Nervous system
1/34
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Central nervous system
it is made up of the brain and spinal chord. It relays information. produces reflexes and automatic responses to certain stimuli
Peripheral nervous system
it is composed of: crainal nerves, ganglia, spinal nerves
Ganglia
collection of neuron cell bodies
nerves
axon or dendrites of many neurons wrapped together in a protetive sheath in the PNS
Cerebrum
most of our thinking occurs. White matter is mylentated and Grey matter is not. The cortext has four lobes where processing occurs. the white matter connects different regions of the cortex
cerebellum
responsivle for muscle memory and coordination. Active during reasoning and problem solving, can live without it.
Thalamus
takes information into the body and sends it to other parts of the brain exculding smell
Hypothalamus
Controls drive hunger, thirst, sleep, emotional responses, fight or flight, feeing, and mating
Amygdala
fear response, recognize emotions, especially fear, in other people
Hippocampus
involved in memory, regulates mood and learning.
What happens if the hippocampus is damaged?
cannot make new memories, only past memories remain. Still able to learn new motor skills.
Where is short term memory stored?
in the hippocampus
Where is long term memories stored?
The cerebral cortex
When will Long term potentiation occur?
signal from senses goes to thalamus, cortex and hippocampus. only if signal is strong enough or repeated LTP can occur
What are the four lobes of the cerebral cortex?
occipital, parietal, frontal, temporal
How is neurogenesis involved with mood?
it creates new nwurons in the hippocampus, which regulates mood.
How can you increase neurogenesis?
Sex, exercise, learning, and eating omega 3s
How do you decrease neurogenesis?
smoking, stress, alcohol, and sleep deprivation
Automatic nervous system
controls smooth and cardiac muscles. its involuntary
Motor nervous system
regulates skeletal muscles and it can be voluntary or involuntary
Effrent
carries signal away from brain
Affrent
brings signal to brain
What are the two efferent signals?
automatic and motor nervous system
Motor neurons
voluntary skeletal muscles
automatic NS
sympathetic, parasympathetic, and enteric
Sympathetic
Fight or flight and exercise
Parasympathetic
Rest and digest
Enteric
2nd brain, neurons run digestive system and send info to brain. Produces 50% of Dopamine and 95% of seratonine.
Describe the LTP process of gultamate
presynaptic neuron stimulated → action potential releases glutamate neurotransmitters at synapse → post synaptic neuron has two glutamate receptors AMPA and NMDA → strong signal occurs enough gultamate released for LTP. → AMPA receptors bind glutamate → opens channels → Sodium flows in causing a slight depolarization→ Depolorization causes NMDA channel to open → Ca entes cells LTP begins→Ca in post synaptic cell activates protein kinases → protein kinasees increase AMPA receptors in membrane → existing AMPA receptores better ath there job → increase gene expression : more AMPA, Makre proteins that increase dendrite formation
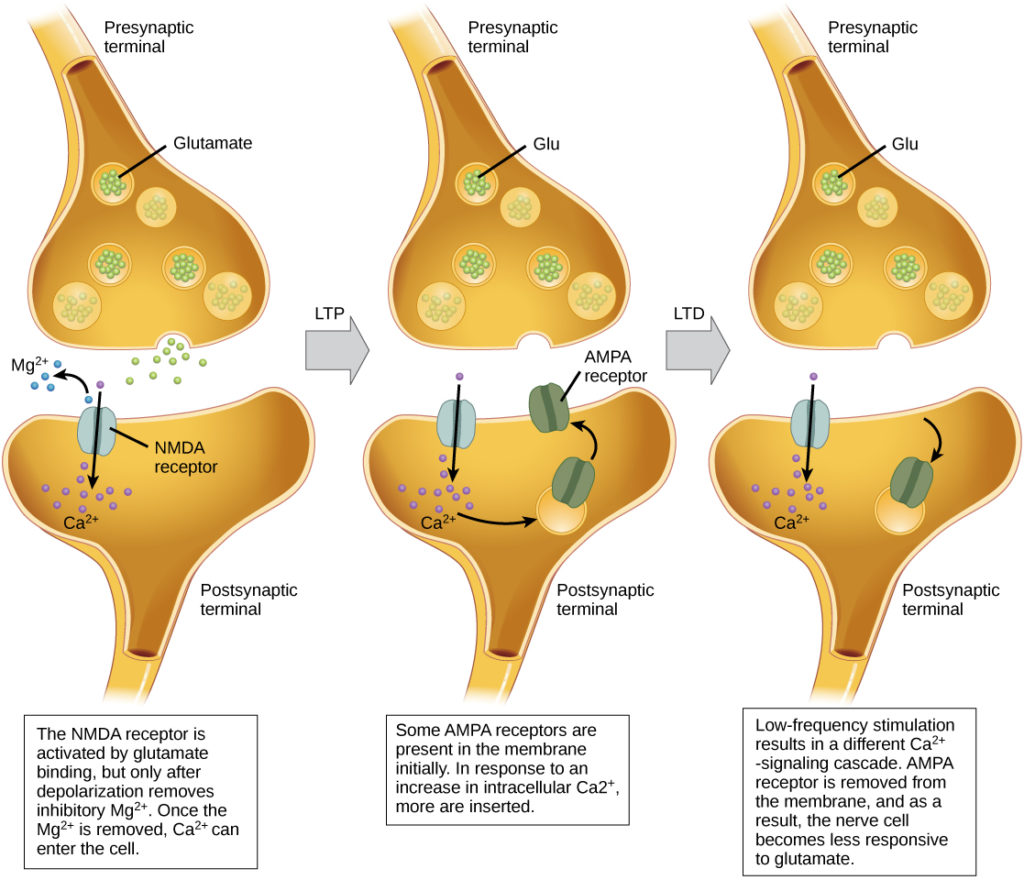
What inhibits NMDA
alcohol
Frontal lobe
decision making
Occipital lobe
visual cortex
temporal lobe
auditory cortex
parietal lobe
sensory cortex
sort these into
parasympathetic or sympathetic responses:
1. Slows heart rate
2. Stimulate pancreas activity
3. Stimulates salivary gland secretions
4. Stimulates glucose release from liver
5. Dilates pupil of the eye
6. Relaxes bronchi in lungs
P
P
P
S
S
S