Soil and Land Module 5
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Soil Hydrology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Water Potential (ψ)
Combined effect of all factors that make water move
Factors affecting ψ
Chemical potential (concentration) - water diffuses from dilute to concentrated solution (osmosis)
Mechanical potential (pressure) - water will flow from high pressure to low pressure (vacuum)
Gravitational potential (height) - water flows downhill
Electrical potential (charge)
These factors sum together to give the overall free energy of a mass of water
Forces restricting soil water movement
Adhesion, Cohesion, Capillarity
Soil Water Potential
More water in soil = more water potential
determined by strength of forces attracting water to soil particles
free water (potential of 0)
Adsorbed water (negative potential)
the lower the soil water potential, the more tightly water is adsorbed to soil particles
consists of sum of matric potential + gravitational potential + osmotic potential
unit mPa, bar = 0.1 mPa = slightly less than 1 atm (14.7 psi)
Types of Soil Water
Saturation
Gravitational water
field capacity (upper storage limit)
Drying
Permanent wilting point (lower storage limit)
hygroscopic water (adhesion water)
available water capacity - can be absorbed by plant roots, between field capacity and wilting point
Water Movement in soil
moves along potential gradients (slope and matric potential of soil)
rate depends on soil permeability (described by hydraulic conductivity)
defined by soil structure and texture
horizon differences influence water movement
Darcy’s Law
combines effect of gradient and hydraulic conductivity
calculates quantity of water (flux) flowing in a saturated soil
used to calculate flow rates in aquifers
hydraulic conductivity diminishes exponentially as soil dries
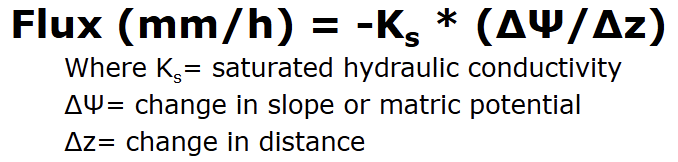
Water Movement in soil
Rates of water movement defined by soil structure and texture, horizon differences influence water movement too
Gravitational flow (saturated flow) - under force of gravity under saturated conditions
Capillary flow (unsaturated flow) - movement in any direction
Water infiltrates the soil the percolates downward through profile
Groundwater Movement and Aquifer Types
Unconfined Aquifer
Confined Aquifer
Darcy’s Law and Landscape Hydrology
Some water flow through aquifers faster than others
as difference in elevation increases, the rate of flow increases
as the distance increases, the rate of flow decreases
