B3.1 and B3.2 Gas Exchange and Transport
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Stan aespa!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Where are the lungs?
thoracic cavity
What seperated the lungs
the heart
Is each lung just one lobe?
No
What are two specialized tissues in the respiratory system?
Alveolus and bronchioles
Describe the alveolus
terminal end of one of the branches of tubes that started as the trachea
Describe the brochioles
small tubes that connect the trachea to the alveolus
What happens every time you inspire and expire
you replace most of the air in millions of alveoli.
What do specific alveolar cells do?
secrete the surfactant
What do surfacants do
coats the inside of each alveolus.
Outline surfacatns
phospholipid/protein film, reduces surface tension to keep alveoli from collapsing
What shape are the alveoli
spherical
what is the significance of the shape of alveoli?
rovides a vast surface area for the diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
What do the capillaries surrounding the alveoli do?
help the diffusion of respiratory gases
What does diffusion allow in the alvaoli?
allows gas to pass from the capillaries into the alveoli and back again
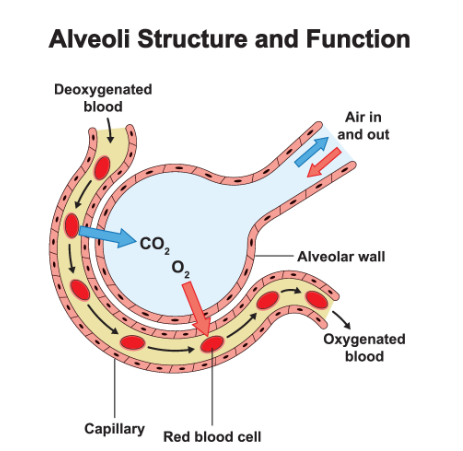
Describe the characteristics of lung tissue
passive and non muscular
The lungs are incapable of….
movement on their own
How do lungs move if they cant by themselves?
Muscles and structures
Which muscles and structures help the lungs move
the diaphram, abdomen muscles, and external and internal muscles
Boyles law?
inverse relationship between pressure and volume.
How do pressure changes happen in the lungs?
Muscles work together to increase or decrease volume of the thoratic cavity
What happens when the diaphtagm contracts?
the dome shape flattens and the volume of thoracic cavity increases
outline inspiration
Diaphragm contracts (moves down) and flattens.
External intercostal muscles contract, lifting ribs up and out.
Thoracic volume increases, lung volume increases.
Pressure inside lungs drops below atmospheric pressure.
Air rushes in to equalize pressure
Outline expiration
Passive: Diaphragm and external intercostals relax; elastic recoil of lungs pushes air out.
Active (Forced): Internal intercostals and abdominal muscles contract, actively pushing air out.
Thoracic volume decreases, lung volume decreases.
Pressure inside lungs increases above atmospheric pressure.
Air is forced out.
What do spirometers do
measure lung volumes
What is Tidal volume
the volume of air that is breathed in or out during a typical cycle
What is Inspiratory reserve volume
Max volume of air breathed in
what is Expiratory reserve volume:
Max volume of air breathed out
what is Vital capacit
the sum of the inspiratory reserve volume, the tidal volume and
What are the pieces of the cardiovascular system
Hearts, veins, arteries, capillaries
Function of the heart
To transport blood to entire body
how many chambers in the heart
4
How many valves in heart
4 one way valves
What are the adaptations of the heart
SA node, Atria, Ventricles, Pulmonary and systemic circulation
fucntion of SA node
generates spontaneous electric impulse to start heart beat
Function of atria
hin chamber that receives low pressure, sends blood to ventricles
function on Ventricles
thick chamber used to send blood out under high pressure
what are the two major routes for bloodflow in the heart
pulmonary circulation (R) and systemic circulation (L)
Which side of the heart is deoxygenated
right
which valves and arteries are deoxygenated blood?
the vena cavas, right atrium, tricuspid valve, rigth ventricle, pulmonary valve, and pulmonary arteries
Where does deoxygenated blood go to
lungs
where does oxygenated blood go
body
Which things in heart are oxygenated
Pulmonary veins, left atrium, mitral-valve, left ventricle, aortic valve, aorta
Arteries go ___ from heart
away
Veins go _____ the heart
towards
Name to arteries
aorta and pulmonary arteries
What does the aorta do
takes oxygenated blood to the body from the left ventricle
Name two veins
vena cava and pulmonary veins
Function of vena cava
brings blood to the right atrium from the body
function of pulmonary veins
brings oxygenated blood to left atrium
Outline atriums
Always receives blood from veins
Always separated by atrioventricular valves
Always low pressure
outline ventricles
Always takes blood away in arteries
Always separated by lunar valves
Always high pressure
outline the right heart
Always deoxygenated
Blood comes from body and goes to lungs
outline left heart
Always deoxygenated
Blood comes from body and goes to lungs
What is the cardiac cycle
one heartbeat
frequency of cardiac cycle….is
heart rate
Systole
When a chamber of the heart contracts, blood is pushed out
Diastole
When a chamber relaxes and blood floods in
What is the cardiac cycle controlled by
SA nodes
What regulates the contraction of the atria
sa node
Where are the AV nodes
ventricles
Ways to measure HR
ECG, pulse, Stethoscope
What are capillaries
smallest of arteries
where do capillaries receive blood from
arterioles
Capillaries take blood from…
venules
Why are capillaries significant?
only large enough to take one cell at a time
very permeable
no cell in the body is far from a capillary
Arteries and veins have different sizes of…
lumen
Adaptations go ___ from heart
away
The wall of each artery contains the proteins…
elastin and collagen
veins go ___ the heart
towards
Plaque
a build of cholesterol and other substances in the lumen of an artery