A Level AQA Economics - Section 10, Government Economic Policy Objectives
1/53
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
what are the four main objectives of government macroeconomic policy
strong and stable economic growth
keeping inflation low
reducing unemployment
equilibrium in the balance of payments
objective 1
strong economic growth, high but not too high to avoid inflation. in general, economic growth will improve the standard of living in a country.
objective 2
the uk government aims for an inflation rate of 2%. the monetary policy committee controls the interest and inflation rates.
objective 3
governments aim to reduce unemployment and move towards full employment. if more people are employed, the economy will be more productive and aggregate demand will increased due to greater income.
objective 4
governments want an equal balance of payment. this is more desirable than a long term deficit or surplus that causes a lack of global competitiveness.
what are the secondary macro objectives
balancing the budget
protecting the environment
achieve greater income equality
how is short run (actual) economic growth calculated
measured by the percentage change in real national output. this is actual growth where the effect of inflation has been removed.
what are increases in actual growth caused by
an increase in aggregate demand/supply, actual growth tends to fluctuate up and down
what is long run (potential) economic growth caused by
an increase in the capacity or productive potential of an economy, usually due to a rise in the quality or quantity of inputs.
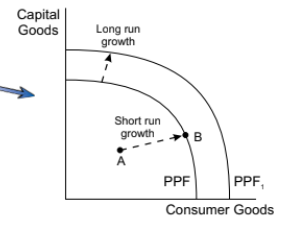
how is long run growth shown
long run growth is shown by an increase in the trend rate of growth, the average rate of economic growth over a period of booms and slumps. this rises smoothly unlike actual economic growth.
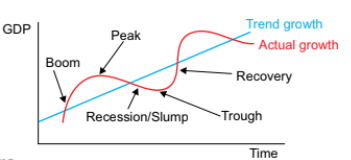
what is the economic cycle
the actual/trend rate of growths fluctuations over time.
what is a boom
when the economy is growing quickly - aggregate demand is rising, leading to a fall in unemployment and a rise in inflation.
what is a recession
when there is negative economic growth for at least two consecutive quarters - unemployment rises and price levels fall
what is a recovery
during a recovery the economy begins to grow again - aggregate demand is rising, unemployment is falling and inflation is rising
what is aggregate demand
the total amount spent on goods and services in an economy
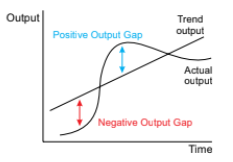
what is a negative output gap
the difference between the level of actual output and trend output when the actual output is below the trend output.
this occurs during a recession when the economy is under performing, so some resources are underused
it means there is downwards pressure on inflation
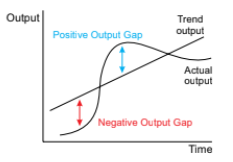
what is a positive output gap
the difference between the level of actual output and trend output when actual output is above trend output.
this will occur during a boom when the economy is overheating, resources are being fully and overused
means an upward pressure on inflation
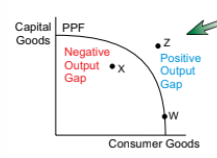
how can an output gap be shown on a PPF
point W shows the economy operating at full capacity
point X is inside the PPF, showing that resources are not being used effectively so there is a negative output gap
point Z is outside the PPF, showing that the economy is producing beyond its potential so there is a positive output gap
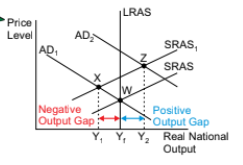
how can output gaps be shown using AS and AD curves
point W shows the economy operating at its full productive potential
point X shows the equilibrium of SRAS1 and AD1 to the left of the SRAS curve. so the economy has the potential to supply at a greater level. the distance between Y1 and 2 is the negative output gap
point Z shows the equilibrium of SRAS1 and AD2 to the right of the LRAS curve. the distance between Y2 and 1 is the positive output gap
what are the benefits to economic growth
leads to an increase in demand for labour, leading to a fall in unemployment and higher incomes for individuals
means that firms are succeeding, so employees may get higher wages. rise in living standards as long as the price level doesnt rise more than wage rates
firms are likely to earn greater profits as consumers have higher incomes and spend more
firms are likely to produce more when theres economic growth which can improve the balance of payments as more exports are sold
causes income and employment to rise, raising government tax revenue and reducing unemployment expenditure
improves the governments fiscal position
benefits to the environment, like firm investment
what are the costs of economic growth
can create income inequality (low and high skilled worker comparison)
higher wages for employees are often linked to an increased in responsibilities which can lead to high stress and reduce productivity
can cause demand pull inflation if demand increases faster than supply
a deficit in the balance of payments is created as people buy more imports, and firms import resources to keep up with demand
industrial expansion may bring about negative externalities like pollution and congestion which harm the environment
scenery and habitats are destroyed when resources are exploited
finite resources can be used up which constrains future growthwhat
what are the benefits of a recession
some firms may benefit like discount retailers
recessions can force firms to face up to their inefficiencies, meaning that firms will cut costs that benefit them in the long run
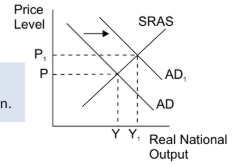
how is short run economic growth brought about
a rise in aggregate demand
lowering interest rates to encourage investment and consumption
increasing welfare benefits to increase government spending and consumption
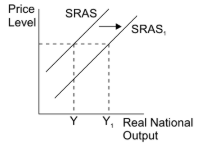
how do aggregate supply increases create short run growth
when SRAS rises the SRAS curve shifts to the right and real national output increases
this is caused by any factor that reduces production costs
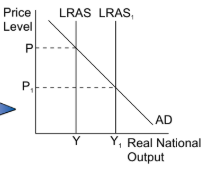
how is long run economic growth created
long run growth is the result of supply side factors increasing the productive potential of an economy, eg:
innovation
investment in modern machinery
using genetically modified crops to increase agricultural output
increase in education and training spending that improves human capital
increasing the population size to grow the workforce
what is economic instability
when economic ups and downs are particularly large and frequent
how is economic instability caused
demand and supply side shocks (domestic or global)
examples of demand side shocks
boosted consumer confidence (rise in house prices)
if a countrys major trading partners to into recession, and demand is significantly reduces
examples of supply side shocks
natural disasters that cause poor harvests
the discovery of a major new source of a raw material
how does keynesian economic theory say how instability is caused
animal spirits - how human behaviour is guided by instincts and emotions rather than economic realities. (people acting irrationally)
what is the herding effect
herding describes how people follow a crowd in the belief that “if everyone is doing something then it must be the right thing to do”
causes speculation and cash hoarding