3 - Mendelian Genetics - Pedigrees and Autosomal vs Sex-linked Traits and GWAS
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
AND
Multiply
OR
Add
Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS)
An approach used in genetics research to associate specific genetic
variations with particular diseases
How is GWAS done?
Involves scanning genomes from many different people, looking for
genetic markers that can be used to predict the presence of a disease
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs)
A change at a single nucleotide (A, T, C, or G) in the DNA sequence.
Are SNPs a causative mutation?
No, they act as markers “associated with” diseases
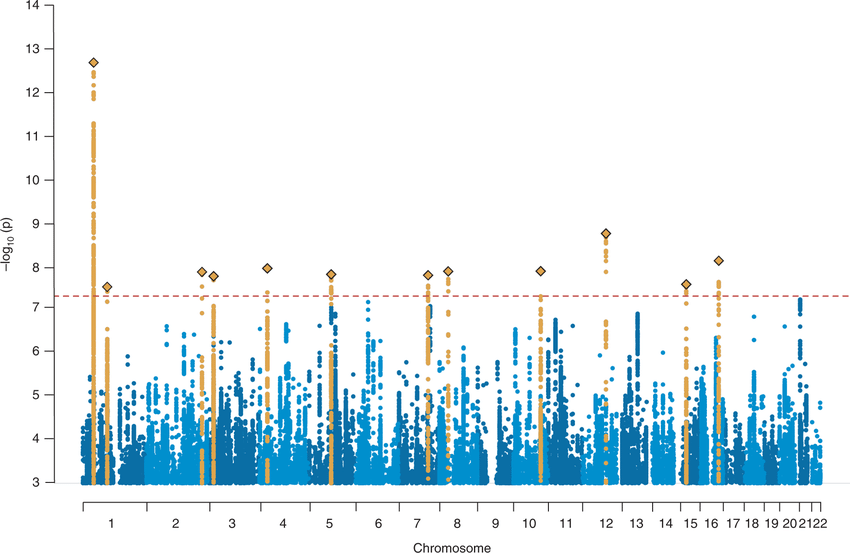
Manhattan Plots
A type of scatter plot used in genome-wide association studies (GWAS) to display SNPs (Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms) across the genome and their statistical significance in association with a trait or disease.
DNA Polarity direction
5’ —> 3’
DNA Synthesis Direction
5’->3’
Why is DNA polar?
The asymmetrical chemical structure of its nucleotides and the way they are connected in a strand. This polarity gives each strand a direction—from the 5′ (five-prime) end to the 3′ (three-prime) end.
RNA Polarity direction
5’->3’
RNA Synthesis direction
5’->3’
mRNA
Made during the process of transcription; messenger RNA — it is a type of RNA that carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where proteins are made
tRNA
Used during translation, transfer RNA — it is a small, folded RNA molecule that delivers amino acids to the ribosome during translation, helping build a protein based on the instructions in mRNA.
rRNA
Ribosomal RNA, a non-coding RNA that forms the core structural and functional components of ribosomes
Are prokaryotes polycistronic or monocistronic?
Polycistronic
Are eukaryotes polycistronic or monocistronic?
Monocistronic
Polycistronic
Multiple genes are encoded on a single mRNA molecule and can
Monocistronic
Each monocistronic mRNA has one start codon and one stop codon, leading to the translation of one protein from one mRNA
Transposable elements
Also known as jumping genes, are segments of DNA that can move from one location to another within a genome
Conservative transposition
Transposable element (TE) moves from one location to another in the genome, but without increasing the number of copies of the element
Replicative transposition
Transposable element (TE) makes a copy of itself and inserts that copy into a new location in the genome, while the original copy remains in its original location
Transposons
Mobile DNA sequences that can move from one location to another within the genome
Inverted repeat at ends of transposon…
allows it to recognize its ends in the “jumping” process
Direct repeats
Generated from the host in the transposition process
Horizontal or Lateral Gene Transfer
From species to species- process by which genetic material is transferred from one organism to another without reproduction (i.e., without being inherited from parent to offspring)
How is lateral/horizontal gene transfer identified?
Can be identified by GC content: the GC% is species differ from the average GC content of the recipient organisms genome
Vertical Gene Transfer
Process by which genetic material is passed from parent to offspring.
Endosymbiont Theory
Proposes that mitochondria and chloroplasts in eukaryotic cells originated from free-living prokaryotic bacteria that were engulfed by an ancestral eukaryotic cell, forming a symbiotic relationship.