SSS week 11
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Myopia
short sightedness
condition in which an image of a distant object becomes focused in front of retina, either bc eyeball axis is too long or because refractive power of object is too strong
corrected by concave (minus) lenses
Hyperopia
far sightedness
refractive error in which image of a distant object becomes focused behidn retina, either bc eyeball axis is too short or bc refractive power is too weak
corrected by convex (plus) lenses
Astigmatism
eye condition that exists when surface of cornea or crystalline lens is irregularly shaped
corrected by toric lenses (football shaped)
Presbyopia
age-related loss of near vision, typicaly starting around 40, caused by eye’s lens becoming less flexible and losing its ability to focus on close objects
age related loss of accomodation
corrected by convex (plus) lenses
Symptoms in an eye exam
abnormal vision
abnormal sensation eg. discomfort
altered appearance
types fo abnormal vision
reduced
central
peripheral
impaired night or colour vision
onset
if sudden —> vascular
or gradual
.
floaters
haemorrhage
inflammation
vitreous degeneration
muscae volitantes
.
flashers
irritative stimulation of retinal or visual pathway
can be unilateral —> retinal deatchment?
bilateral —> migraine/basilar artery insufficiency
.
haloes - rainbow coloured rings around lights due to corneal oedema or increased intraocular pressure
metamorphopsia / micropsia
apparent distortion of straight lines/minification of objects due to retinal oedema or macular degeneration
diplola
binocular
resolves when either eye is covered, due to misalignment of visual axes

monocular
persists when unaffected eye is covered
caused by optical/intraocular problems (not alignment)
typical causes
cataracts, corneal irregularity/scar, refractive error, dry eye, intraocular foreign body
Abnormal sensation types
foreign body sensation
subjective localisation unreliable
causes include: trichiasis, entropion, conjunctivitis, dry eye
local anaesthetic relieves
photophobia
iritis
keratitis
cycloplegic drops relieves
severe deep pain
acute angle closure glaucoma
zoster/shingles
asthenopia (eye strain)
occurs after intensive use of eyes
due to
inadequately corrected refractive error
heterophoria
watery eyes/ discharge
overproduction (due to ocular irritation or FB)
faulty drainage
instability (dry eyes often blepharitis)
Types of altered appearance
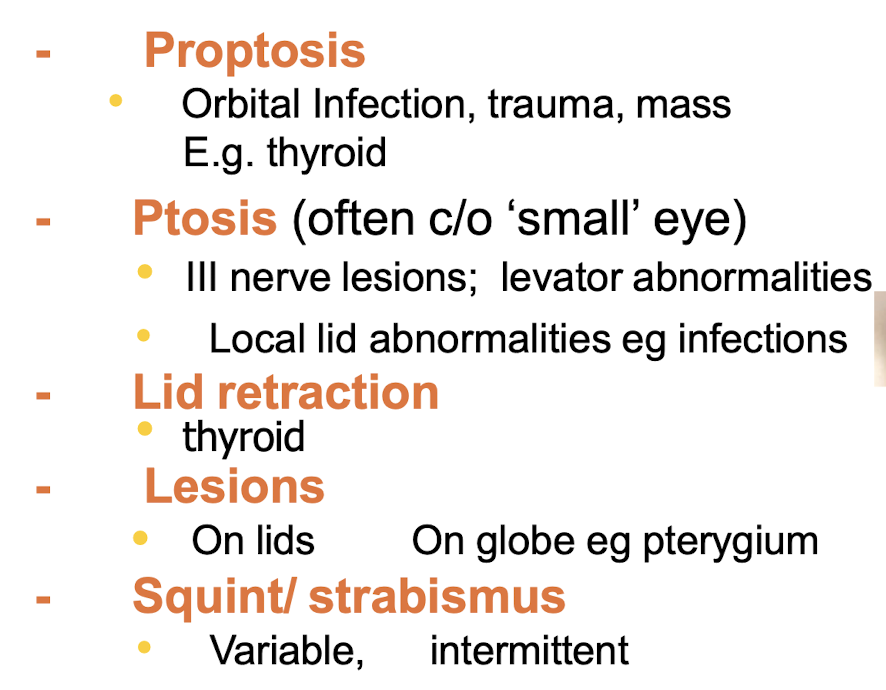
What are the 3 mechanisms of Cellulitis
spread from local infection like sinusitis
skin disruption
haematogenous spread (common under age 2)
GAS/staph/s.pneumo
Periorbital vs orbital cellulitis
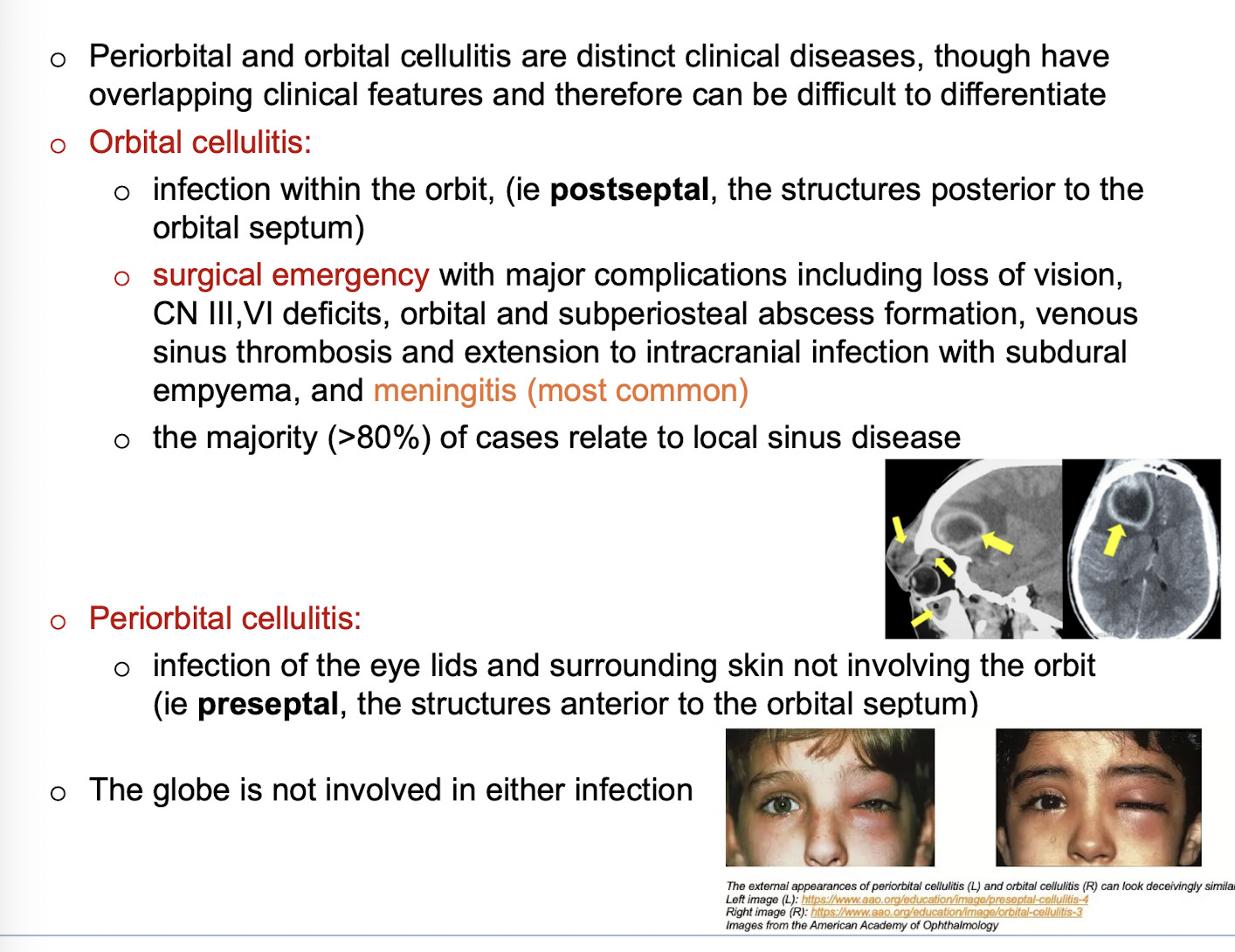
Red flags concerning for orbital cellulitis
painful or restricted eye movements
visual impairment: reduced acuity, relative afferent pupil defect, diplopia
proptosis
severe headache or other features of intracranial involvement
Cellulitis characteristics
