Sound Waves - 8/25
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
speed of sound and frequency are [dependent/independent]
independent. speed of sound has nothing to do with frequency
to men’s voices travel faster or slower than women’s voices?
neither. men’s and women’s voices travel at the same speed
solids are [more/less] elastic than air
more
air is [more/less] elastic than both liquids and solids
less
iron is [more/less] elastic than rubber
more
what are the 3 prerequisites for sound production?
a medium of transmission (air)
a source of energy (hand)
a vibrating object that generates audible pressure (table)
is a listener a prerequisite for sound?
no. just because no one is there to hear a sound does not mean it wasn’t produced
what are the 3 important properties of any medium?
mass, density, elasticity
out of air, liquids, and solids, which has the highest mass, density, and elasticity?
solids have most mass, density, and elasticity
speed of sound is determined by _____ and ____ of a medium, and therefore it _____ according to the medium
elasticity and density, changes
what is mass?
the amount of matter that is present
what is the difference between mass and weight?
weight takes gravitational force into account
if you go to the moon, will your mass change? will your weight?
mass will not change - not affected by gravity
weight will change - is affected by gravity
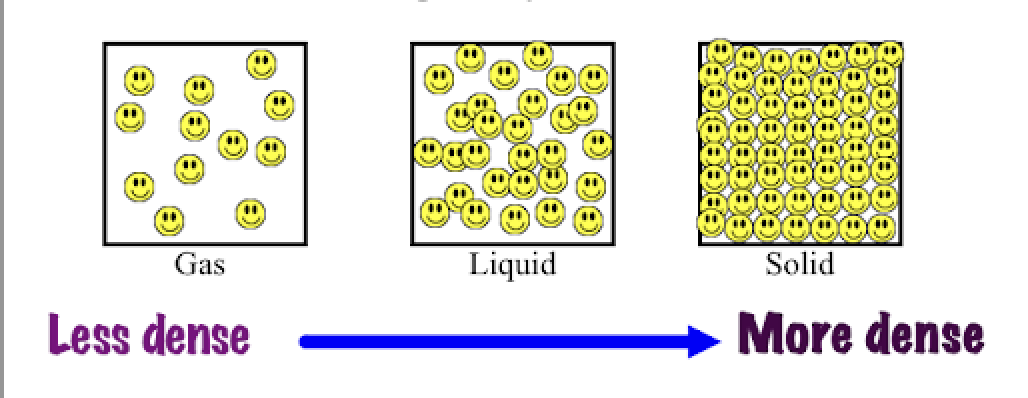
what is density?
amount of mass per unit volume, aka how squished together the particles are
air density [increases/decreases] as elevation increases
this explains why it is harder to breathe as you climb a mountain
decreases
what is elasticity?
the ability of a material to return to its original shape after being deformed
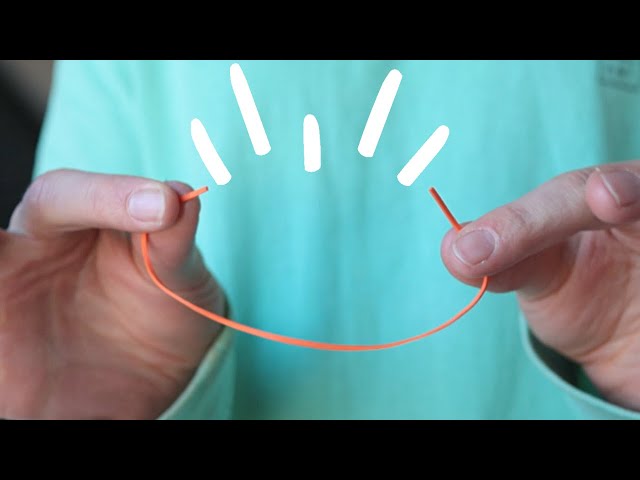
what is elastic limit?
the maximum extent to which a solid may be stretched without permanent alteration of size or shape - the point just before a stretched rubber band breaks
the elastic limit of air is [more/less] than liquid
less
the elastic limit of liquids is [more/less] than solids
less
quicksand has a [higher/lower] elastic limit than water
higher. it’s a solid
![<p>compare the two springs. </p><ul><li><p>the thinner spring takes [more/less] force than the thicker spring</p></li><li><p>the thicker spring has [more/less] elasticity than the thinner spring</p></li><li><p>a thicker rubber band is [harder/easier] to snap</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5e142af3-fba3-4130-8f45-a8f22b0f23a8.png)
compare the two springs.
the thinner spring takes [more/less] force than the thicker spring
the thicker spring has [more/less] elasticity than the thinner spring
a thicker rubber band is [harder/easier] to snap
less force
more elasticity
harder to snap
what is hooke’s law? give the equation and explain it
Fr = -kx, where x is magnitude of spring displacement and k is spring constant.
the magnitude of the restoring force of elasticity is directly proportional to the magnitude of spring displacement
hooke’s law explains that
if you pull a spring with more force downward, it will go back up [faster/slower]
the more you pull a spring downwards, the more the restoring force [increases/decreases]
will go back up faster
the more the restoring force increases
what is stiffness?
how stiff a spring is = the spring constant in hooke’s law equation = k
a stiffer spring requires [more/less] force to compress
more
what is compliance?
how easily a spring can be deformed
what is the relationship between compliance and stiffness?
inverse
the thinner the spring, the more compliant
what are two important properties of the source of a sound?
mass and elasticity
what does newton’s 1st law state?
all bodies remain at rest or in a state of uniform motion unless another force acts in opposition = inertia
what does newton’s 3rd law state?
for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction
what are the 3 basic physical properties?
length, mass, and time
name the 7 derived quantities mentioned in the lecture
displacement, speed, velocity, acceleration, force, pressure, momentum
what are scalar vs vector quantities?
scalar: has magnitude (quantity)
vector: has both magnitude and direction
what is displacement? is it scalar or vector? units?
displacement is a change in position that involves both direction and distance. vector. unit: meters in a direction
what is speed? is it scalar or vector? units?
speed measures how fast an object is moving without reference to direction, so it is scalar. unit: m/s
what is velocity? its equation? scalar or vector? units?
velocity measures how fast an object is moving with reference to its direction, so it is vector. v = d/t. unit: m/s in a direction, eg. 60 m/s to the north
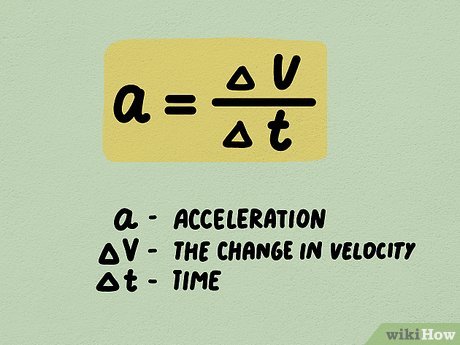
what is acceleration? scalar or vector? units?
acceleration measures the rate at which an object’s velocity changes = a change in speed, direction, or both. a = v/t. vector. unit: m/s2 in a direction
what is force? its equation? scalar or vector? units?
a push or pull that can change an object’s motion. F = ma. vector quantity. unit: Newton (N)
based on the equation F = ma, force is [directly/inversely] proportional to mass
directly. if it has more mass, it needs more force to move it
based on the equation F = ma, force is [directly/inversely] proportional to acceleration
directly. more force = more acceleration
based on the equation F = ma, acceleration is [directly/inversely] proportional to mass
inversely. rearrange equation so that m = F/a. an object with smaller mass will accelerate more
what is pressure? scalar or vector? its equation? unit?
pressure (p) is the amount of force per unit area. scalar. p = F/A. unit: N/m2 or Pascal (Pa)
what is momentum? how to calculate it? scalar or vector? unit?
the measure of an object’s quantity of motion. momentum = mass x velocity. vector. unit: kg x m/s
what is kinetic energy? what is its equation? units?
energy that results from an object in motion. unit: Joules (J)
KE = 1/2mv2
what is potential energy? what is its equation? units?
a form of energy that results from object position or arrangement of parts. it is a stored energy. unit: Joules (J)
PE = mgh
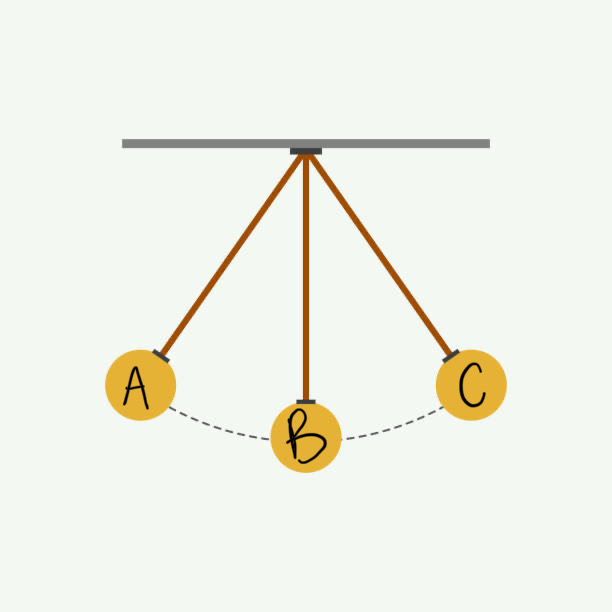
where is potential energy highest? where is kinetic energy highest?
potential energy highest at A and C. kinetic energy highest at B (velocity is highest)
what is work? its equation? units?
work is done when a force moves an object. work = force x displacement, W = Fd. unit: Joules (J)
what is the equation for power (P)?
P = W/t = Fd/t
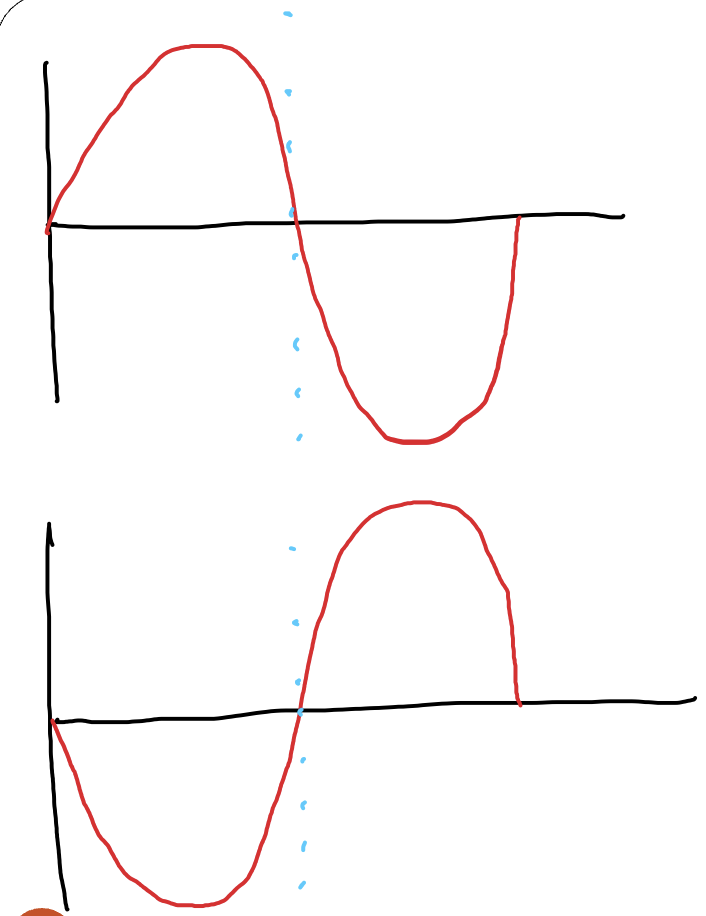
what is the phase difference between these two waves?
180 degrees. mirrored = 180 degree phase difference
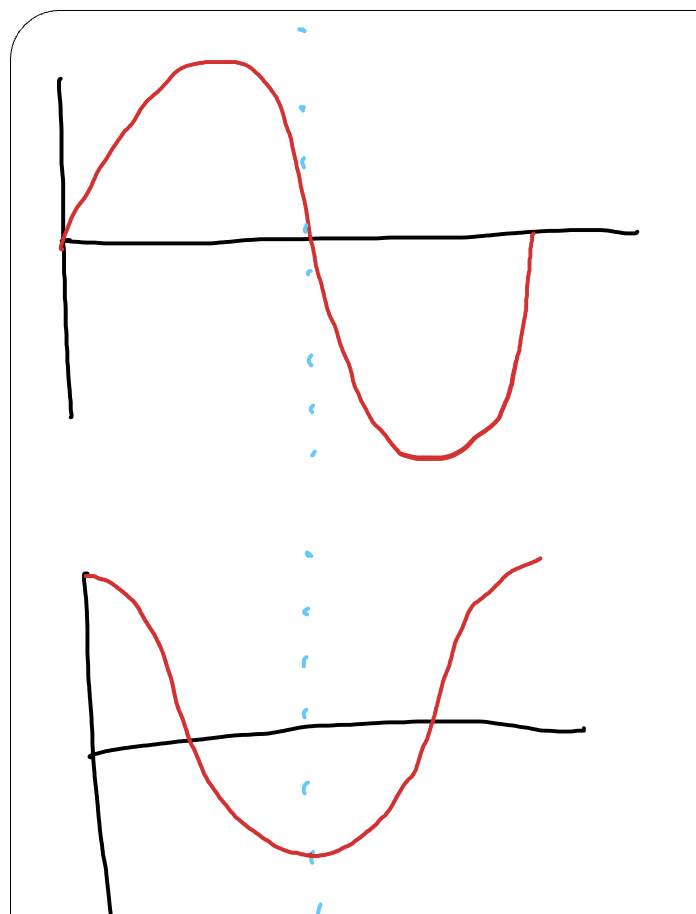
what is the phase difference between these two waves?
90 degrees
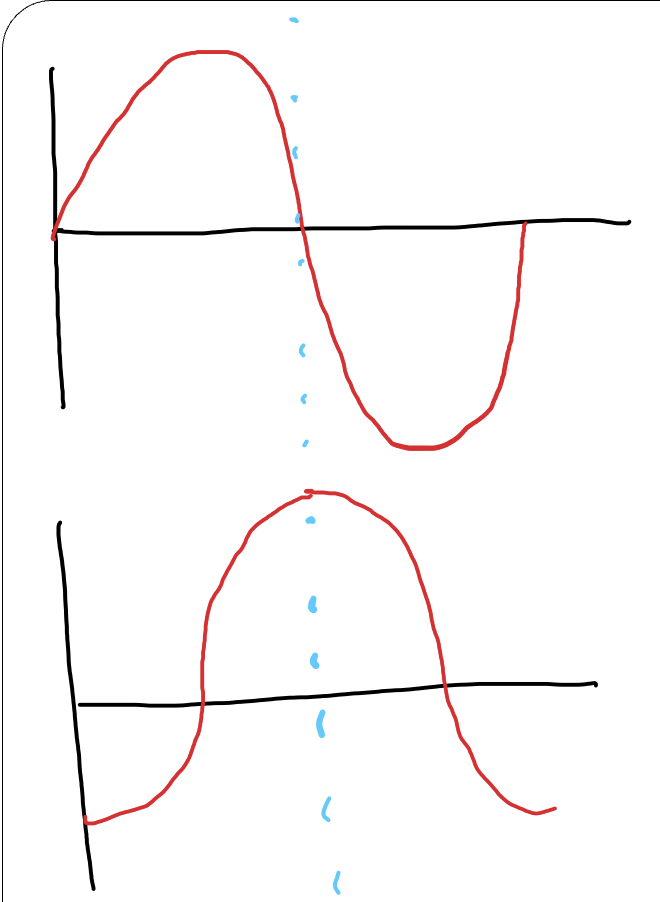
what is the phase difference between these two waves?
270 degrees