Bloodflow & Pressure
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Blood pressure
The pressure exerted by the blood on the inner wall of blood vessels.
Hypotension risks
bloodflow to organs is too low, causing problems in organs.
brain damage begins after only 4 minutes without oxygen, and death can occur after 4 to 6 minutes
Hypertension risks
Damage can occur to the walls of blood vessels from the excess pressure
organs like the brain and kidneys can become damaged
Vasculature
The vessel systems of the body.
A pressure gradient must be maintained across the body’s blood vessels to enable passive transportation of blood
Venous system
Low pressure system
There is less pressure in the veins than the arteries
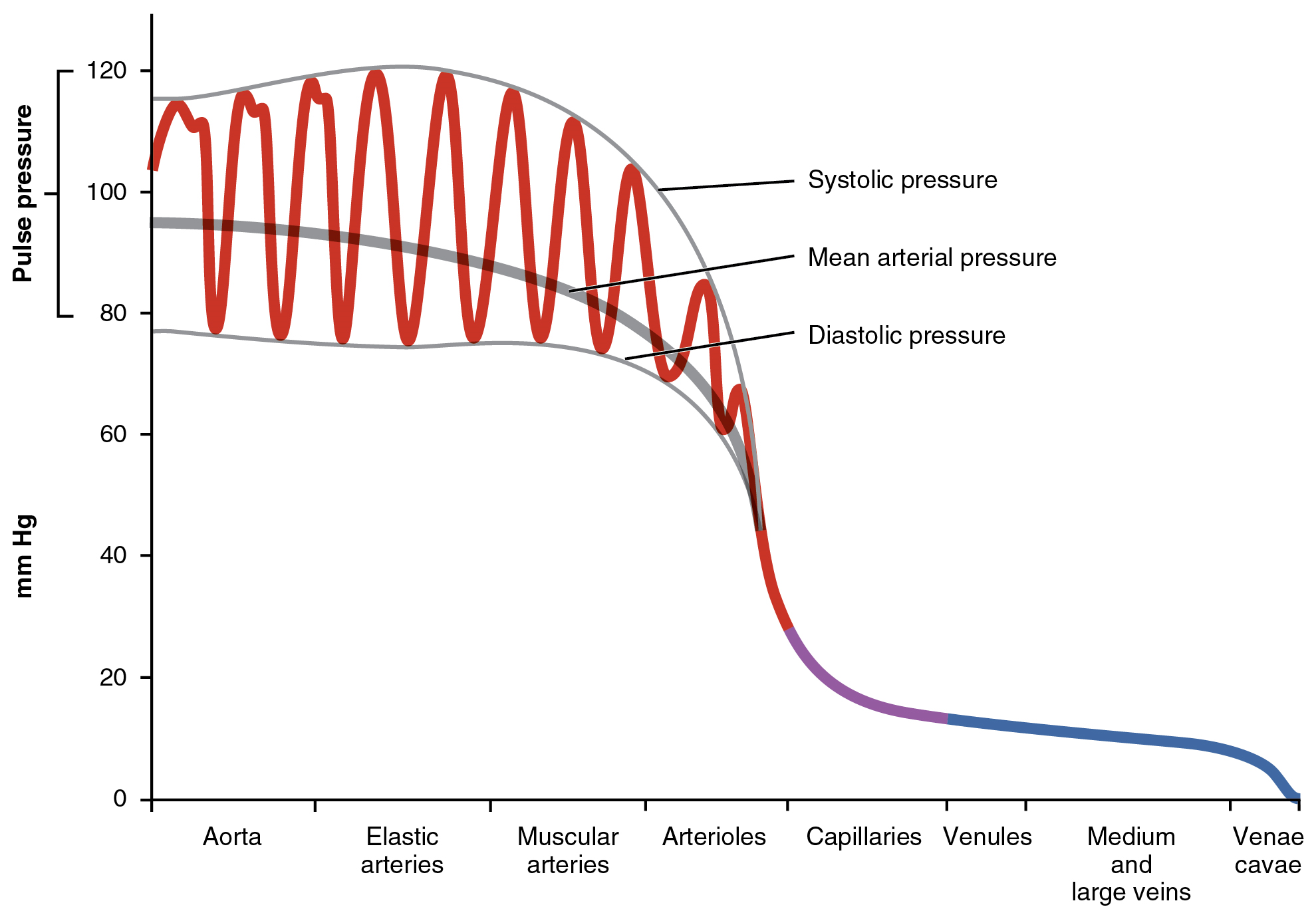
Mean arterial pressure
the average arterial pressure throughout one cardiac cycle (systole and diastole)
Most people need at least 60 mmHg
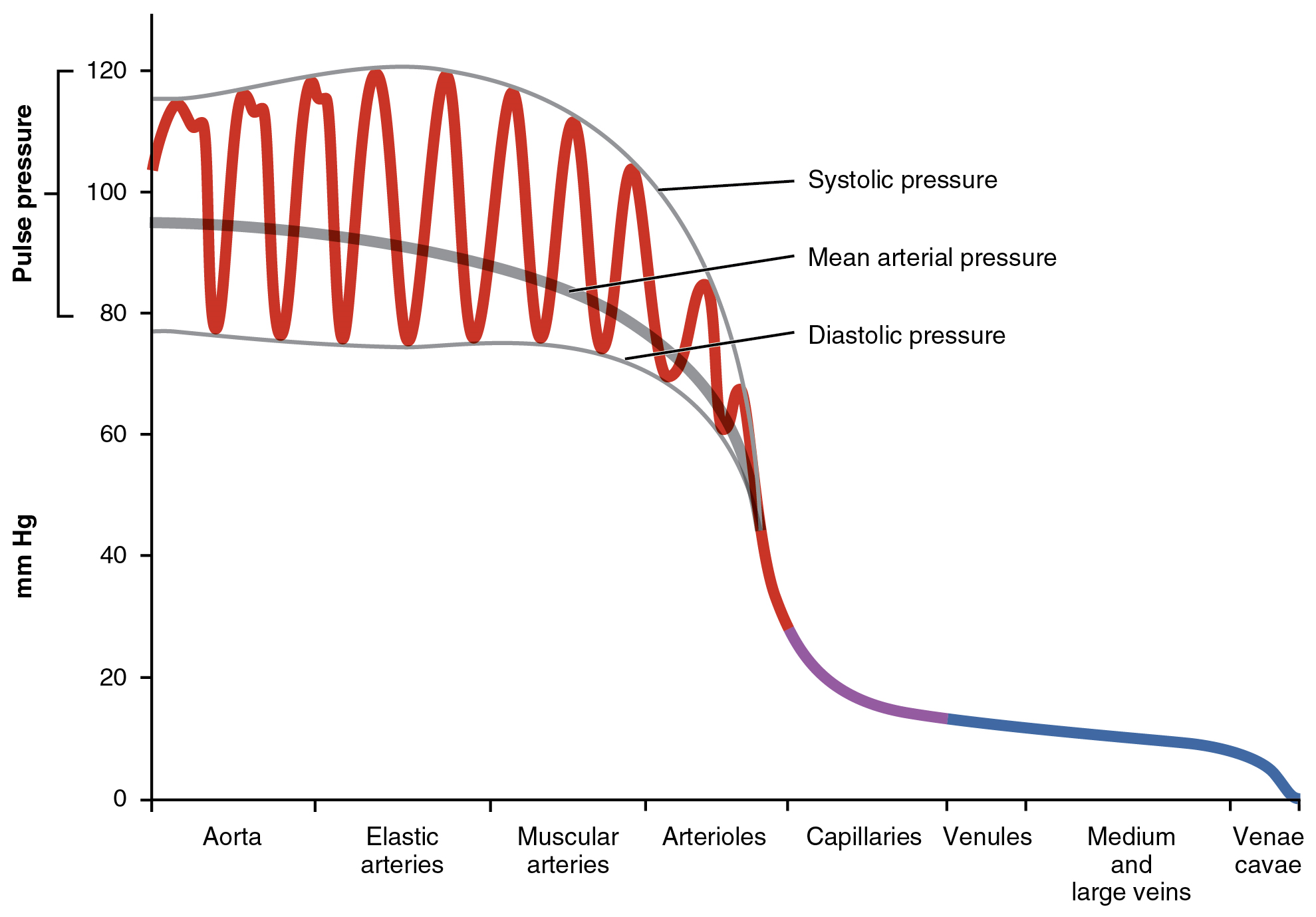
Systolic blood pressure
The pressure exerted against the arterial wall when the ventricles are contracting
Top line of the arterial pressure
Normal 120 mmHg
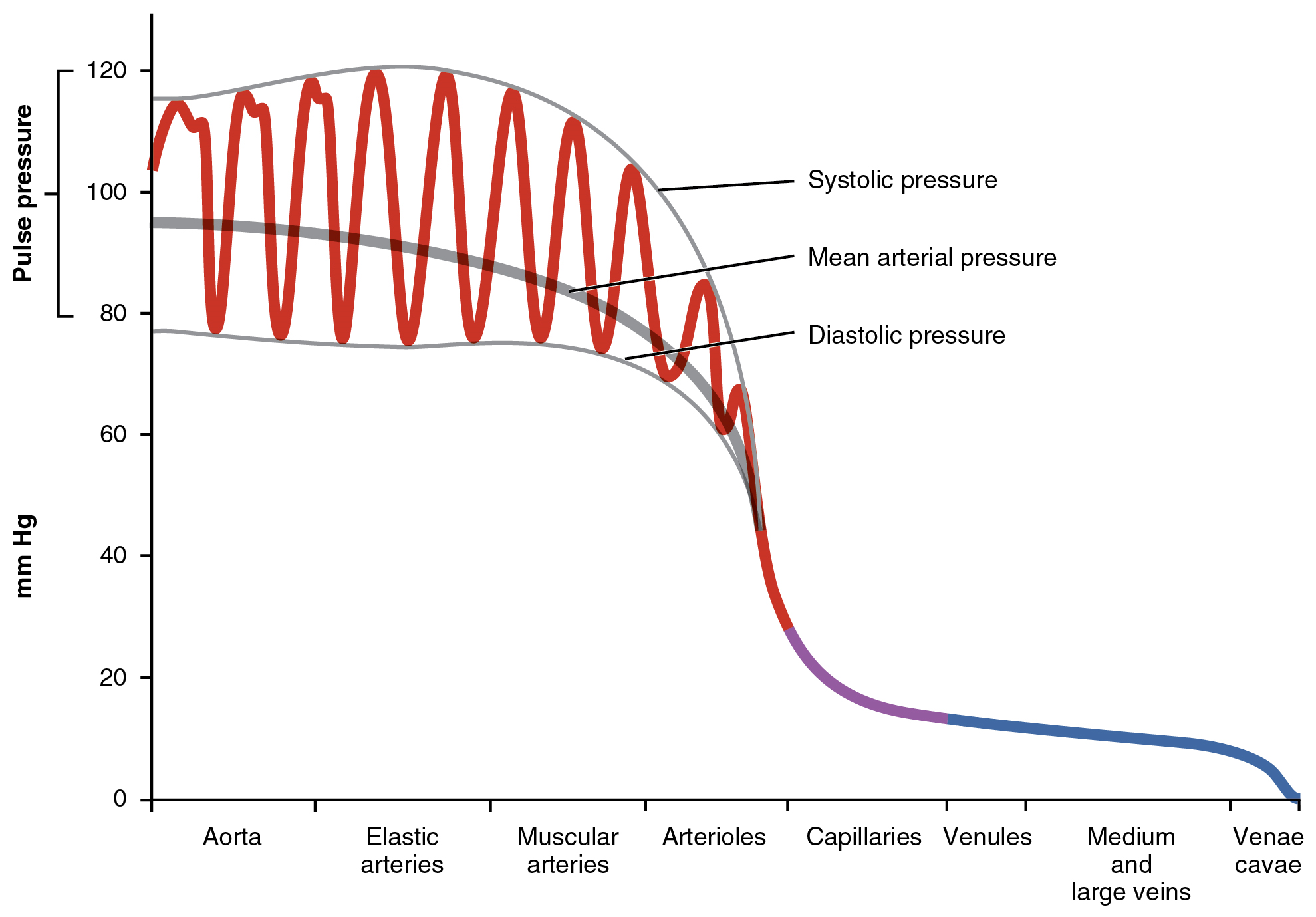
Diastolic Blood pressure
the pressure exerted against the arterial wall when the ventricles are relaxing
Bottom line of the arterial pressure
Normal 80 mmHg

2 Factors effecting blood pressure
Cardiac Output
Peripheral Resistance
Peripheral resistance
Resistance present within arteries towards bloodflow.
Effected by blood vessel diameter
Arterioles have the greatest impact on peripheral resistance (constrict and dilate the most)
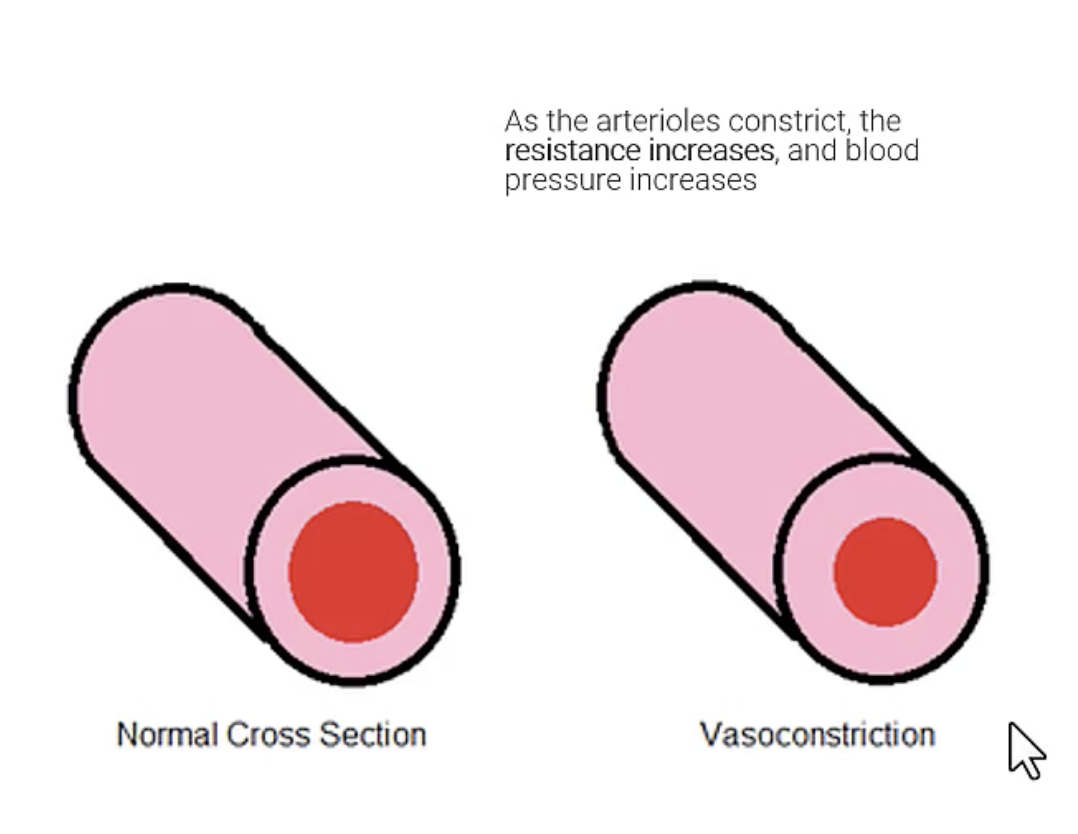
Blood Pressure & Peripheral resistance:
Vasoconstriction
When arterioles constrict, resistance increase, so blood pressure increases.
Blood Pressure & Peripheral resistance:
Vasodilation
When arterioles dilate, resistance decreases, so blood pressure decreases.

Blood Pressure & cardiac output/stroke volume/heart rate
Increasing cardiac output/stroke volume/heart rate increases blood pressure, as there is more blood being pumped out of the heart and pushing against the arterial walls
Blood flow & Vasodilation/vasoconstriction
organs receive either less or more blood depending on how constricted or dilated the arteries are.
Venous return
The volume of heart flowing back to the heart in the systemic veins.
Veins are a low pressure system. Thus, additional mechanisms must be used to increase pressure and thus, bloodflow
avg pressure of around 2 mmHg
Increasing Venous return:
Skeletal muscle pump
when skeletal muscles contract, they squeeze surrounding veins, increasing pressure and venous return.
Increasing Venous return:
Abdominal pump from breathing
When breathing, there is a stage where the abdominal pressure is higher than the thoracic pressure (due to the diaphragm), causing an increased bloodflow and venous return towards the thorax, where the heart is located.
Increasing Venous return:
Nerve system stimulation
Nervous system causes contraction of veins, stimulating the smooth muscle layer in veins, causing them to contract, forcing blood through them.
Blood volume & venous return
increased blood volume causes increased venous return
Effects of increased venous return
• increases blood entering ventricles, which
• increases stroke volume, which
• increases cardiac output