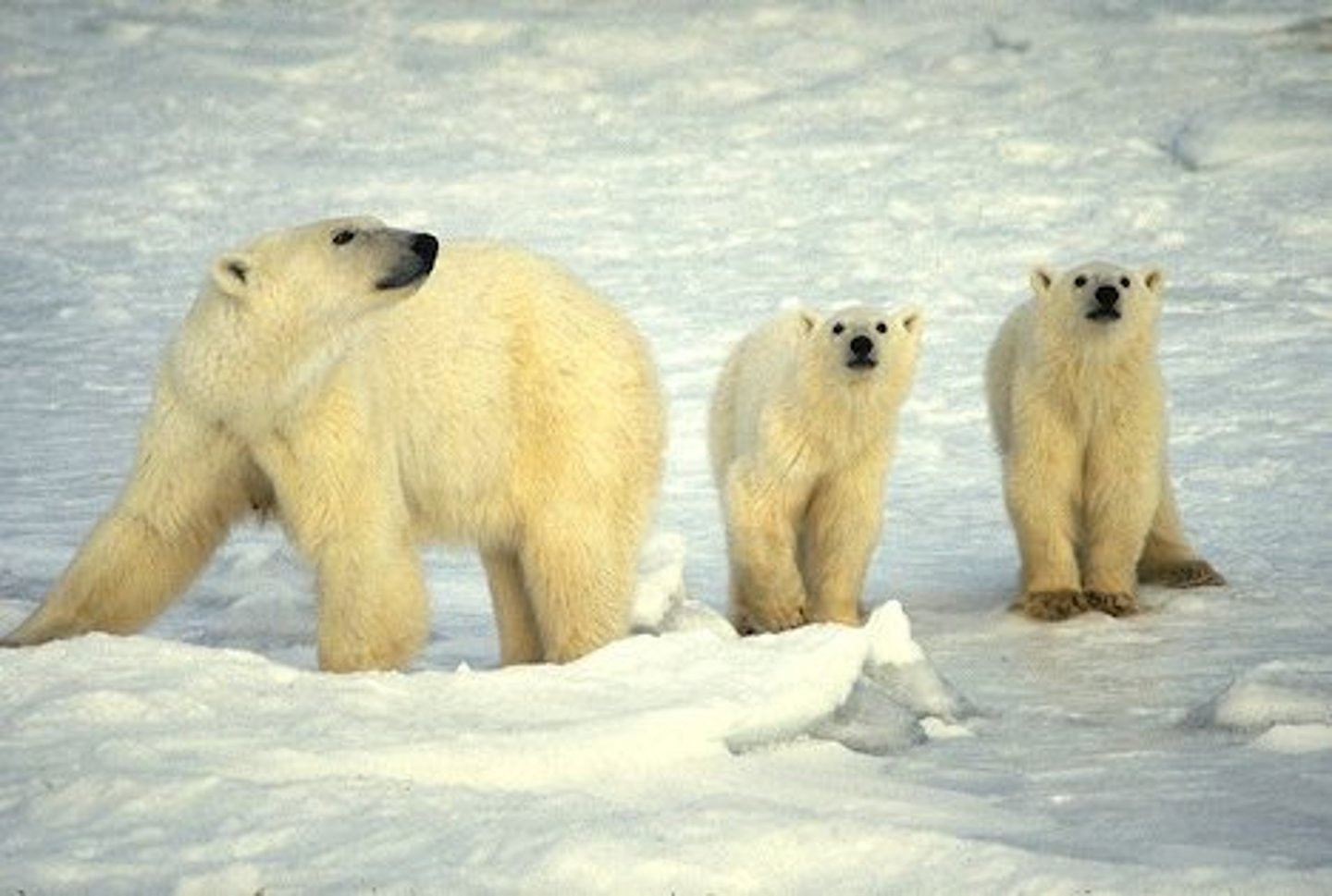
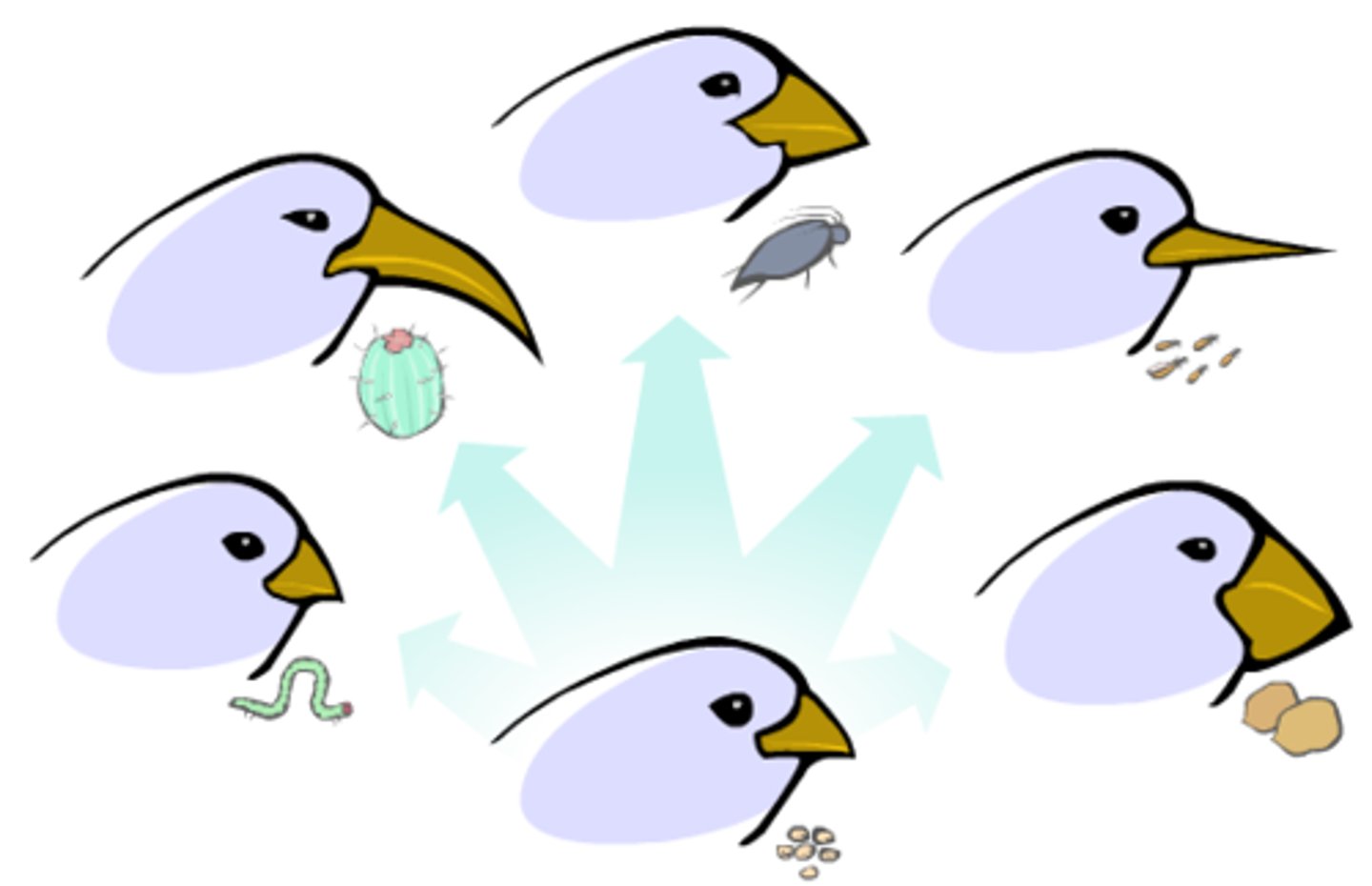
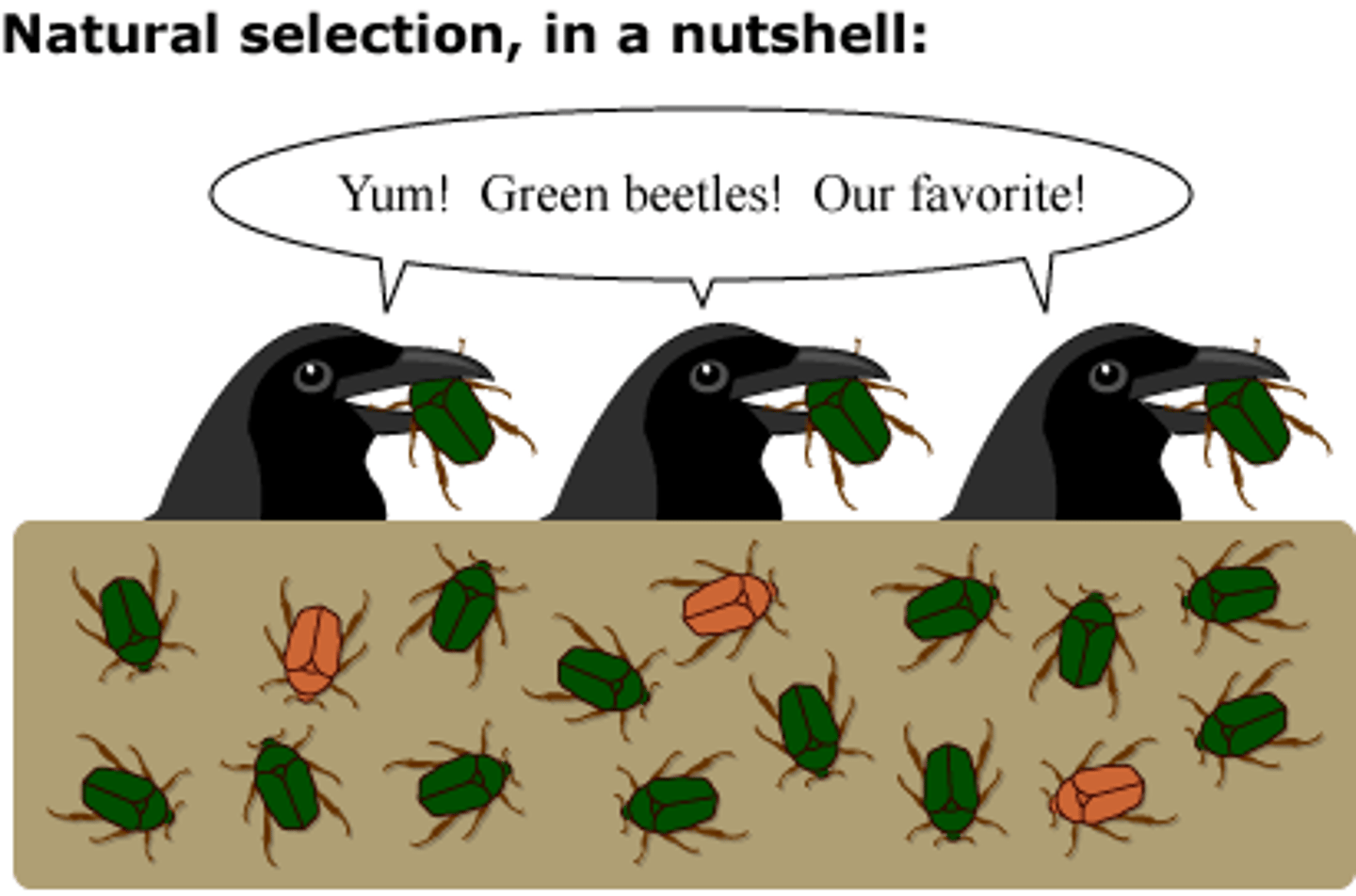
natural selection
Process by which individuals that are better suited to their environment survive and reproduce most successfully; also called survival of the fittest
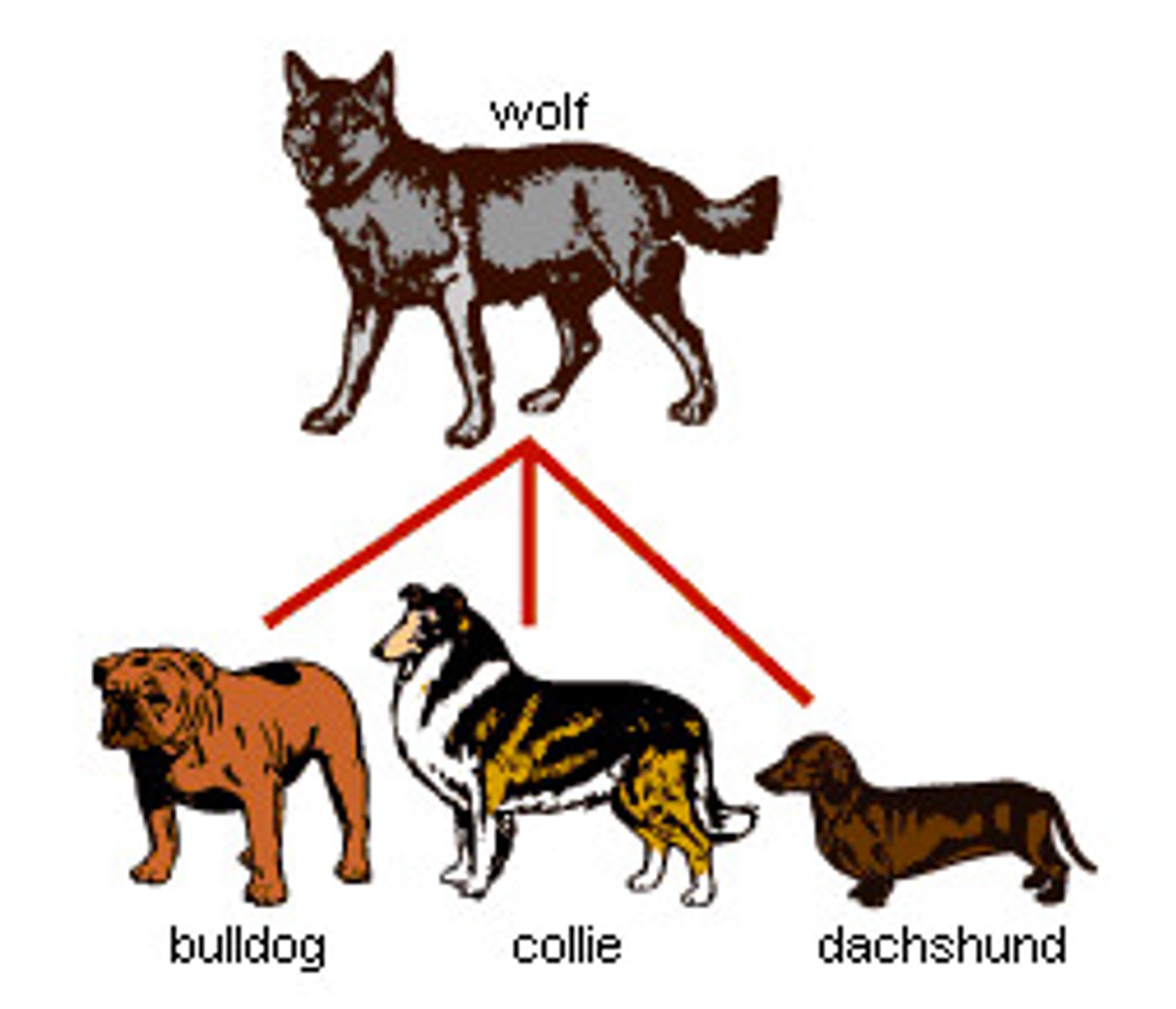
artificial selection
Selection by humans for breeding of useful traits from the natural variation among different organisms
variation
Difference among members of a species.
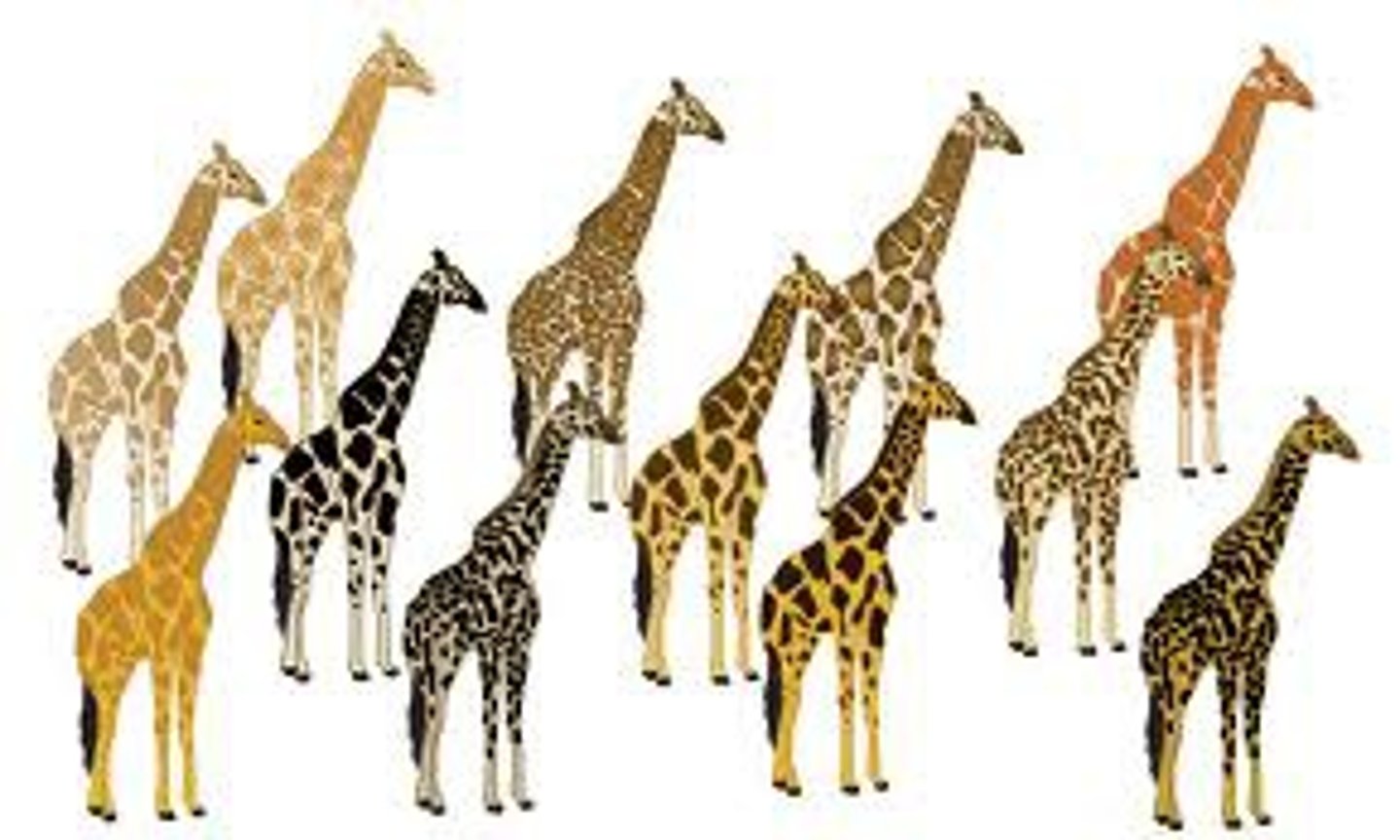

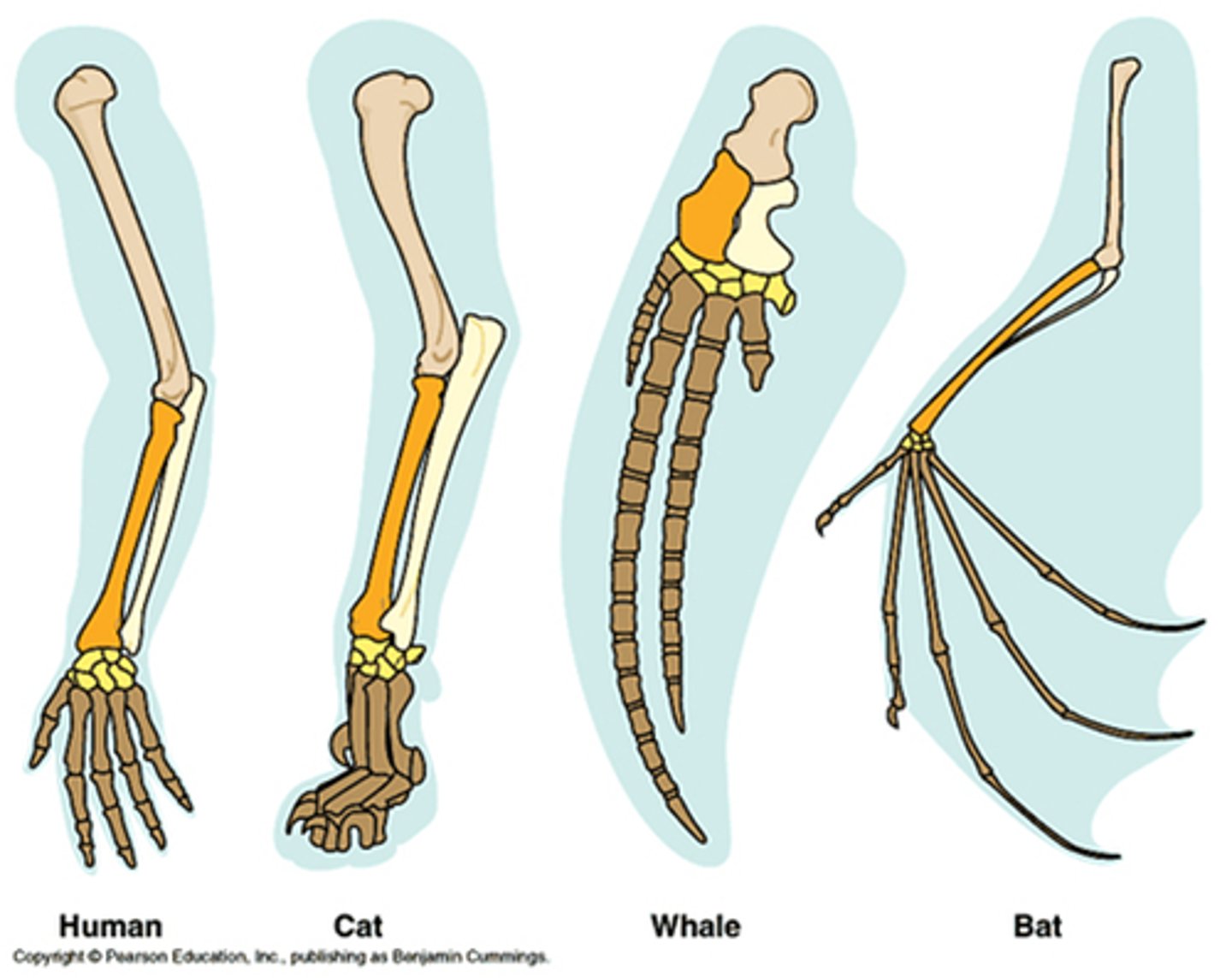
homologous structures
Structures in different species that are similar because of common ancestry.
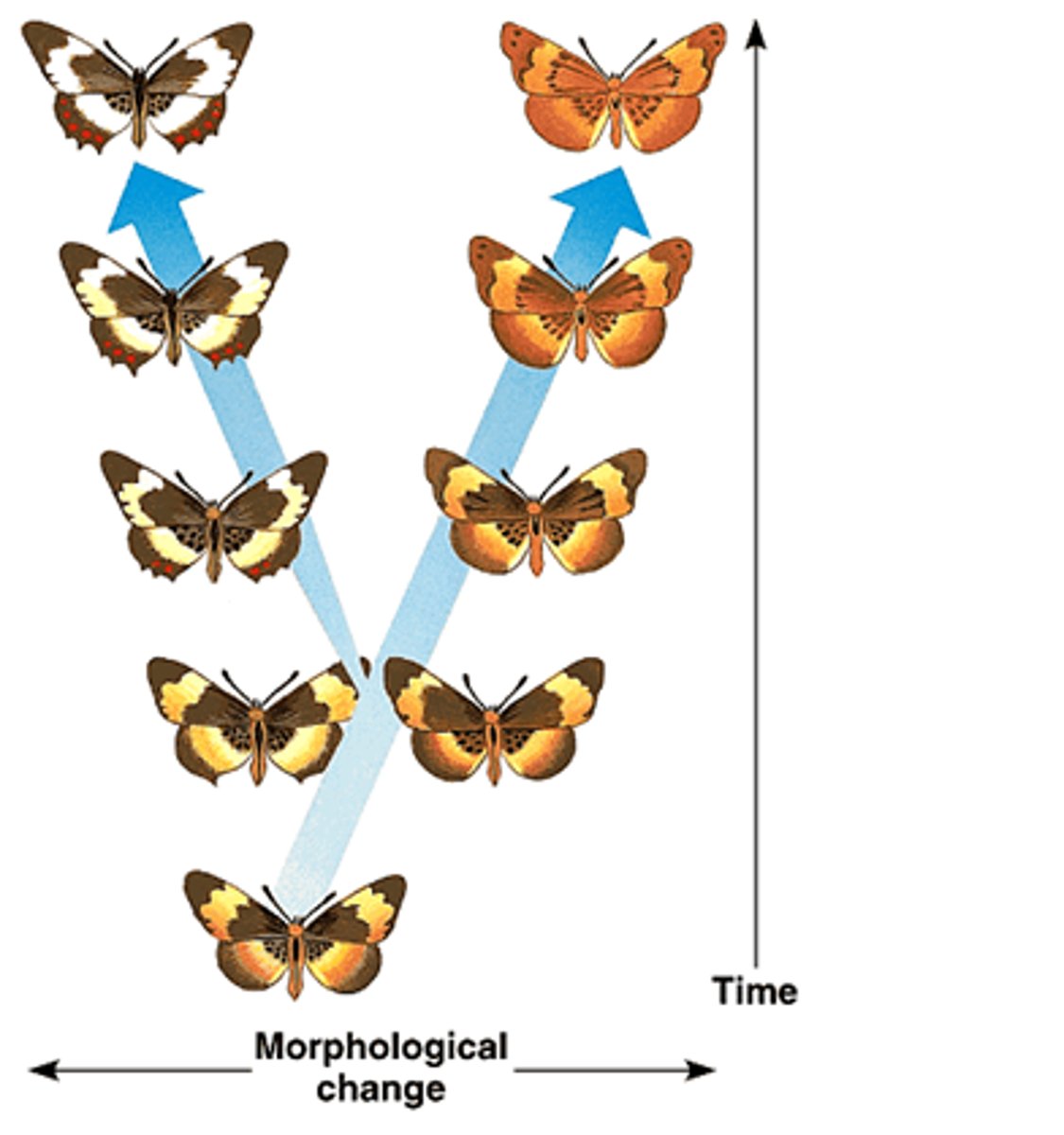
gradualism
The theory that evolution occurs slowly but steadily
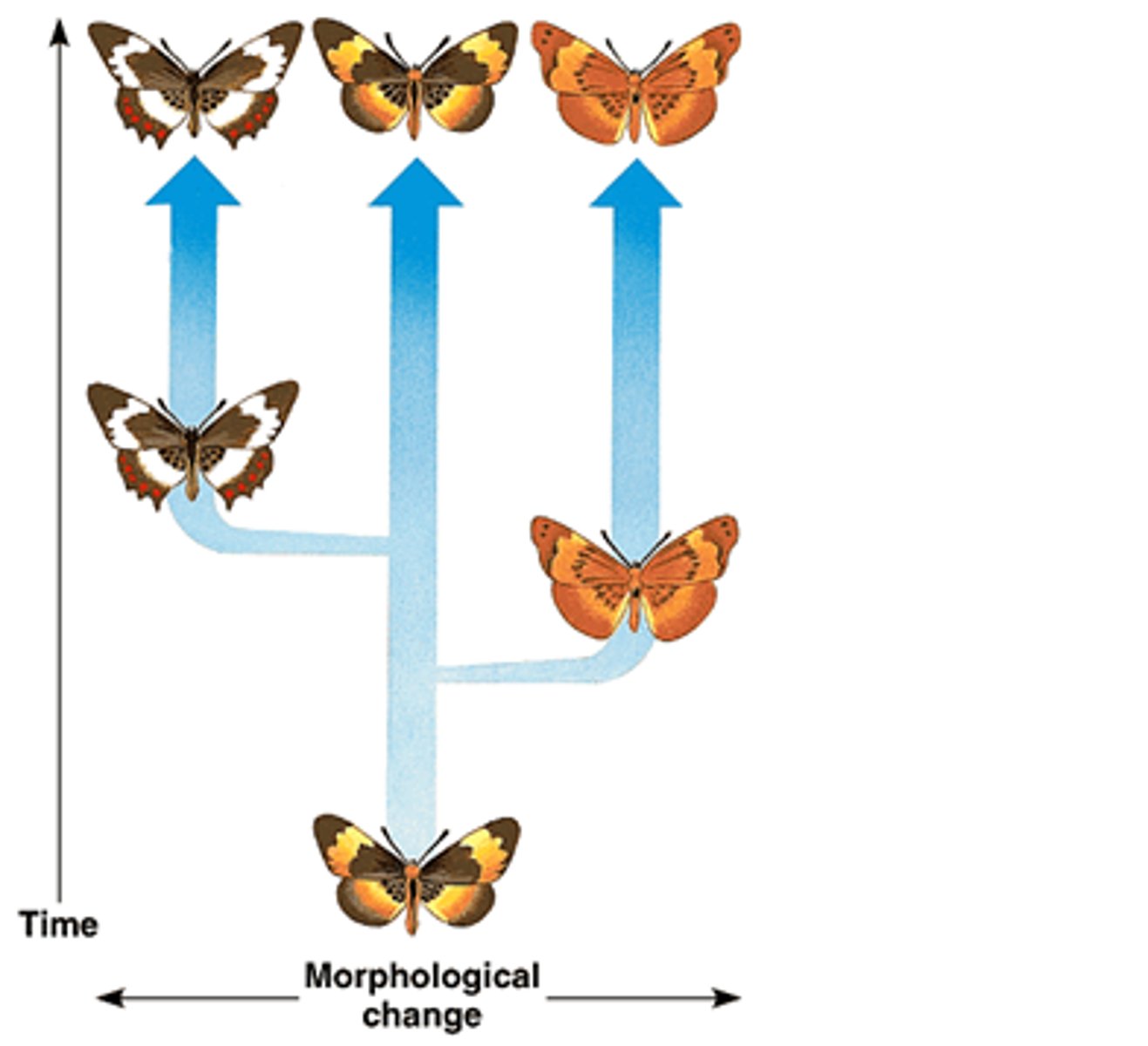
punctuated equilibrium
Pattern of evolution in which long stable periods are interrupted by brief periods of more rapid change
Charles Darwin
Traveled to the Galapagos Islands on the HMS Beagle and later wrote the book "The Origin of Species."

Overproduction
Strategy in which organisms make more offspring than will actually survive.

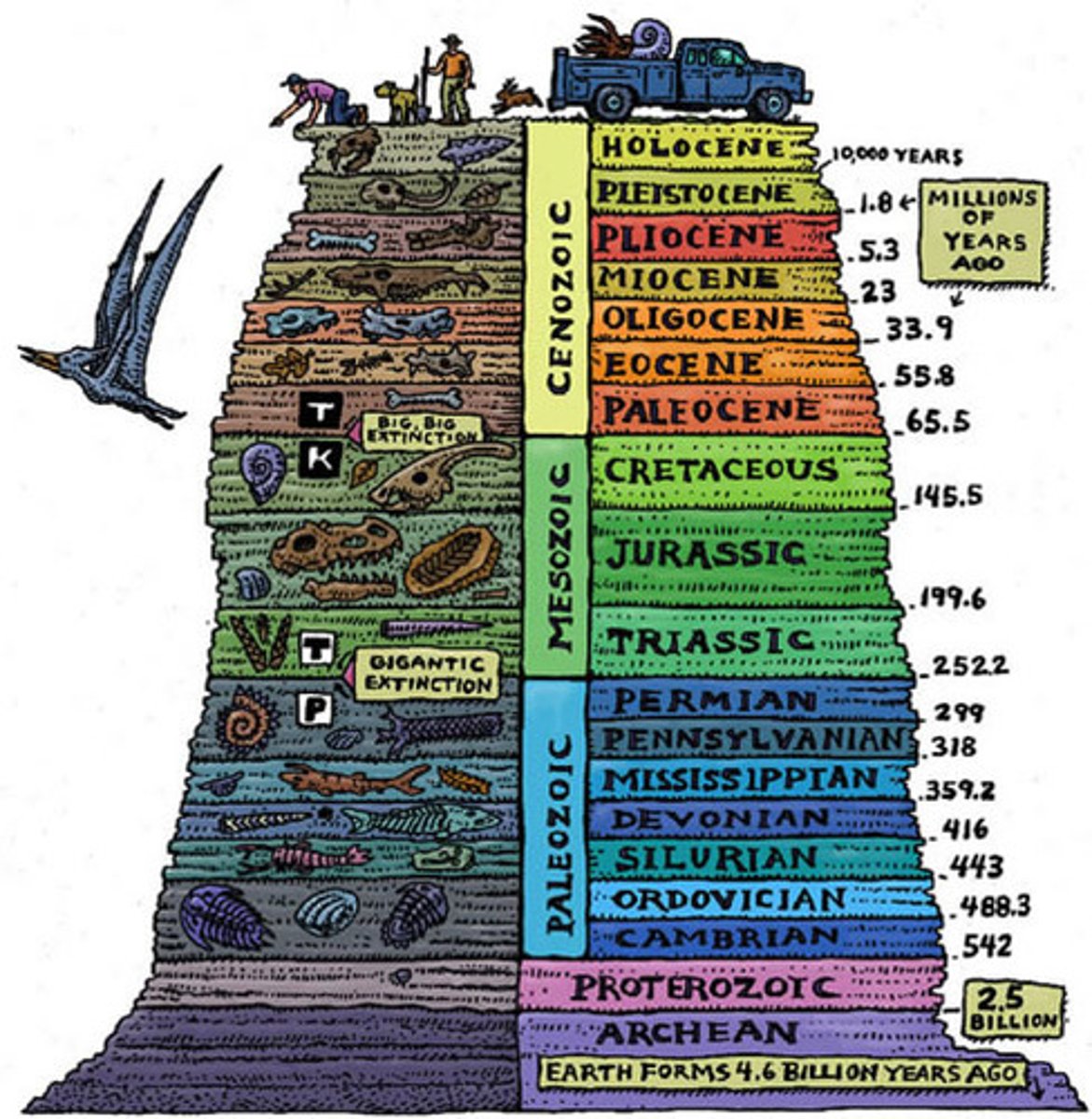
Fossil Record
All the fossils throughout the history of the Earth that are used as evidence of evolution.
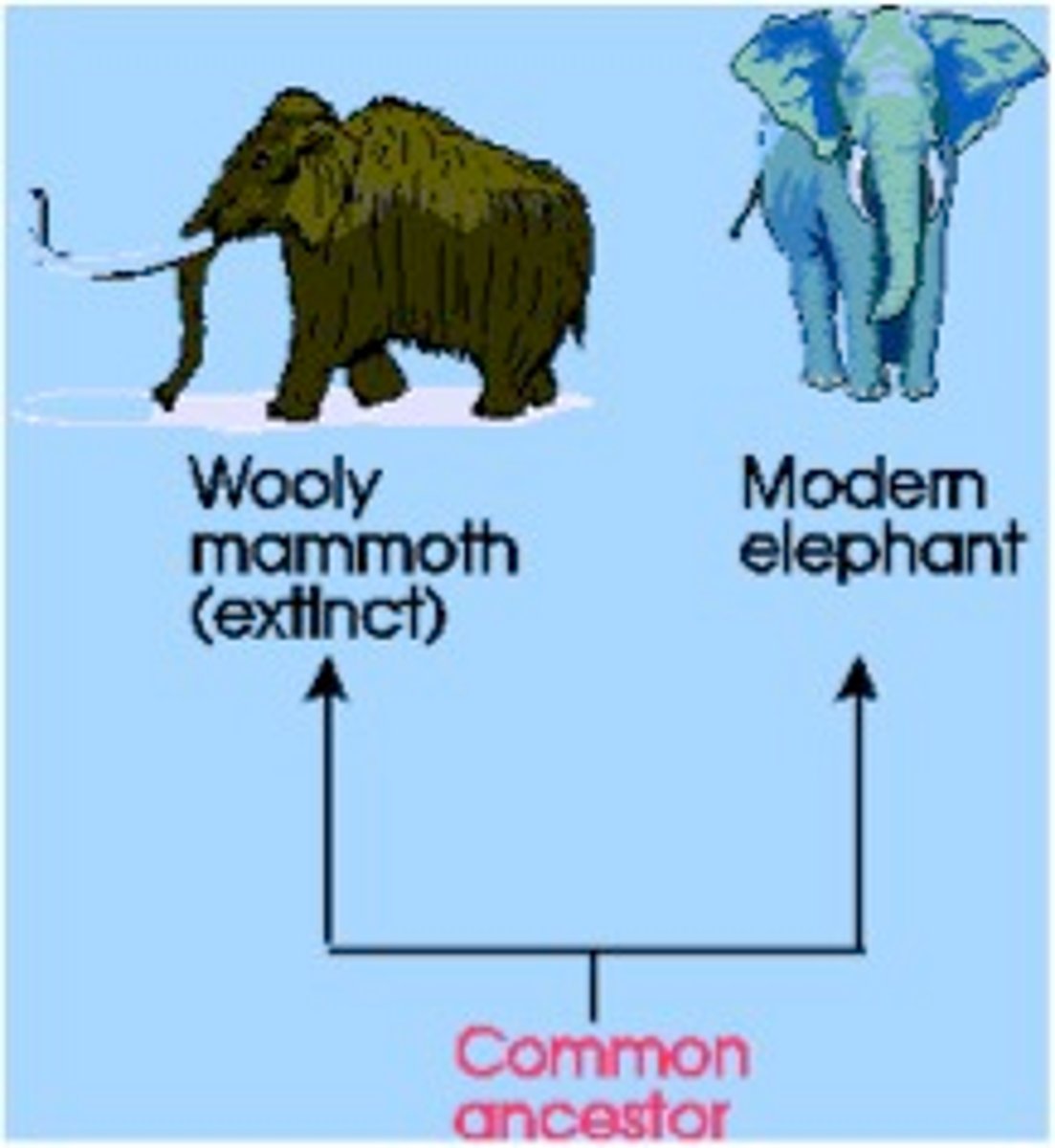
Common Ancestor
An ancestral species from which later species evolved
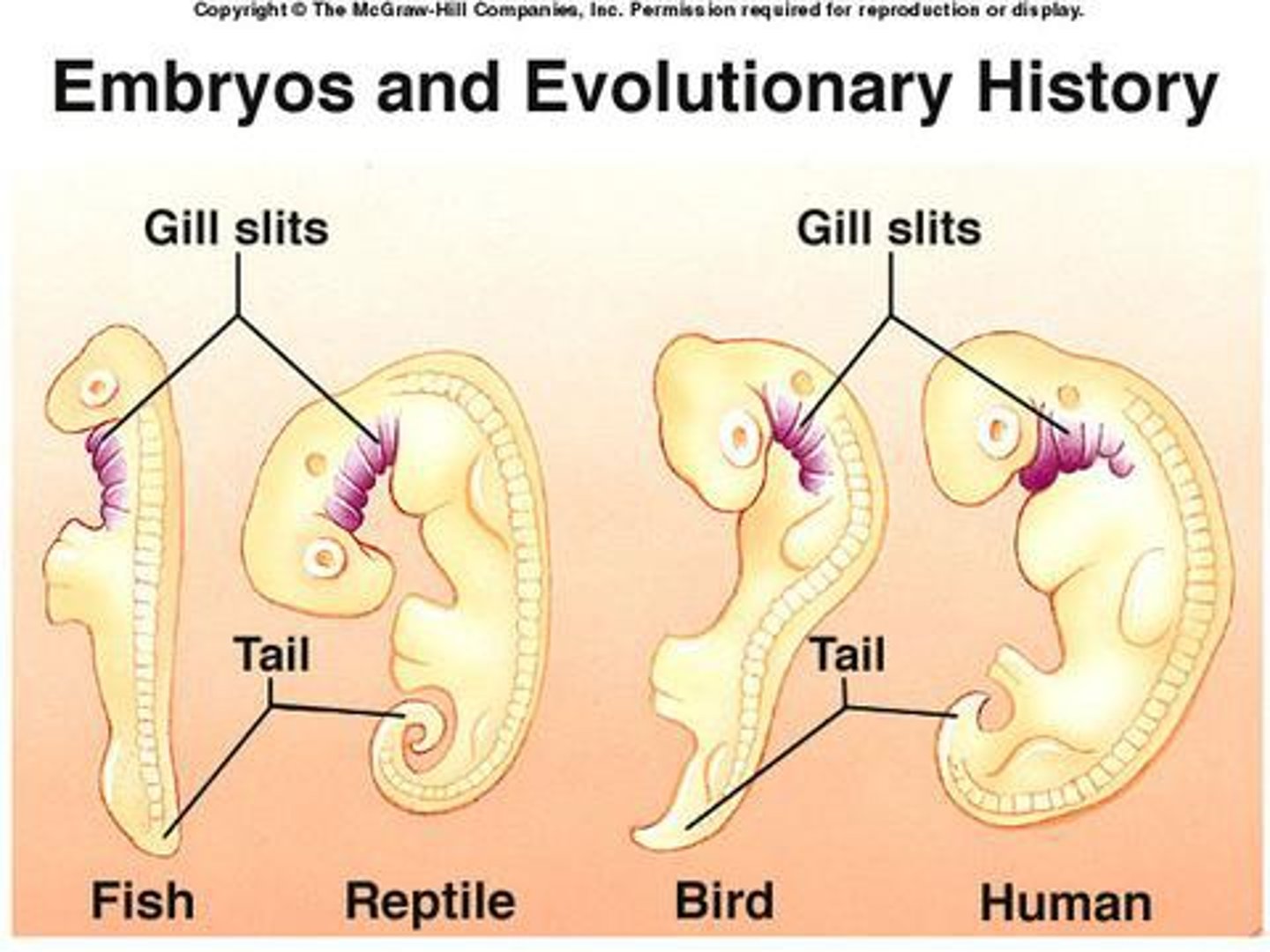
Embryology
Study of developing embryos used as evidence of evolution.
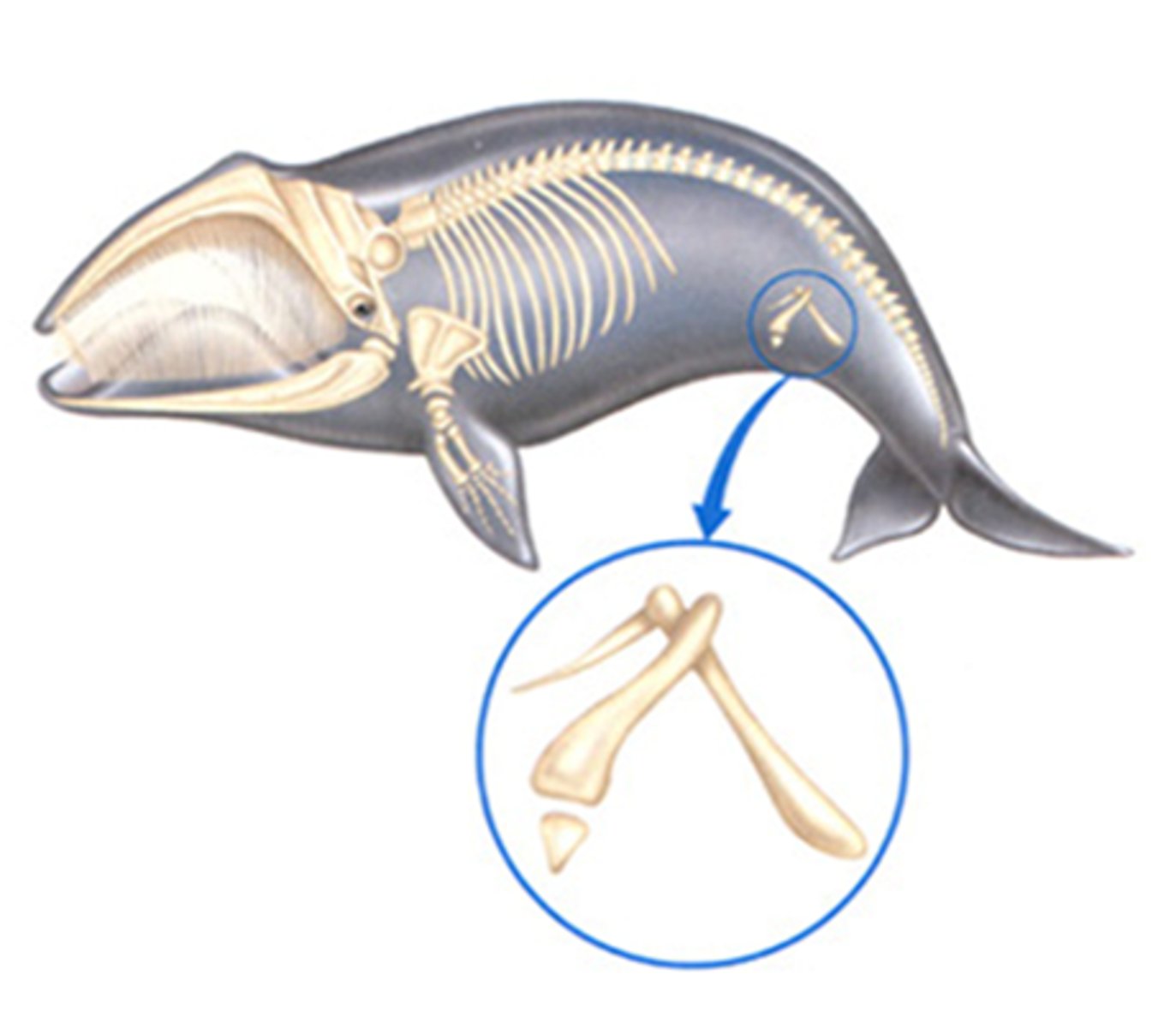
Vestigial Structures
A structure that is present in an organism but no longer serves its original purpose (ex. hip bones in whales)
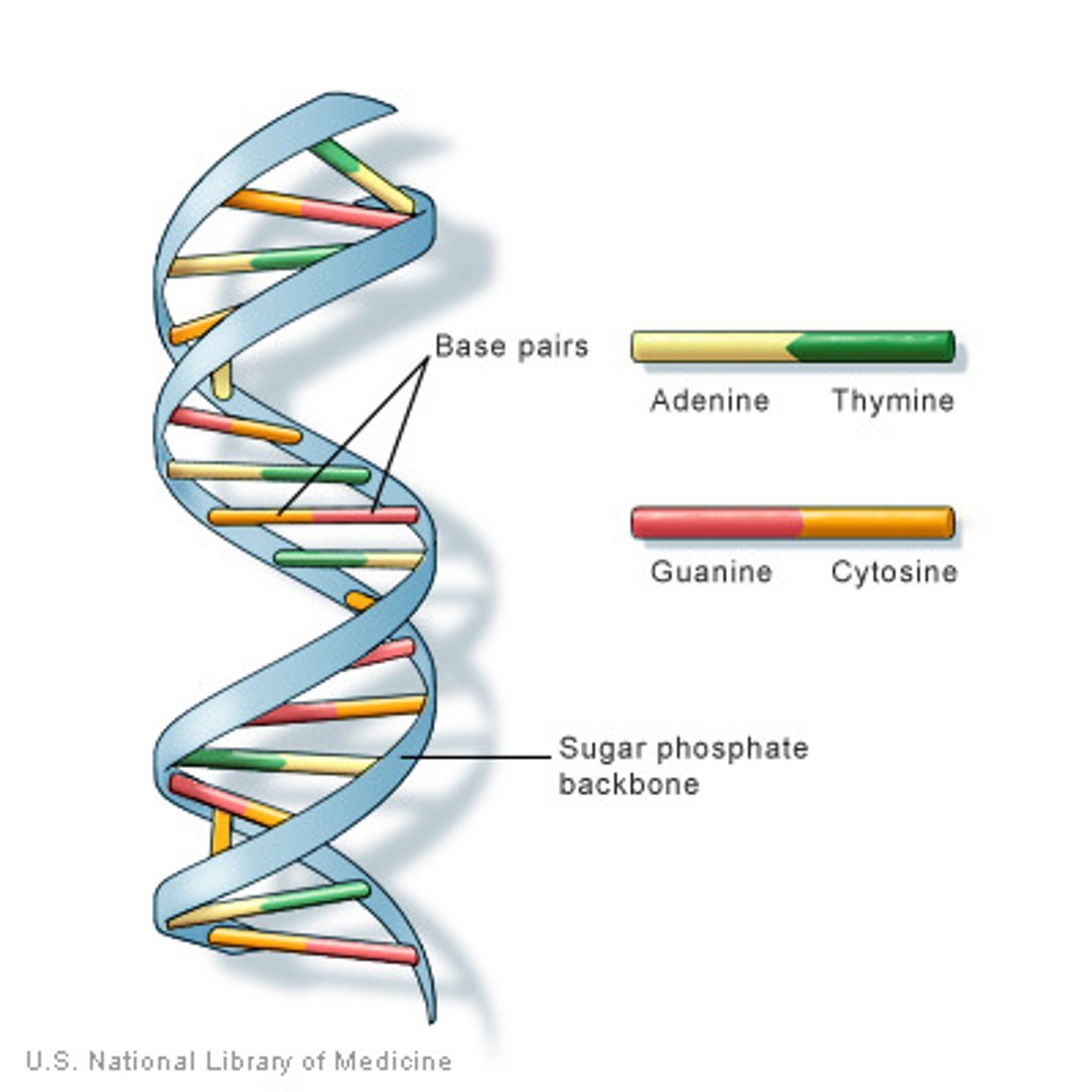
DNA
Genetic information that can be used as evidence of evolution between organisms.
Evidence of Evolution
1) Fossil Record
2) Embryology
3) Homologous Structures
4) DNA
5) Vestigial Structures
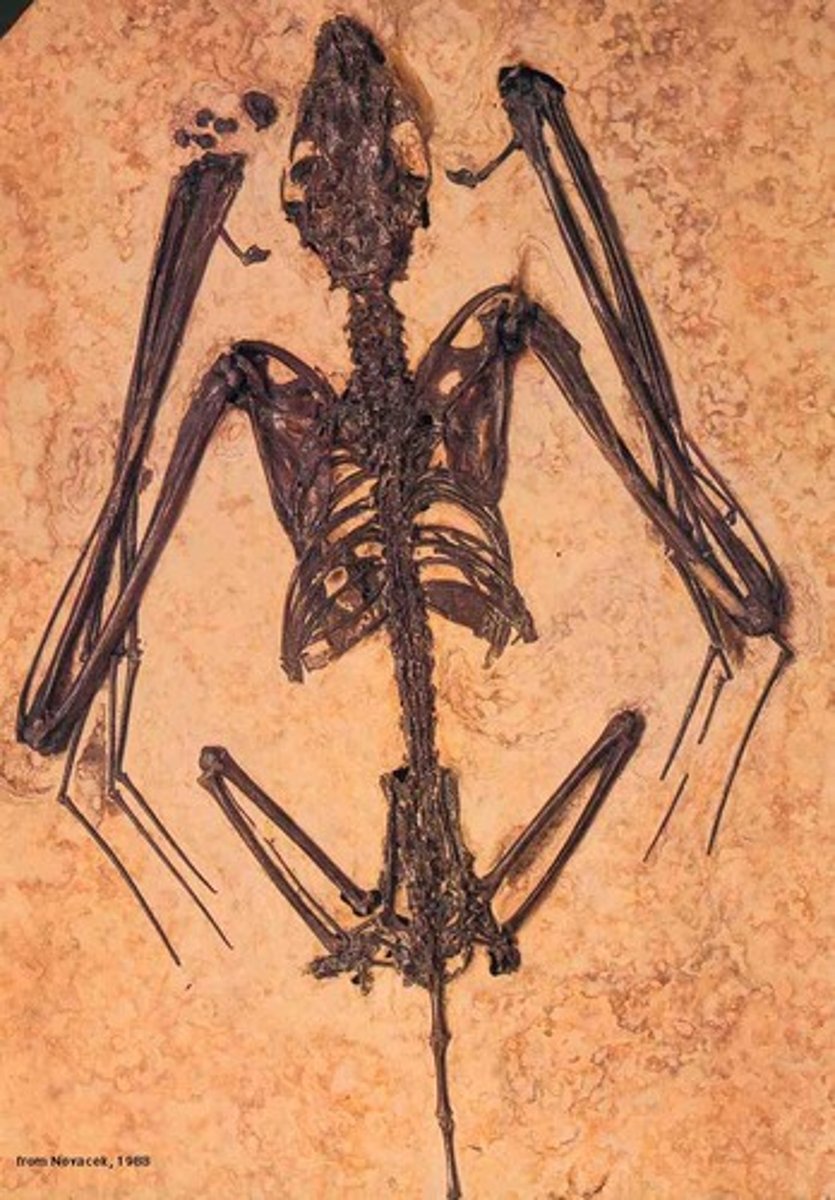
Barrier
something that blocks the way; an obstacle (mountains, rivers, etc.)

Speciation
Formation of new species
allopatric speciation
-speciation due to geographical isolation
-ex) a group of individuals separated from an original population by a large area of land or water
sympatric speciation
The formation of new species in populations that live in the same geographic area
Lamark
before Darwin - use and disuse (parts that are used become bigger and stronger while other parts deteriorate) and inheritance of acquired characteristics (organism can pass on "modifications" to its offspring
Charles Lyell
uniformitarianism: same geological processes that are at work today slowly formed the earth's surface over an immensely long time
Georges Cuvier
(1769-1832) Largely developed paleontology, the study of fossils. Advocated catastrophism.
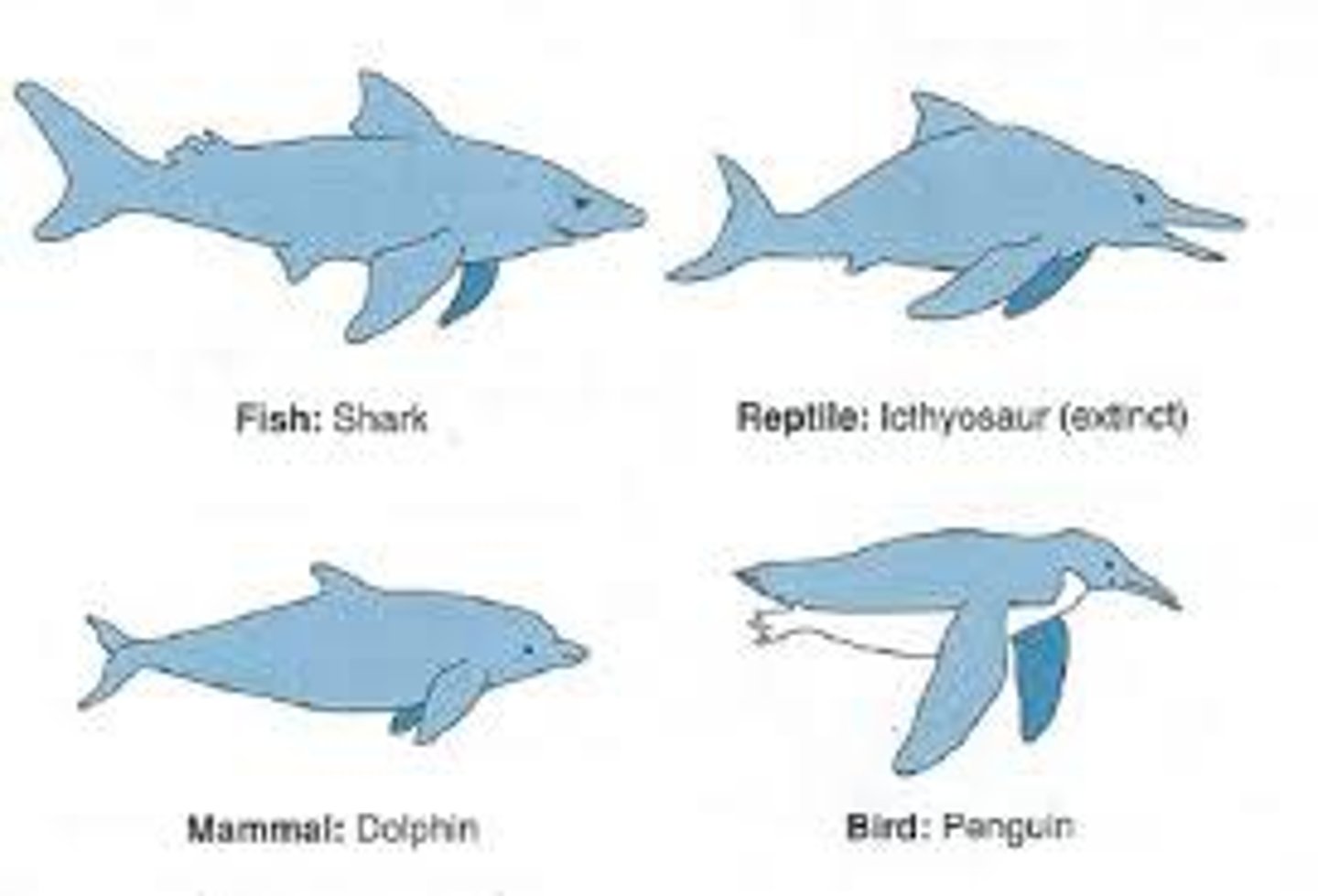
analogous structures
similarities among unrelated species that result from convergent evolution
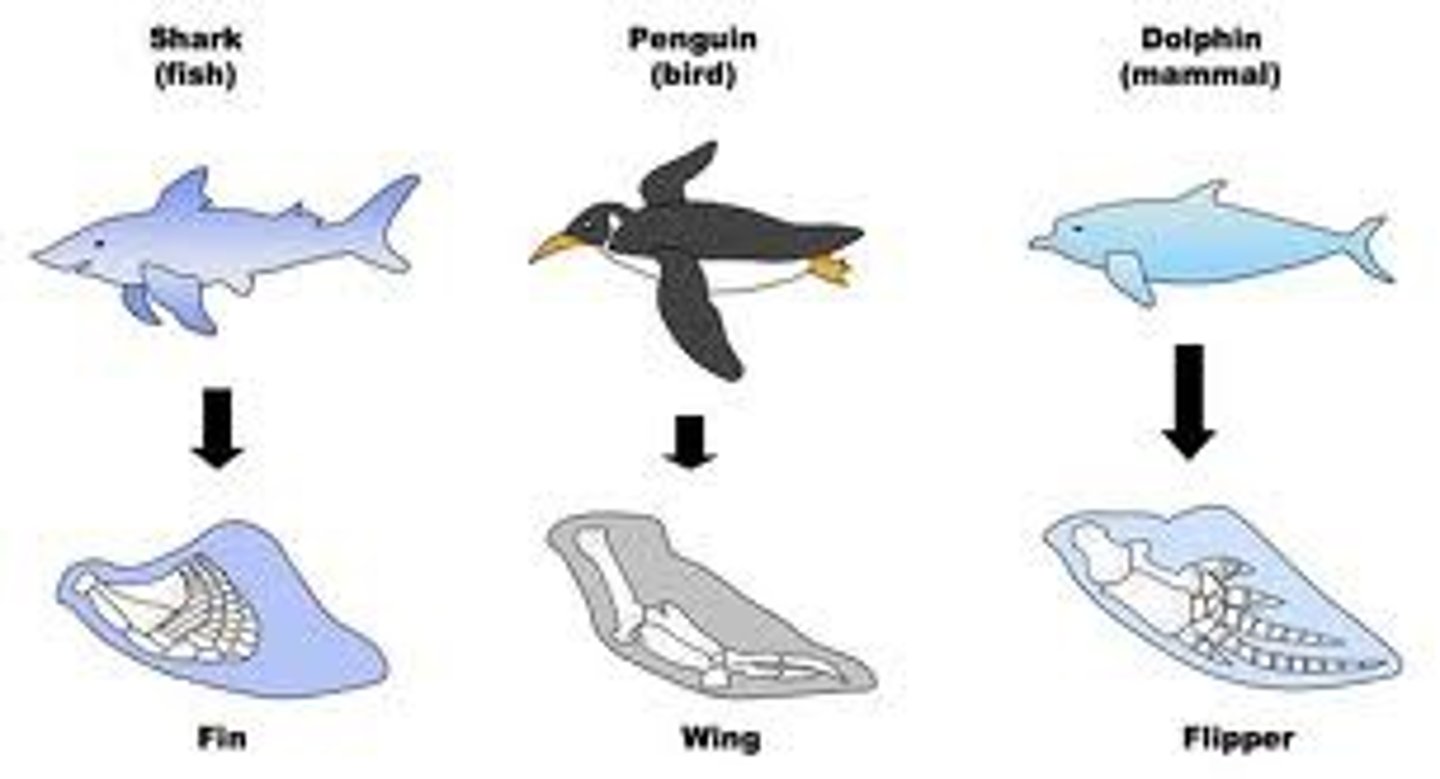
convergent evolution
Process by which unrelated organisms independently evolve similarities when adapting to similar environments
divergent evolution
when two or more species sharing a common ancestor become more different over time
Co-evolution
Process by which two species evolve in response to changes in each other

Extinction
A term that typically describes a species that no longer has any known living individuals.
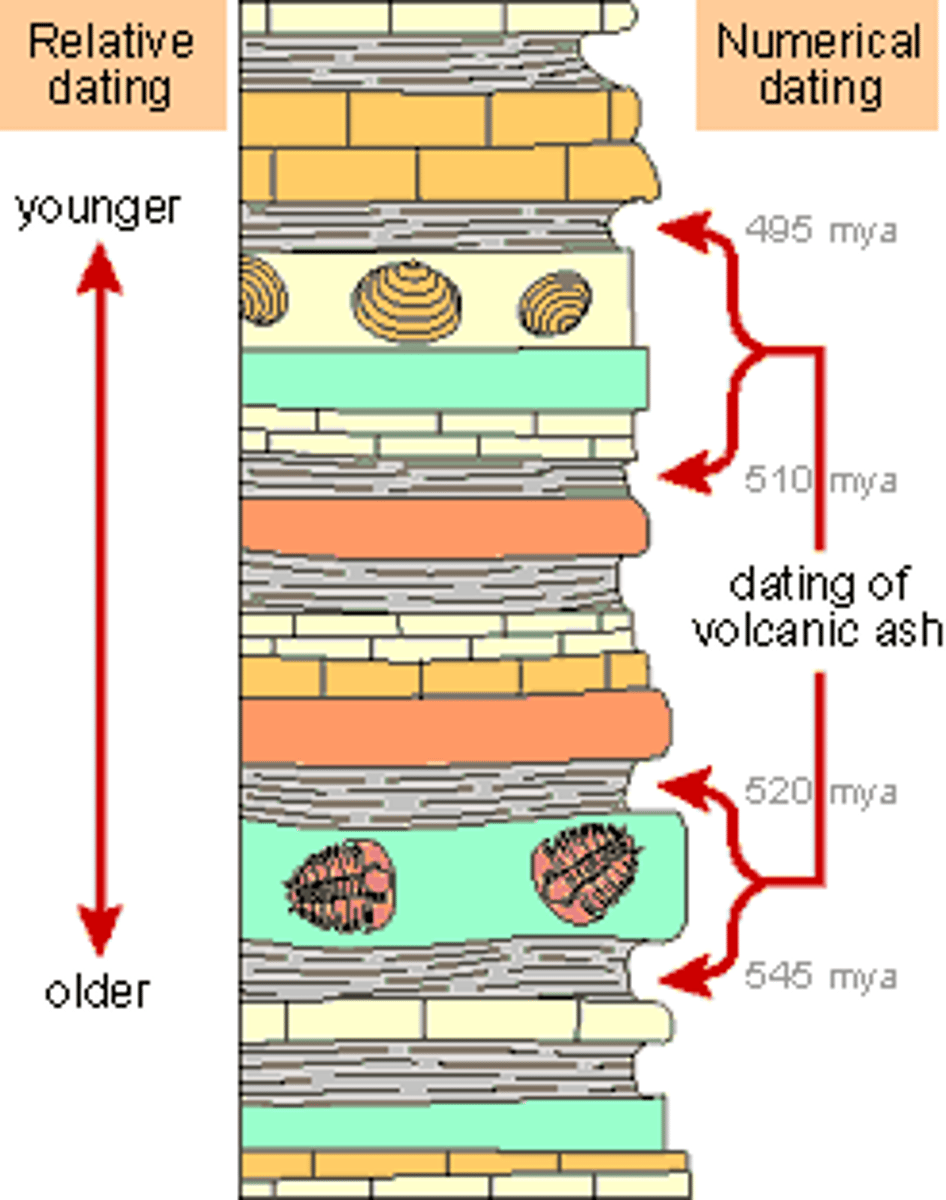
absolute age
The age of a rock given as the number of years since the rock formed.
relative age
The age of a rock compared to the ages of rock layers
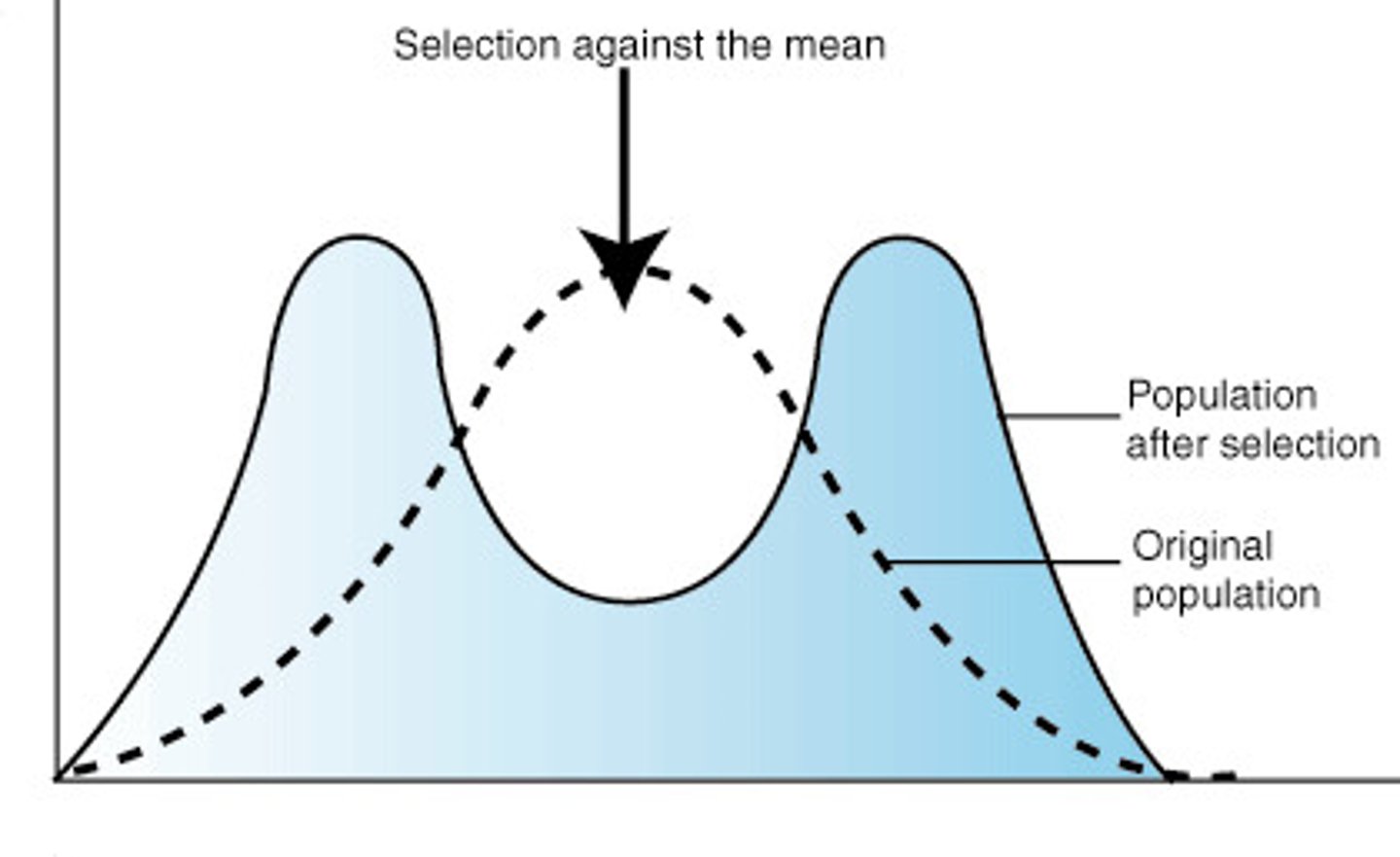
disruptive selection
form of natural selection in which a single curve splits into two; occurs when individuals at the upper and lower ends of a distribution curve have higher fitness than individuals near the middle
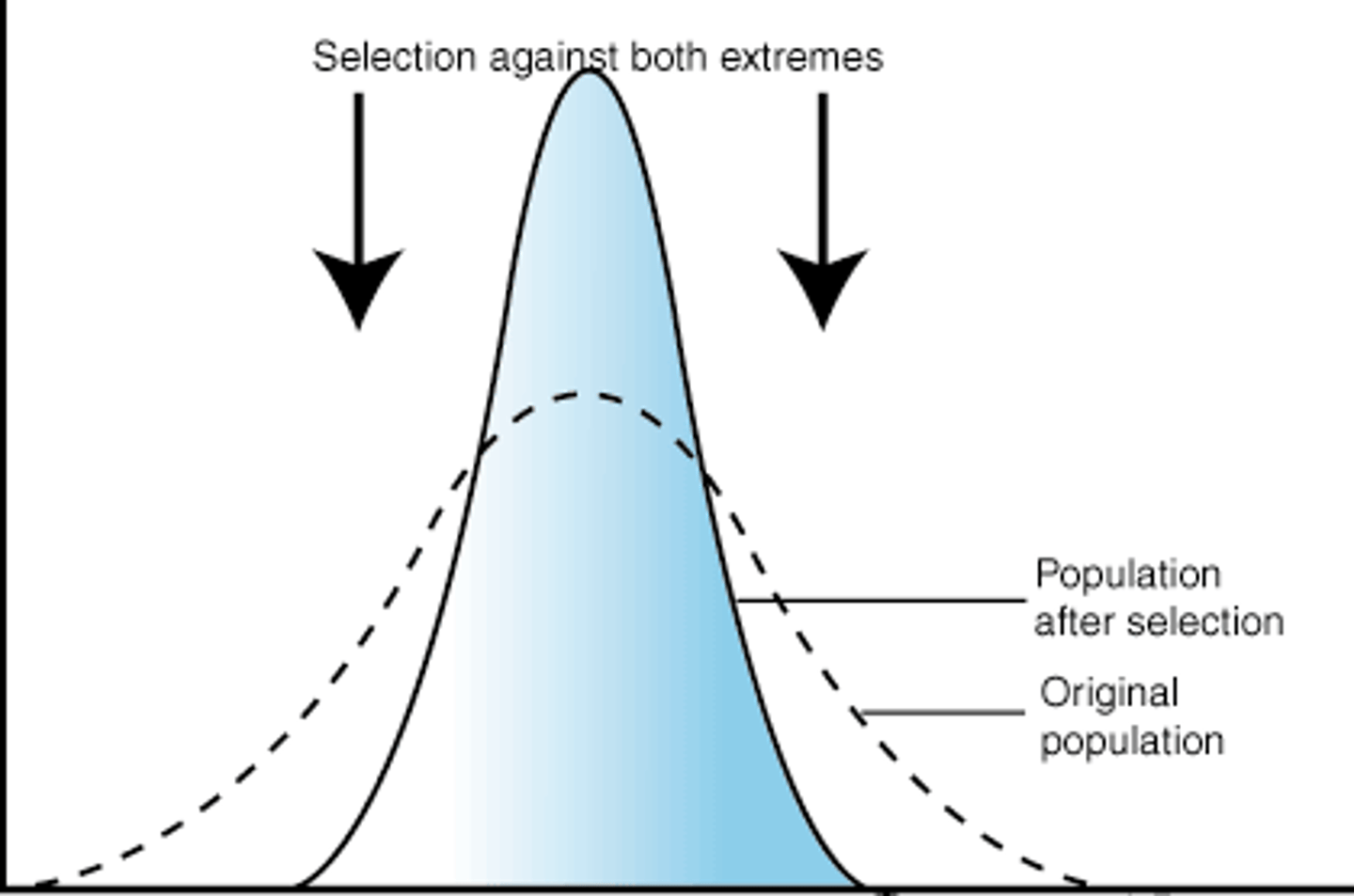
stabilizing selection
Natural selection that favors intermediate variants by acting against extreme phenotypes
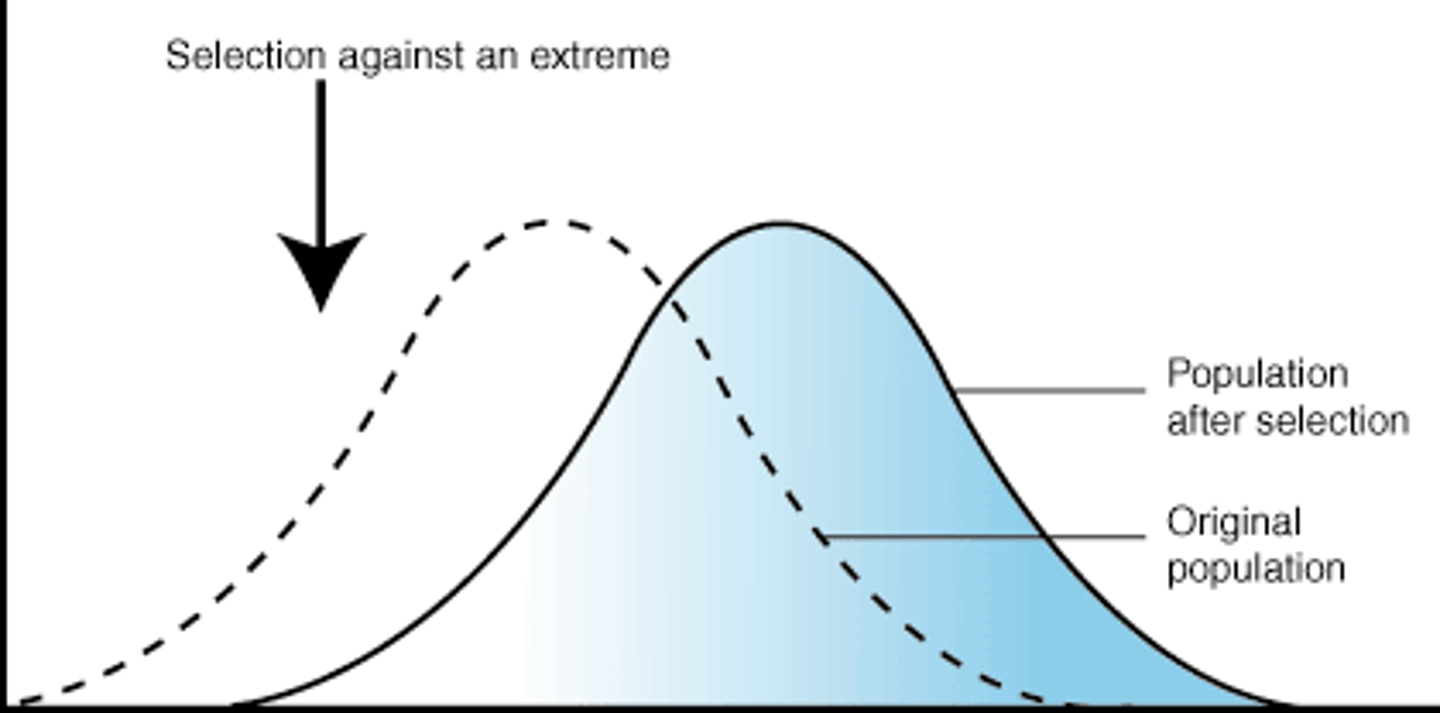
directional selection
Form of natural selection in which the entire curve moves; occurs when individuals at one end of a distribution curve have higher fitness than individuals in the middle or at the other end of the curve
adaptive radiation
the diversification of a group of organisms into forms filling different ecological niches.
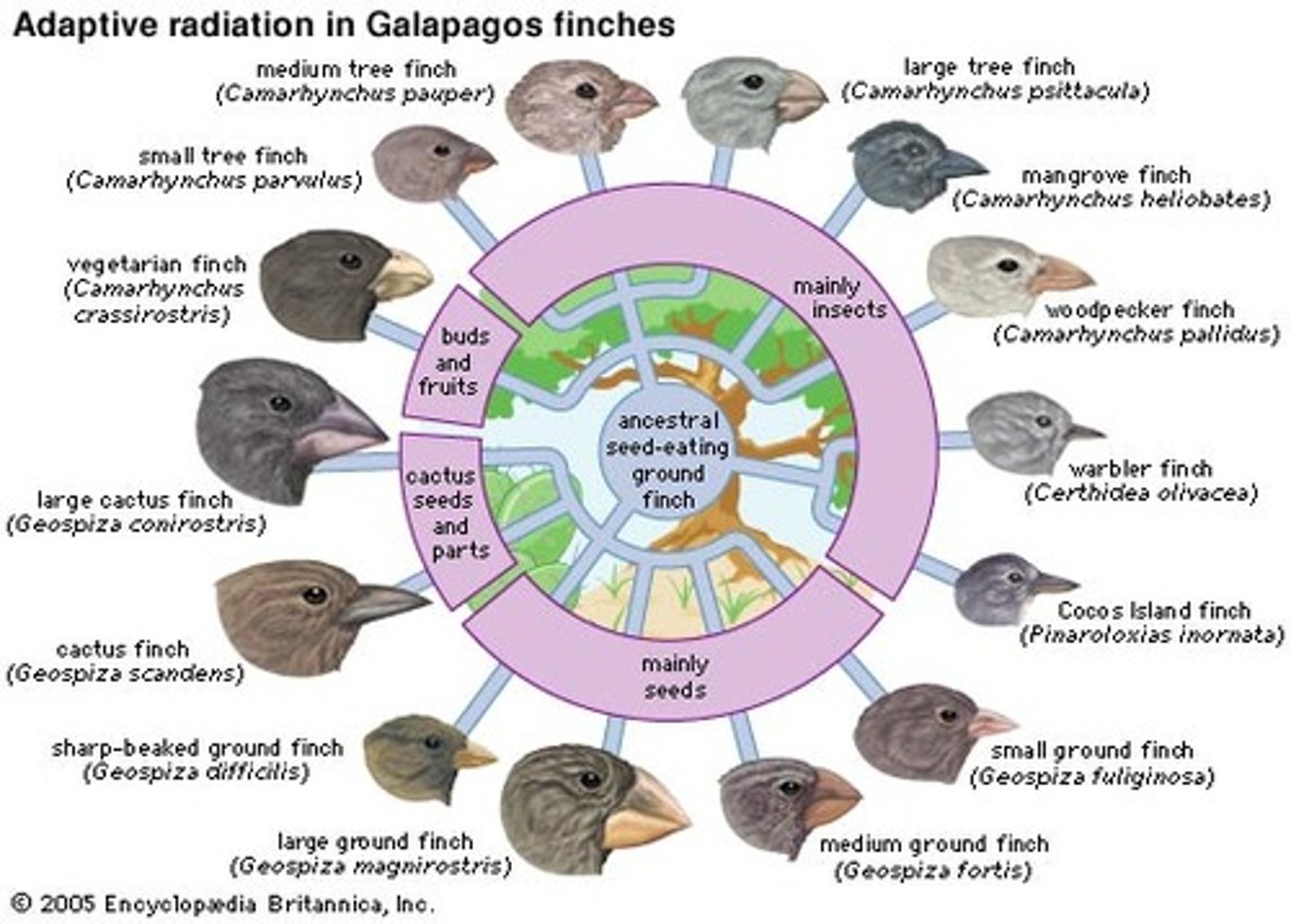
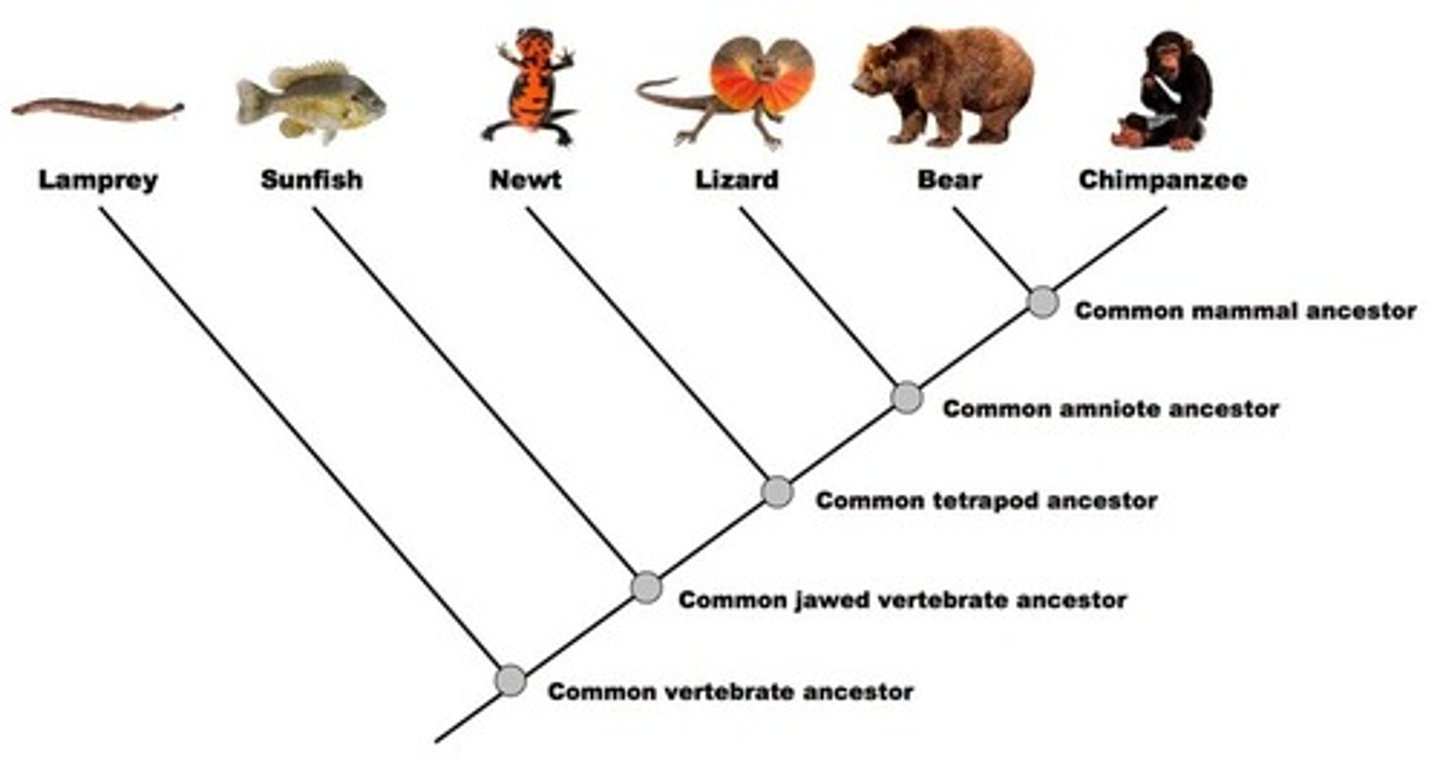
Phylogeny
The evolutionary history of a species or group of related species
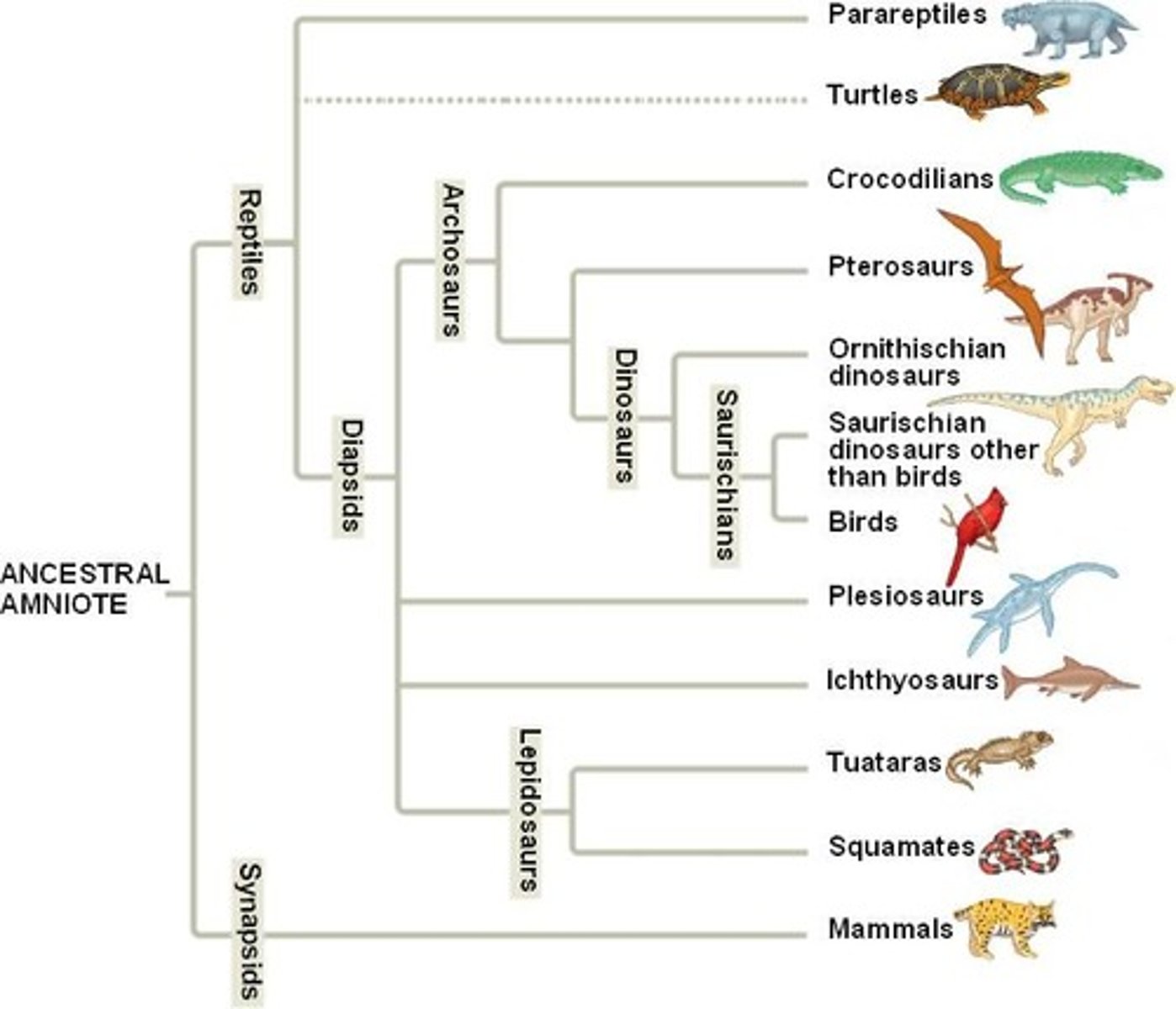
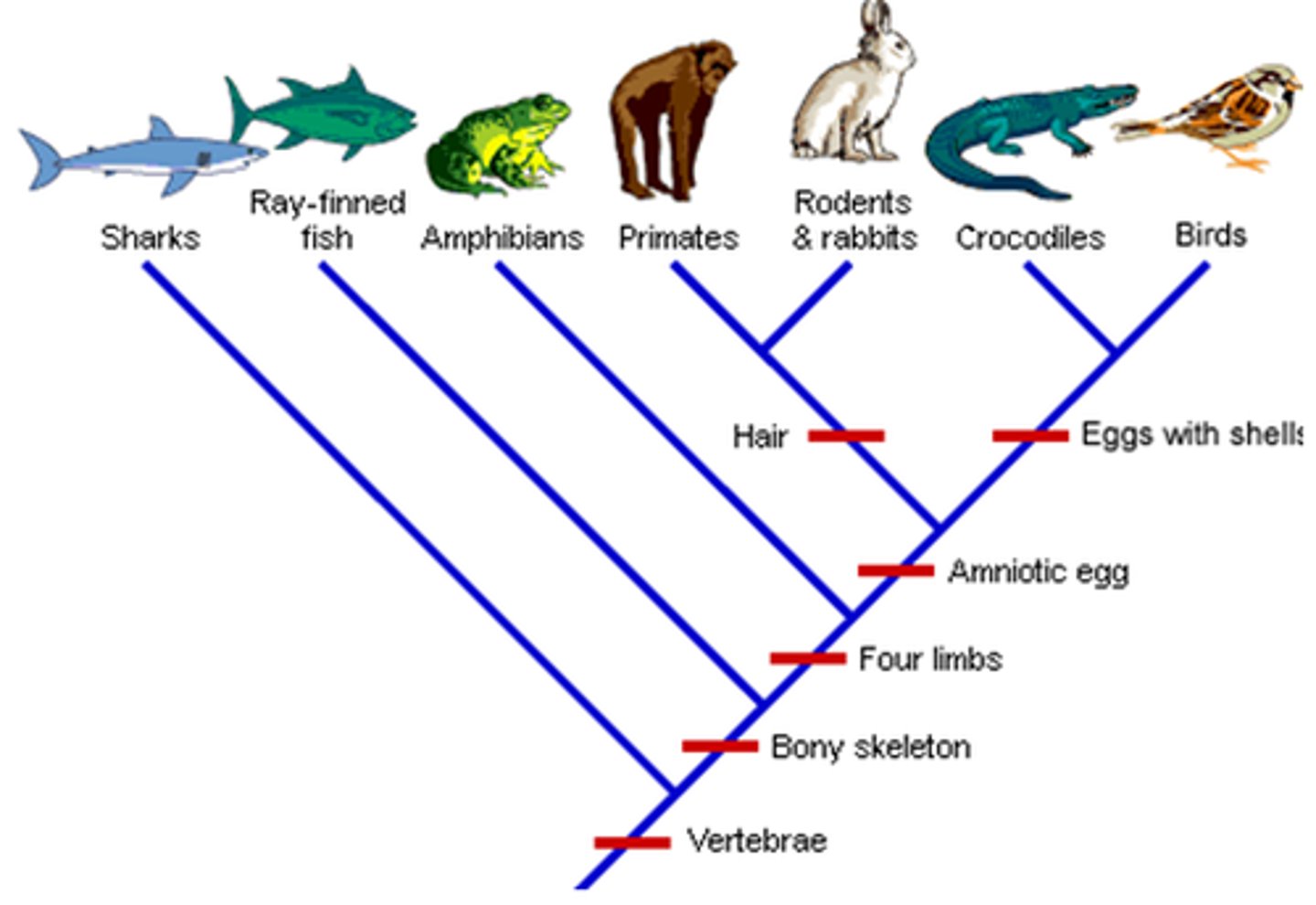
Cladogram
A diagram that is based on patterns of shared, derived traits and that shows the evolutionary relationships between groups of organisms
half-life
length of time required for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay
pre-zygotic barriers
A reproductive barrier that impedes mating between species or hinders fertilization if interspecific mating is attempted.
post zygotic barriers
prevent the hybrid zygote from developing into a viable, fertile adult
temporal isolation
form of reproductive isolation in which two populations reproduce at different times
behavioral isolation
Form of reproductive isolation in which two populations have differences in courtship rituals or other types of behavior that prevent them from interbreeding
habitat isolation
Two species encounter each other rarely, or not at all, because they occupy different habitats, even though not isolated by physical barriers
Cladogram outgroup
The most distantly related species in the cladogram