AP Bio - Unit 6: Gene Expression and BioTechnology (Gene Expression)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:46 PM on 2/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
1
New cards
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
**DNA >** *transcription* **> RNA >** *translation* **> Protein**
explanation of the flow of genetic information
explanation of the flow of genetic information
2
New cards
RNA Polymerase
makes mRNA from DNA
3
New cards
mRNA
messenger RNA, Hold copy of DNA in RNA form for sequencing outside of the nucleus
4
New cards
mRNA editing steps
1. mRNA has to parts, exons and introns
2. in nucleus, SPLICOSOME COMPLEX makes cuts in mRNA
3. introns are removed and exons are kept, mRNA is now “mature”
1. a “poly-a tail” is added to the 3’ end and a GTP5 cap is added on the 5’ end
5
New cards
poly-a tail function
attached to the 3’ end of mRNA to slow down the destruction of mRNA in the cytoplasm
6
New cards
GTP5 cap funtion
guides mRNA to destination and helps it to leave the nucleus
7
New cards
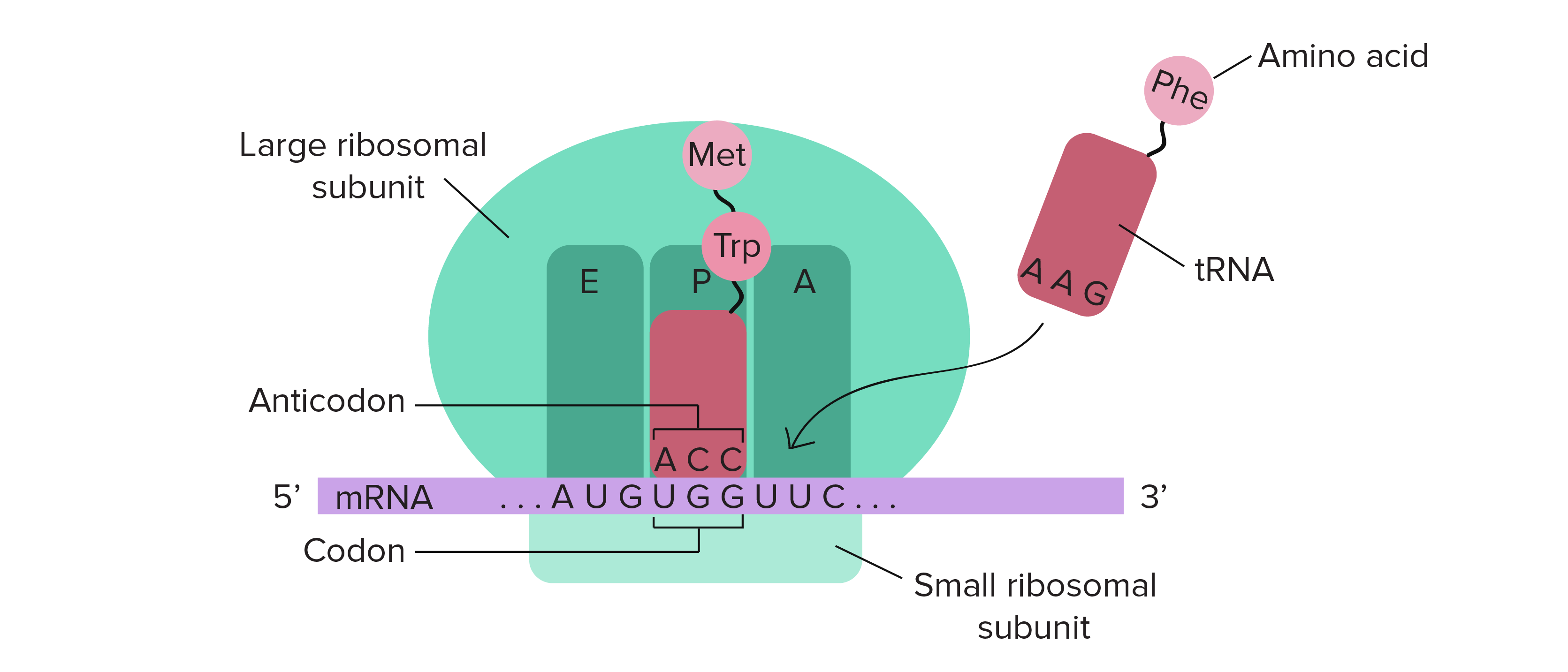
ribosome function
reads mRNA **5’>3’** in codons (nucleotide triplets)
uses EPA complex (arrival, processing, exit)
uses EPA complex (arrival, processing, exit)
8
New cards
Start/Stop codons
Start: AUG (makes amino acid)
Stop: UAA, UAG, UGA (no amino acid)
Stop: UAA, UAG, UGA (no amino acid)
9
New cards
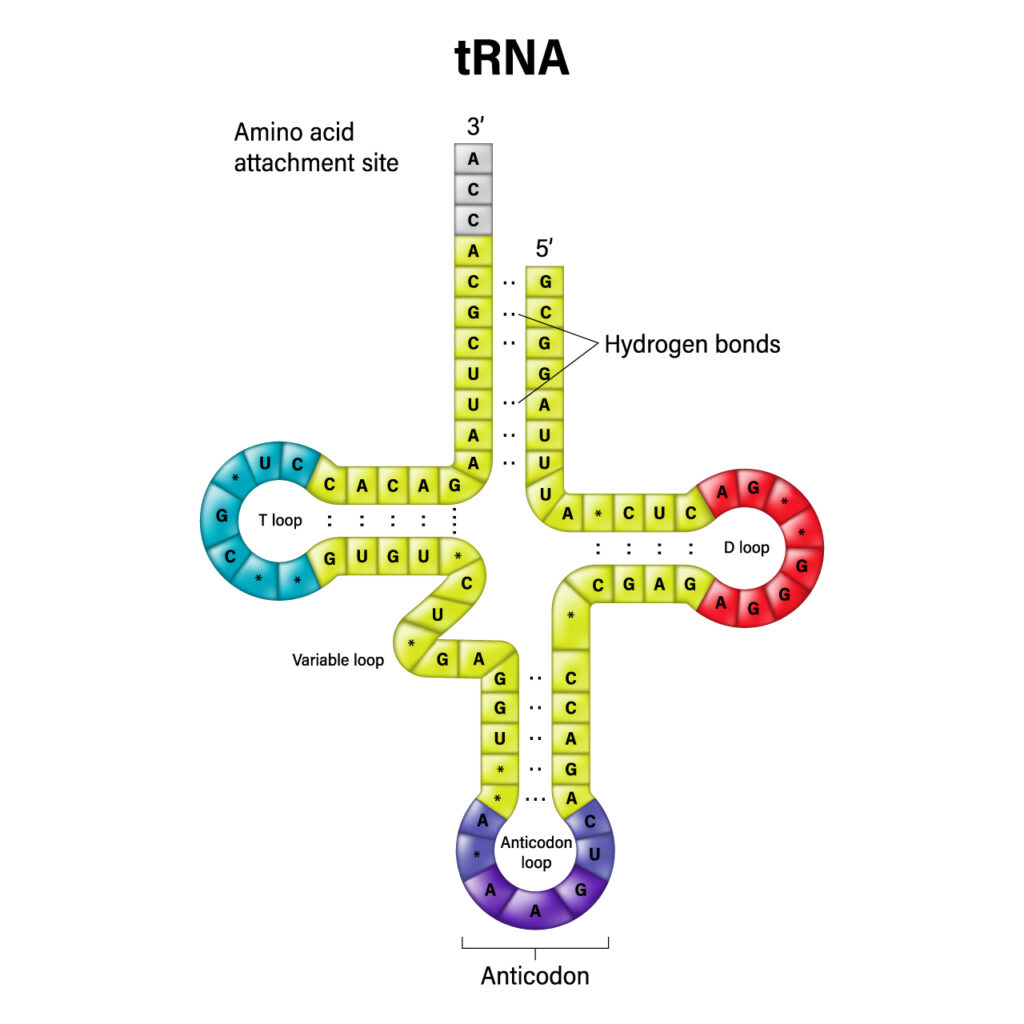
tRNA
transfer RNA, contain amino acid and anti-codon (matches with mRNA) and helps to build poly-peptide chain. made in nucleolus
10
New cards
Mutation
any change in genes, not always bad
mutation at DNA level: significant impact
mutation at RNA level: minor impact but more likely because of lack of “proofreading”
mutation to somate cells isnt passed on, mutation to germ cells is passed to offspring
mutation at DNA level: significant impact
mutation at RNA level: minor impact but more likely because of lack of “proofreading”
mutation to somate cells isnt passed on, mutation to germ cells is passed to offspring
11
New cards
causes of mutation
induced (outside factor) or spontaneous (copying error)
12
New cards
induced mutation example
radiation, chemicals, infectious agents
13
New cards
spontaneous mutation examples
DNA copying, alternative splicing
14
New cards
types of mutations
silent, missense, frame shift, nonsense (from least to most impactful)
15
New cards
silent mutation
nucleotide is changed but amino acid product isnt affected
16
New cards
missense mutation
one amino acid in change but the rest remain the same
17
New cards
frame shift mutation
insertion or deletion of nucleotide that shifts the “reading frame” of the ribosome.
18
New cards
nonsense mutation
missense or frame shift mutation that results in a premature stop codon