ANSC 315 Ectoparasites
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Fleas
insects (arthropods)
Ctenocephaladies felis (“cat flea”)
most common flea of dogs and cats
Causes:
itching
anemia (from blood loss)
flea bite allergic dermatitis
Carry & Spread:
tapeworms (Dipylidium caninum — flea tapeworm)
plague (cats)
haemobartonellosis (cats) — disease of red blood cells
Life Cycle of Fleas
Eggs hatch in 1-2 days → Larvae feed for 4-8 days on debris → An adult flea MAYBE begin to emerge in as little as 5 days → ***An adult flea may live without feeding for as long as 125 days. Adult flea finds a new host and jumps from pet to pet. Unless controlled, it is possible for a flea to live on a host for as long as 2 years. The life cycle may be completed as quickly as 3 weeks.*** → Adult female flea finds a host → Adult female feeds for 2-3 days, then lays eggs.
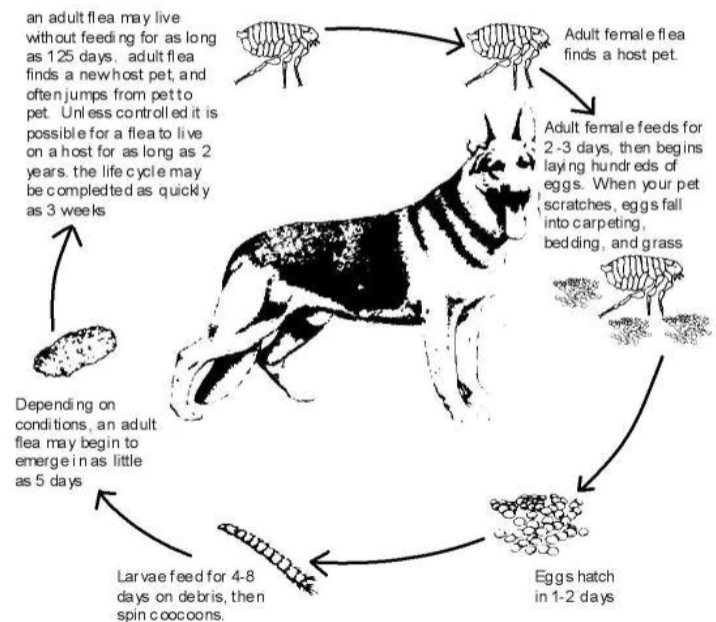
What is the Life Cycle of Fleas?
2-3 weeks
Eggs can Hatch up to ______ After being Laid.
1 year
____ ____ is Very Resistant to Treatment.
pupa stage
Majority of the Flea Life Cycle is Spent _____ the Animal in the Environment.
off
Flea Treatment
environment
animal
Environmental Control of Fleas
access to other animals
removal of adults, eggs, larva, and pupa
vacuuming
launder bedding
flea “bomb” or spray
boric acid or mineral salts — kill larva and eggs, not adults
flea growth regulators applied to the dog — interrupt flea life cycle
Selected Tick-Born Disease
lyme disease
ehrlichia
rocky mountain spotted fever
Animal Applied Flea and Tick Products
sprays
powders
collars
spot on
oral
Compounds
insecticides
insect growth regulators
natural
mechanical
Most to Least Toxic Compounds
MOST
Insecticides
Organo-Phosphates
Carbamates
Pyrethrins
Newer Insecticides
LEAST
Insecticides
most act on nervous system of the insect (some can affect nervous system of mammals)
organo-phosphates
carbamates
monamine oxidase inhibitors (Amitraz)
pyrethrins/synthetic pyrethroids
insect-specific topicals (newer)
Organo-Phosphates
quite toxic
Primary Target: Nervous System
Toxicity:
increased heart rate, shortness of breath, skin flushing, irritation, tremors, nausea, vomiting, blurred vision increased salivation
Chlorpyrifos (dursban), dichlorvos, phosmet, naled, diazinon, malathion, tetrachlorviaphos
Carbamates
Primary Target: Nervous System
toxicity is similar to O-P but generally NOT as severe
carbaryl, propoxur
Pyrethrins
chrysanthemum derivatives
pyrethrins short acting, fairly safe
synthetic pyrethroids — permethrins
last longer
toxic to cats
low toxicity in humans
more commonly — skin irritation, upper respiratory tract irritation
Newer Insecticides
more specific to insect nervous sytem
don’t seem to have same effect on mammalian nervous system
Insect Growth Regulators
interfere with egg hatching or development of adult insect to prevent further breeding and egg laying
not insecticides — do not kill adults
Mange
SCABIES — Sarcoptic Mangw
contagious
very pruritic
zoonotic (don’t live on human for longer than a few hours but can cause itchiness)
burrow into epidermic
common in wild animals
Demodicosis
young animals (usually)
demodex mites (entire life cycle on host)
immunosuppressed animals
local to system signs
Treatment of Mange
wash collars, leaashes, bedding
bathe with antibacterial or antipruritic shampoo
paramite dip (organo-phosphate)
mitaban — demodex, sarcoptes
ivermectin — scabies, some demodex
selamectin — scabies
Cheyletiella
“walking dandruff”
parasitizes keratin layer on skin surface
severe seborrhea sicca — flaking along back
sticky tape prep for diagnosis
zoonotic
dogs, cats, rabbits
Lice
species specific (humans don’t get from animals, vice versa)
pruritic
clean environment to prevent return
Warbles
cuterebra
lays eggs in soil
larval stage in animals
opening to allow larva to breath
leaves animal when becomes a fly
Myiasis (Maggots)
flies deposit eggs on warm, wet, damaged skin
larvae very destructive
“punched out” areas of skin — can group together to cause large areas of decay
disease of neglect
check outdoor pets frequently
avoid matting of hair
minimize flies in outdoor environment