APSC 3064 Test Two
1/183
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
184 Terms
What is the difference between stretching and pandiculation?
Stretching: passive, just pulling on muscles, no brain involvement Pandiculation: active, increases sensation and awareness of muscles, brain is involved
Smooth muscle
Involuntary, no striations, peristalsis, walls of visceral organs, blood vessels and respiratory passageways, diffuse junctions, centrally located nucleus
Cardiac muscle
Involuntary, striated, one nucleus per cell, intercalated disks
Skeletal muscle
Voluntary, striated, multinucleated, attached to bones, causes movement at joints
What is the difference between pacemaker cells and myocytes?
Pacemaker cells: Produce electrical impulses to initiate heartbeat
Myocytes: Contractile cells
Identify and discuss megaesophagus in dogs and cats
Dilation of the esophagus, when it has lost its muscle tone. Animal won’t get adequate nutrition. Risks for aspiration pneumonia (life threatening)
Identify and discuss myopathies and myositis.
Myopathies: Diseases that cause damage to muscles/muscle tissue
Myositis: inflammatory reaction in muscle
Polymyositis
Affects entire body, associated with immune-mediated disorders
(MMM) Masticatory muscle myositis
Inflammatory condition that affects muscles used to chew. Inability to open mouth or eat.
Atrioventricular valves (A-V)
Opens and closes between atriums and ventricles
Tricuspid (right), Mitral (left)
Semilunar valves
Opens and closes between ventricles and pulmonary artery & aorta
Aortic, Pulmonary
Pericardium
Membrane inclosing the heart
Atria
Smaller chambers of the heart, pumps into ventricles
Ventricles
Larger chambers of the heart, pumps into aorta or pulmonary valve
Heart sounds
“Lub”: First sound, ventricles contract, A-V valves close
“Dub”: Second sound, ventricles relax, semilunar valves close
Heart murmurs
Any abnormal heart sounds, “shh” sounds associated with valve disorders
(MVI) Mitral Valve Insufficiency
Mitral regurgitation, valves can’t close properly, associated with heart murmur
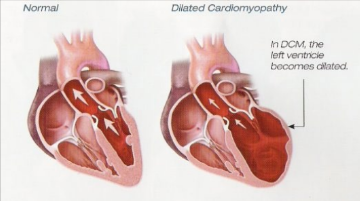
(DCM) Canine Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Decreased ability to generate pressure to pump blood, due to nutritional, infection, and genetic factors. Dilation of the ventricles with ventricular wall thinning.
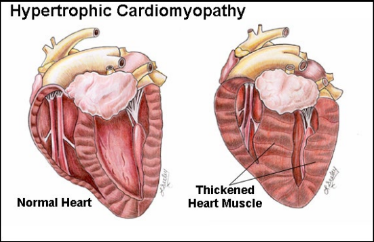
(HCM) Feline Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Muscular walls thicken, decreasing volume in heart chamber and abnormal relaxation of muscle
(ECG) Electrocardiogram
Records fluctuations in body surface electrical potential from due to pacemaker and conduction cells in the heart.
Sinus Arrythmia
Naturally occurring variation in heart rate, rate rises on inspiration, slows on expiration, common in dogs, uncommon in cats
What is heart rate controlled by
Metabolic rate and hormones
Blood pressure
Force exerted by circulating blood on the walls of blood vessels
Blood pressure values
Systolic (max) pressure: 110-160 mmHg
Diastolic (min) pressure: 60-90 mmHg
What is dog cats nutrition largely based off of
Life stage
Unqualified term (Beef, Tuna, etc)
Ingredients must be at least 95% of total weight w/o water, and 70% total weight with water.
Qualifier (dinner, platter, entree, formula, etc)
Ingredients must be at least 26% of total weight w/o water, and 10% total weight with water
“With…” in pet food
Ingredient must be at least 3% of total product
“Flavor” in pet food
No minimum percentage, usually less than 3%
Basal metabolic rate (BMR)
Energy required to maintain homeostasis/survive without moving in a thermoneutral environment. Largely hypothetical
Maintenance energy requirement (MER)
Energy required to support energy equilibrium over a long period of time, (ME intake = heat production)
Daily energy requirement (DER)
Energy required to support energy equilibrium with other factors (standing, walking, playing…)
How to calculate DER (daily energy requirement)
Adjusted BMR since it is the sum of breed, neuter status, age, daily activity, environment temp, etc.
Ideal protein requirements for dogs
1.7g protein/kg BW^0.75
Average quality (plant) protein requirements for dogs
2.1-2.5g protein/kg BW^0.75
Fat requirements of young adult dogs
10-20% DM
Fat requirements for obese-prone adult dogs
7-10% DM
Fiber requirements of dogs
<5% DM
Fiber requirements for obese dogs
>10% DM
Energy requirements for active neutered cats
1.2 x BMR
Energy requirements for active intact cats
1.4-1.6 x BMR
Energy requirements for minimally active cats
1.0 x BMR
Protein requirements for cats (NRC)
16% of DM, must have arginine, taurine, methionine, and cysteine
Fat requirements for cats
9% of DM
Fiber requirements of cats
<5% DM
Bicornuate
1 vagina, cervix, and uterine body. 2 uterine horns
Dogs and Cats
Duplex
1-2 vaginas, 2 uterine horns, cervixes
Rabbit, mouse, opossum
Diffuse
Placenta covers most of the surface
Horses, pigs

Cotyledonary
Placenta is multiple, discrete areas
Ruminants
Zonary
Plancenta is complete/incomplete band
Dogs, cats, seals bears, elephats

Discoid
Placenta is discrete disc shape
Primates, rodents
Mammary glands in cats
4 pairs (2 thoracic, 2 abdominal)
Mammary glands in large dogs
6 pairs
Mammary glands in small dogs
4 pairs
Puberty in small dogs
6-10 months
Puberty in large dogs
18-24 months
How many ova are released during ovulation in small dogs
2-10 ova
How many ova are released during ovulation in large dogs
5-20 ova
When does ovulation occur in dogs
Spontaneous ovulation based on hormonal environment.
Monoestrus
Dogs, one estrus during breeding season
When is the most fertile period for dogs
4-7 days after LH peak
How to recognize estrous cycle in dogs
Sexual behavior, physical signs, vaginal cytology
Estrous cycle for pregnant dog
Proestrus (vulva swollen, bloody discharge, attracted to male but doesn’t mate), Estrus (accepts male, straw-colored discharge), Metestrus/Diestrus (pregnancy and parturition), Anestrus (sexual inactivity)
Estrous cycle for nonpregnant dog
Proestrus (vulva swollen, bloody discharge, attracted to male but doesn’t mate), Estrus (accepts male, straw-colored discharge), Metestrus/Diestrus (False pregnancy), Anestrus (sexual inactivity)
Puberty for short haired vs long-haired cats
Short haired: Occurs earlier
Long haired: Occurs later
Seasonally polyestrous
Multiple estrus cycles during breeding season
Induced Ovulation
In cats, queen ovulates at any time during heat
Reproductive cycle for cat if not bred
Enter interfollicular stage (interestrus) for ~1 week, then goes into estrus again
Reproductive cycle for cat if mated but not pregnant
Diestrus stage (~5-7 weeks), may appear pregnant.
Reproductive cycle for cat if mated successfully
Goes through gestation.
Reproductive cycle of cat
Anestrus (during winter, no heat cycle), Proestrus (1-2 days, vocal female but won’t mate), Estrus (~week, occurs every 17 days if not pregnant, displays lordosis)
Gestation period for dogs
50-60 days
Gestation period for cats
~63 days
Superfecundation
Litters sired by more than one father. Two or more ova from the same cycle were fertilized by sperm from a different male.
Superfetation
Estrus during gestation produces two litters in the same cat. Usually the second litter is too young to survive at birth.
Male dog reproduction system
Sperm produces throughout the year, testes descend few days after birth. Bulbus glandis acts as a tie during mating.
Male cat reproduction system
Penis positioned slightly downward and caudally, penis covered in tiny barbs to stimulate female’s reproductive tract.
Dog mating behavior
Due to hormonal detection of ovulation, courtship length variable, male licks vulva, female stands with tail to one side
Cat mating behavior
Females mate multiple times in a cycle, four matings required to induce ovulation, females aggressive to males immediately after mating.
Pseudopregancy
In dogs and cats, occurs at end of diestrus, same symptoms as pregnant animal, in cats occurs when ovulation is induced but didn’t conceive, treatment not recommended (will go away on its own)
Pyometra
In dogs and cats, hyperplasia and hypertrophy of endometrial glands of the uterus. Lining thickens to cysts if pregnancy doesn’t occur for several cycles. In dogs more than 5 years old. Hard to observe in cats until late stages due to grooming.
Eclampsia
Hypocalcemia (low calcium levels), during peak lactation, life threatening, symptoms are tremors, weakness and a form of paralysis.
Myostatin Gene (MSTN)
Growth differentiation factor, limits skeletal muscle growth
Effects of a mutation of myostatin gene
Little to no production of myostatin protein, less inhibition of muscle growth
Homozygote animals with MSTN mutations
Have significantly increased muscle mass
Hemophilia A
Common genetic coagulation disorder
Cause of Hemophilia A
Spontaneous mutation of F8 gene which provides instructions for Coagulation factor VIII (responsible for normal formation of blood clots.)
Symptoms of Hemophilia A
Spontaneous bleeding in skin causing bruising, excessive bleeding from minor injuries, bleeding into chest cavity/abdomen. Diagnosed by measuring amount of Factor VIII.
How is Hemophilia A inherited
F8 gene is sex-linked on X chromosome. Males have one factor 8 gene, females have two factor 8 genes.
How can Hemophilia A be treated/prevented
Avoid breeding of carriers and test potential carriers.
Differences of lungs between dogs and cats
Left lung: dogs-2 lobes, cats-3 lobes
Right lung: dogs and cats-4 lobes
Upper respiratory tract identification
Nasal cavities, nasopharynx, larynx, trachea
Lower respiratory tract identification
Bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli
Upper respiratory tract function
Trap microorganisms/contaminants, heat up/moisturize air
Lower respiratory tract function
Gas exchange
Mucociliary escalator
Made up of upwards moving cilia covered in a mucus layer. Contaminants get trapped in the mucus layer and are moved up and out of lungs.
Respiratory system regulation
By nervous system through chemoreceptors, blood pH, and changes in lung volume (stretching receptors). Sometimes regulated consciously.
Ventilation
Process in which air moves in and out of the lungs and is made available for gas exchange.
Normal breathing rate in dogs
10-30 breaths/min
Normal breathing rate in cats
20-30 breaths/min