Biology 101
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/205
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:38 PM on 3/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
206 Terms
1
New cards
Biology
The scientific study of life.
2
New cards
Extant
The current evolutionary form of a species.
3
New cards
Courtship Rituals
Behavior and traits that a species looks for that confirms positive genetic procession.
4
New cards
Artificial Selection
The selective breeding of animals, plants, etc.
5
New cards
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
6
New cards
What does Adenine pair with in DNA?
Thymine
7
New cards
What does Cytosine pair with in DNA?
Guanine
8
New cards
Gene
A functional unit of DNA
9
New cards
What are genes transcribed into?
RNA
10
New cards
What does RNA do?
It instructs the cell on how to piece together amino acid chains, which make proteins.
11
New cards
Protein Synthesis
DNA → RNA → Amino Acid Chain → Protein
12
New cards
Describe the glucose control process.
1) High blood glucose signal
2) Pancreas releases insulin
3) Insulin binding stimulates cells to absorb glucose
4) Normal blood glucose level tells body to stop producing insulin.
2) Pancreas releases insulin
3) Insulin binding stimulates cells to absorb glucose
4) Normal blood glucose level tells body to stop producing insulin.
13
New cards
Ionic Bond
The transferring of electrons from one atom to another changes the charge of the atom and forms an ____
14
New cards
Covalent Bond
The sharing of electrons between atoms forms a ____
15
New cards
Non-Polar Covalent Bond
The __**EQUAL**__ sharing of electrons between atoms forms a ____
16
New cards
Polar Covalent Bond
In this bond, electrons are pulled closer to the more electronegative atom in the bond.
17
New cards
Hydrogen Bond
Not a traditional bond, but more of a strong attraction. Form very easily, but they also break very easily.
18
New cards
Ion
An atom or molecule with an electrical charge resulting from the gain or loss of one or more electrons.
19
New cards
Cohesion
The tendency of like molecules to stick together. (surface tension of water)
20
New cards
Adhesion
The clinging of one substance to another. (water droplets to a plant)
21
New cards
Thermal Energy
The energy associated with the random movement of atoms and molecules.
22
New cards
Heat
The transfer of thermal energy from a warm body of matter to a cooler one.
23
New cards
Temperature
The measurement of heat intensity.
24
New cards
Evaporative Cooling
A substance evaporates and the surface of the liquid that remains behind cools down.
25
New cards
Solution
A liquid consisting of a uniform mixture of two or more substances.
26
New cards
Solvent
A dissolving agent.
27
New cards
Solutes
Dissolve when water molecules surround them.
28
New cards
pH Scale
Describes how acidic or basic a solution is.
29
New cards
Buffer
Minimizes changes in pH.
30
New cards
Organic Compounds
Compounds built off of a carbon backbone.
31
New cards
Isomer
Compounds with the same molecular formula, but a different chemical structure.
32
New cards
Hydrocarbons
Compounds composed of only carbon and hydrogen.
33
New cards
Structural Isomers
Isomers with completely different structure.
34
New cards
Geometric Isomers
Isomers with the same structure, but different spatial arrangement of atoms.
35
New cards
Enantiomers
Isomers that are mirror images of one another. Like left and right hands.
36
New cards
Hydrophilic
Having a tendency to mix with, dissolve in, or be wetted by water.
37
New cards
Hydrophobic
Tending to repel or failing to mix with water.
38
New cards
Functional Groups
Give organic molecules specific properties.
39
New cards
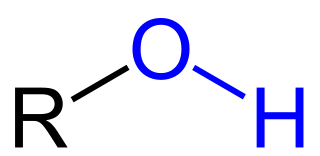
OH
Hydroxyl Group
40
New cards
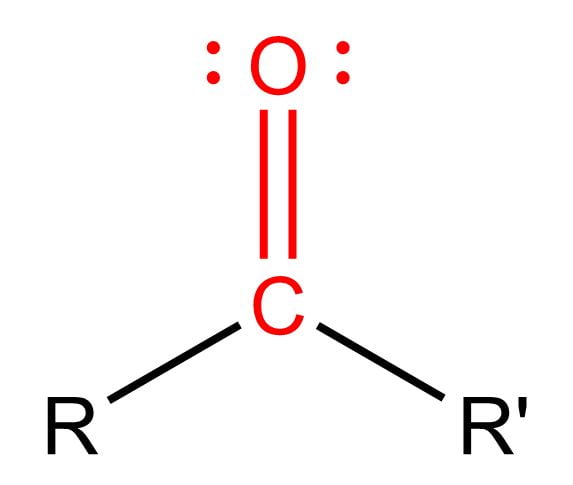
C = O
Carbonyl Group
41
New cards
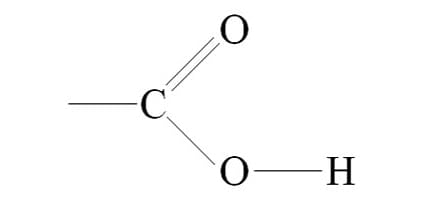
COOH
Carboxyl Group
42
New cards
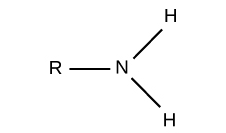
NH2
Amino Group
43
New cards
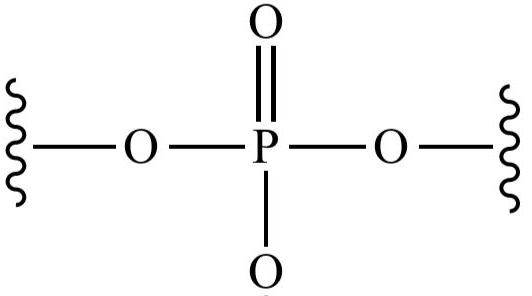
O = PO3 2-
Phosphate Group
44
New cards
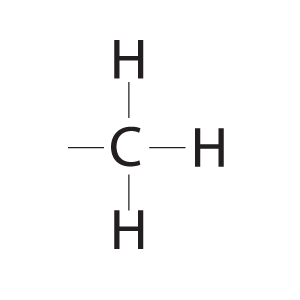
CH3
Methyl Group
45
New cards
Macromolecules
Large biomolecules.
46
New cards
Polymers
Another term for macromolecules, because they are made up of multiple monomers.
47
New cards
Monomers
The building blocks of polymers.
48
New cards
Dehydration Reaction (Condensation Reaction)
The process that links monomers together to form polymers. H2O is formed as a side product.
49
New cards
Hydrolysis
The process that breaks polymers apart. H2O is broken apart.
50
New cards
Carbohydrates
Range from small sugar molecules to large polysaccharides.
51
New cards
CH2O
Monosaccharides contain multiple of this formula. Also contains hydroxyl groups and a carbonyl group.
52
New cards
C6H12O6 + C6H12O6 → C12H22O11 + H2O
Dehydration Reaction Stoichiometry
53
New cards
Disaccharide
Formed by two monomers through a dehydration reaction.
54
New cards
Starch
A polysaccharide used for energy storage consisting of a single, long strand of connected glucose monomers. Found abundantly in potatoes.
55
New cards
Glycogen
A polysaccharide used for energy storage consisting of multiple strands of glucose monomers wound up into fibers. Found in muscle tissue.
56
New cards
Cellulose
A polysaccharide used for structural integrity consisting of multiple strands of glucose monomers, held close to each other by hydrogen bonds and wound tightly into fibers. Found in plant cell walls.
57
New cards
Lipids
A diverse, hydrophobic compound composed largely of carbon hydrogen.
58
New cards
Fats (Triglycerides)
A glycerol molecule linked to three fatty acid tails.
59
New cards
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
A fat with one or more double carbon=carbon bond, which is formed when the fat has less than its maximum amount of hydrogen. Typically found in plant oils.
60
New cards
Saturated Fatty Acids
A fat with the maximum amount of hydrogens. No carbon=carbon double bonds. Typically found in animal fats.
61
New cards
Trans Fats
The process of hydrogenation, or when unsaturated fat is converted to saturated fat by adding hydrogen, creates this.
62
New cards
Phospholipids
Components of cell membranes.
63
New cards
Steroids
Includes cholesterol and some hormones such as Testosterone.
64
New cards
Cholesterol
A common component in animal cell membranes and is the precursor for making steroids.
65
New cards
Amphipathic
The property of being hydrophobic and hydrophilic at the same time. Phospholipid heads are a good example. The heads are hydrophilic and this is why they aim towards the outside and inside of the cell. The tails are hydrophobic which is why they aim away from the outside and inside of cells.
66
New cards
Proteins
Involved in nearly every dynamic function in your body and are extremely diverse in their structure and purpose.
67
New cards
Protein Functions
\-Enzymes
\-Transport proteins embedded in cell membranes
\-Antibodies for immune defense
\-Signal through hormones
\-Receptors
\-Contractile proteins found in muscle cells
\-Structural proteins such as collagen
\-Storage
\-Transport proteins embedded in cell membranes
\-Antibodies for immune defense
\-Signal through hormones
\-Receptors
\-Contractile proteins found in muscle cells
\-Structural proteins such as collagen
\-Storage
68
New cards
Amino Acids
Proteins are made from different arrangements of these 20 different monomers.
69
New cards
Denaturation
The protein unravels, loses its specific shape, and loses its function within the body.
70
New cards
Composition of Amino Acids
__**ALL ARE ATTACHED TO A CENTRAL CARBON**__
\-An amino group
\-A carboxyl group
\-An H atom
\-An R group
\-An amino group
\-A carboxyl group
\-An H atom
\-An R group
71
New cards
What is the R group?
This represents the amino acid that bonds to the central carbon and dictates the identification of the amino acid as a whole.
72
New cards
How are amino acid monomers linked together?
They are linked together through dehydration reactions.
73
New cards
What happens during the linking together of amino acid monomers?
The carboxyl group of one amino acid joins to the amino group of the next amino acid.
74
New cards
Peptide Bond
The binding of amino acid monomers.
75
New cards
Polypeptide
A chain of amino acid monomers.
76
New cards
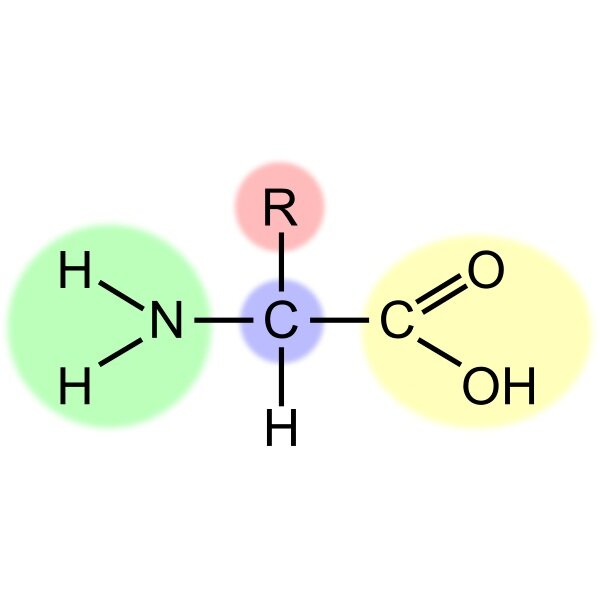
What is this?
An amino acid monomer.
77
New cards
Primary Structure of a Protein
The sequence of amino acid monomers in its polypeptide chain.
78
New cards
Secondary Structure of a Protein
The coiling or folding of the polypeptide chain, stabilized by hydrogen bonds.
79
New cards
Tertiary Structure of a Protein
The overall 3D shape of a polypeptide, resulting from interactions among R groups.
80
New cards
Quaternary Structure of a Protein
It is the association of several protein chains or subunits into a closely packed arrangement. This is only relevant to proteins that have more than one polypeptide, such as Hemoglobin.
81
New cards
Alpha Helix
The term for when hydrogen bonds in a polypeptide chain pull a portion of the amino acid monomers into a helix.
82
New cards
Beta Pleated Sheets
The term for when hydrogen bonds within a polypeptide chain form into a straight, flat, pleated sheets of amino acid monomers.
83
New cards
Nucleotides
Monomers that make up nucleic acids in DNA.
84
New cards
What are nucleotides composed of?
The are composed of a sugar, a phosphate group (which provide structure), and finally a nitrogenous base (which forms connections with other nitrogenous bases).
85
New cards
What does RNA look like?
It is made of a single polynucleotide chain.
86
New cards
What is the function of DNA and RNA?
They serve as blueprints for proteins and control the life of the cell. They are the brain of the cell.
87
New cards
What does *cellulae* mean?
Little rooms.
88
New cards
Purpose of the Light Microscope:
Display living cells.
89
New cards
What is the advantage of a SEM (scanning electron microscope)?
It provides a very detailed surface image of the subject.
90
New cards
What is the advantage of a TEM (transmission electron microscope)?
It provides a very detailed image of of the inner structures of the subject.
91
New cards
Cell Theory states:
\-All living things are made up of cells.
\-All cells come from other cells.
\-All cells come from other cells.
92
New cards
What is the plasma membrane?
A phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins.
93
New cards
Explain what proteins do within the phospholipid bilayer:
\-They form channels that shield ions and other hydrophilic molecules as they pass through the hydrophobic center of the membrane.
\-They also can serve as pumps, using the cell’s energy to transport molecules in or out of the cell.
\-They also can serve as pumps, using the cell’s energy to transport molecules in or out of the cell.
94
New cards
Cytosol
The fluid in which the cell’s organelles “float”.
95
New cards
Prokaryotic Cells
\-No nucleus.
\-DNA is dispersed throughout the cell body.
\-DNA is dispersed throughout the cell body.
96
New cards
Eukaryotic Cells
\-Nucleus.
\-Many membrane-enclosed organelles that perform specific functions.
\-Many membrane-enclosed organelles that perform specific functions.
97
New cards
Organelles
Compartmentalize a cell’s activities.
98
New cards
Function of the Nucleus
It houses the cell’s DNA, which directs protein synthesis.
99
New cards
Function of the Ribosomes
Composed of ribosomal RNA and proteins, they synthesize proteins according to directions from DNA.
100
New cards
Mitochondria
Organelles that carry out cellular respiration in nearly all eukaryotic cells.